
TBR1
Encyclopedia
T-box, brain, 1 is a protein
that in humans is encoded by the TBR1 gene
. This gene is also known by several other names: T-Brain 1, TBR-1, TES-56, and MGC141978. TBR1 is a member of the T-box
family of transcription factor
s that share a common DNA-binding domain. TBR1 is involved in the regulation of neuronal differentiation and is required for normal brain development.
protein, a T-box transcription factor, which plays a role in establishing symmetry during embryonic development. Thus, due to its relation to T-box
genes (such as Tbx-1, Tbx-2, Tbx-3), Tes-56 was renamed Tbr-1.
expressed in postmitotic projection neurons and is critical for normal brain development. The two other genes that form the TBR1 family and closely interact with TBR1 are EOMES
(also known as TBR2) and TBX21
(also known as T-BET). All three of these genes have been shown to be expressed in the developing olfactory bulb. TBR1 has also been observed in the developing cerebral cortex.
TBR1 has several functions. These include involvement in the developmental process, brain development, neuronal differentiation, and regulation of neurons in the developing neocortex.
and Tbr2, has a role in glutamatergic projection neuron differentiation. The transition from radial glial cells to postmitotic projection neurons occurs in three steps, each associated with one of the aforementioned transcription factors. The first starts out with the expression of Pax6 in radial glial cells found primarily at the ventricular surface. In the next step, Pax6 is downregulated and Tbr2 is expressed as the cell differentiates into an intermediate progenitor cell
. Likewise, in the final step, Tbr2 is extremely downregulated to undetectable levels as Tbr1 signals the transition into a postmitotic projection neuron.
interact with CASK-interacting nucleosome assembly protein (CINAP) to modulate the expression of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor
subunit 2b (NMDAR2b).
, a protein that binds to specific DNA sites and thereby regulates the activity of specific genes, Tbr1 is localized in the nucleus where the cell’s DNA is located. Tbr-1 is expressed in glutamergic neurons, which express receptors for the excitatory neurotransmitter
glutamate, as opposed to GABAergic neurons, which express receptors for the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA
.
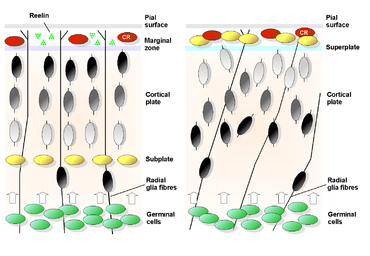
Tbr-1 is expressed mainly in early-born postmitotic neurons of the developing cerebral cortex
—in particular, the preplate and layer VI neurons. The preplate forms the architectural network of neurons that help developing neurons migrate. Successive migrations of neurons divide the preplate such that its inner cells form the cortical plate while its outer cells form the marginal zone. The cortical plate and the marginal zone eventually develop into six cortical layers, known as the neocortex
, present in the mature cerebral cortex. These layers are numbered I-VI with layer VI being deepest and forming first while the remaining layers grow outward from it (from V to I). Layers II-VI develop from the cortical plate and layer I forms from the marginal zone. The subplate, intermediate zone, subventricular zone, and ventricular zone are found progressively deeper to these developing cortical layers. High expression of Tbr-1 is seen in the marginal zone, cortical plate, and subplate of the developing cortex whereas little expression is seen in the subventricular zone. No Tbr-1 expression has been observed in the ventricular zone.
Other regions of Tbr-1 expression are: the olfactory bulbs
and olfactory nuclei; the lateral hypothalamus
region; the entopeduncular nucleus; the eminentia thalami.
. Tbr-1 mutant mice have been found to have reduced Reln expression, resulting in improper neuronal migration, particularly in Cajal-Retzius cells of the marginal zone.
Other studies in mice have found that TBR1 is a repressor or Fezf2. It has also been found to negatively regulate corticalspinal tract formation.
). A T-box-containing cDNA was isolated in the lancelet Branchiostoma belcheri and found to possess a T-domain orthologous to that of the T-Brain subfamily of T-box genes, specifically Tbr1. However, lancelets lack a true brain and no Tbr1 transcripts were found in the neural tissue of the lancelet. This suggests that the neuronal role of Tbr1 evolved in vertebrates after the lancelet lineage had already diverged from that of vertebrates.
(GK) domain of CASK
. It was determined that the C-terminal domain of Tbr-1 in crucial and solely capable of this process. Through luciferase reporter assays of neurons in the hippocampus, it was found that increased Tbr-1/CASK complex expression results in enhanced promoter activity in genes downstream of Tbr-1 such as NMDAR subunit 2b (NMDAR2b), glycine transporter, interleukin-7 receptor (IL-7R
) and OX-2 genes. NMDAR2b experienced the greatest change in activity.
TBR1 and CASK also play an important role in activation of the Reln gene. One study suggests that CASK
, a co-activator of Tbr-1, interacts with CINAP (CASK-interacting nucleosome assembly protein) to form a complex with Tbr-1. The Tbr-1/CASK/CINAP complex regulates expression of NMDAR2b and RELN, which both play important roles in long-term potentiation
.
, which is derived from layer V neurons and is involved in voluntary muscular control, expression of Fezf2 expression must be restricted to layer V. Recent studies show that Tbr-1, expressed in layer VI, binds directly to the Fezf2 gene, preventing Fezf2 expression in layer VI. In this manner, Tbr-1 acts as a transcription repressor of Fezf2.
Mutation of Tbr-1 results in Fezf2 expression in layer VI and malformation of the corticospinal tract. Abnormal activation of Tbr-1 in layer V eliminates corticospinal tract formation.
DOT1L
, which methylates histone H3 lysine 79 (H3K79). Af9 association with DOT1L enhances methylation of H3K79 at the Tbr-1 transcription start site, thereby interfering with RNA polymerase II
(RNAPolII) activity and reducing Tbr-1 expression.
Mutants of Af9 experience increased dimethylation of H3K79 and increased Tbr-1 expression.
. It is also involved in the maintenance of Sox5. It has been found that Sox5 interacts with Tbr1 to regulate Fezf2 transcription.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that in humans is encoded by the TBR1 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. This gene is also known by several other names: T-Brain 1, TBR-1, TES-56, and MGC141978. TBR1 is a member of the T-box
T-box
T-box refers to a group of transcription factors involved in limb and heart development. In humans and some other animals, defects in the TBX5 gene expression can lead to finger-like thumbs and ventricular septal defects in which there is no separation between the left and right ventricle of the...
family of transcription factor
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
s that share a common DNA-binding domain. TBR1 is involved in the regulation of neuronal differentiation and is required for normal brain development.
Gene
The TBR1 gene is located on the q arm of the positive strand of chromosome 2. It is 8,954 base pairs in length. The encoded protein consists of 682 amino acids and has a predicted molecular weight of 74,053 Da. It is composed of 6 exons. TBR1 is one of the three genes that make up the TBR1 subfamily of T-box genes. TBR1 is also known as T-box Brain Protein, T-Brain 1, and TES-56.Discovery
TBR1 was identified in 1995 by the Nina Ireland Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology Center at the University of California, San Francisco. The gene, initially named Tes-56, was found to be largely expressed in the telencephalic vesicles of the developing forebrain of mice. The protein product of Tes-56 was discovered to be very homologous to the BrachyuryBrachyury
Brachyury is a protein that in humans is encoded by the T gene. Brachyury is a transcription factor within the T-box complex of genes. It has been found in all bilaterian animals that have been screened, and is also present in the cnidaria.-History:...
protein, a T-box transcription factor, which plays a role in establishing symmetry during embryonic development. Thus, due to its relation to T-box
T-box
T-box refers to a group of transcription factors involved in limb and heart development. In humans and some other animals, defects in the TBX5 gene expression can lead to finger-like thumbs and ventricular septal defects in which there is no separation between the left and right ventricle of the...
genes (such as Tbx-1, Tbx-2, Tbx-3), Tes-56 was renamed Tbr-1.
Function
TBR1 is a transcription factorTranscription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
expressed in postmitotic projection neurons and is critical for normal brain development. The two other genes that form the TBR1 family and closely interact with TBR1 are EOMES
Eomesodermin
Eomesodermin also known as T-box brain protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EOMES gene.This gene encodes a member of a conserved protein family that shares a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of...
(also known as TBR2) and TBX21
TBX21
T-box transcription factor TBX21 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX21 gene....
(also known as T-BET). All three of these genes have been shown to be expressed in the developing olfactory bulb. TBR1 has also been observed in the developing cerebral cortex.
TBR1 has several functions. These include involvement in the developmental process, brain development, neuronal differentiation, and regulation of neurons in the developing neocortex.
Neuron differentiation
Tbr1, along with Pax6PAX6
Paired box protein Pax-6 also known as aniridia type II protein or oculorhombin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAX6 gene.- Function :PAX6 is a member of the Pax gene family...
and Tbr2, has a role in glutamatergic projection neuron differentiation. The transition from radial glial cells to postmitotic projection neurons occurs in three steps, each associated with one of the aforementioned transcription factors. The first starts out with the expression of Pax6 in radial glial cells found primarily at the ventricular surface. In the next step, Pax6 is downregulated and Tbr2 is expressed as the cell differentiates into an intermediate progenitor cell
Progenitor cell
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that, like a stem cell, has a tendency to differentiate into a specific type of cell, but is already more specific than a stem cell and is pushed to differentiate into its "target" cell...
. Likewise, in the final step, Tbr2 is extremely downregulated to undetectable levels as Tbr1 signals the transition into a postmitotic projection neuron.
Modulation of NMDAR
In cultured hippocampal neurons, Tbr1 and calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine kinase (CASK)CASK
Peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASK gene. This gene is also known by several other names: CMG 2 , calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase 3 and membrane-associated guanylate kinase 2.-Genomics:This gene is located on the short arm of...
interact with CASK-interacting nucleosome assembly protein (CINAP) to modulate the expression of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor
NMDA receptor
The NMDA receptor , a glutamate receptor, is the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function....
subunit 2b (NMDAR2b).
Tissue and cellular distribution
Being a transcription factorTranscription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
, a protein that binds to specific DNA sites and thereby regulates the activity of specific genes, Tbr1 is localized in the nucleus where the cell’s DNA is located. Tbr-1 is expressed in glutamergic neurons, which express receptors for the excitatory neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
glutamate, as opposed to GABAergic neurons, which express receptors for the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA
Gabâ
Gabâ or gabaa, for the people in many parts of the Philippines), is the concept of a non-human and non-divine, imminent retribution. A sort of negative karma, it is generally seen as an evil effect on a person because of their wrongdoings or transgressions...
.
Tbr-1 is expressed mainly in early-born postmitotic neurons of the developing cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
—in particular, the preplate and layer VI neurons. The preplate forms the architectural network of neurons that help developing neurons migrate. Successive migrations of neurons divide the preplate such that its inner cells form the cortical plate while its outer cells form the marginal zone. The cortical plate and the marginal zone eventually develop into six cortical layers, known as the neocortex
Neocortex
The neocortex , also called the neopallium and isocortex , is a part of the brain of mammals. It is the outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres, and made up of six layers, labelled I to VI...
, present in the mature cerebral cortex. These layers are numbered I-VI with layer VI being deepest and forming first while the remaining layers grow outward from it (from V to I). Layers II-VI develop from the cortical plate and layer I forms from the marginal zone. The subplate, intermediate zone, subventricular zone, and ventricular zone are found progressively deeper to these developing cortical layers. High expression of Tbr-1 is seen in the marginal zone, cortical plate, and subplate of the developing cortex whereas little expression is seen in the subventricular zone. No Tbr-1 expression has been observed in the ventricular zone.
Other regions of Tbr-1 expression are: the olfactory bulbs
Olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb is a structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the perception of odors.-Anatomy:In most vertebrates, the olfactory bulb is the most rostral part of the brain. In humans, however, the olfactory bulb is on the inferior side of the brain...
and olfactory nuclei; the lateral hypothalamus
Lateral hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus or lateral hypothalamic area is a part of the hypothalamus.It is concerned with hunger. Damage to this area can cause reduced food intake...
region; the entopeduncular nucleus; the eminentia thalami.
Other species
Human gene TBR1 also has an orthologous gene in zebrafish. Orthologs have also been identified in chimpanzee, dog, cow, rat, and mouse.
Mice
In mice, TBR1 has been found to function in development of the brain, eye, immune system, mesoderm, and placenta. It is also involved in glutamatergic neuronal differentiation in the developing mouse brain. It was discovered that Tbr-1 is expressed by postmitotic cortical neurons in mice and in humans. One target gene of TBR1 in the mouse brain is Reln or ReelinReelin
Reelin is a large secreted extracellular matrix protein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this important role in early development, reelin continues to work in the adult brain. It modulates the...
. Tbr-1 mutant mice have been found to have reduced Reln expression, resulting in improper neuronal migration, particularly in Cajal-Retzius cells of the marginal zone.
Other studies in mice have found that TBR1 is a repressor or Fezf2. It has also been found to negatively regulate corticalspinal tract formation.
Lancelets
The evolution of TBR1 has been studied in amphioxus (lanceletLancelet
The lancelets , also known as amphioxus, are the modern representatives of the subphylum Cephalochordata, formerly thought to be the sister group of the craniates. They are usually found buried in sand in shallow parts of temperate or tropical seas. In Asia, they are harvested commercially as food...
). A T-box-containing cDNA was isolated in the lancelet Branchiostoma belcheri and found to possess a T-domain orthologous to that of the T-Brain subfamily of T-box genes, specifically Tbr1. However, lancelets lack a true brain and no Tbr1 transcripts were found in the neural tissue of the lancelet. This suggests that the neuronal role of Tbr1 evolved in vertebrates after the lancelet lineage had already diverged from that of vertebrates.
Gene regulation
TBR1 both positively and negatively regulates gene expression in postmitotic neurons.CASK
Tbr-1 binds to the guanylate kinaseGuanylate kinase
In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and GMP, whereas its two products are ADP and GDP....
(GK) domain of CASK
CASK
Peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASK gene. This gene is also known by several other names: CMG 2 , calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase 3 and membrane-associated guanylate kinase 2.-Genomics:This gene is located on the short arm of...
. It was determined that the C-terminal domain of Tbr-1 in crucial and solely capable of this process. Through luciferase reporter assays of neurons in the hippocampus, it was found that increased Tbr-1/CASK complex expression results in enhanced promoter activity in genes downstream of Tbr-1 such as NMDAR subunit 2b (NMDAR2b), glycine transporter, interleukin-7 receptor (IL-7R
Interleukin-7 receptor
The interleukin-7 receptor is a protein found on the surface of cells. It is made up of two different smaller protein chains - i.e. it is a heterodimer, and consists of two subunits, interleukin-7 receptor-α and common-γ chain receptor . The common-γ chain receptors is shared with various...
) and OX-2 genes. NMDAR2b experienced the greatest change in activity.
TBR1 and CASK also play an important role in activation of the Reln gene. One study suggests that CASK
CASK
Peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASK gene. This gene is also known by several other names: CMG 2 , calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase 3 and membrane-associated guanylate kinase 2.-Genomics:This gene is located on the short arm of...
, a co-activator of Tbr-1, interacts with CINAP (CASK-interacting nucleosome assembly protein) to form a complex with Tbr-1. The Tbr-1/CASK/CINAP complex regulates expression of NMDAR2b and RELN, which both play important roles in long-term potentiation
Long-term potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation is a long-lasting enhancement in signal transmission between two neurons that results from stimulating them synchronously. It is one of several phenomena underlying synaptic plasticity, the ability of chemical synapses to change their strength...
.
Fezf2
The cerebral cortex is constructed in layers (6 total). For proper development and migration of neurons of the corticospinal tractCorticospinal tract
The corticospinal or pyramidal tract is a collection of axons that travel between the cerebral cortex of the brain and the spinal cord....
, which is derived from layer V neurons and is involved in voluntary muscular control, expression of Fezf2 expression must be restricted to layer V. Recent studies show that Tbr-1, expressed in layer VI, binds directly to the Fezf2 gene, preventing Fezf2 expression in layer VI. In this manner, Tbr-1 acts as a transcription repressor of Fezf2.
Mutation of Tbr-1 results in Fezf2 expression in layer VI and malformation of the corticospinal tract. Abnormal activation of Tbr-1 in layer V eliminates corticospinal tract formation.
Af9
Studies suggest that the Af9 protein acts as a repressor of Tbr-1 in the upper layers of the six-layer developing cerebral cortex, thereby confining Tbr-1 to the lower cortical layers layers (preplate, subplate, layer VI). This process is regulated through interaction of Af9 with the methyltransferaseMethyltransferase
A methyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that transfers a methyl group from a donor to an acceptor.Methylation often occurs on nucleic bases in DNA or amino acids in protein structures...
DOT1L
DOT1L
DOT1-like, histone H3 methyltransferase , also known as DOT1L, is a gene found in humans, as well as other eukaryotes.-Further reading:...
, which methylates histone H3 lysine 79 (H3K79). Af9 association with DOT1L enhances methylation of H3K79 at the Tbr-1 transcription start site, thereby interfering with RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II is an enzyme found in eukaryotic cells. It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mRNA and most snRNA and microRNA. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase...
(RNAPolII) activity and reducing Tbr-1 expression.
Mutants of Af9 experience increased dimethylation of H3K79 and increased Tbr-1 expression.
Bhlhb5
Bhlhb5 is a gene marker in the mouse brain, which is responsible for procurement of caudal identity. It is expressed at high levels in caudal regions, but is not generally observed in the frontal cortex. TBR1 is expressed at very high levels in the frontal cortex and very lower levels in the caudal regions. Using TBR1 null mutants, it was found that Bhlhb5 is up-regulated in the absence of TBR1. This up-regulation of Bhlhb5 led to the conclusion that TBR1 suppresses caudal identity.Sox5
Tbr1 is involved in the downstream regulation of Sox5SOX5
Transcription factor SOX-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX5 gene.-Further reading:...
. It is also involved in the maintenance of Sox5. It has been found that Sox5 interacts with Tbr1 to regulate Fezf2 transcription.

