Straddle
Encyclopedia
In finance
, a straddle is an investment strategy
involving the purchase or sale of particular option
derivatives
that allows the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying
security moves, regardless of the direction of price movement. The purchase of particular option derivatives is known as a long straddle, while the sale of the option derivatives is known as a short straddle. If a big move is expected in the underlying but the direction is not surely known (like when a company is announcing result, or a federal bank is making some policy announcement), straddle and strangle
are two options strategies that can be used in such a case. Both strategies consist of buying an equal number of call and put options with the same expiry date. The value of a straddle is due to the convexity
of its payout: going long or short an at-the-money straddle corresponds to buying or selling Gamma.
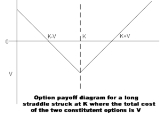
 A long straddle involves going long, i.e., purchasing, both a call option
A long straddle involves going long, i.e., purchasing, both a call option
and a put option
on some stock
, interest rate
, index
or other underlying
. The two options are bought at the same strike price
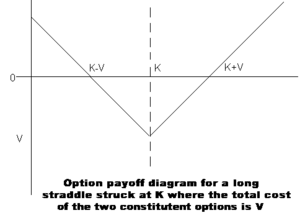
and expire at the same time. The owner of a long straddle makes a profit if the underlying price moves a long way from the strike price, either above or below. Thus, an investor may take a long straddle position if he thinks the market is highly volatile
, but does not know in which direction it is going to move. This position is a limited risk, since the most a purchaser may lose is the cost of both options. At the same time, there is unlimited profit potential.
For example, company XYZ is set to release its quarterly financial results in two weeks. A trader believes that the release of these results will cause a large movement in the price of XYZ's stock, but does not know whether the price will go up or down. He can enter into a long straddle, where he gets a profit no matter which way the price of XYZ stock moves, if the price changes enough either way. If the price goes up enough, he uses the call option
and ignores the put option
. If the price goes down, he uses the put option
and ignores the call option
. If the price does not change enough, he loses money, up to the total amount paid for the two options. The risk is limited by the total premium paid for the options, as opposed to the short straddle where the risk is virtually unlimited.
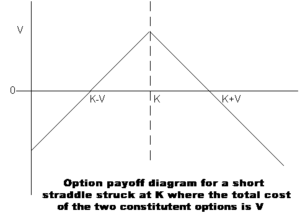 A short straddle is a non-directional options trading strategy that involves simultaneously selling a put and a call of the same underlying security, strike price and expiration date. The profit is limited to the premiums of the put and call, but it is risky because if the underlying security's price goes very high up or very low down, the potential losses are virtually unlimited. The deal breaks even if the intrinsic value of the put or the call equals the sum of the premiums of the put and call. This strategy is called "nondirectional" because the short straddle profits when the underlying security changes little in price before the expiration of the straddle. The short straddle can also be classified as a credit spread because the sale of the short straddle results in a credit of the premiums of the put and call.
A short straddle is a non-directional options trading strategy that involves simultaneously selling a put and a call of the same underlying security, strike price and expiration date. The profit is limited to the premiums of the put and call, but it is risky because if the underlying security's price goes very high up or very low down, the potential losses are virtually unlimited. The deal breaks even if the intrinsic value of the put or the call equals the sum of the premiums of the put and call. This strategy is called "nondirectional" because the short straddle profits when the underlying security changes little in price before the expiration of the straddle. The short straddle can also be classified as a credit spread because the sale of the short straddle results in a credit of the premiums of the put and call.
A short straddle position is highly risky, because the potential loss is unlimited due to the sale of the call and the put options which expose the investor to unlimited losses (on the call) or losses equal to the strike price (on the put), whereas profitability is limited to the premium gained by the initial sale of the options. The Collar
is a more conservative "opposite" that limits gains and losses.
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, a straddle is an investment strategy
Investment strategy
In finance, an investment strategy is a set of rules, behaviors or procedures, designed to guide an investor's selection of an investment portfolio...
involving the purchase or sale of particular option
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
derivatives
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
that allows the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying
Underlying
In finance, the underlying of a derivative is an asset, basket of assets, index, or even another derivative, such that the cash flows of the derivative depend on the value of this underlying...
security moves, regardless of the direction of price movement. The purchase of particular option derivatives is known as a long straddle, while the sale of the option derivatives is known as a short straddle. If a big move is expected in the underlying but the direction is not surely known (like when a company is announcing result, or a federal bank is making some policy announcement), straddle and strangle
Strangle (options)
In finance, a strangle is an investment strategy involving the purchase or sale of particular option derivatives that allows the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying security moves, with relatively minimal exposure to the direction of price movement...
are two options strategies that can be used in such a case. Both strategies consist of buying an equal number of call and put options with the same expiry date. The value of a straddle is due to the convexity
Convexity (finance)
In mathematical finance, convexity refers to non-linearities in a financial model. In other words, if the price of an underlying variable changes, the price of an output does not change linearly, but depends on the second derivative of the modeling function...
of its payout: going long or short an at-the-money straddle corresponds to buying or selling Gamma.
Long straddle

Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
and a put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
on some stock
Stock
The capital stock of a business entity represents the original capital paid into or invested in the business by its founders. It serves as a security for the creditors of a business since it cannot be withdrawn to the detriment of the creditors...
, interest rate
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
, index
Index (economics)
In economics and finance, an index is a statistical measure of changes in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from...
or other underlying
Underlying
In finance, the underlying of a derivative is an asset, basket of assets, index, or even another derivative, such that the cash flows of the derivative depend on the value of this underlying...
. The two options are bought at the same strike price
Strike price
In options, the strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price of the underlying instrument at that time.Formally, the strike...
and expire at the same time. The owner of a long straddle makes a profit if the underlying price moves a long way from the strike price, either above or below. Thus, an investor may take a long straddle position if he thinks the market is highly volatile
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
, but does not know in which direction it is going to move. This position is a limited risk, since the most a purchaser may lose is the cost of both options. At the same time, there is unlimited profit potential.
For example, company XYZ is set to release its quarterly financial results in two weeks. A trader believes that the release of these results will cause a large movement in the price of XYZ's stock, but does not know whether the price will go up or down. He can enter into a long straddle, where he gets a profit no matter which way the price of XYZ stock moves, if the price changes enough either way. If the price goes up enough, he uses the call option
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
and ignores the put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
. If the price goes down, he uses the put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
and ignores the call option
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
. If the price does not change enough, he loses money, up to the total amount paid for the two options. The risk is limited by the total premium paid for the options, as opposed to the short straddle where the risk is virtually unlimited.
Short straddle

A short straddle position is highly risky, because the potential loss is unlimited due to the sale of the call and the put options which expose the investor to unlimited losses (on the call) or losses equal to the strike price (on the put), whereas profitability is limited to the premium gained by the initial sale of the options. The Collar
Collar (finance)
In finance, a collar is an option strategy that limits the range of possible positive or negative returns on an underlying to a specific range.-Structure:A collar is created by an investor being:* Long the underlying...
is a more conservative "opposite" that limits gains and losses.

