
Surface brightness
Encyclopedia
The overall brightness of an extended astronomical object
such as a galaxy
, star cluster
, or nebula
, can be measured by its total magnitude, integrated magnitude or integrated visual magnitude; a related concept is surface brightness, which specifies the brightness of a standard-sized piece of an extended object.
can be used by applying apertures or slits of different sizes diameter. The background light is then subtracted from the measurement to obtain the total brightness. The resulting magnitude value is the same as a point-like source that is emitting the same amount of energy.
The apparent magnitude
of an astronomical object is generally given as an integrated value—if a galaxy
is quoted as having a magnitude of 12.5, it means we see the same total amount of light from the galaxy as we would from a star with magnitude 12.5. However, while a star
is so small it is effectively a point source in most observations (the largest angular diameter
, that of R Doradus
, is 0.057 ± 0.005 arcsec), the galaxy may extend over several arcseconds or arcminutes. Therefore, the galaxy will be harder to see than the star against the airglow
background light. Quoting an object's surface brightness gives an indication of how easily observable it is.
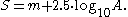
Surface brightness is constant with luminosity distance. For nearby objects, the luminosity distance is equal to the physical distance of the object. For a nearby object emitting a given amount of light, radiative flux
decreases with the square of the distance to the object, but the physical area corresponding to a given solid angle
(e. g. 1 square arcsecond) increases in the same fashion, resulting in the same surface brightness.
by
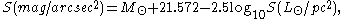
where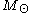 and
and 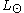 are the absolute magnitude
are the absolute magnitude
and the luminosity of the Sun in chosen color-band
respectively.
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
such as a galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
, star cluster
Star cluster
Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than...
, or nebula
Nebula
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases...
, can be measured by its total magnitude, integrated magnitude or integrated visual magnitude; a related concept is surface brightness, which specifies the brightness of a standard-sized piece of an extended object.
General description
The total magnitude is a measure of the brightness of an extended object such as a nebula, cluster or galaxy. It can be obtained by summing up the luminosity over the area of the object. Alternatively, a photometerPhotometer
In its widest sense, a photometer is an instrument for measuring light intensity or optical properties of solutions or surfaces. Photometers are used to measure:*Illuminance*Irradiance*Light absorption*Scattering of light*Reflection of light*Fluorescence...
can be used by applying apertures or slits of different sizes diameter. The background light is then subtracted from the measurement to obtain the total brightness. The resulting magnitude value is the same as a point-like source that is emitting the same amount of energy.
The apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of an astronomical object is generally given as an integrated value—if a galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
is quoted as having a magnitude of 12.5, it means we see the same total amount of light from the galaxy as we would from a star with magnitude 12.5. However, while a star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
is so small it is effectively a point source in most observations (the largest angular diameter
Angular diameter
The angular diameter or apparent size of an object as seen from a given position is the “visual diameter” of the object measured as an angle. In the vision sciences it is called the visual angle. The visual diameter is the diameter of the perspective projection of the object on a plane through its...
, that of R Doradus
R Doradus
R Doradus is the name of a red giant Mira variable star in the far-southern constellation Dorado, although visually it appears more closely associated with the constellation Reticulum. Its distance from Earth is 204 ± 9 light-years...
, is 0.057 ± 0.005 arcsec), the galaxy may extend over several arcseconds or arcminutes. Therefore, the galaxy will be harder to see than the star against the airglow
Airglow
Airglow is the very weak emission of light by a planetary atmosphere. In the case of Earth's atmosphere, this optical phenomenon causes the night sky to never be completely dark .-Development:The airglow phenomenon was first identified in 1868 by Swedish scientist...
background light. Quoting an object's surface brightness gives an indication of how easily observable it is.
Calculating surface brightness
Surface brightnesses are usually quoted in magnitudes per square arcsecond. Because the magnitude is logarithmic, calculating surface brightness cannot be done by simple division of magnitude by area. Instead, for a source with magnitude m extending over an area of A square arcseconds, the surface brightness S is given by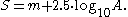
Surface brightness is constant with luminosity distance. For nearby objects, the luminosity distance is equal to the physical distance of the object. For a nearby object emitting a given amount of light, radiative flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
decreases with the square of the distance to the object, but the physical area corresponding to a given solid angle
Solid angle
The solid angle, Ω, is the two-dimensional angle in three-dimensional space that an object subtends at a point. It is a measure of how large that object appears to an observer looking from that point...
(e. g. 1 square arcsecond) increases in the same fashion, resulting in the same surface brightness.
Relationship to physical units
The surface brightness in magnitude units is related to the surface brightness in physical units of solar luminosities per square parsecParsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
by
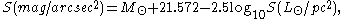
where
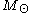 and
and 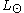 are the absolute magnitude
are the absolute magnitudeAbsolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
and the luminosity of the Sun in chosen color-band
Photometric system
In astronomy, a Photometric system is a set of well-defined passbands , with a known sensitivity to incident radiation. The sensitivity usually depends on the optical system, detectors and filters used. For each photometric system a set of primary standard stars is provided.The first known...
respectively.

