
Root-raised-cosine filter
Encyclopedia
In signal processing
, a root-raised-cosine filter (RRC), sometimes known as square-root-raised-cosine filter (SRRC), is frequently used as the transmit and receive filter in a digital communication system to perform matched filtering. The combined response of two such filters is that of the raised-cosine filter
. It obtains its name from the fact that its frequency response,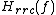 , is the square root of the frequency response of the raised-cosine filter,
, is the square root of the frequency response of the raised-cosine filter, 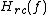 :
:
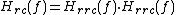
or:
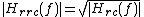
The RRC filter is characterised by two values; β, the roll-off
factor, and Ts, the reciprocal of the symbol-rate.
The impulse response
of such a filter can be given as:
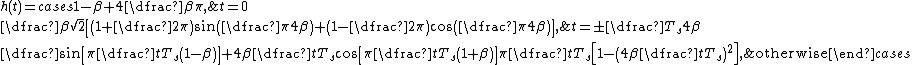 ,
,
though there are other forms as well.
Unlike the raised-cosine filter, the impulse response is not zero at the intervals of ±Ts. However, the combined transmit and receive filters form a raised-cosine filter which does have zero at the intervals of ±Ts. Only in the case of β=0 does the root raised-cosine have zeros at ±Ts.
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, a root-raised-cosine filter (RRC), sometimes known as square-root-raised-cosine filter (SRRC), is frequently used as the transmit and receive filter in a digital communication system to perform matched filtering. The combined response of two such filters is that of the raised-cosine filter
Raised-cosine filter
The raised-cosine filter is a filter frequently used for pulse-shaping in digital modulation due to its ability to minimise intersymbol interference...
. It obtains its name from the fact that its frequency response,
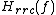 , is the square root of the frequency response of the raised-cosine filter,
, is the square root of the frequency response of the raised-cosine filter, 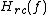 :
: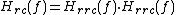
or:
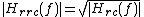
Mathematical Description
The RRC filter is characterised by two values; β, the roll-off
Roll-off
Roll-off is a term commonly used to describe the steepness of a transmission function with frequency, particularly in electrical network analysis, and most especially in connection with filter circuits in the transition between a passband and a stopband...
factor, and Ts, the reciprocal of the symbol-rate.
The impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
of such a filter can be given as:
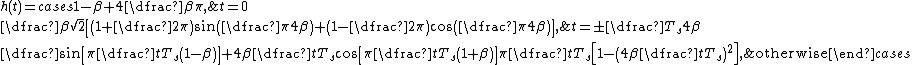 ,
,though there are other forms as well.
Unlike the raised-cosine filter, the impulse response is not zero at the intervals of ±Ts. However, the combined transmit and receive filters form a raised-cosine filter which does have zero at the intervals of ±Ts. Only in the case of β=0 does the root raised-cosine have zeros at ±Ts.

