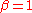
Raised-cosine filter
Encyclopedia
The raised-cosine filter is a filter
frequently used for pulse-shaping in digital modulation
due to its ability to minimise intersymbol interference
(ISI). Its name stems from the fact that the non-zero portion of the frequency spectrum
of its simplest form (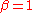 ) is a cosine function, 'raised' up to sit above the
) is a cosine function, 'raised' up to sit above the  (horizontal) axis.
(horizontal) axis.
, i.e., one that has the property of vestigial symmetry. This means that its spectrum exhibits odd symmetry
about , where
, where  is the symbol-period of the communications system.
is the symbol-period of the communications system.
Its frequency-domain description is a piecewise
function
, given by:
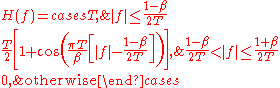
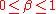
and characterised by two values;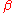 , the roll-off factor, and
, the roll-off factor, and  , the reciprocal of the symbol-rate.
, the reciprocal of the symbol-rate.
The impulse response
of such a filter is given by:
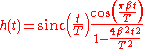 , in terms of the normalised sinc function.
, in terms of the normalised sinc function.
factor,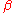 , is a measure of the excess bandwidth of the filter, i.e. the bandwidth occupied beyond the Nyquist bandwidth of
, is a measure of the excess bandwidth of the filter, i.e. the bandwidth occupied beyond the Nyquist bandwidth of  . If we denote the excess bandwidth as
. If we denote the excess bandwidth as 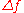 , then:
, then:
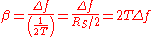
where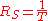 is the symbol-rate.
is the symbol-rate.
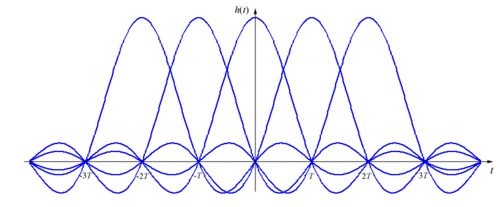
The graph shows the amplitude response as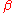 is varied between 0 and 1, and the corresponding effect on the impulse response
is varied between 0 and 1, and the corresponding effect on the impulse response
. As can be seen, the time-domain ripple level increases as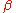 decreases. This shows that the excess bandwidth of the filter can be reduced, but only at the expense of an elongated impulse response.
decreases. This shows that the excess bandwidth of the filter can be reduced, but only at the expense of an elongated impulse response.
As 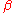 approaches 0, the roll-off zone becomes infinitesimally narrow, hence:
approaches 0, the roll-off zone becomes infinitesimally narrow, hence:
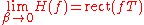
where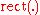 is the rectangular function, so the impulse response approaches
is the rectangular function, so the impulse response approaches 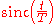 . Hence, it converges to an ideal or brick-wall filter in this case.
. Hence, it converges to an ideal or brick-wall filter in this case.
When 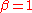 , the non-zero portion of the spectrum is a pure raised cosine, leading to the simplification:
, the non-zero portion of the spectrum is a pure raised cosine, leading to the simplification:
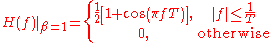
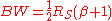 (0
(0
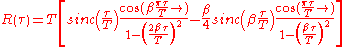
The auto-correlation result can be used to analyze various sampling offset results when analyzed with auto-correlation.
 When used to filter a symbol stream, a Nyquist filter has the property of eliminating ISI, as its impulse response is zero at all
When used to filter a symbol stream, a Nyquist filter has the property of eliminating ISI, as its impulse response is zero at all 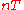 (where
(where  is an integer), except
is an integer), except  .
.
Therefore, if the transmitted waveform is correctly sampled at the receiver, the original symbol values can be recovered completely.
However, in many practical communications systems, a matched filter
is used in the receiver, due to the effects of white noise
. For zero ISI, it is the net response of the transmit and receive filters that must equal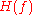 :
:
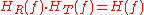
And therefore:
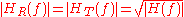
These filters are called root-raised-cosine
filters.
Filter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
frequently used for pulse-shaping in digital modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
due to its ability to minimise intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
(ISI). Its name stems from the fact that the non-zero portion of the frequency spectrum
Frequency spectrum
The frequency spectrum of a time-domain signal is a representation of that signal in the frequency domain. The frequency spectrum can be generated via a Fourier transform of the signal, and the resulting values are usually presented as amplitude and phase, both plotted versus frequency.Any signal...
of its simplest form (
 ) is a cosine function, 'raised' up to sit above the
) is a cosine function, 'raised' up to sit above the  (horizontal) axis.
(horizontal) axis.Mathematical description
The raised-cosine filter is an implementation of a low-pass Nyquist filterNyquist ISI criterion
In communications, the Nyquist ISI criterion describes the conditions which, when satisfied by a communication channel, result in no intersymbol interference or ISI...
, i.e., one that has the property of vestigial symmetry. This means that its spectrum exhibits odd symmetry
Symmetry
Symmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
about
 , where
, where  is the symbol-period of the communications system.
is the symbol-period of the communications system.Its frequency-domain description is a piecewise
Piecewise
On mathematics, a piecewise-defined function is a function whose definition changes depending on the value of the independent variable...
function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
, given by:
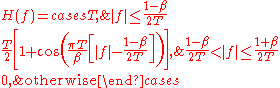
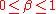
and characterised by two values;
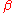 , the roll-off factor, and
, the roll-off factor, and  , the reciprocal of the symbol-rate.
, the reciprocal of the symbol-rate.The impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
of such a filter is given by:
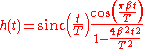 , in terms of the normalised sinc function.
, in terms of the normalised sinc function.Roll-off factor
The roll-offRoll-off
Roll-off is a term commonly used to describe the steepness of a transmission function with frequency, particularly in electrical network analysis, and most especially in connection with filter circuits in the transition between a passband and a stopband...
factor,
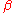 , is a measure of the excess bandwidth of the filter, i.e. the bandwidth occupied beyond the Nyquist bandwidth of
, is a measure of the excess bandwidth of the filter, i.e. the bandwidth occupied beyond the Nyquist bandwidth of  . If we denote the excess bandwidth as
. If we denote the excess bandwidth as 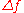 , then:
, then: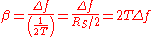
where
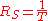 is the symbol-rate.
is the symbol-rate.The graph shows the amplitude response as
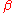 is varied between 0 and 1, and the corresponding effect on the impulse response
is varied between 0 and 1, and the corresponding effect on the impulse responseImpulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
. As can be seen, the time-domain ripple level increases as
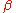 decreases. This shows that the excess bandwidth of the filter can be reduced, but only at the expense of an elongated impulse response.
decreases. This shows that the excess bandwidth of the filter can be reduced, but only at the expense of an elongated impulse response.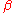 approaches 0, the roll-off zone becomes infinitesimally narrow, hence:
approaches 0, the roll-off zone becomes infinitesimally narrow, hence: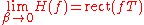
where
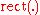 is the rectangular function, so the impulse response approaches
is the rectangular function, so the impulse response approaches 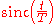 . Hence, it converges to an ideal or brick-wall filter in this case.
. Hence, it converges to an ideal or brick-wall filter in this case. , the non-zero portion of the spectrum is a pure raised cosine, leading to the simplification:
, the non-zero portion of the spectrum is a pure raised cosine, leading to the simplification: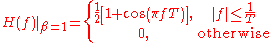
Bandwidth
The bandwidth of a raised cosine filter is most commonly defined as the width of the non-zero portion of its spectrum, i.e.: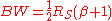 (0
(0Auto-correlation function
The auto-correlation function of raised cosine function is as follows: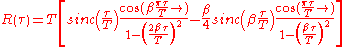
The auto-correlation result can be used to analyze various sampling offset results when analyzed with auto-correlation.
Application

 (where
(where  is an integer), except
is an integer), except  .
.Therefore, if the transmitted waveform is correctly sampled at the receiver, the original symbol values can be recovered completely.
However, in many practical communications systems, a matched filter
Matched filter
In telecommunications, a matched filter is obtained by correlating a known signal, or template, with an unknown signal to detect the presence of the template in the unknown signal. This is equivalent to convolving the unknown signal with a conjugated time-reversed version of the template...
is used in the receiver, due to the effects of white noise
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
. For zero ISI, it is the net response of the transmit and receive filters that must equal
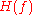 :
: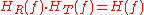
And therefore:
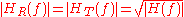
These filters are called root-raised-cosine
Root-raised-cosine filter
In signal processing, a root-raised-cosine filter , sometimes known as square-root-raised-cosine filter , is frequently used as the transmit and receive filter in a digital communication system to perform matched filtering. The combined response of two such filters is that of the raised-cosine filter...
filters.
External links
- Technical article entitled "The care and feeding of digital, pulse-shaping filters" originally published in RF Design, written by Ken Gentile.