
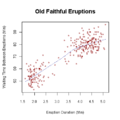
Scatterplot
Encyclopedia
Mathematical diagram
Mathematical diagrams are diagrams in the field of mathematics, and diagrams using mathematics such as charts and graphs, that are mainly designed to convey mathematical relationships, for example, comparisons over time.- Argand diagram :...
using Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
to display values for two variable
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
s for a set of data.
The data is displayed as a collection of points, each having the value of one variable determining the position on the horizontal axis and the value of the other variable determining the position on the vertical axis. This kind of plot
Plot (graphics)
A plot is a graphical technique for representing a data set, usually as a graph showing the relationship between two or more variables. The plot can be drawn by hand or by a mechanical or electronic plotter. Graphs are a visual representation of the relationship between variables, very useful for...
is also called a scatter chart, scattergram, scatter diagram or scatter graph.
Overview
A scatter plot is used when a variable exists that is under the control of the experimenter. If a parameter exists that is systematically incremented and/or decremented by the other, it is called the control parameter or independent variableIndependent variable
The terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
and is customarily plotted along the horizontal axis. The measured or dependent variable is customarily plotted along the vertical axis. If no dependent variable exists, either type of variable can be plotted on either axis and a scatter plot will illustrate only the degree of correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
(not causation
Causality
Causality is the relationship between an event and a second event , where the second event is understood as a consequence of the first....
) between two variables.
A scatter plot can suggest various kinds of correlations between variables with a certain confidence interval
Confidence interval
In statistics, a confidence interval is a particular kind of interval estimate of a population parameter and is used to indicate the reliability of an estimate. It is an observed interval , in principle different from sample to sample, that frequently includes the parameter of interest, if the...
. Correlations may be positive (rising), negative (falling), or null (uncorrelated). If the pattern of dots slopes from lower left to upper right, it suggests a positive correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
between the variables being studied. If the pattern of dots slopes from upper left to lower right, it suggests a negative correlation. A line of best fit
Curve fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function...
(alternatively called 'trendline') can be drawn in order to study the correlation between the variables. An equation for the correlation between the variables can be determined by established best-fit procedures. For a linear correlation, the best-fit procedure is known as linear regression
Linear regression
In statistics, linear regression is an approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar variable y and one or more explanatory variables denoted X. The case of one explanatory variable is called simple regression...
and is guaranteed to generate a correct solution in a finite time. No universal best-fit procedure is guaranteed to generate a correct solution for arbitrary relationships. A scatter plot is also very useful when we wish to see how two comparable data sets agree with each other. In this case, an identity line
Identity line
In a 2-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, with x representing the abscissa and y the ordinate, the identity line is the y = x line. The line, sometimes called the 1:1 line, has a slope of 1...
, i.e., a y=x line, or an 1:1 line, is often drawn as a reference. The more the two data sets agree, the more the scatters tend to concentrate in the vicinity of the identity line; if the two data sets are numerically identical, the scatters fall on the identity line exactly.
One of the most powerful aspects of a scatter plot, however, is its ability to show nonlinear relationships between variables. Furthermore, if the data is represented by a mixture model of simple relationships, these relationships will be visually evident as superimposed patterns.
The scatter diagram is one of the seven basic tools of quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
.
Example
For example, to display values for "lung capacity" (first variable) and how long that person could hold his breath, a researcher would choose a group of people to study, then measure each one's lung capacity (first variable) and how long that person could hold his breath (second variable). The researcher would then plot the data in a scatter plot, assigning "lung capacity" to the horizontal axis, and "time holding breath" to the vertical axis.A person with a lung capacity of 400 ml who held his breath for 21.7 seconds would be represented by a single dot on the scatter plot at the point (400, 21.7) in the Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
. The scatter plot of all the people in the study would enable the researcher to obtain a visual comparison of the two variables in the data set, and will help to determine what kind of relationship there might be between the two variables.
External links
- What is a scatterplot?
- Correlation scatter-plot matrix - for ordered-categorical data - Explanation and R code
- Tool for visualizing scatter plots
- Density scatterplot for large datasets (hundreds of millions of points)

