Solar chemical
Encyclopedia
Solar chemical refers to a number of possible processes that harness solar energy by absorbing sunlight in a chemical reaction
in a way similar to photosynthesis
in plants but without using living organisms. It is also called artificial photosynthesis
. No practical process has yet emerged.
A promising approach is to use focused sunlight to provide the energy needed to split water into its constituent hydrogen
and oxygen
in the presence of a metallic catalyst such as zinc
. This is normally done in a two step process so that hydrogen and oxygen are not produced in the same chamber leading to potentially explosive consequences.
It is also possible to use solar light to drive industrial chemical reactions and applications without a requirement for fossil fuel.
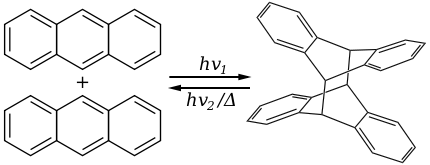
into dianthracene was investigated as a means of storing solar energy. The photodimerization of the naphthalene series has also been investigated.
Photoisomerization is the light induced formation of isomer
s. Various ketones, azepines and norbornadiene
s among other compounds have been investigated as potential energy storing isomers. The norbornadiene
-quadricyclane
couple is of most potential interest for solar energy storage processes. The controlled release of the strain energy stored in quadricyclane (about 110 k J/mole
) back to norbornadiene is made possible. Also, many different derivatives of norbornadiene has been investigated for this reaction.
Photoelectrochemical cell
Photoelectrochemical cells or PECs are solar cells which generate electrical energy from light, including visible light. Some photoelectrochemical cells simply produce electrical energy, while others produce hydrogen in a process similar to the electrolysis of water.-Photogeneration cell:In this...
in a way similar to photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
in plants but without using living organisms. It is also called artificial photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in...
. No practical process has yet emerged.
A promising approach is to use focused sunlight to provide the energy needed to split water into its constituent hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
in the presence of a metallic catalyst such as zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
. This is normally done in a two step process so that hydrogen and oxygen are not produced in the same chamber leading to potentially explosive consequences.
It is also possible to use solar light to drive industrial chemical reactions and applications without a requirement for fossil fuel.
Sunlight energy storing chemicals
Photodimerization is the light induced formation of dimers. As early as 1909, the dimerization of anthraceneAnthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal-tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes...
into dianthracene was investigated as a means of storing solar energy. The photodimerization of the naphthalene series has also been investigated.
Photoisomerization is the light induced formation of isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
s. Various ketones, azepines and norbornadiene
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound. This bicyclic hydrocarbon is the most stable diolefin derived from the norbornane and norbornene. Norbornadiene is primarily of interest as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis, but it has been heavily studied due to its high reactivity and distinctive...
s among other compounds have been investigated as potential energy storing isomers. The norbornadiene
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound. This bicyclic hydrocarbon is the most stable diolefin derived from the norbornane and norbornene. Norbornadiene is primarily of interest as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis, but it has been heavily studied due to its high reactivity and distinctive...
-quadricyclane
Quadricyclane
Quadricyclane is a strained, multi-cyclic hydrocarbon with potential uses as an additive for rocket propellants as well in solar energy conversion. These uses are limited, however, by the molecule's decomposition at relatively low temperatures .-Structure and properties:Quadricyclane is a highly...
couple is of most potential interest for solar energy storage processes. The controlled release of the strain energy stored in quadricyclane (about 110 k J/mole
Joule per mole
The joule per mole is an SI derived unit of energy per amount of material. Energy is measured in joules, and the amount of material is measured in moles....
) back to norbornadiene is made possible. Also, many different derivatives of norbornadiene has been investigated for this reaction.
External links
- ANU Thermochemical energy storage system - Australian National University, Canberra.
- Laboratory for Solar Technology - Paul Scherrer Institute , Villigen, Switzerland.
- Power & Energy Magazine , March 2004 article on Paul Scherrer Institute work
- Solar Chemistry Project Plataforma Solar de Almería, Spain,
- Isracast - Israel,
- Hydrogen Solar- UK.