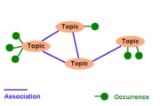
Topic map
Encyclopedia
Topic Maps is a standard for the representation and interchange of knowledge, with an emphasis on the findability
of information. Topic maps were originally developed in the late 1990's as a way to represent back-of-the-book index
structures so that multiple indexes from different sources could be merged. However, the developers quickly realized that with a little additional generalization, they could create a meta-model with potentially far wider application. The ISO
standard is formally known as ISO/IEC 13250:2003.
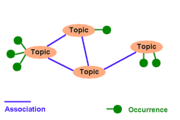
A topic map represents information using
Topic Maps are similar to concept map
s and mind map
s in many respects, though only Topic Maps are standardized. Topic Maps are a form of semantic web
technology, and some work has been undertaken on interoperability between the W3C's RDF
/OWL
/SPARQL
family of semantic web standards and the ISO
's family of Topic Maps standards.
The semantic expressivity
of Topic Maps is, in many ways, equivalent to that of RDF
, but the major differences are that Topic Maps (i) provide a higher level of semantic abstraction
(providing a template of topics, associations and occurrences, while RDF only provides a template of two arguments linked by one relationship) and (hence) (ii) allow n-ary relationships (hypergraph
s) between any number of nodes, while RDF is limited to triplet
s.
of the topic map.
Topic Maps explicitly support the concept of merging of identity between multiple topics or topic maps. Furthermore, because ontologies are topic maps themselves, they can also be merged thus allowing for the automated integration of information from diverse sources into a coherent new topic map. Features such as subject identifiers (URI
s given to topics) and PSIs (Published Subject Indicators) are used to control merging between differing taxonomies. Scoping on names provides a way to organise the various names given to a particular topic by different sources.
. TMMN uses only a very small number of symbols — "blob", "label", "line", "dotted line", and "arrow" — to represent the relationships and basic elements of the Topic Maps model, namely Topics, Names, Associations (& Roles), Scope, and Occurrences (including Subject Identifiers & Subject Locators). The "Martian" refers to the archetypal "Martian Scientist", namely, the ability to communicate knowledge across linguistic and cultural barriers, known and unknown. It was developed as part of the musicDNA
project.
Advanced Topic Maps Martian Notation is currently under development by the musicDNA
community and includes shorthand notation for various types of whole-part relationships.
A format called linear topic map notation (LTM) serves as a kind of shorthand for writing topic maps in plain text editors. This is useful for writing short personal topic maps or exchanging partial topic maps by email. The format can be converted to XTM.
There is another format called AsTMa which serves a similar purpose. When writing topic maps manually it is much more compact, but of course can be converted to XTM. Alternatively, it can be used directly with the Perl
Module TM (which also supports LTM).
/WG3 committee (ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 34, Working Group 3 - Document description and processing languages - Information Association).
The Topic Maps (ISO/IEC 13250) reference model and data model standards are defined in a way that is independent of any specific serialization or syntax.
XML Serialization formats
Note that XTM 1.0 predates and therefore is not compatible with the more recent versions of the (ISO/IEC 13250) standard.
Other (proposed or standardized) serialization formats include:
The above standards are all recently proposed or defined as part of ISO/IEC 13250. As described below, there are also other, serialization formats such as LTM, AsTMa= that have not been put forward as standards.
A de facto API
standard called Common Topic Maps Application Programming Interface (TMAPI) was published in April 2004 and is supported by many Topic Maps implementations or vendors:
Query standard
In normal use it is often desirable to have a way to arbitrarily query the data within a particular Topic Maps store. Many implementations provide a syntax by which this can be achieved (kind of like 'SQL for Topic Maps') but the syntax tends to vary a lot between different implementations. With this in mind, work has gone into defining a standardized syntax for querying topic maps:
Constraint standards
It can also be desirable to define a set of constraints that can be used to guarantee or check the semantic validity of topic maps data for a particular domain. (Kind of like database constraints for topic maps). Constraints can be used to define things like 'every document needs an author' or 'all managers must be human'. There are often implementation specific ways of achieving these goals, but work has gone into defining a standardized constraint language as follows:
Earlier standards
The "Topic Maps" concept has existed for a long time. The HyTime standard was proposed as far back as 1992 (or earlier?). Earlier versions of ISO 13250 (than the current revision) also exist. More information about such standards can be found at the ISO Topic Maps site.
Findability
Findability is a term for the ease with which information contained on a website can be found, both from outside the website and by users already on the website. Although findability has relevance outside the World Wide Web, it is usually used in the context of the web...
of information. Topic maps were originally developed in the late 1990's as a way to represent back-of-the-book index
Back-of-the-book index
-Introduction:A back-of-the-book index is a collection of entries - often alphabetically arranged - which are made in order to allow users to locate information in a given book ....
structures so that multiple indexes from different sources could be merged. However, the developers quickly realized that with a little additional generalization, they could create a meta-model with potentially far wider application. The ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
standard is formally known as ISO/IEC 13250:2003.

A topic map represents information using
- topics, representing any concept, from people, countries, and organizations to software modules, individual files, and events,
- associations, representing hypergraphHypergraphIn mathematics, a hypergraph is a generalization of a graph, where an edge can connect any number of vertices. Formally, a hypergraph H is a pair H = where X is a set of elements, called nodes or vertices, and E is a set of non-empty subsets of X called hyperedges or links...
relationships between topics, and - occurrences representing information resources relevant to a particular topic.
Topic Maps are similar to concept map
Concept map
For concept maps in generic programming, see Concept .A concept map is a diagram showing the relationships among concepts. It is a graphical tool for organizing and representing knowledge....
s and mind map
Mind map
A mind map is a diagram used to represent words, ideas, tasks, or other items linked to and arranged around a central key word or idea. Especially in British English, the terms spidergram and spidergraph are more common, but they can cause confusion with the term spider diagram used in mathematics...
s in many respects, though only Topic Maps are standardized. Topic Maps are a form of semantic web
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web is a collaborative movement led by the World Wide Web Consortium that promotes common formats for data on the World Wide Web. By encouraging the inclusion of semantic content in web pages, the Semantic Web aims at converting the current web of unstructured documents into a "web of...
technology, and some work has been undertaken on interoperability between the W3C's RDF
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model...
/OWL
Web Ontology Language
The Web Ontology Language is a family of knowledge representation languages for authoring ontologies.The languages are characterised by formal semantics and RDF/XML-based serializations for the Semantic Web...
/SPARQL
SPARQL
SPARQL is an RDF query language; its name is an acronym that stands for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language. It was made a standard by the RDF Data Access Working Group of the World Wide Web Consortium, and considered as one of the key technologies of semantic web...
family of semantic web standards and the ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
's family of Topic Maps standards.
The semantic expressivity
Expressive power
In computer science, the expressive power of a language describes the ideas expressible in that language.For example, the Web Ontology Language expression language profile lacks ideas which can be expressed in OWL2 RL . OWL2 EL may therefore be said to have less expressive power than OWL2 RL...
of Topic Maps is, in many ways, equivalent to that of RDF
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model...
, but the major differences are that Topic Maps (i) provide a higher level of semantic abstraction
Semantic data model
A semantic data model in software engineering has various meanings:# It is a conceptual data model in which semantic information is included. This means that the model describes the meaning of its instances...
(providing a template of topics, associations and occurrences, while RDF only provides a template of two arguments linked by one relationship) and (hence) (ii) allow n-ary relationships (hypergraph
Hypergraph
In mathematics, a hypergraph is a generalization of a graph, where an edge can connect any number of vertices. Formally, a hypergraph H is a pair H = where X is a set of elements, called nodes or vertices, and E is a set of non-empty subsets of X called hyperedges or links...
s) between any number of nodes, while RDF is limited to triplet
Tuple
In mathematics and computer science, a tuple is an ordered list of elements. In set theory, an n-tuple is a sequence of n elements, where n is a positive integer. There is also one 0-tuple, an empty sequence. An n-tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair...
s.
Ontology and merging
Topics, associations, and occurrences can all be typed, where the types must be defined by the one or more creators of the topic map(s). The definitions of allowed types is known as the ontologyOntology (computer science)
In computer science and information science, an ontology formally represents knowledge as a set of concepts within a domain, and the relationships between those concepts. It can be used to reason about the entities within that domain and may be used to describe the domain.In theory, an ontology is...
of the topic map.
Topic Maps explicitly support the concept of merging of identity between multiple topics or topic maps. Furthermore, because ontologies are topic maps themselves, they can also be merged thus allowing for the automated integration of information from diverse sources into a coherent new topic map. Features such as subject identifiers (URI
Uniform Resource Identifier
In computing, a uniform resource identifier is a string of characters used to identify a name or a resource on the Internet. Such identification enables interaction with representations of the resource over a network using specific protocols...
s given to topics) and PSIs (Published Subject Indicators) are used to control merging between differing taxonomies. Scoping on names provides a way to organise the various names given to a particular topic by different sources.
Notation
There are different ways of notating Topic Maps graphically, in addition to GTM, listed below. One recently-developed example is Topic Maps Martian Notation. TMMN (its acronym) is a simple graphical notation used to explain the Topic Maps data model, and map out both ontologies and representative instance data. It is designed for use on whiteboard or paper, as well as within any diagram-based software including everyday presentation tools such as PowerPoint and OpenOffice.orgOpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org, commonly known as OOo or OpenOffice, is an open-source application suite whose main components are for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, and databases. OpenOffice is available for a number of different computer operating systems, is distributed as free software...
. TMMN uses only a very small number of symbols — "blob", "label", "line", "dotted line", and "arrow" — to represent the relationships and basic elements of the Topic Maps model, namely Topics, Names, Associations (& Roles), Scope, and Occurrences (including Subject Identifiers & Subject Locators). The "Martian" refers to the archetypal "Martian Scientist", namely, the ability to communicate knowledge across linguistic and cultural barriers, known and unknown. It was developed as part of the musicDNA
MusicDNA
musicDNA is a file system that consists of an ontology that describes the underlying structure of the events that make up musical history - "who did what, where, and when" together with a set of user interfaces that allow subscribers to view, add and edit entries. musicDNA is implemented using a...
project.
Advanced Topic Maps Martian Notation is currently under development by the musicDNA
MusicDNA
musicDNA is a file system that consists of an ontology that describes the underlying structure of the events that make up musical history - "who did what, where, and when" together with a set of user interfaces that allow subscribers to view, add and edit entries. musicDNA is implemented using a...
community and includes shorthand notation for various types of whole-part relationships.
Data format
The specification is summarized in the abstract as follows: "This specification provides a model and grammar for representing the structure of information resources used to define topics, and the associations (relationships) between topics. Names, resources, and relationships are said to be characteristics of abstract subjects, which are called topics. Topics have their characteristics within scopes: i.e. the limited contexts within which the names and resources are regarded as their name, resource, and relationship characteristics. One or more interrelated documents employing this grammar is called a topic map."A format called linear topic map notation (LTM) serves as a kind of shorthand for writing topic maps in plain text editors. This is useful for writing short personal topic maps or exchanging partial topic maps by email. The format can be converted to XTM.
There is another format called AsTMa which serves a similar purpose. When writing topic maps manually it is much more compact, but of course can be converted to XTM. Alternatively, it can be used directly with the Perl
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Perl was originally developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions and become widely popular...
Module TM (which also supports LTM).
Current standard
The most recent work standardizing Topic Maps (ISO/IEC 13250) is taking place under the umbrella of the ISO/IEC JTC1/SC34ISO/IEC JTC1/SC34
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34 titled as Document description and processing languages is a subcommittee of the ISO/IEC JTC1 joint technical committee, which is a collaborative effort of both the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission.-Scope and Terms...
/WG3 committee (ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 34, Working Group 3 - Document description and processing languages - Information Association).
The Topic Maps (ISO/IEC 13250) reference model and data model standards are defined in a way that is independent of any specific serialization or syntax.
XML Serialization formats
- In the year 2000 Topic Maps was defined in an XML syntax XTM. This is now commonly known as "XTM 1.0" and is still in fairly common use.
- The ISO standards committee published an updated XML syntax in 2006, XTM 2.0 which is increasingly in use today.
Note that XTM 1.0 predates and therefore is not compatible with the more recent versions of the (ISO/IEC 13250) standard.
Other (proposed or standardized) serialization formats include:
- CXTM - Canonical XML Topic Maps format (canonicalization of topic maps)
- CTM - a Compact Topic Maps Notation (not based on XML)
- GTM - a Graphical Topic Maps Notation
The above standards are all recently proposed or defined as part of ISO/IEC 13250. As described below, there are also other, serialization formats such as LTM, AsTMa= that have not been put forward as standards.
Related standards
Topic Maps APIA de facto API
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
standard called Common Topic Maps Application Programming Interface (TMAPI) was published in April 2004 and is supported by many Topic Maps implementations or vendors:
- TMAPI - Common Topic Maps Application Programming Interface
- TMAPI 2.0 Topic Maps Application Programming Interface (v2.0)
Query standard
In normal use it is often desirable to have a way to arbitrarily query the data within a particular Topic Maps store. Many implementations provide a syntax by which this can be achieved (kind of like 'SQL for Topic Maps') but the syntax tends to vary a lot between different implementations. With this in mind, work has gone into defining a standardized syntax for querying topic maps:
- ISO 18048: TMQL - Topic Maps Query Language
Constraint standards
It can also be desirable to define a set of constraints that can be used to guarantee or check the semantic validity of topic maps data for a particular domain. (Kind of like database constraints for topic maps). Constraints can be used to define things like 'every document needs an author' or 'all managers must be human'. There are often implementation specific ways of achieving these goals, but work has gone into defining a standardized constraint language as follows:
- ISO 19756: TMCL - Topic Maps Constraint Language
Earlier standards
The "Topic Maps" concept has existed for a long time. The HyTime standard was proposed as far back as 1992 (or earlier?). Earlier versions of ISO 13250 (than the current revision) also exist. More information about such standards can be found at the ISO Topic Maps site.
See also
- Back-of-the-book indexBack-of-the-book index-Introduction:A back-of-the-book index is a collection of entries - often alphabetically arranged - which are made in order to allow users to locate information in a given book ....
- Semantic WebSemantic WebThe Semantic Web is a collaborative movement led by the World Wide Web Consortium that promotes common formats for data on the World Wide Web. By encouraging the inclusion of semantic content in web pages, the Semantic Web aims at converting the current web of unstructured documents into a "web of...
- Concept mapConcept mapFor concept maps in generic programming, see Concept .A concept map is a diagram showing the relationships among concepts. It is a graphical tool for organizing and representing knowledge....
- Mind mapMind mapA mind map is a diagram used to represent words, ideas, tasks, or other items linked to and arranged around a central key word or idea. Especially in British English, the terms spidergram and spidergraph are more common, but they can cause confusion with the term spider diagram used in mathematics...
- UMLUnified Modeling LanguageUnified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
- Ontology (information science)
- MetamodelingMetamodelingMetamodeling, or meta-modeling in software engineering and systems engineering among other disciplines, is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems...
External links
- Information portal about Topic Maps
- Home page of the Topic Maps ISO standards
- ISO/IEC 13250 Topic Maps, Second Edition
- XML Topic Maps (XTM) 1.0 Specification
- What Are Topic Maps?
- Towards knowledge organization with Topic Maps
- An Introduction to Topic Maps (MSDN)
- tinyTiM - The tiny Topic Maps engine (Open Source)
- Mappa - Topic Maps engine for Python (Open Source)
- Information portal of the Topic Maps Lab
- Topic Maps Snippets, news from the Topic Maps community
- topicmap.com, portal covering tools, conferences, papers and news
- Topic engine in Cfengine for configuration management with semantic knowledge map
- QuaaxTM - A PHP Topic Maps engine (Open Source)
- TMXTM.it - Italian website about Topic Maps and XTM

