Thermal management of high power LED
Encyclopedia
High power light-emitting diode
s (LEDs) are likely to replace other technologies such as incandescent and fluorescent bulbs in signaling, solid state lighting, and vehicle headlights because they save energy and extend the light's lifetime. LEDs that use from 500 milliwatts to as much as 10 watt
s in a single package have become standard, and researchers expect to use even more power in the future. Some of the electricity in an LED becomes heat rather than light. If that heat is not removed, the LEDs run at high temperatures, which not only lowers their efficiency, but also makes the LED more dangerous and less reliable
. Thus, thermal management of high power LEDs is a crucial area of research and development.
 In order to maintain a low junction temperature
In order to maintain a low junction temperature
to keep good performance of an LED
, every method of releasing heat from LEDs should be considered. Conduction
, convection
, and radiation
are the three means of heat transfer. Typically, LEDs are encapsulated in a transparent resin
, which is a poor thermal conductor. Nearly all heat produced is conducted through the back side of the chip. Heat is generated from the PN junction by electrical energy that was not converted to useful light, and conducted to outside ambience through a long and extensive path, from junction to solder
point, solder point to board, and board to the heat sink
and then to the atmosphere. The heat path of tungsten
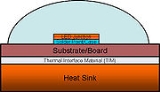
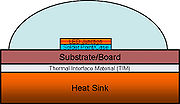
light bulbs is almost all straight into the atmosphere, starting from filament to the glass and ending with the thermal resistance from glass to the atmosphere. A typical LED side view and its thermal model are shown in the figures.
Intuitively, one can see that the junction temperature
will be lower if the thermal impedance is smaller and likewise, with a lower ambient temperature. To maximize the useful ambient temperature range for a given power
dissipation, the total thermal resistance from junction to ambient must be minimized. The values for the thermal resistance vary widely depending on the material or component supplier. For example, RJC will range from 2.6oC/W to 18oC/W, depending on the LED
manufacturer. The thermal interface material’s (TIM) thermal resistance will also vary depending on the type of material selected. Common TIMs are epoxy
, thermal grease, pressure sensitive adhesive and solder. In the most cases, power LEDs
will be mounted on metal-core printed circuit boards (MCPCB), which will be attached to a heat sink. Heat flows from the LED
junction through the MCPCB to the heat sink by way of conduction, and the heat sink diffuses heat to the ambient surroundings by convection. So, we can also add convection to the thermal model at the end of the heat transmission path. In the package design, the surface flatness and quality of each component, applied mounting pressure
, contact area, the type of interface material and its thickness are all important parameters to thermal resistance design.
is commonly used to bond LED and board, and board and heat sinks. Using a thermal conductive adhesive can further optimize the thermal performance.
s provide a path for heat from the LED source to outside medium. Heat sinks can dissipate power in three ways: conduction
(heat transfer from one solid to another), convection
(heat transfer from a solid to a moving fluid, for most LED applications the fluid will be air), or radiation
(heat transfer from two bodies of different surface temperatures through electromagnetic waves).
Light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode is a semiconductor light source. LEDs are used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for other lighting...
s (LEDs) are likely to replace other technologies such as incandescent and fluorescent bulbs in signaling, solid state lighting, and vehicle headlights because they save energy and extend the light's lifetime. LEDs that use from 500 milliwatts to as much as 10 watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s in a single package have become standard, and researchers expect to use even more power in the future. Some of the electricity in an LED becomes heat rather than light. If that heat is not removed, the LEDs run at high temperatures, which not only lowers their efficiency, but also makes the LED more dangerous and less reliable
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is an engineering field, that deals with the study, evaluation, and life-cycle management of reliability: the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It is often measured as a probability of...
. Thus, thermal management of high power LEDs is a crucial area of research and development.
Heat transfer procedure


Junction temperature
Junction temperature is the highest temperature of the actual semiconductor in an electronic device. In operation it is higher than case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior...
to keep good performance of an LED
LEd
LEd is a TeX/LaTeX editing software working under Microsoft Windows. It is a freeware product....
, every method of releasing heat from LEDs should be considered. Conduction
Heat conduction
In heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
, convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
, and radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
are the three means of heat transfer. Typically, LEDs are encapsulated in a transparent resin
Resin
Resin in the most specific use of the term is a hydrocarbon secretion of many plants, particularly coniferous trees. Resins are valued for their chemical properties and associated uses, such as the production of varnishes, adhesives, and food glazing agents; as an important source of raw materials...
, which is a poor thermal conductor. Nearly all heat produced is conducted through the back side of the chip. Heat is generated from the PN junction by electrical energy that was not converted to useful light, and conducted to outside ambience through a long and extensive path, from junction to solder
Solder
Solder is a fusible metal alloy used to join together metal workpieces and having a melting point below that of the workpiece.Soft solder is what is most often thought of when solder or soldering are mentioned and it typically has a melting range of . It is commonly used in electronics and...
point, solder point to board, and board to the heat sink
Heat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
and then to the atmosphere. The heat path of tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
light bulbs is almost all straight into the atmosphere, starting from filament to the glass and ending with the thermal resistance from glass to the atmosphere. A typical LED side view and its thermal model are shown in the figures.
Intuitively, one can see that the junction temperature
Junction temperature
Junction temperature is the highest temperature of the actual semiconductor in an electronic device. In operation it is higher than case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior...
will be lower if the thermal impedance is smaller and likewise, with a lower ambient temperature. To maximize the useful ambient temperature range for a given power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
dissipation, the total thermal resistance from junction to ambient must be minimized. The values for the thermal resistance vary widely depending on the material or component supplier. For example, RJC will range from 2.6oC/W to 18oC/W, depending on the LED
LEd
LEd is a TeX/LaTeX editing software working under Microsoft Windows. It is a freeware product....
manufacturer. The thermal interface material’s (TIM) thermal resistance will also vary depending on the type of material selected. Common TIMs are epoxy
Epoxy
Epoxy, also known as polyepoxide, is a thermosetting polymer formed from reaction of an epoxide "resin" with polyamine "hardener". Epoxy has a wide range of applications, including fiber-reinforced plastic materials and general purpose adhesives....
, thermal grease, pressure sensitive adhesive and solder. In the most cases, power LEDs
LEDS
LEDS can be initials for:* Law Enforcement Data System* Link Eleven Display System* Low Energy Dislocation Structure* Land Electronic Defence System * LEDs * Life-Events and Difficulties Schedule...
will be mounted on metal-core printed circuit boards (MCPCB), which will be attached to a heat sink. Heat flows from the LED
LEd
LEd is a TeX/LaTeX editing software working under Microsoft Windows. It is a freeware product....
junction through the MCPCB to the heat sink by way of conduction, and the heat sink diffuses heat to the ambient surroundings by convection. So, we can also add convection to the thermal model at the end of the heat transmission path. In the package design, the surface flatness and quality of each component, applied mounting pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, contact area, the type of interface material and its thickness are all important parameters to thermal resistance design.
Passive thermal designs
Some considerations for passive thermal designs to ensure good thermal management for high power LED operation include:Adhesive
AdhesiveAdhesive
An adhesive, or glue, is a mixture in a liquid or semi-liquid state that adheres or bonds items together. Adhesives may come from either natural or synthetic sources. The types of materials that can be bonded are vast but they are especially useful for bonding thin materials...
is commonly used to bond LED and board, and board and heat sinks. Using a thermal conductive adhesive can further optimize the thermal performance.
Heat sink
Heat sinkHeat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
s provide a path for heat from the LED source to outside medium. Heat sinks can dissipate power in three ways: conduction
Heat conduction
In heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
(heat transfer from one solid to another), convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
(heat transfer from a solid to a moving fluid, for most LED applications the fluid will be air), or radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
(heat transfer from two bodies of different surface temperatures through electromagnetic waves).
- Material – The thermal conductivity of the material that the heat sink is made from directly affects the dissipation efficiency through conduction. Normally this is aluminum, although copperCopperCopper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
may be used with an advantage for flat-sheet heat sinks. New materials include thermoplastics that are used when heat dissipation requirements are lower than normal or complex shape would be advantaged by injection molding, and natural graphite solutions which offer better thermal transfer than copper with a lower weight than aluminum plus the ability to be formed into complex 2 dimensional shapes. Graphite is considered an exotic cooling solution and does come at a higher production cost. Heat pipes may also be added to aluminum or copper heat sinks to reduce spreading resistance. - Shape - Thermal transfer takes place at the surface of the heat sink. Therefore, heat sinks should be designed to have a large surface area. This goal can be reached by using a large number of fine finFinA fin is a surface used for stability and/or to produce lift and thrust or to steer while traveling in water, air, or other fluid media, . The first use of the word was for the limbs of fish, but has been extended to include other animal limbs and man-made devices...
s or by increasing the size of the heat sink itself. - Surface Finish - Thermal radiation of heat sinks is a function of surface finish, especially at higher temperatures. A painted surface will have a greater emissivityEmissivityThe emissivity of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit energy by radiation. It is the ratio of energy radiated by a particular material to energy radiated by a black body at the same temperature...
than a bright, unpainted one. The effect is most remarkable with flat-plate heat sinks, where about one-third of the heat is dissipated by radiation. Moreover, a perfectly flat contact area allows the use of a thinner layer of thermal compound, which will reduce the thermal resistance between the heat sink and LED source. On the other hand, anodizing or etchingEtchingEtching is the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio in the metal...
will also decrease the thermal resistance. - Mounting method- Heat-sink mountings with screws or springs are often better than regular clips, thermal conductive glue or sticky tape.
PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
- MCPCB - MCPCB (Metal Core PCBPrinted circuit boardA printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
) are those boards which incorporate a base metal material as heat spreader as an integral part of the circuit board. The metal core usually consists of aluminum alloy. Furthermore MCPCB can take advantage of incorporating a dielectricDielectricA dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
polymerPolymerA polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
layer with high thermal conductivityThermal conductivityIn physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
for lower thermal resistance. - Separation - Separating the LED drive circuitry from the LED board prevents the heat generated by the driver from raising the LED junction temperature.
Package type
- Flip chip - The concept is similar to flip-chip in package configuration widely used in the siliconSiliconSilicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
integrated circuitIntegrated circuitAn integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
industry. Briefly speaking, the LED die is assembled face down on the sub-mount, which is usually silicon or ceramicCeramicA ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
, acting as the heat spreader and supporting substrate. The flip-chip joint can be eutectic, high-leadLeadLead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, lead-free solderSolderSolder is a fusible metal alloy used to join together metal workpieces and having a melting point below that of the workpiece.Soft solder is what is most often thought of when solder or soldering are mentioned and it typically has a melting range of . It is commonly used in electronics and...
or goldGoldGold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
stub. The primary source of light comes from the back side of the LED chip, and there is usually a built-in reflective layer between the light emitter and the solder joints to reflect the light emitted downwards up. Several companies have adopted flip-chip packages for their high-power LED, achieving bout 60% reduction in the thermal resistance of the LED while keeping its thermal reliability.
See also
- LED lampLED lampAn LED lamp is a solid-state lamp that uses light-emitting diodes as the source of light. The LEDs involved may be conventional semiconductor light-emitting diodes, organic LEDs , or polymer light-emitting diodes devices, although PLED technologies are not currently commercially available.Since...
- solid state lighting (SSL) - Thermal resistance in electronicsThermal resistance in electronicsThermal resistance is a heat property - and a measure of a temperature difference, by which an object - or material resist a heat flow...
- Thermal management of electronic devices and systemsThermal management of electronic devices and systemsHeat generated by electronic devices and circuitry must be dissipated to improve reliability and prevent premature failure. Techniques for heat dissipation can include heatsinks and fans for air cooling, and other forms of computer cooling such as liquid cooling....
- Active cooling
- Synthetic JetSynthetic JetIn fluid dynamics, a synthetic jet flow — is a type of jet flow, which is synthesized from the ambient fluid.A jet flow is a fluid flow in which a stream of one fluid mixes with a surrounding medium. An example is a water jet that forms when you put your thumb over the end of a hose. The water...

