
Succinate - coenzyme Q reductase
Encyclopedia
Succinate dehydrogenase or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or Complex II is an enzyme
complex, bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane of mammalian mitochondria and many bacterial cells
. It is the only enzyme that participates in both the citric acid cycle
and the electron transport chain
.
In step 8 of the citric acid cycle
, SQR catalyzes the oxidation of succinate to fumarate with the reduction
of ubiquinone to ubiquinol
. This occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
by coupling
the two reactions together.
SQRs are composed of four subunits
: two hydrophilic and two hydrophobic. The first two subunits
, a flavoprotein
(SdhA) and an iron
-sulfur
protein
(SdhB), are hydrophilic. SdhA contains a covalently attached flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactor
and the succinate binding site
and SdhB contains three iron
-sulfur
clusters: [2Fe-2S], [4Fe-4S], and [3Fe-4S]. The second two subunits
are hydrophobic membrane anchor subunits
, SdhC and SdhD. Human mitochondria consists of two distinct isoforms of SdhA (Fp subunits type I and type II), these isoforms are also found in Ascaris suum and Caenorhabditis elegans. The subunits
form a membrane-bound cytochrome b
with six transmembrane helices containing one heme b
group and a ubiquinone-binding site, which can be seen in Image 4. Two phospholipid
molecules, one cardiolipin
and one phosphatidylethanolamine
, are also found in the SdhC and SdhD subunits
(not shown in the image). They serve to occupy the hydrophobic space below the heme b
. These subunits
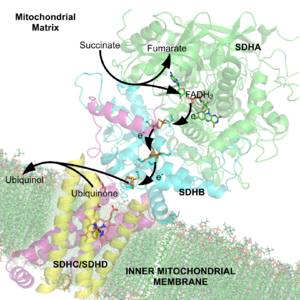
are displayed in image 3. SdhA is green, SdhB is teal, SdhC is fuchsia, and SdhD is yellow. Around SdhC and SdhD is a phospholipid membrane with the intermembrane space at the top of the image.
Ubiquinone Binding Site: Ubiquinone’s binding site
, image 4, is located in a gap composed of SdhB, SdhC, and SdhD. Ubiquinone is stabilized by the side chains of His207 of subunit B, Ser27 and Arg31 of subunit C, and Tyr83 of subunit D. The quinone ring is surrounded by Ile28 of subunit C and Pro160 of subunit B. These residues
, along with Il209, Trp163, and Trp164 of subunit B, and Ser27 (C atom) of subunit C, form the hydrophobic environment of the quinone
-binding pocket (not shown in the image).
Succinate Binding Site: SdhA provides the binding site
for the oxidation of succinate. The side chains Thr254, His354, and Arg399 of subunit A stabilize the molecule
while FAD
oxidizes and carries the electrons to the first of the iron
-sulfur
clusters, [2Fe-2S]. This can be seen in image 5.
Redox Centers: The succinate-binding site and ubiquinone-binding site are connected by a chain of redox centers including FAD
and the iron
-sulfur
clusters. This chain extends over 40 Å through the enzyme
monomer
. All edge-to-edge distances between the centers are less than the suggested 14 Å limit for physiological electron transfer
. This electron transfer
is demonstrated in image 8.
Little is known about the exact succinate oxidation mechanism
. However, the crystal structure
shows that FAD
, Glu255, Arg286, and His242 of subunit A (not shown) are good candidates for the initial deprotonation
step. Thereafter, there are two possible elimination mechanisms: E2 or E1cb. In the E2 elimination, the mechanism is concerted. The basic residue
or cofactor
deprotonates the alpha carbon
, and FAD
accepts the hydride
from the beta carbon, oxidizing the bound succinate to fumarate--refer to image 6. In E1cb, an enolate intermediate is formed, shown in image 7, before FAD
accepts the hydride
. Further research is required to determine which elimination mechanism succinate undergoes in Succinate Dehydrogenase. Oxidized fumarate, now loosely bound to the active site
, is free to exit the protein
.
Electron Tunneling:
After the electrons are derived from succinate oxidation via FAD
, they tunnel along the [Fe-S] relay until they reach the [3Fe-4S] cluster. These electrons are subsequently transferred to an awaiting ubiquinone molecule
within the active site
. The Iron
-Sulfur
electron
tunneling system is shown in image 9.
Ubiquinone Reduction:
The O1 carbonyl
oxygen
of ubiquinone is oriented at the active site (image 4) by hydrogen bond
interactions with Tyr83 of subunit D. The presence of electrons in the [3Fe-4S] iron sulphur cluster induces the movement of ubiquinone into a second orientation. This facilitates a second hydrogen bond
interaction between the O4 carbonyl group of ubiquinone and Ser27 of subunit C. Following the first single electron
reduction
step, a semiquinone
radical species is formed. The second electron
arrives from the [3Fe-4S] cluster to provide full reduction of the ubiquinone to ubiquinol
. This mechanism of the ubiquinone reduction is shown in image 8.
 Heme Functionality:
Heme Functionality:
Although the functionality of the heme
in succinate dehydrogenase is still being researched, some studies have asserted that the first electron
delivered to ubiquinone via [3Fe-4S] may tunnel back and forth between the heme
and the ubiquinone intermediate
. In this way, the heme
cofactor
acts as an electron
sink. Its role is to prevent the interaction of the intermediate with molecular oxygen to produce reactive oxygen species
(ROS). The heme
group, relative to ubiquinone, is shown in image 4.
It has also been proposed that a gating mechanism
may be in place to prevent the electrons from tunneling directly to the heme
from the [3Fe-4S] cluster. A potential candidate is residue
His207, which lies directly between the cluster and the heme
. His207 of subunit B is in direct proximity to the [3Fe-4S] cluster, the bound ubiquinone, and the heme
; and could modulate electron
flow between these redox centers.
Proton Transfer:
To fully reduce the quinone
in SQR, two electrons as well as two protons are needed. It has been argued that a water molecule (HOH39) arrives at the active site
and is coordinated by His207 of subunit B, Arg31 of subunit C, and Asp82 of subunit D. The semiquinone
species is protonated by protons delivered from HOH39, completing the ubiquinone reduction to ubiquinol
. His207 and Asp82 most likely facilitate this process. Other studies claim that Tyr83 of subunit D is coordinated to a nearby histidine
as well as the O1 carbonyl
oxygen
of ubiquinone. The histidine
residue
decreases the pKa
of tyrosine
, making it more suitable to donate its proton
to the reduced ubiquinone intermediate.
. Succinate-analogue inhibitors include the synthetic compound malonate
as well as the TCA cycle intermediates, malate
and oxaloacetate. Indeed, oxaloacetate is one of the most potent inhibitors of Complex II. Why a common TCA cycle intermediate would inhibit Complex II is not entirely understood, though it may exert a protective role in minimizing reverse-electron transfer mediated production of superoxide by Complex I.
from the genome
has also been shown to be lethal at the embryonic stage in mice.
Mammilian succinate dehydrogenase functions not only in mitochondrial energy generation, but also has a role in oxygen
sensing and tumor
suppression; and, therefore, is the object of ongoing research.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
complex, bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane of mammalian mitochondria and many bacterial cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
. It is the only enzyme that participates in both the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
and the electron transport chain
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain couples electron transfer between an electron donor and an electron acceptor with the transfer of H+ ions across a membrane. The resulting electrochemical proton gradient is used to generate chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate...
.
In step 8 of the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
, SQR catalyzes the oxidation of succinate to fumarate with the reduction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
of ubiquinone to ubiquinol
Ubiquinol
Ubiquinol is an electron-rich form of coenzyme Q10.The natural ubiquinol form of coenzyme Q10 is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-poly prenyl-1,4-benzoquinol, where the polyprenylated side chain is 9-10 units long in mammals...
. This occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Biological membrane
A biological membrane or biomembrane is an enclosing or separatingmembrane that acts as a selective barrier, within or around a cell. It consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins that may constitute close to 50% of membrane content...
by coupling
Coupling
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded.The...
the two reactions together.
Structure
Subunits: Mammalian, mitochondrial, and many bacterial monomerMonomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
SQRs are composed of four subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
: two hydrophilic and two hydrophobic. The first two subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
, a flavoprotein
Flavoprotein
Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin: the flavin adenine dinucleotide or flavin mononucleotide ....
(SdhA) and an iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
(SdhB), are hydrophilic. SdhA contains a covalently attached flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
and the succinate binding site
Binding site
In biochemistry, a binding site is a region on a protein, DNA, or RNA to which specific other molecules and ions—in this context collectively called ligands—form a chemical bond...
and SdhB contains three iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
clusters: [2Fe-2S], [4Fe-4S], and [3Fe-4S]. The second two subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
are hydrophobic membrane anchor subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
, SdhC and SdhD. Human mitochondria consists of two distinct isoforms of SdhA (Fp subunits type I and type II), these isoforms are also found in Ascaris suum and Caenorhabditis elegans. The subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
form a membrane-bound cytochrome b
Cytochrome b
Cytochrome b/b6 is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes. In addition, it commonly refers to a region of mtDNA used for population genetics and phylogenetics.- Function :...
with six transmembrane helices containing one heme b
Heme b
Heme B or haem B is the most abundant heme, both hemoglobin and myoglobin are examples of oxygen transport proteins that contain heme B. The peroxidase family of enzymes also contain heme B...
group and a ubiquinone-binding site, which can be seen in Image 4. Two phospholipid
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of all cell membranes as they can form lipid bilayers. Most phospholipids contain a diglyceride, a phosphate group, and a simple organic molecule such as choline; one exception to this rule is sphingomyelin, which is derived from...
molecules, one cardiolipin
Cardiolipin
Cardiolipin is an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it constitutes about 20% of the total lipid composition. The only other place that cardiolipin can be found is in the membranes of most bacteria. The name ‘cardiolipin’ is derived from the fact that it was first...
and one phosphatidylethanolamine
Phosphatidylethanolamine
Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,...
, are also found in the SdhC and SdhD subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
(not shown in the image). They serve to occupy the hydrophobic space below the heme b
Heme b
Heme B or haem B is the most abundant heme, both hemoglobin and myoglobin are examples of oxygen transport proteins that contain heme B. The peroxidase family of enzymes also contain heme B...
. These subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
are displayed in image 3. SdhA is green, SdhB is teal, SdhC is fuchsia, and SdhD is yellow. Around SdhC and SdhD is a phospholipid membrane with the intermembrane space at the top of the image.
Ubiquinone Binding Site: Ubiquinone’s binding site
Binding site
In biochemistry, a binding site is a region on a protein, DNA, or RNA to which specific other molecules and ions—in this context collectively called ligands—form a chemical bond...
, image 4, is located in a gap composed of SdhB, SdhC, and SdhD. Ubiquinone is stabilized by the side chains of His207 of subunit B, Ser27 and Arg31 of subunit C, and Tyr83 of subunit D. The quinone ring is surrounded by Ile28 of subunit C and Pro160 of subunit B. These residues
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
, along with Il209, Trp163, and Trp164 of subunit B, and Ser27 (C atom) of subunit C, form the hydrophobic environment of the quinone
Quinone
A quinone is a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds," resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure."...
-binding pocket (not shown in the image).
Succinate Binding Site: SdhA provides the binding site
Binding site
In biochemistry, a binding site is a region on a protein, DNA, or RNA to which specific other molecules and ions—in this context collectively called ligands—form a chemical bond...
for the oxidation of succinate. The side chains Thr254, His354, and Arg399 of subunit A stabilize the molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
while FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
oxidizes and carries the electrons to the first of the iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
clusters, [2Fe-2S]. This can be seen in image 5.
Redox Centers: The succinate-binding site and ubiquinone-binding site are connected by a chain of redox centers including FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
and the iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
clusters. This chain extends over 40 Å through the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
. All edge-to-edge distances between the centers are less than the suggested 14 Å limit for physiological electron transfer
Electron transfer
Electron transfer is the process by which an electron moves from an atom or a chemical species to another atom or chemical species...
. This electron transfer
Electron transfer
Electron transfer is the process by which an electron moves from an atom or a chemical species to another atom or chemical species...
is demonstrated in image 8.
Mechanism
Succinate Oxidation:Little is known about the exact succinate oxidation mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
. However, the crystal structure
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
shows that FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
, Glu255, Arg286, and His242 of subunit A (not shown) are good candidates for the initial deprotonation
Deprotonation
Deprotonation is the removal of a proton from a molecule, forming the conjugate base.The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its pKa value. A low pKa value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base...
step. Thereafter, there are two possible elimination mechanisms: E2 or E1cb. In the E2 elimination, the mechanism is concerted. The basic residue
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
or cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
deprotonates the alpha carbon
Alpha carbon
The alpha carbon in organic chemistry refers to the first carbon that attaches to a functional group . By extension, the second carbon is the beta carbon, and so on....
, and FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
accepts the hydride
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is the anion of hydrogen, H−, or, more commonly, a compound in which one or more hydrogen centres have nucleophilic, reducing, or basic properties. In compounds that are regarded as hydrides, hydrogen is bonded to a more electropositive element or group...
from the beta carbon, oxidizing the bound succinate to fumarate--refer to image 6. In E1cb, an enolate intermediate is formed, shown in image 7, before FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
accepts the hydride
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is the anion of hydrogen, H−, or, more commonly, a compound in which one or more hydrogen centres have nucleophilic, reducing, or basic properties. In compounds that are regarded as hydrides, hydrogen is bonded to a more electropositive element or group...
. Further research is required to determine which elimination mechanism succinate undergoes in Succinate Dehydrogenase. Oxidized fumarate, now loosely bound to the active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
, is free to exit the protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
.
Electron Tunneling:
After the electrons are derived from succinate oxidation via FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
, they tunnel along the [Fe-S] relay until they reach the [3Fe-4S] cluster. These electrons are subsequently transferred to an awaiting ubiquinone molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
within the active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
. The Iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-Sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
tunneling system is shown in image 9.
Ubiquinone Reduction:
The O1 carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
of ubiquinone is oriented at the active site (image 4) by hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
interactions with Tyr83 of subunit D. The presence of electrons in the [3Fe-4S] iron sulphur cluster induces the movement of ubiquinone into a second orientation. This facilitates a second hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
interaction between the O4 carbonyl group of ubiquinone and Ser27 of subunit C. Following the first single electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
reduction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
step, a semiquinone
Semiquinone
Semiquinone is a free radical resulting from the removal of one hydrogen atom with its electron during the process of dehydrogenation of a hydroquinone to quinone or alternatively the addition of a single H atom to a quinone....
radical species is formed. The second electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
arrives from the [3Fe-4S] cluster to provide full reduction of the ubiquinone to ubiquinol
Ubiquinol
Ubiquinol is an electron-rich form of coenzyme Q10.The natural ubiquinol form of coenzyme Q10 is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-poly prenyl-1,4-benzoquinol, where the polyprenylated side chain is 9-10 units long in mammals...
. This mechanism of the ubiquinone reduction is shown in image 8.

Although the functionality of the heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
in succinate dehydrogenase is still being researched, some studies have asserted that the first electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
delivered to ubiquinone via [3Fe-4S] may tunnel back and forth between the heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
and the ubiquinone intermediate
Intermediate
Intermediate means "occurring between two extremes, or in the middle of a range". It comes from the Latin word 'intermedia' which literally means 'among the middle' and may refer to:...
. In this way, the heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
acts as an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
sink. Its role is to prevent the interaction of the intermediate with molecular oxygen to produce reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
(ROS). The heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
group, relative to ubiquinone, is shown in image 4.
It has also been proposed that a gating mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
may be in place to prevent the electrons from tunneling directly to the heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
from the [3Fe-4S] cluster. A potential candidate is residue
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
His207, which lies directly between the cluster and the heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
. His207 of subunit B is in direct proximity to the [3Fe-4S] cluster, the bound ubiquinone, and the heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
; and could modulate electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
flow between these redox centers.
Proton Transfer:
To fully reduce the quinone
Quinone
A quinone is a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds," resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure."...
in SQR, two electrons as well as two protons are needed. It has been argued that a water molecule (HOH39) arrives at the active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
and is coordinated by His207 of subunit B, Arg31 of subunit C, and Asp82 of subunit D. The semiquinone
Semiquinone
Semiquinone is a free radical resulting from the removal of one hydrogen atom with its electron during the process of dehydrogenation of a hydroquinone to quinone or alternatively the addition of a single H atom to a quinone....
species is protonated by protons delivered from HOH39, completing the ubiquinone reduction to ubiquinol
Ubiquinol
Ubiquinol is an electron-rich form of coenzyme Q10.The natural ubiquinol form of coenzyme Q10 is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-poly prenyl-1,4-benzoquinol, where the polyprenylated side chain is 9-10 units long in mammals...
. His207 and Asp82 most likely facilitate this process. Other studies claim that Tyr83 of subunit D is coordinated to a nearby histidine
Histidine
Histidine Histidine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged imidazole functional group. It is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by German physician Albrecht Kossel in 1896. Histidine is an essential amino acid in humans...
as well as the O1 carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
of ubiquinone. The histidine
Histidine
Histidine Histidine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged imidazole functional group. It is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by German physician Albrecht Kossel in 1896. Histidine is an essential amino acid in humans...
residue
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
decreases the pKa
PKA
PKA, pKa, or other similar variations may stand for:* pKa, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American social fraternity...
of tyrosine
Tyrosine
Tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of the 22 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. Its codons are UAC and UAU. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group...
, making it more suitable to donate its proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
to the reduced ubiquinone intermediate.
Inhibitors
There are two distinct classes of inhibitors of complex II. Those that bind in the succinate pocket and those that bind in the ubiquinone pocket. Ubiquinone type inhibitors include carboxin and thenoyltrifluoroacetoneThenoyltrifluoroacetone
Thenoyltrifluoroacetone, C8H5F3O2S, is a chemical compound used pharmacologically as a chelating agent. It is an inhibitor of cellular respiration by blocking the respiratory chain at complex II....
. Succinate-analogue inhibitors include the synthetic compound malonate
Malonate
The malonate or propanedioate ion is CH222− . Malonate compounds include salts and esters of malonic acid, such as*diethyl malonate, 2,*dimethyl malonate, 2,...
as well as the TCA cycle intermediates, malate
Malate
Malate is the ionized form of malic acid. It is an important chemical compound in biochemistry. In the C4 carbon fixation process, malate is a source of CO2 in the Calvin cycle....
and oxaloacetate. Indeed, oxaloacetate is one of the most potent inhibitors of Complex II. Why a common TCA cycle intermediate would inhibit Complex II is not entirely understood, though it may exert a protective role in minimizing reverse-electron transfer mediated production of superoxide by Complex I.
Role in Disease
The fundamental role of succinate-coenzyme Q reductase in the electron transfer chain of mitochondria makes it vital in most multicellular organisms, removal of this enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
from the genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
has also been shown to be lethal at the embryonic stage in mice.
- SdhA mutations can lead to Leigh syndrome, mitochondrial encephalopathyEncephalopathyEncephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can be caused by many different illnesses.-Terminology:...
, and optic atrophy. - SdhB mutations can lead to tumorogenesis in chromaffin cells, causing hereditary paragangliomaParagangliomaA paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites . About 97% are benign and cured by surgical removal; the remaining 3% are malignant because they are able to produce distant metastases...
and hereditary pheochromocytomaPheochromocytomaA pheochromocytoma or phaeochromocytoma is a neuroendocrine tumor of the medulla of the adrenal glands , or extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue that failed to involute after birth and secretes excessive amounts of catecholamines, usually noradrenaline , and adrenaline to a lesser extent...
. Tumors tend to be malignantMalignantMalignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
. It can also lead to decreased life-span and increased production of superoxideSuperoxideA superoxide, also known by the obsolete name hyperoxide, is a compound that possesses the superoxide anion with the chemical formula O2−. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide. It is important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O2, which occurs widely in nature...
ions. - SdhC mutations can lead to decreased life-span, increased production of superoxideSuperoxideA superoxide, also known by the obsolete name hyperoxide, is a compound that possesses the superoxide anion with the chemical formula O2−. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide. It is important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O2, which occurs widely in nature...
ions, hereditary paragangliomaParagangliomaA paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites . About 97% are benign and cured by surgical removal; the remaining 3% are malignant because they are able to produce distant metastases...
and hereditary pheochromocytomaPheochromocytomaA pheochromocytoma or phaeochromocytoma is a neuroendocrine tumor of the medulla of the adrenal glands , or extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue that failed to involute after birth and secretes excessive amounts of catecholamines, usually noradrenaline , and adrenaline to a lesser extent...
. Tumors tend to be benignBenignA benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
. These mutations are uncommon. - SdhD mutations can lead to hereditary paragangliomaParagangliomaA paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites . About 97% are benign and cured by surgical removal; the remaining 3% are malignant because they are able to produce distant metastases...
and hereditary pheochromocytomaPheochromocytomaA pheochromocytoma or phaeochromocytoma is a neuroendocrine tumor of the medulla of the adrenal glands , or extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue that failed to involute after birth and secretes excessive amounts of catecholamines, usually noradrenaline , and adrenaline to a lesser extent...
. Tumors tend to be benignBenignA benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
, and occur often in the head and neck regions. These mutations can also decrease life-span and increase production of superoxideSuperoxideA superoxide, also known by the obsolete name hyperoxide, is a compound that possesses the superoxide anion with the chemical formula O2−. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide. It is important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O2, which occurs widely in nature...
ions.
Mammilian succinate dehydrogenase functions not only in mitochondrial energy generation, but also has a role in oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
sensing and tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
suppression; and, therefore, is the object of ongoing research.

