Tetrapanax
Encyclopedia
Tetrapanax papyriferus (Tung-tsau or Rice-paper Plant) is an evergreen
shrub
in the family
Araliaceae
, the sole species
in the genus
Tetrapanax. Its botanical name
is unusual in that its specific epithet varies from one source to another, sometimes being rendered as "papyriferum" or "papyrifer". It is endemic
to Taiwan
, but widely cultivated
in East Asia
and sometimes in other tropical regions as well.*
The pith
from the stem is used to make a substance commonly known as rice paper
, but more properly termed pith paper.
The species was once included in the genus Fatsia
as Fatsia papyrifera.
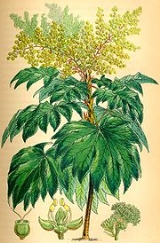
at the top (superficially similar to a palm
crown). The leaves are carried on 40-60 cm petioles, the leaf blade orbicular, 30-50 cm across, deeply palmately lobed with 5-11 primary lobes, the central lobes larger and Y-forked near the end. It spreads extensively by sprouts from the root
system underground. The inflorescence
is a large panicle
of hemispherical to globular umbel
s near the end of the stem. The flowers have 4 or 5 small white petals. The fruit
is a small drupe
.
Evergreen
In botany, an evergreen plant is a plant that has leaves in all seasons. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which completely lose their foliage during the winter or dry season.There are many different kinds of evergreen plants, both trees and shrubs...
shrub
Shrub
A shrub or bush is distinguished from a tree by its multiple stems and shorter height, usually under 5–6 m tall. A large number of plants may become either shrubs or trees, depending on the growing conditions they experience...
in the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Araliaceae
Araliaceae
Araliaceae is a family of flowering plants, also known as the Aralia family or Ivy family. The family includes 254 species of trees, shrubs, lianas and perennial herbaceous plants into 2 subfamilies...
, the sole species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
in the genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
Tetrapanax. Its botanical name
Botanical name
A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar and/or Group epithets must conform to the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants...
is unusual in that its specific epithet varies from one source to another, sometimes being rendered as "papyriferum" or "papyrifer". It is endemic
Endemic (ecology)
Endemism is the ecological state of being unique to a defined geographic location, such as an island, nation or other defined zone, or habitat type; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, all species of lemur are endemic to the...
to Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, but widely cultivated
Horticulture
Horticulture is the industry and science of plant cultivation including the process of preparing soil for the planting of seeds, tubers, or cuttings. Horticulturists work and conduct research in the disciplines of plant propagation and cultivation, crop production, plant breeding and genetic...
in East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
and sometimes in other tropical regions as well.*
The pith
Pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. In eudicots, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocots, it extends also into flowering stems and roots...
from the stem is used to make a substance commonly known as rice paper
Rice paper
Rice paper usually refers to paper made from parts of the rice plant, like rice straw or rice flour. The term is also used for paper made from or containing other plants, such as hemp, bamboo or mulberry...
, but more properly termed pith paper.
The species was once included in the genus Fatsia
Fatsia
Fatsia is a small genus of three species of evergreen shrubs native to southern Japan and Taiwan. They have stout, sparsely branched stems bearing spirally-arranged, large leathery, palmately lobed leaves 20-50 cm in width, on a petiole up to 50 cm long, and small creamy-white flowers in...
as Fatsia papyrifera.
Description
It grows to 3-7 m tall, with usually unbranched stems 2 cm diameter bearing a rosette of large leavesLeaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
at the top (superficially similar to a palm
Arecaceae
Arecaceae or Palmae , are a family of flowering plants, the only family in the monocot order Arecales. There are roughly 202 currently known genera with around 2600 species, most of which are restricted to tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate climates...
crown). The leaves are carried on 40-60 cm petioles, the leaf blade orbicular, 30-50 cm across, deeply palmately lobed with 5-11 primary lobes, the central lobes larger and Y-forked near the end. It spreads extensively by sprouts from the root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
system underground. The inflorescence
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Strictly, it is the part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed and which is accordingly modified...
is a large panicle
Panicle
A panicle is a compound raceme, a loose, much-branched indeterminate inflorescence with pedicellate flowers attached along the secondary branches; in other words, a branched cluster of flowers in which the branches are racemes....
of hemispherical to globular umbel
Umbel
An umbel is an inflorescence which consists of a number of short flower stalks which are equal in length and spread from a common point, somewhat like umbrella ribs....
s near the end of the stem. The flowers have 4 or 5 small white petals. The fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
is a small drupe
Drupe
In botany, a drupe is a fruit in which an outer fleshy part surrounds a shell of hardened endocarp with a seed inside. These fruits develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with superior ovaries...
.

