
Sterol O-acyltransferase
Encyclopedia
Sterol O-acyltransferase is an intracellular protein
located in the endoplasmic reticulum
that forms cholesteryl ester
s from cholesterol
.
Sterol O-acyltransferase catalyzes
the chemical reaction
:
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are acyl-CoA
and cholesterol
, whereas its two products
are CoA
and cholesteryl ester
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
s, specifically those acyltransferase
s transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. This enzyme participates in bile acid
biosynthesis
.
transferase
, more simply referred to as ACAT, also known as sterol O-acyltransferase (SOAT), belongs to the class of enzyme
s known as acyltransferases. The role of this enzyme is to transfer fatty acyl groups from one molecule to another. ACAT is an important enzyme in bile acid
biosynthesis
.
In nearly all mammalian cells, ACAT catalyzes the intracellular esterification of cholesterol
and formation of cholesteryl esters. The esterification of cholesterol
mediated by ACAT is functionally significant for several reasons. ACAT-mediated esterification of cholesterol limits its solubility in the cell membrane lipids
and thus promotes accumulation of cholesterol ester in the fat droplets within cytoplasm
; this process is important because the toxic accumulation of free cholesterol in various cell membrane fractions is prevented. Most of the cholesterol absorbed during intestinal transport undergoes ACAT-mediated esterification before incorporation in chylomicrons. In the liver
, ACAT-mediated esterification of cholesterol is involved in the production and release of apoB-containing lipoproteins. ACAT also plays an important role in foam cell formation and atherosclerosis by participating in accumulating cholesterol esters in macrophages and vascular tissue. The rate-controlling enzyme in cholesterol catabolism
, hepatic cholesterol 7-hydroxylase, is believed to be regulated partly by ACAT.
Acyl-CoA + Cholesterol ←→ CoA + Cholesteryl ester
and SOAT2
. SOAT1 is characterized by its ubiquitous presence in tissues with the exception of the intestine, where SOAT2 is prevalent. The different isoforms are also associated with different pathologies associated with abnormalities in lipid metabolism
.
. A follow-up study reports that SOAT1 RNAi reduced cellular SOAT1 protein and cholesteryl ester levels while causing a slight increase in free cholesterol content of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. The data also showed that a modest decrease in SOAT activity led to suppressive effects on Abeta generation.
In another study, non-human primates revealed a positive correlation between liver cholesteryl ester secretion rate and the development of coronal artery atherosclerosis. The results of the experiment are indicative that under all of the conditions of cellular cholesterol availability tested, the relative level of SOAT2 expression affects the cholesteryl ester content, and therefore the atherogenecity of nascent apoB-containing lipoproteins.
, acyl-CoA:sterol acyltransferase (ASAT) is functionally equivalent to ACAT. Although studies in vitro
and in yeast suggest that the acyl-CoA binding protein (ACBP) may modulate long-chain fatty acyl-CoA (LCFA-CoA) distribution, the physiological function in mammals is unresolved. Recent research suggests that ACBP expression may play a role in LCFA-CoA metabolism in a physiological context.
In S. cerevisiae
, the accumulation of ergosteryl esters accompanies entry into the stationary phase and sporulation. Researchers have identified two genes
in yeast, SAT-1 and SAT-2, that encode for the different isozymes of ASAT. In yeast, SAT-1 is the major catlytic isoform. Mitotic
cell growth and spore
germination
are not compromised when these genes are deleted, but diploids that are homozygous for a SAT-1 null mutation
exhibit a decrease in sporulation efficiency.
ester synthesis is performed by an enzyme different from mammalian ACAT and yeast ASAT; it is performed by Phospholipid:Sterol Acyltransferase (PSAT). A recent study shows that PSAT is involved in the regulation of the pool of free sterols and the amount of free sterol intermediates in the membranes. It is also described to be the only intracellular enzyme discovered as of yet that catalyzes an acyl-CoA independent sterol ester formation. PSAT is therefore considered to have a similar physiological function in plant cells as ACAT in animal cells.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
located in the endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
that forms cholesteryl ester
Cholesteryl ester
A cholesteryl ester is, as its name would imply, an ester of cholesterol. The ester bond is formed between the carboxylate group of a fatty acid and the hydroxyl group of cholesterol. Cholesteryl Esters have a lower solubility in water than Cholesterol and, in other words, are more hydrophobic...
s from cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
.
Sterol O-acyltransferase catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
:
- acyl-CoA + cholesterol
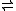 CoA + cholesterol ester
CoA + cholesterol ester
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are acyl-CoA
Acyl-CoA
Acyl-CoA is a group of coenzymes involved in the metabolism of fatty acids. It is a temporary compound formed when coenzyme A attaches to the end of a long-chain fatty acid inside living cells. The compound undergoes beta oxidation, forming one or more molecules of acetyl-CoA...
and cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are CoA
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All sequenced genomes encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it as a substrate...
and cholesteryl ester
Cholesteryl ester
A cholesteryl ester is, as its name would imply, an ester of cholesterol. The ester bond is formed between the carboxylate group of a fatty acid and the hydroxyl group of cholesterol. Cholesteryl Esters have a lower solubility in water than Cholesterol and, in other words, are more hydrophobic...
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s, specifically those acyltransferase
Acyltransferase
Acyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that acts upon acyl groups.Examples include:* Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase* Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase...
s transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. This enzyme participates in bile acid
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. Bile salts are bile acids compounded with a cation, usually sodium. In humans, the salts of taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid represent approximately eighty percent of all bile salts. The two major bile acids are cholic...
biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
.
Class and Structure
Acyl-CoA cholesterol acylAcyl
An acyl group is a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids.In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid . Therefore, it has the formula RCO-, where R represents an alkyl group that is...
transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
, more simply referred to as ACAT, also known as sterol O-acyltransferase (SOAT), belongs to the class of enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s known as acyltransferases. The role of this enzyme is to transfer fatty acyl groups from one molecule to another. ACAT is an important enzyme in bile acid
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. Bile salts are bile acids compounded with a cation, usually sodium. In humans, the salts of taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid represent approximately eighty percent of all bile salts. The two major bile acids are cholic...
biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
.
In nearly all mammalian cells, ACAT catalyzes the intracellular esterification of cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
and formation of cholesteryl esters. The esterification of cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
mediated by ACAT is functionally significant for several reasons. ACAT-mediated esterification of cholesterol limits its solubility in the cell membrane lipids
Membrane lipids
The three major classes of membrane lipids are phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol.-Phospholipids :Phospholipids and glycolipids consist of two long, nonpolar hydrocarbon chains linked to a hydrophilic head group....
and thus promotes accumulation of cholesterol ester in the fat droplets within cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
; this process is important because the toxic accumulation of free cholesterol in various cell membrane fractions is prevented. Most of the cholesterol absorbed during intestinal transport undergoes ACAT-mediated esterification before incorporation in chylomicrons. In the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, ACAT-mediated esterification of cholesterol is involved in the production and release of apoB-containing lipoproteins. ACAT also plays an important role in foam cell formation and atherosclerosis by participating in accumulating cholesterol esters in macrophages and vascular tissue. The rate-controlling enzyme in cholesterol catabolism
Catabolism
Catabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units and release energy. In catabolism, large molecules such as polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins are broken down into smaller units such as monosaccharides, fatty acids, nucleotides, and amino...
, hepatic cholesterol 7-hydroxylase, is believed to be regulated partly by ACAT.
Mechanism
The mechanism scheme is as follows:Acyl-CoA + Cholesterol ←→ CoA + Cholesteryl ester
Isoforms
There are two isoforms of SOAT (also sometimes referred to as ACAT) that have been reported to date: SOAT1SOAT1
Sterol O-acyltransferase 1, also known as SOAT1, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the SOAT1 gene.- Function :...
and SOAT2
SOAT2
Sterol O-acyltransferase 2, also known as SOAT2, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the SOAT2 gene.- Function :This gene is a member of a small family of Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferases. The gene encodes a membrane-bound enzyme localized in the endoplasmic reticulum that produces...
. SOAT1 is characterized by its ubiquitous presence in tissues with the exception of the intestine, where SOAT2 is prevalent. The different isoforms are also associated with different pathologies associated with abnormalities in lipid metabolism
Lipid metabolism
Lipid metabolism refers to the processes that involve the intercourse and degradation of lipids.The types of lipids involved include:* Bile salts* Cholesterols* Eicosanoids* Glycolipids* Ketone bodies* Fatty acids - see also fatty acid metabolism...
.
SOAT1
Previous studies have shown that SOAT modulates proteolytic processing in cell-based and animal models of Alzheimer's diseaseAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
. A follow-up study reports that SOAT1 RNAi reduced cellular SOAT1 protein and cholesteryl ester levels while causing a slight increase in free cholesterol content of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. The data also showed that a modest decrease in SOAT activity led to suppressive effects on Abeta generation.
SOAT2
In a recent study, it was shown that SOAT2 activity is upregulated as a result of chronic renal failure. This study was specific to hepatic SOAT, which plays a major role in hepatic production and release of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), release of cholesterol, foam cell formation, and atherogenesis.In another study, non-human primates revealed a positive correlation between liver cholesteryl ester secretion rate and the development of coronal artery atherosclerosis. The results of the experiment are indicative that under all of the conditions of cellular cholesterol availability tested, the relative level of SOAT2 expression affects the cholesteryl ester content, and therefore the atherogenecity of nascent apoB-containing lipoproteins.
Yeast
In yeastYeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
, acyl-CoA:sterol acyltransferase (ASAT) is functionally equivalent to ACAT. Although studies in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
and in yeast suggest that the acyl-CoA binding protein (ACBP) may modulate long-chain fatty acyl-CoA (LCFA-CoA) distribution, the physiological function in mammals is unresolved. Recent research suggests that ACBP expression may play a role in LCFA-CoA metabolism in a physiological context.
In S. cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
, the accumulation of ergosteryl esters accompanies entry into the stationary phase and sporulation. Researchers have identified two genes
Gênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
in yeast, SAT-1 and SAT-2, that encode for the different isozymes of ASAT. In yeast, SAT-1 is the major catlytic isoform. Mitotic
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
cell growth and spore
Spore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
germination
Germination
Germination is the process in which a plant or fungus emerges from a seed or spore, respectively, and begins growth. The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However the growth of a sporeling from a spore, for example the...
are not compromised when these genes are deleted, but diploids that are homozygous for a SAT-1 null mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
exhibit a decrease in sporulation efficiency.
Plant Synthesis of Steryl Esters
In plants cellular sterolSterol
Sterols, also known as steroid alcohols, are a subgroup of the steroids and an important class of organic molecules. They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol...
ester synthesis is performed by an enzyme different from mammalian ACAT and yeast ASAT; it is performed by Phospholipid:Sterol Acyltransferase (PSAT). A recent study shows that PSAT is involved in the regulation of the pool of free sterols and the amount of free sterol intermediates in the membranes. It is also described to be the only intracellular enzyme discovered as of yet that catalyzes an acyl-CoA independent sterol ester formation. PSAT is therefore considered to have a similar physiological function in plant cells as ACAT in animal cells.

