
Trace distance
Encyclopedia
In quantum mechanics
, and especially quantum information
and the study of open quantum system
s, the trace distance T is a metric
on the space of density matrices
. It is just half of the trace norm of the difference of the matrices:
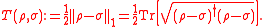
The purpose of the factor of two is to restrict the trace distance between two normalized density matrices to the range [0, 1] and to simplify formulas in which the trace distance appears.
Since density matrices are Hermitian,

where the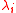 are eigenvalues of the Hermitian, but not necessarily positive, matrix
are eigenvalues of the Hermitian, but not necessarily positive, matrix 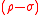 .
.
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, and especially quantum information
Quantum information
In quantum mechanics, quantum information is physical information that is held in the "state" of a quantum system. The most popular unit of quantum information is the qubit, a two-level quantum system...
and the study of open quantum system
Open quantum system
In physics, an open quantum system is a quantum system which is found to be in interaction with an external quantum system, the environment...
s, the trace distance T is a metric
Metric (mathematics)
In mathematics, a metric or distance function is a function which defines a distance between elements of a set. A set with a metric is called a metric space. A metric induces a topology on a set but not all topologies can be generated by a metric...
on the space of density matrices
Density matrix
In quantum mechanics, a density matrix is a self-adjoint positive-semidefinite matrix of trace one, that describes the statistical state of a quantum system...
. It is just half of the trace norm of the difference of the matrices:
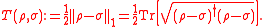
The purpose of the factor of two is to restrict the trace distance between two normalized density matrices to the range [0, 1] and to simplify formulas in which the trace distance appears.
Since density matrices are Hermitian,

where the
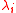 are eigenvalues of the Hermitian, but not necessarily positive, matrix
are eigenvalues of the Hermitian, but not necessarily positive, matrix 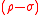 .
.

