
Transition time
Encyclopedia
The transition time 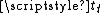 is the time a dynamical system
is the time a dynamical system
needs to switch between two different stable state
s, when responding to a stable input signal. In a logic circuit (a discrete-time dynamical system
whose state
is representable as a boolean-valued vector function
of time) undergoing a change of state
, it identifies the rise time
or the fall time
of the output voltage
. It is therefore correct to speak of two types of transition times
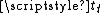 is the time a dynamical system
is the time a dynamical systemDynamical system (definition)
The dynamical system concept is a mathematical formalization for any fixed "rule" which describes the time dependence of a point's position in its ambient space...
needs to switch between two different stable state
State (computer science)
In computer science and automata theory, a state is a unique configuration of information in a program or machine. It is a concept that occasionally extends into some forms of systems programming such as lexers and parsers....
s, when responding to a stable input signal. In a logic circuit (a discrete-time dynamical system
Dynamical system (definition)
The dynamical system concept is a mathematical formalization for any fixed "rule" which describes the time dependence of a point's position in its ambient space...
whose state
State (computer science)
In computer science and automata theory, a state is a unique configuration of information in a program or machine. It is a concept that occasionally extends into some forms of systems programming such as lexers and parsers....
is representable as a boolean-valued vector function
Boolean-valued function
A boolean-valued function, in some usages is a predicate or a proposition, is a function of the type f : X → B, where X is an arbitrary set and where B is a boolean domain....
of time) undergoing a change of state
State (computer science)
In computer science and automata theory, a state is a unique configuration of information in a program or machine. It is a concept that occasionally extends into some forms of systems programming such as lexers and parsers....
, it identifies the rise time
Rise time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
or the fall time
Fall time
In electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
of the output voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
. It is therefore correct to speak of two types of transition times
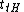 : transition time Low-to-High. It is the rise timeRise timeIn electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
: transition time Low-to-High. It is the rise timeRise timeIn electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
of a logic gateLogic gateA logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and...
's output voltage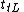 : transition time High-to-Low. It is the fall timeFall timeIn electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
: transition time High-to-Low. It is the fall timeFall timeIn electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
of a logic gateLogic gateA logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and...
's output voltage
See also
- Fall timeFall timeIn electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
- Logic circuit
- Rise timeRise timeIn electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
- State (computer science)State (computer science)In computer science and automata theory, a state is a unique configuration of information in a program or machine. It is a concept that occasionally extends into some forms of systems programming such as lexers and parsers....
- Slew rateSlew rateIn electronics, the slew rate represents the maximum rate of change of a signal at any point in a circuit.Limitations in slew rate capability can give rise to non linear effects in electronic amplifiers...
- Time constantTime constantIn physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter \tau , is the risetime characterizing the response to a time-varying input of a first-order, linear time-invariant system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a system that can be modeled by a single first order...

