Tourette syndrome
Encyclopedia
Tourette syndrome is an inherited
neuropsychiatric
disorder with onset in childhood, characterized by multiple physical (motor) tic
s and at least one vocal (phonic) tic; these tics characteristically wax and wane. Tourette's is defined as part of a spectrum
of tic disorder
s, which includes transient and chronic tics.
Tourette's was once considered a rare and bizarre syndrome
, most often associated with the exclamation of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks (coprolalia
), but this symptom is present in only a small minority of people with Tourette's. Tourette's is no longer considered a rare condition, but it may not always be correctly identified because most cases are classified as mild. Between 1 and 10 children per 1,000 have Tourette's; as many as 10 per 1,000 people may have tic disorders, with the more common tics of eye blinking, coughing, throat clearing, sniffing, and facial movements. Tourette's does not adversely affect intelligence or life expectancy
. The severity of the tics decreases for most children as they pass through adolescence, and extreme Tourette's in adulthood is a rarity. Notable individuals with Tourette's are found in all walks of life.
Genetic
and environmental factors play a role in the etiology
of Tourette's, but the exact causes are unknown. In most cases, medication is unnecessary. There is no effective medication for every case of tics, but there are medications and therapies that can help when their use is warranted. Explanation and reassurance alone are often sufficient treatment; education is an important part of any treatment plan.
The eponym
was bestowed by Jean-Martin Charcot
(1825–1893) on behalf of his resident, Georges Albert Édouard Brutus Gilles de la Tourette
(1859–1904), a French physician and neurologist
, who published an account of nine patients with Tourette's in 1885.
s are sudden, repetitive, stereotyped, nonrhythmic movements (motor tics) and utterances (phonic tics) that involve discrete muscle groups. Motor tics are movement-based tics, while phonic tics are involuntary sounds produced by moving air through the nose, mouth, or throat.
Tourette's is one of several tic disorder
s, which are classified by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(DSM) according to type (motor or phonic tics) and duration (transient or chronic). Transient tic disorder consists of multiple motor tics, phonic tics or both, with a duration between four weeks and twelve months. Chronic tic disorder is either single or multiple, motor or phonic tics (but not both), which are present for more than a year. Tourette's is diagnosed when multiple motor tics, and at least one phonic tic, are present for more than a year. Tic disorders are defined similarly by the World Health Organization
(International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, ICD-10
codes).
Although Tourette's is the more severe expression of the spectrum
of tic disorders, most cases are mild. The severity of symptoms varies widely among people with Tourette's, and mild cases may be undetected.
Coprolalia
(the spontaneous utterance of socially objectionable or taboo words or phrases) is the most publicized symptom of Tourette's, but it is not required for a diagnosis of Tourette's and only about 10% of Tourette's patients exhibit it. Echolalia
(repeating the words of others) and palilalia
(repeating one's own words) occur in a minority of cases, while the most common initial motor and vocal tics are, respectively, eye blinking and throat clearing.
In contrast to the abnormal movements of other movement disorder
s (for example, chorea
s, dystonia
s, myoclonus
, and dyskinesia
s), the tics of Tourette's are stereotypic, temporarily suppressible, nonrhythmic, and often preceded by an unwanted premonitory urge. Immediately preceding tic onset, most individuals with Tourette's are aware of an urge, similar to the need to sneeze or scratch an itch. Individuals describe the need to tic as a buildup of tension, pressure, or energy which they consciously choose to release, as if they "had to do it" to relieve the sensation or until it feels "just right". Examples of the premonitory urge are the feeling of having something in one's throat, or a localized discomfort in the shoulders, leading to the need to clear one's throat or shrug the shoulders. The actual tic may be felt as relieving this tension or sensation, similar to scratching an itch. Another example is blinking to relieve an uncomfortable sensation in the eye. These urges and sensations, preceding the expression of the movement or vocalization as a tic, are referred to as "premonitory sensory phenomena
" or premonitory urges. Because of the urges that precede them, tics are described as semi-voluntary or "unvoluntary", rather than specifically involuntary; they may be experienced as a voluntary, suppressible response to the unwanted premonitory urge. Published descriptions of the tics of Tourette's identify sensory phenomena as the core symptom
of the syndrome, even though they are not included in the diagnostic criteria.
While individuals with tics are sometimes able to suppress their tics for limited periods of time, doing so often results in an explosion of tics afterward. People with Tourette's may seek a secluded spot to release their symptoms, or there may be a marked increase in tics after a period of suppression at school or at work. Some people with Tourette's may not be aware of the premonitory urge. Children may be less aware of the premonitory urge associated with tics than are adults, but their awareness tends to increase with maturity. They may have tics for several years before becoming aware of premonitory urges. Children may suppress tics while in the doctor's office, so they may need to be observed while they are not aware they are being watched. The ability to suppress tics varies among individuals, and may be more developed in adults than children.
Although there is no such thing as a "typical" case of Tourette syndrome, the condition follows a fairly reliable course in terms of the age of onset and the history of the severity of symptoms. Tics may appear up to the age of eighteen, but the most typical age of onset is from five to seven. A 1998 study published by Leckman et al. of the Yale Child Study Center
showed that the ages of highest tic severity are eight to twelve (average ten), with tics steadily declining for most patients as they pass through adolescence. The most common, first-presenting tics are eye blinking, facial movements, sniffing and throat clearing. Initial tics present most frequently in midline body regions where there are many muscles, usually the head, neck and facial region. This can be contrasted with the stereotyped movements of other disorders (such as stim
s and stereotypies of the autism spectrum disorders), which typically have an earlier age of onset, are more symmetrical, rhythmical and bilateral, and involve the extremities (e.g., flapping the hands). Tics that appear early in the course of the condition are frequently confused with other conditions, such as allergies, asthma
, and vision problems: pediatricians, allergists and ophthalmologists are typically the first to see a child with tics.
Among patients whose symptoms are severe enough to warrant referral to clinics, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
(ADHD) are often associated with Tourette's. Not all persons with Tourette's have ADHD or OCD or other comorbid conditions (co-occurring diagnoses other than Tourette's), although in clinical populations, a high percentage of patients presenting for care do have ADHD. One author reports that a ten-year overview of patient records revealed about 40% of patients with Tourette's have "TS-only" or "pure TS", referring to Tourette syndrome in the absence of ADHD, OCD and other disorders. Another author reports that 57% of 656 patients presenting with tic disorders had uncomplicated tics, while 43% had tics plus comorbid conditions. "Full-blown Tourette's" is a term used to describe patients who have significant comorbid conditions in addition to tics.
.
 A person with Tourette's has about a 50% chance of passing the gene(s) to one of his or her children, but Tourette's is a condition of variable expression
A person with Tourette's has about a 50% chance of passing the gene(s) to one of his or her children, but Tourette's is a condition of variable expression
and incomplete penetrance
. Thus, not everyone who inherits the genetic vulnerability will show symptoms; even close family members may show different severities of symptoms, or no symptoms at all. The gene(s) may express as Tourette's, as a milder tic disorder (transient or chronic tics), or as obsessive–compulsive symptoms without tics. Only a minority of the children who inherit the gene(s) have symptoms severe enough to require medical attention. Gender appears to have a role in the expression of the genetic vulnerability: males are more likely than females to express tics.
Non-genetic, environmental, infectious, or psychosocial
factors—while not causing Tourette's—can influence its severity. Autoimmune processes may affect tic onset and exacerbation in some cases. In 1998, a team at the US National Institute of Mental Health
proposed a hypothesis that both obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and tic disorders may arise in a subset of children as a result of a poststreptococcal
autoimmune process. Children who meet five diagnostic criteria are classified, according to the hypothesis, as having Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infections (PANDAS). This contentious hypothesis is the focus of clinical and laboratory research, but remains unproven.
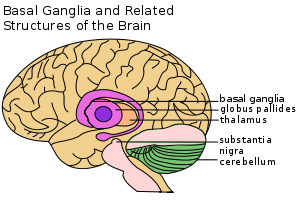
The exact mechanism affecting the inherited vulnerability to Tourette's has not been established, and the precise etiology is unknown. Tics are believed to result from dysfunction in cortical and subcortical regions, the thalamus, basal ganglia
and frontal cortex
. Neuroanatomic
models implicate failures in circuits connecting the brain's cortex and subcortex, and imaging techniques
implicate the basal ganglia and frontal cortex.
Some forms of OCD may be genetically linked to Tourette's. A subset of OCD is thought to be etiologically
related to Tourette's and may be a different expression of the same factors that are important for the expression of tics. The genetic relationship of ADHD to Tourette syndrome, however, has not been fully established.
or other causes of tourettism
—must be ruled out before conferring a Tourette's diagnosis.
There are no specific medical or screening tests that can be used in diagnosing Tourette's; it is frequently misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed, partly because of the wide expression of severity, ranging from mild (the majority of cases) or moderate, to severe (the rare, but more widely-recognized and publicized cases). Coughing, eye blinking and tics that mimic asthma are commonly misdiagnosed.
The diagnosis is made based on observation of the individual's symptoms and family history, and after ruling out secondary causes of tic disorders.
In patients with a typical onset and a family history of tics or obsessive–compulsive disorder, a basic physical and neurological examination may be sufficient.
There is no requirement that other comorbid conditions (such as ADHD or OCD) be present, but if a physician believes that there may be another condition present that could explain tics, tests may be ordered as necessary to rule out that condition. An example of this is when diagnostic confusion between tics and seizure
activity exists, which would call for an EEG
, or if there are symptoms that indicate an MRI to rule out brain abnormalities. TSH
levels can be measured to rule out hypothyroidism
, which can be a cause of tics. Brain imaging studies are not usually warranted. In teenagers and adults presenting with a sudden onset of tics and other behavioral symptoms, a urine drug screen for cocaine
and stimulants might be necessary. If a family history of liver disease
is present, serum copper and ceruloplasmin
levels can rule out Wilson's disease
. Most cases are diagnosed by merely observing a history of tics.
Secondary causes of tics (not related to inherited Tourette syndrome) are commonly referred to as tourettism
. Dystonia
s, choreas, other genetic conditions, and secondary causes of tics should be ruled out in the differential diagnosis
for Tourette syndrome. Other conditions that may manifest tics or stereotyped movements include developmental disorder
s, autism spectrum disorders, and stereotypic movement disorder
; Sydenham's chorea
; idiopathic
dystonia; and genetic conditions such as Huntington's disease
, neuroacanthocytosis
, Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome, Duchenne muscular dystrophy
, Wilson's disease, and tuberous sclerosis
. Other possibilities include chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome
, Klinefelter's syndrome
, XYY syndrome
and fragile X syndrome
. Acquired causes of tics include drug-induced tics, head trauma, encephalitis
, stroke
, and carbon monoxide poisoning
. The symptoms of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
may also be confused with Tourette syndrome. Most of these conditions are rarer than tic disorders, and a thorough history and examination may be enough to rule them out, without medical or screening tests.
s. Disruptive behaviors, impaired functioning, or cognitive impairment in patients with comorbid Tourette's and ADHD may be accounted for by the comorbid ADHD, highlighting the importance of identifying and treating comorbid conditions. Disruption from tics is commonly overshadowed by comorbid conditions that present greater interference to the child. Tic disorders in the absence of ADHD do not appear to be associated with disruptive behavior or functional impairment, while impairment in school, family, or peer relations is greater in patients who have more comorbid conditions and often determines whether therapy is needed.
Because comorbid conditions such as OCD and ADHD can be more impairing than tics, these conditions are included in an evaluation of patients presenting with tics. "It is critical to note that the comorbid conditions may determine functional status more strongly than the tic disorder," according to Samuel Zinner, MD. The initial assessment of a patient referred for a tic disorder should include a thorough evaluation, including a family history of tics, ADHD, obsessive–compulsive symptoms, and other chronic medical, psychiatric and neurological conditions. Children and adolescents with TS who have learning difficulties are candidates for psychoeducational testing, particularly if the child also has ADHD. Undiagnosed comorbid conditions may result in functional impairment, and it is necessary to identify and treat these conditions to improve functioning. Complications may include depression
, sleep problems
, social discomfort and self-injury
.
 The treatment of Tourette's focuses on identifying and helping the individual manage the most troubling or impairing symptoms. Most cases of Tourette's are mild, and do not require pharmacological
The treatment of Tourette's focuses on identifying and helping the individual manage the most troubling or impairing symptoms. Most cases of Tourette's are mild, and do not require pharmacological
treatment; instead, psychobehavioral therapy, education, and reassurance may be sufficient. Treatments, where warranted, can be divided into those that target tics and comorbid conditions, which, when present, are often a larger source of impairment than the tics themselves. Not all people with tics have comorbid conditions, but when those conditions are present, they often take treatment priority.
There is no cure for Tourette's and no medication that works universally for all individuals without significant adverse effects. Knowledge, education and understanding are uppermost in management plans for tic disorders. The management of the symptoms of Tourette's may include pharmacological, behavior
al and psychological
therapies. While pharmacological intervention is reserved for more severe symptoms, other treatments (such as supportive psychotherapy or cognitive behavioral therapy) may help to avoid or ameliorate depression
and social isolation, and to improve family support. Educating a patient, family, and surrounding community (such as friends, school, and church) is a key treatment strategy, and may be all that is required in mild cases.
 Medication is available to help when symptoms interfere with functioning. The classes of medication with the most proven efficacy in treating tics—typical and atypical
Medication is available to help when symptoms interfere with functioning. The classes of medication with the most proven efficacy in treating tics—typical and atypical
neuroleptics
including risperidone
(trade name Risperdal), ziprasidone
(Geodon), haloperidol
(Haldol), pimozide
(Orap) and fluphenazine
(Prolixin)—can have long-term and short-term adverse effects
. The antihypertensive
agents clonidine
(trade name Catapres) and guanfacine
(Tenex) are also used to treat tics; studies show variable efficacy, but a lower side effect profile than the neuroleptics. Stimulants and other medications may be useful in treating ADHD when it co-occurs with tic disorders. Drugs from several other classes of medications can be used when stimulant trials fail, including guanfacine
(trade name Tenex), atomoxetine (Strattera) and tricyclic antidepressant
s. Clomipramine
(Anafranil), a tricyclic, and SSRIs
—a class of antidepressant
s including fluoxetine
(Prozac), sertraline
(Zoloft), and fluvoxamine
(Luvox)—may be prescribed when a Tourette's patient also has symptoms of obsessive–compulsive disorder. Several other medications have been tried, including nicotine patch
es, but evidence to support their use is unconvincing.
Because children with tics often present to physicians when their tics are most severe, and because of the waxing and waning nature of tics, it is recommended that medication not be started immediately or changed often. Frequently, the tics subside with explanation, reassurance, understanding of the condition and a supportive environment. When medication is used, the goal is not to eliminate symptoms: it should be used at the lowest possible dose that manages symptoms without adverse effects, given that these may be more disturbing than the symptoms for which they were prescribed.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a useful treatment when OCD is present, and there is increasing evidence supporting the use of habit reversal
in the treatment of tics. Relaxation technique
s, such as exercise, yoga or meditation, may be useful in relieving the stress that may aggravate tics, but the majority of behavioral interventions (such as relaxation training and biofeedback
, with the exception of habit reversal) have not been systematically evaluated and are not empirically supported therapies for Tourette's.
 Tourette syndrome is a spectrum disorder—its severity ranges over a spectrum from mild to severe. The majority of cases are mild and require no treatment. In these cases, the impact of symptoms on the individual may be mild, to the extent that casual observers might not know of their condition. The overall prognosis is positive, but a minority of children with Tourette syndrome have severe symptoms that persist into adulthood. A study of 46 subjects at 19 years of age found that the symptoms of 80% had minimum to mild impact on their overall functioning, and that the other 20% experienced at least a moderate impact on their overall functioning. The rare minority of severe cases can inhibit or prevent individuals from holding a job or having a fulfilling social life. In a follow-up study of thirty-one adults with Tourette's, all patients completed high school, 52% finished at least two years of college, and 71% were full-time employed or were pursuing higher education.
Tourette syndrome is a spectrum disorder—its severity ranges over a spectrum from mild to severe. The majority of cases are mild and require no treatment. In these cases, the impact of symptoms on the individual may be mild, to the extent that casual observers might not know of their condition. The overall prognosis is positive, but a minority of children with Tourette syndrome have severe symptoms that persist into adulthood. A study of 46 subjects at 19 years of age found that the symptoms of 80% had minimum to mild impact on their overall functioning, and that the other 20% experienced at least a moderate impact on their overall functioning. The rare minority of severe cases can inhibit or prevent individuals from holding a job or having a fulfilling social life. In a follow-up study of thirty-one adults with Tourette's, all patients completed high school, 52% finished at least two years of college, and 71% were full-time employed or were pursuing higher education.
Regardless of symptom severity, individuals with Tourette's have a normal life span
. Although the symptoms may be lifelong and chronic for some, the condition is not degenerative
or life-threatening. Intelligence is normal in those with Tourette's, although there may be learning disabilities. Severity of tics early in life does not predict tic severity in later life, and prognosis is generally favorable, although there is no reliable means of predicting the outcome for a particular individual. The gene or genes associated with Tourette's have not been identified, and there is no potential "cure". A higher rate of migraine
s than the general population and sleep disturbances
are reported.
Several studies have demonstrated that the condition in most children improves with maturity. Tics may be at their highest severity at the time that they are diagnosed, and often improve with understanding of the condition by individuals and their families and friends. The statistical age of highest tic severity is typically between eight and twelve, with most individuals experiencing steadily declining tic severity as they pass through adolescence. One study showed no correlation with tic severity and the onset of puberty, in contrast with the popular belief that tics increase at puberty. In many cases, a complete remission of tic symptoms occurs after adolescence. However, a study using videotape to record tics in adults found that, although tics diminished in comparison with childhood, and all measures of tic severity improved by adulthood, 90% of adults still had tics. Half of the adults who considered themselves tic-free still displayed evidence of tics.
It is not uncommon for the parents of affected children to be unaware that they, too, may have had tics as children. Because Tourette's tends to subside with maturity, and because milder cases of Tourette's are now more likely to be recognized, the first realization that a parent had tics as a child may not come until their offspring is diagnosed. It is not uncommon for several members of a family to be diagnosed together, as parents bringing children to a physician for an evaluation of tics become aware that they, too, had tics as a child.
 Children with Tourette's may suffer socially if their tics are viewed as "bizarre". If a child has disabling tics, or tics that interfere with social or academic functioning, supportive psychotherapy
Children with Tourette's may suffer socially if their tics are viewed as "bizarre". If a child has disabling tics, or tics that interfere with social or academic functioning, supportive psychotherapy
or school accommodations can be helpful. Because comorbid conditions (such as ADHD or OCD) can cause greater impact on overall functioning than tics, a thorough evaluation for comorbidity is called for when symptoms and impairment warrant.
A supportive environment and family generally gives those with Tourette's the skills to manage the disorder. People with Tourette's may learn to camouflage socially inappropriate tics or to channel the energy of their tics into a functional endeavor. Accomplished musicians, athletes, public speakers, and professionals from all walks of life are found among people with Tourette's. Outcomes in adulthood are associated more with the perceived significance of having severe tics as a child than with the actual severity of the tics. A person who was misunderstood, punished, or teased at home or at school will fare worse than children who enjoyed an understanding and supportive environment.
is much higher among children than adults. Children are five to twelve times more likely than adults to be identified as having tic disorder
s; as many as 1 in 100 people experience tic disorders, including chronic tics and transient tics in childhood. The emerging consensus is that 1–10 children per 1,000 have Tourette's, with several studies supporting a tighter range of 6–8 children per 1,000. Using year 2000 census data, a prevalence range of 1–10 per 1,000 yields an estimate of 53,000–530,000 school-age children with Tourette's in the US, and a prevalence estimate of 10 per 1,000 means that in 2001 about 553,000 people in the UK age 5 or older would have Tourette's. Most cases would be mild and almost unrecognizable in older individuals.
Tourette's is associated with several comorbid conditions, or co-occurring diagnoses, which are often the major source of impairment for an affected child. Among patients whose symptoms are severe enough to warrant referral to specialty Tourette's clinics, only a small minority have no other conditions, and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
(ADHD) are often present. In children with Tourette's, ADHD is associated with functional impairment, disruptive behavior, and tic severity. Other comorbid conditions include self-injurious behaviors (SIB), anxiety
, depression, personality disorder
s, oppositional defiant disorder
, and conduct disorder
s. One author reports that a ten-year overview of patient records revealed about 40% of patients with Tourette's have "TS-only" or "pure TS", referring to Tourette syndrome in the absence of ADHD, OCD and other disorders.
Tourette syndrome was once thought to be rare: in 1972, the US National Institutes of Health
(NIH) believed there were fewer than 100 cases in the United States, and a 1973 registry reported only 485 cases worldwide. However, multiple studies published since 2000 have consistently demonstrated that the prevalence is much higher than previously thought. Discrepancies across current and prior prevalence estimates come from several factors: ascertainment bias in earlier samples
drawn from clinically referred cases, assessment methods that may fail to detect milder cases, and differences in diagnostic criteria and thresholds. There were few broad-based community studies published before 2000 and until the 1980s, most epidemiological studies of Tourette syndrome were based on individuals referred to tertiary care or specialty clinics. Children with milder symptoms are unlikely to be referred to specialty clinics, so these studies have an inherent bias
towards more severe cases. Studies of Tourette syndrome are vulnerable to error because tics vary in intensity and expression
, are often intermittent, and are not always recognized by clinicians, patients, family members, friends or teachers; approximately 20% of persons with Tourette syndrome do not recognize that they have tics. Recent studies—recognizing that tics may often be undiagnosed and hard to detect—use direct classroom observation and multiple informants (parent, teacher, and trained observers), and therefore record more cases than older studies relying on referrals. As the diagnostic threshold and assessment methodology have moved towards recognition of milder cases, the result is an increase in estimated prevalence.
, reported the first case of Tourette syndrome in 1825, describing Marquise de Dampierre, an important woman of nobility in her time. Jean-Martin Charcot, an influential French physician, assigned his resident Georges Albert Édouard Brutus Gilles de la Tourette, a French physician and neurologist, to study patients at the Salpêtrière
Hospital, with the goal of defining an illness distinct from hysteria
and from chorea
.
In 1885, Gilles de la Tourette published an account of nine patients, Study of a Nervous Affliction, concluding that a new clinical category should be defined. The eponym was later bestowed by Charcot after and on behalf of Gilles de la Tourette.
Little progress was made over the next century in explaining or treating tics, and a psychogenic view prevailed well into the 20th century. The possibility that movement disorders, including Tourette syndrome, might have an organic origin
was raised when an encephalitis
epidemic
from 1918–1926 led to a subsequent epidemic of tic disorders.
During the 1960s and 1970s, as the beneficial effects of haloperidol
(Haldol) on tics became known, the psychoanalytic approach to Tourette syndrome was questioned. The turning point came in 1965, when Arthur K. Shapiro
—described as "the father of modern tic disorder research"—treated a Tourette’s patient with haloperidol, and published a paper criticizing the psychoanalytic approach.
Since the 1990s, a more neutral view of Tourette's has emerged, in which biological vulnerability and adverse environmental events are seen to interact. In 2000, the American Psychiatric Association
published the DSM-IV-TR, revising the text of DSM-IV to no longer require that symptoms of tic disorders cause distress or impair functioning.
Findings since 1999 have advanced TS science in the areas of genetics, neuroimaging
, neurophysiology
, and neuropathology
. Questions remain regarding how best to classify Tourette syndrome, and how closely Tourette's is related to other movement disorders or psychiatric
disorders. Good epidemiologic data is still lacking, and available treatments
are not risk free and not always well tolerated. High-profile media coverage focuses on treatments that do not have established safety or efficacy, such as deep brain stimulation
, and alternative therapies involving unstudied efficacy and side effects are pursued by many parents.
 Not everyone with Tourette's wants treatment or a "cure", especially if that means they may "lose" something else in the process. Some people believe that there may be latent advantages associated with genetic vulnerability to the syndrome. There is evidence to support the clinical lore that children with "TS-only" (Tourette's in the absence of comorbid conditions) are unusually gifted: neuropsychological studies have identified advantages in children with TS-only. One study found that children with TS-only are faster than the average for their age group on timed tests of motor coordination
Not everyone with Tourette's wants treatment or a "cure", especially if that means they may "lose" something else in the process. Some people believe that there may be latent advantages associated with genetic vulnerability to the syndrome. There is evidence to support the clinical lore that children with "TS-only" (Tourette's in the absence of comorbid conditions) are unusually gifted: neuropsychological studies have identified advantages in children with TS-only. One study found that children with TS-only are faster than the average for their age group on timed tests of motor coordination
.
Notable individuals with Tourette syndrome are found in all walks of life, including musicians, athletes and authors. The best-known example of a person who may have used obsessive–compulsive traits to advantage is Samuel Johnson
, the 18th-century English man of letters, who likely had Tourette syndrome as evidenced by the writings of James Boswell
. Johnson wrote A Dictionary of the English Language
in 1747, and was a prolific writer, poet, and critic.
Although it has been speculated that Mozart had Tourette's,* Simkin B. "Mozart's scatological disorder". BMJ. 1992 Dec 19–26;305(6868):1563–7. PMID 1286388 no Tourette's expert or organization has presented credible evidence to support such a conclusion, and there are problems with the arguments supporting the diagnosis: tics are not transferred to the written form, as is supposed with Mozart's scatological writings; the medical history in retrospect is not thorough; side effects due to other conditions may be misinterpreted; "it is not proven whether written documents can account for the existence of a vocal tic" and "the evidence of motor tics in Mozart’s life is doubtful".
The entertainment industry has been criticized for depicting those with Tourette syndrome as social misfits whose only tic is coprolalia, which has furthered stigmatization and the public's misunderstanding of those with Tourette's. The coprolalic symptoms of Tourette's are also fodder for radio and television talk shows in the US and in the British media.
Heredity
Heredity is the passing of traits to offspring . This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes predisposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. Through heredity, variations exhibited by individuals can accumulate and cause some species to evolve...
neuropsychiatric
Neuropsychiatry
Neuropsychiatry is the branch of medicine dealing with mental disorders attributable to diseases of the nervous system. It preceded the current disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, in as much as psychiatrists and neurologists had a common training....
disorder with onset in childhood, characterized by multiple physical (motor) tic
Tic
A tic is a sudden, repetitive, nonrhythmic, stereotyped motor movement or vocalization involving discrete muscle groups. Tics can be invisible to the observer, such as abdominal tensing or toe crunching. Common motor and phonic tics are, respectively, eye blinking and throat clearing...
s and at least one vocal (phonic) tic; these tics characteristically wax and wane. Tourette's is defined as part of a spectrum
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum in psychiatry is a range of linked conditions, such that there is "not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups". The subgroups may be linked together by clinical appearance or by shared underlying causation...
of tic disorder
Tic disorder
Tic disorders are defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders based on type and duration of tics...
s, which includes transient and chronic tics.
Tourette's was once considered a rare and bizarre syndrome
Syndrome
In medicine and psychology, a syndrome is the association of several clinically recognizable features, signs , symptoms , phenomena or characteristics that often occur together, so that the presence of one or more features alerts the physician to the possible presence of the others...
, most often associated with the exclamation of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks (coprolalia
Coprolalia
Coprolalia is involuntary swearing or the involuntary utterance of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks. Coprolalia comes from the Greek κόπρος meaning "feces" and λαλιά from lalein, "to talk"...
), but this symptom is present in only a small minority of people with Tourette's. Tourette's is no longer considered a rare condition, but it may not always be correctly identified because most cases are classified as mild. Between 1 and 10 children per 1,000 have Tourette's; as many as 10 per 1,000 people may have tic disorders, with the more common tics of eye blinking, coughing, throat clearing, sniffing, and facial movements. Tourette's does not adversely affect intelligence or life expectancy
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
. The severity of the tics decreases for most children as they pass through adolescence, and extreme Tourette's in adulthood is a rarity. Notable individuals with Tourette's are found in all walks of life.
Genetic
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
and environmental factors play a role in the etiology
Etiology
Etiology is the study of causation, or origination. The word is derived from the Greek , aitiologia, "giving a reason for" ....
of Tourette's, but the exact causes are unknown. In most cases, medication is unnecessary. There is no effective medication for every case of tics, but there are medications and therapies that can help when their use is warranted. Explanation and reassurance alone are often sufficient treatment; education is an important part of any treatment plan.
The eponym
Eponym
An eponym is the name of a person or thing, whether real or fictitious, after which a particular place, tribe, era, discovery, or other item is named or thought to be named...
was bestowed by Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot was a French neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He is known as "the founder of modern neurology" and is "associated with at least 15 medical eponyms", including Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis...
(1825–1893) on behalf of his resident, Georges Albert Édouard Brutus Gilles de la Tourette
Georges Gilles de la Tourette
Georges Albert Édouard Brutus Gilles de la Tourette was a French neurologist who is the eponym of Tourette syndrome, a neurological condition...
(1859–1904), a French physician and neurologist
Neurology
Neurology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue,...
, who published an account of nine patients with Tourette's in 1885.
Classification
TicTic
A tic is a sudden, repetitive, nonrhythmic, stereotyped motor movement or vocalization involving discrete muscle groups. Tics can be invisible to the observer, such as abdominal tensing or toe crunching. Common motor and phonic tics are, respectively, eye blinking and throat clearing...
s are sudden, repetitive, stereotyped, nonrhythmic movements (motor tics) and utterances (phonic tics) that involve discrete muscle groups. Motor tics are movement-based tics, while phonic tics are involuntary sounds produced by moving air through the nose, mouth, or throat.
Tourette's is one of several tic disorder
Tic disorder
Tic disorders are defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders based on type and duration of tics...
s, which are classified by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
(DSM) according to type (motor or phonic tics) and duration (transient or chronic). Transient tic disorder consists of multiple motor tics, phonic tics or both, with a duration between four weeks and twelve months. Chronic tic disorder is either single or multiple, motor or phonic tics (but not both), which are present for more than a year. Tourette's is diagnosed when multiple motor tics, and at least one phonic tic, are present for more than a year. Tic disorders are defined similarly by the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, ICD-10
ICD-10
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision is a medical classification list for the coding of diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases, as maintained by the...
codes).
Although Tourette's is the more severe expression of the spectrum
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum in psychiatry is a range of linked conditions, such that there is "not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups". The subgroups may be linked together by clinical appearance or by shared underlying causation...
of tic disorders, most cases are mild. The severity of symptoms varies widely among people with Tourette's, and mild cases may be undetected.
Characteristics
Tics are movements or sounds "that occur intermittently and unpredictably out of a background of normal motor activity", having the appearance of "normal behaviors gone wrong". The tics associated with Tourette's change in number, frequency, severity and anatomical location. Waxing and waning—the ongoing increase and decrease in severity and frequency of tics—occurs differently in each individual. Tics also occur in "bouts of bouts", which vary for each person.Coprolalia
Coprolalia
Coprolalia is involuntary swearing or the involuntary utterance of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks. Coprolalia comes from the Greek κόπρος meaning "feces" and λαλιά from lalein, "to talk"...
(the spontaneous utterance of socially objectionable or taboo words or phrases) is the most publicized symptom of Tourette's, but it is not required for a diagnosis of Tourette's and only about 10% of Tourette's patients exhibit it. Echolalia
Echolalia
Echolalia is the automatic repetition of vocalizations made by another person. It is closely related to echopraxia, the automatic repetition of movements made by another person....
(repeating the words of others) and palilalia
Palilalia
Palilalia is the repetition or echoing of one's own spoken words. It can be a complex tic, like echolalia and coprolalia and may sound like stuttering; all can be symptoms of Tourette syndrome, obsessive–compulsive disorder, or autism...
(repeating one's own words) occur in a minority of cases, while the most common initial motor and vocal tics are, respectively, eye blinking and throat clearing.
In contrast to the abnormal movements of other movement disorder
Movement disorder
Movement disorders include:* Akathisia * Akinesia * Associated Movements * Athetosis...
s (for example, chorea
Chorea (disease)
Choreia is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias. The term choreia is derived from the Greek word χορεία , see choreia , as the quick movements of the feet or hands are vaguely comparable to dancing or piano playing.The term...
s, dystonia
Dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder, in which sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The disorder may be hereditary or caused by other factors such as birth-related or other physical trauma, infection, poisoning or reaction to...
s, myoclonus
Myoclonus
Myoclonus is brief, involuntary twitching of a muscle or a group of muscles. It describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. Brief twitches are perfectly normal. The myoclonic twitches are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions; they also can result from brief...
, and dyskinesia
Dyskinesia
Dyskinesia is a movement disorder which consists of effects including diminished voluntary movements and the presence of involuntary movements, similar to tics or choreia. Dyskinesia can be anything from a slight tremor of the hands to uncontrollable movement of, most commonly, the upper body but...
s), the tics of Tourette's are stereotypic, temporarily suppressible, nonrhythmic, and often preceded by an unwanted premonitory urge. Immediately preceding tic onset, most individuals with Tourette's are aware of an urge, similar to the need to sneeze or scratch an itch. Individuals describe the need to tic as a buildup of tension, pressure, or energy which they consciously choose to release, as if they "had to do it" to relieve the sensation or until it feels "just right". Examples of the premonitory urge are the feeling of having something in one's throat, or a localized discomfort in the shoulders, leading to the need to clear one's throat or shrug the shoulders. The actual tic may be felt as relieving this tension or sensation, similar to scratching an itch. Another example is blinking to relieve an uncomfortable sensation in the eye. These urges and sensations, preceding the expression of the movement or vocalization as a tic, are referred to as "premonitory sensory phenomena
Sensory phenomena
Sensory phenomena are general feelings, urges or bodily sensations that precede or accompany repetitive behaviors associated with Tourette syndrome and tic disorders...
" or premonitory urges. Because of the urges that precede them, tics are described as semi-voluntary or "unvoluntary", rather than specifically involuntary; they may be experienced as a voluntary, suppressible response to the unwanted premonitory urge. Published descriptions of the tics of Tourette's identify sensory phenomena as the core symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
of the syndrome, even though they are not included in the diagnostic criteria.
While individuals with tics are sometimes able to suppress their tics for limited periods of time, doing so often results in an explosion of tics afterward. People with Tourette's may seek a secluded spot to release their symptoms, or there may be a marked increase in tics after a period of suppression at school or at work. Some people with Tourette's may not be aware of the premonitory urge. Children may be less aware of the premonitory urge associated with tics than are adults, but their awareness tends to increase with maturity. They may have tics for several years before becoming aware of premonitory urges. Children may suppress tics while in the doctor's office, so they may need to be observed while they are not aware they are being watched. The ability to suppress tics varies among individuals, and may be more developed in adults than children.
Although there is no such thing as a "typical" case of Tourette syndrome, the condition follows a fairly reliable course in terms of the age of onset and the history of the severity of symptoms. Tics may appear up to the age of eighteen, but the most typical age of onset is from five to seven. A 1998 study published by Leckman et al. of the Yale Child Study Center
Yale Child Study Center
The Yale Child Study Center is a department at the Yale University School of Medicine. The center conducts research and provides clinical services and medical training related to children and families...
showed that the ages of highest tic severity are eight to twelve (average ten), with tics steadily declining for most patients as they pass through adolescence. The most common, first-presenting tics are eye blinking, facial movements, sniffing and throat clearing. Initial tics present most frequently in midline body regions where there are many muscles, usually the head, neck and facial region. This can be contrasted with the stereotyped movements of other disorders (such as stim
Stimming
Stimming is a repetitive body movement, such as hand flapping, that is hypothesized to stimulate one or more senses. The term is shorthand for self-stimulation. Repetitive movement, or stereotypy, is often referred to as stimming under the hypothesis that it has a function related to sensory input....
s and stereotypies of the autism spectrum disorders), which typically have an earlier age of onset, are more symmetrical, rhythmical and bilateral, and involve the extremities (e.g., flapping the hands). Tics that appear early in the course of the condition are frequently confused with other conditions, such as allergies, asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
, and vision problems: pediatricians, allergists and ophthalmologists are typically the first to see a child with tics.
Among patients whose symptoms are severe enough to warrant referral to clinics, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is a developmental disorder. It is primarily characterized by "the co-existence of attentional problems and hyperactivity, with each behavior occurring infrequently alone" and symptoms starting before seven years of age.ADHD is the most commonly studied and...
(ADHD) are often associated with Tourette's. Not all persons with Tourette's have ADHD or OCD or other comorbid conditions (co-occurring diagnoses other than Tourette's), although in clinical populations, a high percentage of patients presenting for care do have ADHD. One author reports that a ten-year overview of patient records revealed about 40% of patients with Tourette's have "TS-only" or "pure TS", referring to Tourette syndrome in the absence of ADHD, OCD and other disorders. Another author reports that 57% of 656 patients presenting with tic disorders had uncomplicated tics, while 43% had tics plus comorbid conditions. "Full-blown Tourette's" is a term used to describe patients who have significant comorbid conditions in addition to tics.
Causes
The exact cause of Tourette's is unknown, but it is well established that both genetic and environmental factors are involved. Genetic studies have shown that the overwhelming majority of cases of Tourette's are inherited, although the exact mode of inheritance is not yet known, and no gene has been identified. In some cases, Tourette's is sporadic, that is, it is not inherited from parents. In other cases, tics are associated with disorders other than Tourette's, a phenomenon known as tourettismTourettism
Tourettism refers to the presence of Tourette-like symptoms in the absence of Tourette syndrome, as the result of other diseases or conditions, known as "secondary causes"....
.

Expressivity
Expressivity is a term used in genetics to refer to variations in a phenotype among individuals carrying a particular genotype. The term can be used to characterize qualitatively or quantitatively the extent of phenotypic variation given a particular genotype. The term is analogous to the...
and incomplete penetrance
Penetrance
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant of a gene that also express an associated trait . In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is the proportion of individuals with the mutation who exhibit clinical symptoms...
. Thus, not everyone who inherits the genetic vulnerability will show symptoms; even close family members may show different severities of symptoms, or no symptoms at all. The gene(s) may express as Tourette's, as a milder tic disorder (transient or chronic tics), or as obsessive–compulsive symptoms without tics. Only a minority of the children who inherit the gene(s) have symptoms severe enough to require medical attention. Gender appears to have a role in the expression of the genetic vulnerability: males are more likely than females to express tics.
Non-genetic, environmental, infectious, or psychosocial
Psychosocial
For a concept to be psychosocial means it relates to one's psychological development in, and interaction with, a social environment. The individual needs not be fully aware of this relationship with his or her environment. It was first commonly used by psychologist Erik Erikson in his stages of...
factors—while not causing Tourette's—can influence its severity. Autoimmune processes may affect tic onset and exacerbation in some cases. In 1998, a team at the US National Institute of Mental Health
National Institute of Mental Health
The National Institute of Mental Health is one of 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health...
proposed a hypothesis that both obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and tic disorders may arise in a subset of children as a result of a poststreptococcal
Streptococcus
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning...
autoimmune process. Children who meet five diagnostic criteria are classified, according to the hypothesis, as having Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infections (PANDAS). This contentious hypothesis is the focus of clinical and laboratory research, but remains unproven.
The exact mechanism affecting the inherited vulnerability to Tourette's has not been established, and the precise etiology is unknown. Tics are believed to result from dysfunction in cortical and subcortical regions, the thalamus, basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
and frontal cortex
Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is an area in the brain of humans and other mammals, located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned anterior to the parietal lobe and superior and anterior to the temporal lobes...
. Neuroanatomic
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can begin to speak of...
models implicate failures in circuits connecting the brain's cortex and subcortex, and imaging techniques
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging includes the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function/pharmacology of the brain...
implicate the basal ganglia and frontal cortex.
Some forms of OCD may be genetically linked to Tourette's. A subset of OCD is thought to be etiologically
Etiology
Etiology is the study of causation, or origination. The word is derived from the Greek , aitiologia, "giving a reason for" ....
related to Tourette's and may be a different expression of the same factors that are important for the expression of tics. The genetic relationship of ADHD to Tourette syndrome, however, has not been fully established.
Diagnosis
According to the revised fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR), Tourette’s may be diagnosed when a person exhibits both multiple motor and one or more vocal tics (although these do not need to be concurrent) over the period of a year, with no more than three consecutive tic-free months. The previous DSM-IV included a requirement for "marked distress or significant impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning", but this requirement was removed in the most recent update of the manual, in recognition that clinicians see patients who meet all the other criteria for Tourette's, but do not have distress or impairment. The onset must have occurred before the age of 18, and cannot be attributed to the "direct physiological effects of a substance or a general medical condition". Hence, other medical conditions that include tics or tic-like movements—such as autismAutism spectrum
The term "autism spectrum" is often used to describe disorders that are currently classified as pervasive developmental disorders. Pervasive developmental disorders include autism, Asperger syndrome, Childhood disintegrative disorder, Rett syndrome and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise...
or other causes of tourettism
Tourettism
Tourettism refers to the presence of Tourette-like symptoms in the absence of Tourette syndrome, as the result of other diseases or conditions, known as "secondary causes"....
—must be ruled out before conferring a Tourette's diagnosis.
There are no specific medical or screening tests that can be used in diagnosing Tourette's; it is frequently misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed, partly because of the wide expression of severity, ranging from mild (the majority of cases) or moderate, to severe (the rare, but more widely-recognized and publicized cases). Coughing, eye blinking and tics that mimic asthma are commonly misdiagnosed.
The diagnosis is made based on observation of the individual's symptoms and family history, and after ruling out secondary causes of tic disorders.
Tourettism
Tourettism refers to the presence of Tourette-like symptoms in the absence of Tourette syndrome, as the result of other diseases or conditions, known as "secondary causes"....
In patients with a typical onset and a family history of tics or obsessive–compulsive disorder, a basic physical and neurological examination may be sufficient.
There is no requirement that other comorbid conditions (such as ADHD or OCD) be present, but if a physician believes that there may be another condition present that could explain tics, tests may be ordered as necessary to rule out that condition. An example of this is when diagnostic confusion between tics and seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
activity exists, which would call for an EEG
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography is the recording of electrical activity along the scalp. EEG measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current flows within the neurons of the brain...
, or if there are symptoms that indicate an MRI to rule out brain abnormalities. TSH
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyrotrophin-stimulating hormone is a peptide hormone synthesized and secreted by thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland, which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid gland.- Physiology :...
levels can be measured to rule out hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide but it can be caused by other causes such as several conditions of the thyroid gland or, less commonly, the pituitary gland or...
, which can be a cause of tics. Brain imaging studies are not usually warranted. In teenagers and adults presenting with a sudden onset of tics and other behavioral symptoms, a urine drug screen for cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. The name comes from "coca" in addition to the alkaloid suffix -ine, forming cocaine. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic...
and stimulants might be necessary. If a family history of liver disease
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
is present, serum copper and ceruloplasmin
Ceruloplasmin
Ceruloplasmin is a ferroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CP gene.Ceruloplasmin is the major copper-carrying protein in the blood, and in addition plays a role in iron metabolism. It was first described in 1948...
levels can rule out Wilson's disease
Wilson's disease
Wilson's disease or hepatolenticular degeneration is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder in which copper accumulates in tissues; this manifests as neurological or psychiatric symptoms and liver disease...
. Most cases are diagnosed by merely observing a history of tics.
Secondary causes of tics (not related to inherited Tourette syndrome) are commonly referred to as tourettism
Tourettism
Tourettism refers to the presence of Tourette-like symptoms in the absence of Tourette syndrome, as the result of other diseases or conditions, known as "secondary causes"....
. Dystonia
Dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder, in which sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The disorder may be hereditary or caused by other factors such as birth-related or other physical trauma, infection, poisoning or reaction to...
s, choreas, other genetic conditions, and secondary causes of tics should be ruled out in the differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of an entity where multiple alternatives are possible , and may also refer to any of the included candidate alternatives A differential diagnosis (sometimes abbreviated DDx, ddx, DD, D/Dx, or ΔΔ) is a...
for Tourette syndrome. Other conditions that may manifest tics or stereotyped movements include developmental disorder
Developmental disorder
Developmental disorders occur at some stage in a child's development, often retarding the development. These may include,psychological or physical disorders. The disorder is an impairment in the normal development of motor or cognitive skills that are developed before age 18 in which they are...
s, autism spectrum disorders, and stereotypic movement disorder
Stereotypic movement disorder
Stereotypic movement disorder is a disorder of childhood involving repetitive, nonfunctional motor behavior , that markedly interferes with normal activities or results in bodily injury, and persists for four weeks or longer. The behavior must not be due to the direct effects of a substance or...
; Sydenham's chorea
Sydenham's chorea
Sydenham's chorea or chorea minor is a disease characterized by rapid, uncoordinated jerking movements affecting primarily the face, feet and hands. Sydenham's chorea results from childhood infection with Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci and is reported to occur in 20-30% of patients with...
; idiopathic
Idiopathic
Idiopathic is an adjective used primarily in medicine meaning arising spontaneously or from an obscure or unknown cause. From Greek ἴδιος, idios + πάθος, pathos , it means approximately "a disease of its own kind". It is technically a term from nosology, the classification of disease...
dystonia; and genetic conditions such as Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder , is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. It typically becomes noticeable in middle age. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea...
, neuroacanthocytosis
Neuroacanthocytosis
Neuroacanthocytosis is a term that refers to a group of genetically diverse conditions complicated by movement disorders, neurological problems and spiculated red blood cells...
, Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome, Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a recessive X-linked form of muscular dystrophy, which results in muscle degeneration, difficulty walking, breathing, and death. The incidence is 1 in 3,000 boys. Females and males are affected, though females are rarely affected and are more often carriers...
, Wilson's disease, and tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis or tuberous sclerosis complex is a rare multi-system genetic disease that causes non-malignant tumors to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, eyes, lungs, and skin. A combination of symptoms may include seizures, developmental delay, behavioral...
. Other possibilities include chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome
Down syndrome
Down syndrome, or Down's syndrome, trisomy 21, is a chromosomal condition caused by the presence of all or part of an extra 21st chromosome. It is named after John Langdon Down, the British physician who described the syndrome in 1866. The condition was clinically described earlier in the 19th...
, Klinefelter's syndrome
Klinefelter's syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome, 46/47, XXY, or XXY syndrome is a condition in which human males have an extra X chromosome. While females have an XX chromosomal makeup, and males an XY, affected individuals have at least two X chromosomes and at least one Y chromosome...
, XYY syndrome
XYY syndrome
XYY syndrome is an aneuploidy of the sex chromosomes in which a human male receives an extra Y-chromosome, giving a total of 47 chromosomes instead of the more usual 46. This produces a 47,XYY karyotype...
and fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome , Martin–Bell syndrome, or Escalante's syndrome , is a genetic syndrome that is the most commonly known single-gene cause of autism and the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability...
. Acquired causes of tics include drug-induced tics, head trauma, encephalitis
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. Encephalitis with meningitis is known as meningoencephalitis. Symptoms include headache, fever, confusion, drowsiness, and fatigue...
, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, and carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs after enough inhalation of carbon monoxide . Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas, but, being colorless, odorless, tasteless, and initially non-irritating, it is very difficult for people to detect...
. The symptoms of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Lesch–Nyhan syndrome , also known as Nyhan's syndrome, Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome and Juvenile gout, is a rare inherited disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase , produced by mutations in the HPRT gene located on X chromosome. LNS affects about...
may also be confused with Tourette syndrome. Most of these conditions are rarer than tic disorders, and a thorough history and examination may be enough to rule them out, without medical or screening tests.
Screening
Although not all people with Tourette's have comorbid conditions, most Tourette's patients presenting for clinical care at specialty referral centers may exhibit symptoms of other conditions along with their motor and phonic tics. Associated conditions include attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADD or ADHD), obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), learning disabilities and sleep disorderSleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of the sleep patterns of a person or animal. Some sleep disorders are serious enough to interfere with normal physical, mental and emotional functioning...
s. Disruptive behaviors, impaired functioning, or cognitive impairment in patients with comorbid Tourette's and ADHD may be accounted for by the comorbid ADHD, highlighting the importance of identifying and treating comorbid conditions. Disruption from tics is commonly overshadowed by comorbid conditions that present greater interference to the child. Tic disorders in the absence of ADHD do not appear to be associated with disruptive behavior or functional impairment, while impairment in school, family, or peer relations is greater in patients who have more comorbid conditions and often determines whether therapy is needed.
Because comorbid conditions such as OCD and ADHD can be more impairing than tics, these conditions are included in an evaluation of patients presenting with tics. "It is critical to note that the comorbid conditions may determine functional status more strongly than the tic disorder," according to Samuel Zinner, MD. The initial assessment of a patient referred for a tic disorder should include a thorough evaluation, including a family history of tics, ADHD, obsessive–compulsive symptoms, and other chronic medical, psychiatric and neurological conditions. Children and adolescents with TS who have learning difficulties are candidates for psychoeducational testing, particularly if the child also has ADHD. Undiagnosed comorbid conditions may result in functional impairment, and it is necessary to identify and treat these conditions to improve functioning. Complications may include depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
, sleep problems
Sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of the sleep patterns of a person or animal. Some sleep disorders are serious enough to interfere with normal physical, mental and emotional functioning...
, social discomfort and self-injury
Self-harm
Self-harm or deliberate self-harm includes self-injury and self-poisoning and is defined as the intentional, direct injuring of body tissue most often done without suicidal intentions. These terms are used in the more recent literature in an attempt to reach a more neutral terminology...
.
Management

Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the branch of medicine and biology concerned with the study of drug action. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function...
treatment; instead, psychobehavioral therapy, education, and reassurance may be sufficient. Treatments, where warranted, can be divided into those that target tics and comorbid conditions, which, when present, are often a larger source of impairment than the tics themselves. Not all people with tics have comorbid conditions, but when those conditions are present, they often take treatment priority.
There is no cure for Tourette's and no medication that works universally for all individuals without significant adverse effects. Knowledge, education and understanding are uppermost in management plans for tic disorders. The management of the symptoms of Tourette's may include pharmacological, behavior
Behavior
Behavior or behaviour refers to the actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with its environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment...
al and psychological
Psychology
Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society...
therapies. While pharmacological intervention is reserved for more severe symptoms, other treatments (such as supportive psychotherapy or cognitive behavioral therapy) may help to avoid or ameliorate depression
Depression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
and social isolation, and to improve family support. Educating a patient, family, and surrounding community (such as friends, school, and church) is a key treatment strategy, and may be all that is required in mild cases.

Atypical antipsychotic
The atypical antipsychotics are a group of antipsychotic tranquilizing drugs used to treat psychiatric conditions. Some atypical antipsychotics are FDA approved for use in the treatment of schizophrenia...
neuroleptics
Antipsychotic
An antipsychotic is a tranquilizing psychiatric medication primarily used to manage psychosis , particularly in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. A first generation of antipsychotics, known as typical antipsychotics, was discovered in the 1950s...
including risperidone
Risperidone
Risperidone is a second generation or atypical antipsychotic, sold under the trade name . It is used to treat schizophrenia , schizoaffective disorder, the mixed and manic states associated with bipolar disorder, and irritability in people with autism...
(trade name Risperdal), ziprasidone
Ziprasidone
Ziprasidone was the fifth atypical antipsychotic to gain FDA approval . In the United States, Ziprasidone is Food and Drug Administration approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, and the intramuscular injection form of ziprasidone is approved for acute agitation in schizophrenic patients...
(Geodon), haloperidol
Haloperidol
Haloperidol is a typical antipsychotic. It is in the butyrophenone class of antipsychotic medications and has pharmacological effects similar to the phenothiazines....
(Haldol), pimozide
Pimozide
Pimozide is an antipsychotic drug of the diphenylbutylpiperidine class. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1963. It has a high potency compared to chlorpromazine . On a weight basis it is even more potent than haloperidol. It also has special neurologic indications for Tourette syndrome...
(Orap) and fluphenazine
Fluphenazine
Fluphenazine is a typical antipsychotic drug used for the treatment of psychoses such as schizophrenia and acute manic phases of bipolar disorder. It belongs to the piperazine class of phenothiazines....
(Prolixin)—can have long-term and short-term adverse effects
Adverse effect (medicine)
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
. The antihypertensive
Antihypertensive
The antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension . Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from...
agents clonidine
Clonidine
Clonidine is a sympatholytic medication used to treat medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, some pain conditions, ADHD and anxiety/panic disorder...
(trade name Catapres) and guanfacine
Guanfacine
Guanfacine is a sympatholytic. It is an agonist of the α2A subtype of norepinephrine receptors. These receptors are concentrated heavily in the prefrontal cortex and the locus coeruleus, with the potential to improve attention abilities via modulating post-synaptic α2A receptors in the prefrontal...
(Tenex) are also used to treat tics; studies show variable efficacy, but a lower side effect profile than the neuroleptics. Stimulants and other medications may be useful in treating ADHD when it co-occurs with tic disorders. Drugs from several other classes of medications can be used when stimulant trials fail, including guanfacine
Guanfacine
Guanfacine is a sympatholytic. It is an agonist of the α2A subtype of norepinephrine receptors. These receptors are concentrated heavily in the prefrontal cortex and the locus coeruleus, with the potential to improve attention abilities via modulating post-synaptic α2A receptors in the prefrontal...
(trade name Tenex), atomoxetine (Strattera) and tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants are heterocyclic chemical compounds used primarily as antidepressants. The TCAs were first discovered in the early 1950s and were subsequently introduced later in the decade; they are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms...
s. Clomipramine
Clomipramine
Clomipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant . It was developed in the 1960s by the Swiss drug manufacturer Geigy and has been in clinical use worldwide ever since.- Indications :...
(Anafranil), a tricyclic, and SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors or serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitor are a class of compounds typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of depression, anxiety disorders, and some personality disorders. The efficacy of SSRIs is disputed...
—a class of antidepressant
Antidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
s including fluoxetine
Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor class. It is manufactured and marketed by Eli Lilly and Company...
(Prozac), sertraline
Sertraline
Sertraline hydrochloride is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor class. It was introduced to the market by Pfizer in 1991. Sertraline is primarily used to treat major depression in adult outpatients as well as obsessive–compulsive, panic, and social anxiety disorders in...
(Zoloft), and fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine is an antidepressant which functions as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor . Fluvoxamine was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1993 for the treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder . Fluvoxamine CR is approved to treat social anxiety disorder...
(Luvox)—may be prescribed when a Tourette's patient also has symptoms of obsessive–compulsive disorder. Several other medications have been tried, including nicotine patch
Nicotine patch
A nicotine patch is a transdermal patch that releases nicotine into the body through the skin. It is used as an aid in nicotine replacement therapy , a process for smoking cessation. The first published study of the pharmacokinetics of a transdermal nicotine patch in humans was authored by Jed E....
es, but evidence to support their use is unconvincing.
Because children with tics often present to physicians when their tics are most severe, and because of the waxing and waning nature of tics, it is recommended that medication not be started immediately or changed often. Frequently, the tics subside with explanation, reassurance, understanding of the condition and a supportive environment. When medication is used, the goal is not to eliminate symptoms: it should be used at the lowest possible dose that manages symptoms without adverse effects, given that these may be more disturbing than the symptoms for which they were prescribed.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a useful treatment when OCD is present, and there is increasing evidence supporting the use of habit reversal
Habit reversal training
Habit reversal training is a "multicomponent behavioral treatment package originally developed to address a wide variety of repetitive behavior disorders"....
in the treatment of tics. Relaxation technique
Relaxation technique
A relaxation technique is any method, process, procedure, or activity that helps a person to relax; to attain a state of increased calmness; or otherwise reduce levels of anxiety, stress or anger...
s, such as exercise, yoga or meditation, may be useful in relieving the stress that may aggravate tics, but the majority of behavioral interventions (such as relaxation training and biofeedback
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is the process of becoming aware of various physiological functions using instruments that provide information on the activity of those same systems, with a goal of being able to manipulate them at will...
, with the exception of habit reversal) have not been systematically evaluated and are not empirically supported therapies for Tourette's.
Prognosis

Regardless of symptom severity, individuals with Tourette's have a normal life span
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
. Although the symptoms may be lifelong and chronic for some, the condition is not degenerative
Degeneration (medical)
Degeneration is deterioration in the medical sense. Generally, it is the change from a higher to a lower form. More specifically, it is the change of tissue to a lower or less functionally active form....
or life-threatening. Intelligence is normal in those with Tourette's, although there may be learning disabilities. Severity of tics early in life does not predict tic severity in later life, and prognosis is generally favorable, although there is no reliable means of predicting the outcome for a particular individual. The gene or genes associated with Tourette's have not been identified, and there is no potential "cure". A higher rate of migraine
Migraine
Migraine is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by moderate to severe headaches, and nausea...
s than the general population and sleep disturbances
Sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of the sleep patterns of a person or animal. Some sleep disorders are serious enough to interfere with normal physical, mental and emotional functioning...
are reported.
Several studies have demonstrated that the condition in most children improves with maturity. Tics may be at their highest severity at the time that they are diagnosed, and often improve with understanding of the condition by individuals and their families and friends. The statistical age of highest tic severity is typically between eight and twelve, with most individuals experiencing steadily declining tic severity as they pass through adolescence. One study showed no correlation with tic severity and the onset of puberty, in contrast with the popular belief that tics increase at puberty. In many cases, a complete remission of tic symptoms occurs after adolescence. However, a study using videotape to record tics in adults found that, although tics diminished in comparison with childhood, and all measures of tic severity improved by adulthood, 90% of adults still had tics. Half of the adults who considered themselves tic-free still displayed evidence of tics.
It is not uncommon for the parents of affected children to be unaware that they, too, may have had tics as children. Because Tourette's tends to subside with maturity, and because milder cases of Tourette's are now more likely to be recognized, the first realization that a parent had tics as a child may not come until their offspring is diagnosed. It is not uncommon for several members of a family to be diagnosed together, as parents bringing children to a physician for an evaluation of tics become aware that they, too, had tics as a child.

Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a general term referring to any form of therapeutic interaction or treatment contracted between a trained professional and a client or patient; family, couple or group...
or school accommodations can be helpful. Because comorbid conditions (such as ADHD or OCD) can cause greater impact on overall functioning than tics, a thorough evaluation for comorbidity is called for when symptoms and impairment warrant.
A supportive environment and family generally gives those with Tourette's the skills to manage the disorder. People with Tourette's may learn to camouflage socially inappropriate tics or to channel the energy of their tics into a functional endeavor. Accomplished musicians, athletes, public speakers, and professionals from all walks of life are found among people with Tourette's. Outcomes in adulthood are associated more with the perceived significance of having severe tics as a child than with the actual severity of the tics. A person who was misunderstood, punished, or teased at home or at school will fare worse than children who enjoyed an understanding and supportive environment.
Epidemiology
Tourette syndrome is found among all social, racial and ethnic groups, has been reported in all parts of the world, and is three to four times more frequent among males than among females. The tics of Tourette syndrome begin in childhood and tend to remit or subside with maturity; thus, a diagnosis may no longer be warranted for many adults, and prevalencePrevalence
In epidemiology, the prevalence of a health-related state in a statistical population is defined as the total number of cases of the risk factor in the population at a given time, or the total number of cases in the population, divided by the number of individuals in the population...
is much higher among children than adults. Children are five to twelve times more likely than adults to be identified as having tic disorder
Tic disorder
Tic disorders are defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders based on type and duration of tics...
s; as many as 1 in 100 people experience tic disorders, including chronic tics and transient tics in childhood. The emerging consensus is that 1–10 children per 1,000 have Tourette's, with several studies supporting a tighter range of 6–8 children per 1,000. Using year 2000 census data, a prevalence range of 1–10 per 1,000 yields an estimate of 53,000–530,000 school-age children with Tourette's in the US, and a prevalence estimate of 10 per 1,000 means that in 2001 about 553,000 people in the UK age 5 or older would have Tourette's. Most cases would be mild and almost unrecognizable in older individuals.
Tourette's is associated with several comorbid conditions, or co-occurring diagnoses, which are often the major source of impairment for an affected child. Among patients whose symptoms are severe enough to warrant referral to specialty Tourette's clinics, only a small minority have no other conditions, and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is a developmental disorder. It is primarily characterized by "the co-existence of attentional problems and hyperactivity, with each behavior occurring infrequently alone" and symptoms starting before seven years of age.ADHD is the most commonly studied and...
(ADHD) are often present. In children with Tourette's, ADHD is associated with functional impairment, disruptive behavior, and tic severity. Other comorbid conditions include self-injurious behaviors (SIB), anxiety
Anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorder is a blanket term covering several different forms of abnormal and pathological fear and anxiety. Conditions now considered anxiety disorders only came under the aegis of psychiatry at the end of the 19th century. Gelder, Mayou & Geddes explains that anxiety disorders are...
, depression, personality disorder
Personality disorder
Personality disorders, formerly referred to as character disorders, are a class of personality types and behaviors. Personality disorders are noted on Axis II of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders or DSM-IV-TR of the American Psychiatric Association.Personality disorders are...
s, oppositional defiant disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder is a diagnosis described by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders as an ongoing pattern of disobedient, hostile and defiant behavior toward authority figures which goes beyond the bounds of normal childhood behavior...
, and conduct disorder
Conduct disorder
Conduct disorder is psychological disorder diagnosed in childhood that presents itself through a repetitive and persistent pattern of behavior in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate norms are violated...
s. One author reports that a ten-year overview of patient records revealed about 40% of patients with Tourette's have "TS-only" or "pure TS", referring to Tourette syndrome in the absence of ADHD, OCD and other disorders.
Tourette syndrome was once thought to be rare: in 1972, the US National Institutes of Health
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health are an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and are the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. Its science and engineering counterpart is the National Science Foundation...
(NIH) believed there were fewer than 100 cases in the United States, and a 1973 registry reported only 485 cases worldwide. However, multiple studies published since 2000 have consistently demonstrated that the prevalence is much higher than previously thought. Discrepancies across current and prior prevalence estimates come from several factors: ascertainment bias in earlier samples
Sampling (statistics)
In statistics and survey methodology, sampling is concerned with the selection of a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population....
drawn from clinically referred cases, assessment methods that may fail to detect milder cases, and differences in diagnostic criteria and thresholds. There were few broad-based community studies published before 2000 and until the 1980s, most epidemiological studies of Tourette syndrome were based on individuals referred to tertiary care or specialty clinics. Children with milder symptoms are unlikely to be referred to specialty clinics, so these studies have an inherent bias
Biased sample
In statistics, sampling bias is when a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others. It results in a biased sample, a non-random sample of a population in which all individuals, or instances, were not equally likely to...
towards more severe cases. Studies of Tourette syndrome are vulnerable to error because tics vary in intensity and expression
Penetrance
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant of a gene that also express an associated trait . In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is the proportion of individuals with the mutation who exhibit clinical symptoms...
, are often intermittent, and are not always recognized by clinicians, patients, family members, friends or teachers; approximately 20% of persons with Tourette syndrome do not recognize that they have tics. Recent studies—recognizing that tics may often be undiagnosed and hard to detect—use direct classroom observation and multiple informants (parent, teacher, and trained observers), and therefore record more cases than older studies relying on referrals. As the diagnostic threshold and assessment methodology have moved towards recognition of milder cases, the result is an increase in estimated prevalence.
History and research directions
The first presentation of Tourette syndrome is thought to be in a 1489 book, Malleus maleficarum ("Witch's hammer") by Jakob Sprenger and Heinrich Kraemer, describing a priest whose tics were "believed to be related to possession by the devil". A French doctor, Jean Marc Gaspard ItardJean Marc Gaspard Itard
Jean Marc Gaspard Itard was a French physician born in Provence.Without a university education and working at a bank, he was forced to enter the army during the French Revolution but presented himself as a physician at that time...
, reported the first case of Tourette syndrome in 1825, describing Marquise de Dampierre, an important woman of nobility in her time. Jean-Martin Charcot, an influential French physician, assigned his resident Georges Albert Édouard Brutus Gilles de la Tourette, a French physician and neurologist, to study patients at the Salpêtrière
Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital
The Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital is a teaching hospital located in Paris, France. Part of the Assistance publique - Hôpitaux de Paris, it is one of Europe's largest hospitals...
Hospital, with the goal of defining an illness distinct from hysteria
Hysteria
Hysteria, in its colloquial use, describes unmanageable emotional excesses. People who are "hysterical" often lose self-control due to an overwhelming fear that may be caused by multiple events in one's past that involved some sort of severe conflict; the fear can be centered on a body part, or,...
and from chorea
Chorea (disease)
Choreia is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias. The term choreia is derived from the Greek word χορεία , see choreia , as the quick movements of the feet or hands are vaguely comparable to dancing or piano playing.The term...
.
In 1885, Gilles de la Tourette published an account of nine patients, Study of a Nervous Affliction, concluding that a new clinical category should be defined. The eponym was later bestowed by Charcot after and on behalf of Gilles de la Tourette.
Little progress was made over the next century in explaining or treating tics, and a psychogenic view prevailed well into the 20th century. The possibility that movement disorders, including Tourette syndrome, might have an organic origin
Organic disease
An organic disease is one which involves or affects physiology or bodily organs. A disease in which there is a physiological change to some tissue or organ of the body....
was raised when an encephalitis
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. Encephalitis with meningitis is known as meningoencephalitis. Symptoms include headache, fever, confusion, drowsiness, and fatigue...
epidemic
Epidemic
In epidemiology, an epidemic , occurs when new cases of a certain disease, in a given human population, and during a given period, substantially exceed what is expected based on recent experience...
from 1918–1926 led to a subsequent epidemic of tic disorders.
During the 1960s and 1970s, as the beneficial effects of haloperidol
Haloperidol
Haloperidol is a typical antipsychotic. It is in the butyrophenone class of antipsychotic medications and has pharmacological effects similar to the phenothiazines....
(Haldol) on tics became known, the psychoanalytic approach to Tourette syndrome was questioned. The turning point came in 1965, when Arthur K. Shapiro
Arthur K. Shapiro
Arthur K. Shapiro was a psychiatrist and expert on Tourette syndrome. His "contributions to the understanding of Tourette syndrome completely changed the prevailing view of this disorder"; he has been described as "the father of modern tic disorder research" and is "revered by his colleagues as...
—described as "the father of modern tic disorder research"—treated a Tourette’s patient with haloperidol, and published a paper criticizing the psychoanalytic approach.
Since the 1990s, a more neutral view of Tourette's has emerged, in which biological vulnerability and adverse environmental events are seen to interact. In 2000, the American Psychiatric Association
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the most influential worldwide. Its some 38,000 members are mainly American but some are international...
published the DSM-IV-TR, revising the text of DSM-IV to no longer require that symptoms of tic disorders cause distress or impair functioning.
Findings since 1999 have advanced TS science in the areas of genetics, neuroimaging
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging includes the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function/pharmacology of the brain...
, neurophysiology
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a part of physiology. Neurophysiology is the study of nervous system function...
, and neuropathology
Neuropathology
Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either small surgical biopsies or whole autopsy brains. Neuropathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology, neurology, and neurosurgery...
. Questions remain regarding how best to classify Tourette syndrome, and how closely Tourette's is related to other movement disorders or psychiatric
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the study and treatment of mental disorders. These mental disorders include various affective, behavioural, cognitive and perceptual abnormalities...
disorders. Good epidemiologic data is still lacking, and available treatments
Treatment of Tourette syndrome
Tourette syndrome is an inherited neuropsychiatric disorder with onset in childhood, characterized by the presence of motor and phonic tics...
are not risk free and not always well tolerated. High-profile media coverage focuses on treatments that do not have established safety or efficacy, such as deep brain stimulation
Deep brain stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical treatment involving the implantation of a medical device called a brain pacemaker, which sends electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain...
, and alternative therapies involving unstudied efficacy and side effects are pursued by many parents.
Society and culture

Motor coordination
thumb|right|Motor coordination is shown in this animated sequence by [[Eadweard Muybridge]] of himself throwing a diskMotor coordination is the combination of body movements created with the kinematic and kinetic parameters that result in intended actions. Such movements usually smoothly and...
.
Notable individuals with Tourette syndrome are found in all walks of life, including musicians, athletes and authors. The best-known example of a person who may have used obsessive–compulsive traits to advantage is Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson , often referred to as Dr. Johnson, was an English author who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, essayist, moralist, literary critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer...
, the 18th-century English man of letters, who likely had Tourette syndrome as evidenced by the writings of James Boswell
James Boswell
James Boswell, 9th Laird of Auchinleck was a lawyer, diarist, and author born in Edinburgh, Scotland; he is best known for the biography he wrote of one of his contemporaries, the English literary figure Samuel Johnson....
. Johnson wrote A Dictionary of the English Language
A Dictionary of the English Language
Published on 15 April 1755 and written by Samuel Johnson, A Dictionary of the English Language, sometimes published as Johnson's Dictionary, is among the most influential dictionaries in the history of the English language....
in 1747, and was a prolific writer, poet, and critic.
Although it has been speculated that Mozart had Tourette's,* Simkin B. "Mozart's scatological disorder". BMJ. 1992 Dec 19–26;305(6868):1563–7. PMID 1286388 no Tourette's expert or organization has presented credible evidence to support such a conclusion, and there are problems with the arguments supporting the diagnosis: tics are not transferred to the written form, as is supposed with Mozart's scatological writings; the medical history in retrospect is not thorough; side effects due to other conditions may be misinterpreted; "it is not proven whether written documents can account for the existence of a vocal tic" and "the evidence of motor tics in Mozart’s life is doubtful".
The entertainment industry has been criticized for depicting those with Tourette syndrome as social misfits whose only tic is coprolalia, which has furthered stigmatization and the public's misunderstanding of those with Tourette's. The coprolalic symptoms of Tourette's are also fodder for radio and television talk shows in the US and in the British media.
Further reading
- Kushner, HI. A cursing brain?: The histories of Tourette syndrome. Harvard University PressHarvard University PressHarvard University Press is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. In 2005, it published 220 new titles. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. Its current director is William P...
, 2000. ISBN 0-674-00386-1. - Olson, S. "Making Sense of Tourette's" (PDF). Science. 2004 Sep 3;305(5689):1390–92. PMID 15353772
External links
—Organizations- Tourette's Syndrome: minimizing confusion—a blog by Roger Freeman, MD, clinical head of the Neuropsychiatry Clinic, British Columbia's Children's HospitalBritish Columbia's Children's HospitalBC Children's Hospital is a medical facility located in Vancouver, British Columbia, and is an agency of the Provincial Health Services Authority. It specializes in health care for patients from birth to age 16. It is also a teaching and research facility for children's medicine...
, professional advisory board member of the Tourette Syndrome Foundation of CanadaTourette Syndrome Foundation of CanadaThe Tourette Syndrome Foundation of Canada is a Canadian voluntary organization based in Toronto, Ontario. It was formed in 1976, and is dedicated to improving the quality of life for those with or affected by Tourette syndrome through programs of education, advocacy, self-help and the promotion...
, and former member of the Tourette Syndrome AssociationTourette Syndrome AssociationThe Tourette Syndrome Association , based in Bayside, New York, United States, is a non-profit voluntary organization and the only national health-related organization serving people with Tourette syndrome. It was founded in 1972 by five couples, parents of children with Tourette syndrome...
Medical Advisory Board. Dr. Freeman has over 180 journal-published articles on PubMed. - Tourette syndrome: Newly diagnosed—a 3-hour video/slide presentation by John Walkup, MD, deputy director of the Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Johns Hopkins HospitalJohns Hopkins HospitalThe Johns Hopkins Hospital is the teaching hospital and biomedical research facility of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, located in Baltimore, Maryland . It was founded using money from a bequest by philanthropist Johns Hopkins...
and 2007 Chair of the Tourette Syndrome AssociationTourette Syndrome AssociationThe Tourette Syndrome Association , based in Bayside, New York, United States, is a non-profit voluntary organization and the only national health-related organization serving people with Tourette syndrome. It was founded in 1972 by five couples, parents of children with Tourette syndrome...
Medical Advisory Board

