
Serpens
Encyclopedia
Serpens is a constellation
of the northern hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy
and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union
.
It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus
, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between μ Ser in Serpens Caput and ν Ser in Serpens Cauda. The brighest star in Serpens is Unukalhai or Cor Serpentis "Serpent's Heart", with an apparent magnitude of 2.63.
s goes in order of brightness among both halves.
Only one of the stars in Serpens is brighter than third magnitude
, so the constellation is not easy to perceive. α Serpentis
, named Unukalhai, is in the head part. δ Serpentis
, also in the head, is a double star 210 light-years from Earth. θ Serpentis
. also named Alya ("the snake" in Arabic), in the tail, is also double.
Stars in the head include α
, β
, γ, δ
, ε
, ι
, κ
, λ
, μ
, π
, ρ
, σ
, τ
, χ
and ω Serpentis
. Stars in the tail include ζ
, η
, θ
, ν
, ξ
, and ο Serpentis
.
, a globular cluster
located approximately 8° southwest of α Serpentis in the head.
Messier 16
is a young open cluster
associated with the Eagle Nebula
, a diffuse nebula which is a region of current star formation in the tail.
MWC 922, a nebula
in the Mount Wilson Catalog, is a Symmetric Bipolar Nebula notable for its appearance as a perfectly symmetrical square or rectangle. It is also known as IRAS
18184-1302, and located at RA: 18:21:16 DEC: -13:01:27, near M16 in Serpens Cauda. The MWC is from Mount Wilson Observatory
.
Part of the Milky Way
passes through the tail, as illustrated by the shaded regions of the star map.
The Serpens South star cluster
was uncovered by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope
in the southern portion of the Serpens cloud. The discovery was possible due to the infrared observation capabilities of the SST because at visible wavelengths the stars are completely obscured by interstellar dust in the Serpens cloud.
Hoag's Object
is a perfectly shaped ring galaxy
.
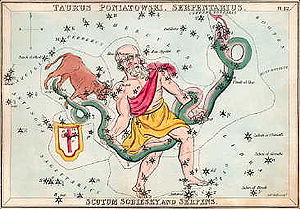 Aratus
Aratus
describes the constellation as follows:
There were two "serpent" constellations in Babylonian astronomy, known as Mušḫuššu and Bašmu. It appears that Mušḫuššu was depicted as a hybrid of dragon, lion and bird, and loosely corresponds to Hydra
.
Bašmu was a horned serpent (c.f. Ningishzida
) and loosely corresponds to the Ὄφις constellation of Eudoxus of Cnidus
on which the Ὄφις (Serpens) of Ptolemy is based.
was a United States Navy
Crater class cargo ship
named after the constellation.
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
of the northern hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
.
It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century...
, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between μ Ser in Serpens Caput and ν Ser in Serpens Cauda. The brighest star in Serpens is Unukalhai or Cor Serpentis "Serpent's Heart", with an apparent magnitude of 2.63.
Stars
Since Serpens is regarded as one constellation despite being split into two halves, the ordering of Bayer designationBayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek letter, followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name...
s goes in order of brightness among both halves.
Only one of the stars in Serpens is brighter than third magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
, so the constellation is not easy to perceive. α Serpentis
Alpha Serpentis
Alpha Serpentis is a triple star system in the constellation Serpens, in its head . Alpha Serpentis has the proper names Unukalhai, from the Arabic عنق الحية ‘Unuq al-Ħayyah "the Serpent's Neck", and Cor Serpentis from the Latin "the Heart of the Serpent"...
, named Unukalhai, is in the head part. δ Serpentis
Delta Serpentis
Delta Serpentis is a star system in the constellation Serpens, in its head . It was a member of indigenous Arabic asterism al-Nasaq al-Yamānī, "the Southern Line" of al-Nasaqān "the Two Lines"., along with α Ser , ε Ser , δ Oph , ε Oph , ζ Oph and γ Oph .According to the...
, also in the head, is a double star 210 light-years from Earth. θ Serpentis
Theta Serpentis
Theta Serpentis is a star system in the constellation Serpens. It is approximately 132 light years from Earth. Theta Serpentis also has the traditional name Alya, or Alga, from the Arabic الية ’alyah "fat tail ".In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi al Mouakket, this star...
. also named Alya ("the snake" in Arabic), in the tail, is also double.
Stars in the head include α
Alpha Serpentis
Alpha Serpentis is a triple star system in the constellation Serpens, in its head . Alpha Serpentis has the proper names Unukalhai, from the Arabic عنق الحية ‘Unuq al-Ħayyah "the Serpent's Neck", and Cor Serpentis from the Latin "the Heart of the Serpent"...
, β
Beta Serpentis
Beta Serpentis is a star system in the constellation Serpens, in its head . It was a member of indigenous Arabic asterism al-Nasaq al-Sha'āmī, "the Northern Line" of al-Nasaqān "the Two Lines", along with β Her , γ Her and γ Ser .According to the catalogue of stars in the Technical Memorandum...
, γ, δ
Delta Serpentis
Delta Serpentis is a star system in the constellation Serpens, in its head . It was a member of indigenous Arabic asterism al-Nasaq al-Yamānī, "the Southern Line" of al-Nasaqān "the Two Lines"., along with α Ser , ε Ser , δ Oph , ε Oph , ζ Oph and γ Oph .According to the...
, ε
Epsilon Serpentis
Epsilon Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens, in its head .It was a member of indigenous Arabic asterism al-Nasaq al-Yamānī, "the Southern Line" of al-Nasaqān "the Two Lines"., along with α Ser , δ Ser , δ Oph , ε Oph , ζ Oph and γ Oph .According to the...
, ι
Iota Serpentis
Iota Serpentis is a star system in the constellation Serpens, in its head . It is approximately 192 light years from Earth....
, κ
Kappa Serpentis
Kappa Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens, in its head .Kappa Serpentis is a red M-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +4.09. It is approximately 348 light years from Earth....
, λ
Lambda Serpentis
Lambda Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens, in its head .- Hunt for substellar objects :...
, μ
Mu Serpentis
Mu Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens, in its head . Mu Serpentis is a white A-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of +3.54...
, π
Pi Serpentis
Pi Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens, in its head .Pi Serpentis is a white A-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of +4.82. It is approximately 177 light years from Earth....
, ρ
Rho Serpentis
Rho Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens.Rho Serpentis is an orange K-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +4.74. It is approximately 395 light years from Earth....
, σ
Sigma Serpentis
Sigma Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens.Sigma Serpentis is a yellow-white F-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of +4.82. It is approximately 89.2 light years from Earth....
, τ
Tau Serpentis
The Bayer designation Tau Serpentis is shared by a collection of eight stars, τ1 Serpentis through τ8 Serpentis, in the head of the constellation Serpens. They are distributed within a box of size 40 minutes in right ascension by 3.5° in declination...
, χ
Chi Serpentis
Chi Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens.Chi Serpentis is a white A-type main sequence dwarf with a mean apparent magnitude of +5.34. It is approximately 228 light years from Earth. It is classified as an Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum type variable star, and its magnitude varies by 0.03...
and ω Serpentis
Omega Serpentis
Omega Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens.Omega Serpentis is a yellow G-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +5.21. It is approximately 263 light years from Earth. It is a member of the Ursa Major Stream....
. Stars in the tail include ζ
Zeta Serpentis
Zeta Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens.Zeta Serpentis is a yellow-white F-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of +4.62. It is approximately 75.7 light years from Earth....
, η
Eta Serpentis
Eta Serpentis is a binary star in the constellation Serpens. The primary, Eta Serpentis A, is an orange K-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +3.23. It has a distant 12th magnitude companion, Eta Serpentis B, 3 arcminutes away...
, θ
Theta Serpentis
Theta Serpentis is a star system in the constellation Serpens. It is approximately 132 light years from Earth. Theta Serpentis also has the traditional name Alya, or Alga, from the Arabic الية ’alyah "fat tail ".In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi al Mouakket, this star...
, ν
Nu Serpentis
Nu Serpentis is a binary star in the constellation Serpens. It is approximately 193 light years from Earth.The primary component, Nu Serpentis A, is a white A-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of +4.32. It is separated from Nu Serpentis B, a magnitude +8.4 companion, by 46...
, ξ
Xi Serpentis
Xi Serpentis is a triple star system in the constellation Serpens. The primary star, Xi Serpentis A, is a yellow-white F-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +3.54. It is a spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 2.29 days. A 13th magnitude companion, Xi Serpentis B, is located 25...
, and ο Serpentis
Omicron Serpentis
Omicron Serpentis is a star in the constellation Serpens.Omicron Serpentis is a white A-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of +4.24. It is approximately 168 light years from Earth. It is classified as a Delta Scuti type variable star and its apparent magnitude varies by 0.01...
.
Deep-sky objects
Messier 5Messier 5
Messier 5 or M5 is a globular cluster in the constellation Serpens. It was discovered by Gottfried Kirch in 1702...
, a globular cluster
Globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is...
located approximately 8° southwest of α Serpentis in the head.
Messier 16
Eagle Nebula
The Eagle Nebula is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745-46. Its name derives from its shape which is resemblant of an eagle...
is a young open cluster
Open cluster
An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist...
associated with the Eagle Nebula
Eagle Nebula
The Eagle Nebula is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745-46. Its name derives from its shape which is resemblant of an eagle...
, a diffuse nebula which is a region of current star formation in the tail.
MWC 922, a nebula
Nebula
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases...
in the Mount Wilson Catalog, is a Symmetric Bipolar Nebula notable for its appearance as a perfectly symmetrical square or rectangle. It is also known as IRAS
IRAS
The Infrared Astronomical Satellite was the first-ever space-based observatory to perform a survey of the entire sky at infrared wavelengths....
18184-1302, and located at RA: 18:21:16 DEC: -13:01:27, near M16 in Serpens Cauda. The MWC is from Mount Wilson Observatory
Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a 5,715 foot peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles...
.
Part of the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
passes through the tail, as illustrated by the shaded regions of the star map.
The Serpens South star cluster
Serpens south
The Serpens South star cluster is a relatively dense group of 50 young stars, 35 of which are protostars just beginning to form. The cluster is situated in the southern portion of the Serpens cloud, located approximately 848 light-years away from Earth....
was uncovered by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope , formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003...
in the southern portion of the Serpens cloud. The discovery was possible due to the infrared observation capabilities of the SST because at visible wavelengths the stars are completely obscured by interstellar dust in the Serpens cloud.
Hoag's Object
Hoag's Object
Hoag's Object is a non-typical galaxy of the type known as a ring galaxy. The appearance of this object has interested amateur astronomers as much as its uncommon structure has fascinated professionals...
is a perfectly shaped ring galaxy
Ring galaxy
A ring galaxy is a galaxy with a ring-like appearance. The ring consists of massive, relatively young blue stars, which are extremely bright. The central region contains relatively little luminous matter. Some astronomers believe that ring galaxies are formed when a smaller galaxy passes through...
.
History

Aratus
Aratus was a Greek didactic poet. He is best known today for being quoted in the New Testament. His major extant work is his hexameter poem Phaenomena , the first half of which is a verse setting of a lost work of the same name by Eudoxus of Cnidus. It describes the constellations and other...
describes the constellation as follows:
- Both [hands of Ophiuchus] firmly clutch the Serpent, which encircles the waist of Ophiuchus, but he, steadfast with both his feet well set, tramples a huge monster, even the Scorpion, standing upright on his eye and breast. Now the Serpent is wreathed about his two hands – a little above his right hand, but in many folds high above his left. ... Toward the Crown leans the Serpent’s jaw, but beneath his coiling form seek thou for the mighty Claws [Libra]
There were two "serpent" constellations in Babylonian astronomy, known as Mušḫuššu and Bašmu. It appears that Mušḫuššu was depicted as a hybrid of dragon, lion and bird, and loosely corresponds to Hydra
Hydra (constellation)
Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees. It has a long history, having been included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake...
.
Bašmu was a horned serpent (c.f. Ningishzida
Ningishzida
Ningishzida is a Mesopotamian deity of the underworld. His name in Sumerian is translated as "lord of the good tree" by Thorkild Jacobsen....
) and loosely corresponds to the Ὄφις constellation of Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar and student of Plato. Since all his own works are lost, our knowledge of him is obtained from secondary sources, such as Aratus's poem on astronomy...
on which the Ὄφις (Serpens) of Ptolemy is based.
Namesakes
USS Serpens (AK-97)USS Serpens (AK-97)
USS Serpens was a United States Coast Guard-manned in the service of the United States Navy in World War II. It was the first ship of the Navy to have this name. It is named after Serpens, a constellation in the northern hemisphere....
was a United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
Crater class cargo ship
Crater class cargo ship
Crater-class cargo ship is a category of freighter that was constructed for use by the United States Navy during World War II under Maritime Commission EC2-S-C1 type....
named after the constellation.

