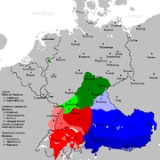
Upper German
Encyclopedia
Upper German is a family of High German
dialect
s spoken primarily in southern Germany
, Austria
, Switzerland
and Northern Italy
.
or Austro-Bavarian. However, there are several dialect
s in these two groups besides the more widespread versions of Alemannic and Austro-Bavarian.
(including Erzgebirgisch
, often overlooked and incorrectly classified as part of Upper Saxon
) and South Franconian
dialect groups, also collectively known as High Franconian, should be included as part of Upper German or instead classified as Central German
is an open question, as they have traits of both Upper and Central German and are frequently described as a transitional zone. Hence, either scheme can be encountered.
Based on the fact that Langobardic
has undergone the High German consonant shift
completely, it is also often classified as Upper German
. However, if the High German consonant shift occurred late (7th/8th century), which now seems to be the prevalent view, it would seem to be anachronistic to do so. On the other hand, if Langobardic was still essentially identical to Bavarian or Alemannic at the time, the anachronism would disappear, and in fact, what is attested in Langobardic cannot really be shown to be systematically different in any particular point from the earliest attested form of Bavarian in the 8th century, apart from a few divergent phonological developments, which, however, seem to postdate the sound shift.
High German languages
The High German languages or the High German dialects are any of the varieties of standard German, Luxembourgish and Yiddish, as well as the local German dialects spoken in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Luxembourg and in neighboring portions of Belgium and the...
dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s spoken primarily in southern Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
and Northern Italy
Northern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
.
Family tree
Upper German can be generally classified as AlemannicAlemannic German
Alemannic is a group of dialects of the Upper German branch of the Germanic language family. It is spoken by approximately ten million people in six countries: Switzerland, Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, France and Italy...
or Austro-Bavarian. However, there are several dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s in these two groups besides the more widespread versions of Alemannic and Austro-Bavarian.
- Alemannic GermanAlemannic GermanAlemannic is a group of dialects of the Upper German branch of the Germanic language family. It is spoken by approximately ten million people in six countries: Switzerland, Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, France and Italy...
(G: )- Swabian GermanSwabian GermanSwabian is one of the Alemannic dialects of High German. It is spoken in Swabia, a region which covers much of Germany's southwestern state Baden-Württemberg, including its capital Stuttgart, the rural area known as the Swabian Alb, and Bavaria...
(G: , spoken mostly in SwabiaSwabiaSwabia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.-Geography:Like many cultural regions of Europe, Swabia's borders are not clearly defined...
, numbered 3) - Low Alemannic GermanLow Alemannic GermanLow Alemannic is a branch of Alemannic German and is often considered to be part of the German language, even though it is only partly intelligible to speakers of German.Variants:*Vorarlbergisch*Upper Rhenish*Alsatian, spoken in the Alsace, France...
(G: , numbered 4)- AlsatianAlsatian languageAlsatian is a Low Alemannic German dialect spoken in most of Alsace, a region in eastern France which has passed between French and German control many times.-Language family:...
(Al & G: , spoken in AlsaceAlsaceAlsace is the fifth-smallest of the 27 regions of France in land area , and the smallest in metropolitan France. It is also the seventh-most densely populated region in France and third most densely populated region in metropolitan France, with ca. 220 inhabitants per km²...
, FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, numbered 5) - Alemán ColonieroAlemán ColonieroAlemán Coloniero, spoken in Colonia Tovar, Venezuela, is a dialect that belongs to the Low Alemannic branch of German.-Characteristics:The language, like other Alemannic dialects, is not mutually intelligible with Standard German. It is spoken by descendants of Germans from the Black Forest region...
(G & , spoken in VenezuelaVenezuelaVenezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
) - Basel GermanBasel GermanBasel German or Baseldytsch is the dialect of the city of Basel, Switzerland. Among the Swiss German dialects, it is the only Low Alemannic one.- Aspirated plosives :...
(Baseldytsch: , G: )
- Alsatian
- High Alemannic GermanHigh Alemannic GermanHigh Alemannic is a branch of Alemannic German and is often considered to be part of the German language, even though it is only partly intelligible to non-Alemannic speakers....
(Al & G: , numbered 6)- Bernese GermanBernese GermanBernese German is the dialect of High Alemannic German spoken in the Swiss plateau part of the canton of Bern and in some neighbouring regions.- Varieties :There is a lot of regional variation within Bernese German dialects...
(Bernese: , G: ) - Zürich GermanZürich GermanZürich German, or Züritüütsch is the High Alemannic dialect spoken in the Canton of Zürich, Switzerland.It is divided in six sub-dialects, covering the entire Canton with the exception of the parts north of the Thur and the Rhine....
(G: , Zürich German: )
- Bernese German
- Highest Alemannic GermanHighest Alemannic GermanHighest Alemannic is a branch of Alemannic German and is often considered to be part of the German language, even though mutual intelligibility with Standard German and other non-Alemannic German dialects is very limited....
(Al & G: , numbered 6)- Walliser German (G: Walliser German: Wallisertitsch, spoken in the Wallis CantonValaisThe Valais is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland in the southwestern part of the country, around the valley of the Rhône from its headwaters to Lake Geneva, separating the Pennine Alps from the Bernese Alps. The canton is one of the drier parts of Switzerland in its central Rhône valley...
of SwitzerlandSwitzerlandSwitzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
)- Walser GermanWalser GermanThe Walser language , also known as Walliser German , is a group of Highest Alemannic dialects spoken in Walser settlements in parts of Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, and Austria and in the German-speaking part of the Canton of Wallis , in the uppermost Rhône valley.The terms Walser and...
(G: )
- Walser German
- Walliser German (G: Walliser German: Wallisertitsch, spoken in the Wallis Canton
- Swabian German
- Austro-BavarianAustro-BavarianBavarian , also Austro-Bavarian, is a major group of Upper German varieties spoken in the south east of the German language area.-History and origin:...
(A-B: , G: , spoken in AustriaAustriaAustria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, South TyrolSouth TyrolSouth Tyrol , also known by its Italian name Alto Adige, is an autonomous province in northern Italy. It is one of the two autonomous provinces that make up the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province has an area of and a total population of more than 500,000 inhabitants...
, Italy, and in BavariaBavariaBavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, Germany)- Northern Austro-BavarianNorthern Austro-BavarianNorthern Bavarian is a dialect of the Bavarian language, together with Central Bavarian and Southern Bavarian. The language is mostly spoken in the Upper Palatinate, although not in Regensburg, which is a primarily Central Bavarian–speaking area, according to a linguistic survey done in the late...
(A-B: , G: , spoken in Upper PalatinateUpper PalatinateThe Upper Palatinate is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of Bavaria.- History :The region took its name first in the early 16th century, because it was by the Treaty of Pavia one of the main portions of the territory of the Wittelsbach Elector...
, Bavaria, numbered 7) - Central Austro-BavarianCentral Austro-BavarianThe Central Bavarian Germanic dialects forming a subgroup of the Bavarian dialects. The subgroup covers all dialects spoken along the rivers Isar and Danube, on the northern side of the Alps....
(A-B: , G: , spoken in Bavaria and Austria, numbered 8)- Viennese GermanViennese GermanViennese German is the city dialect spoken in Vienna, the capital of Austria and is counted among the Bavarian dialects. Even in Lower Austria, the state surrounding the city, many of its expressions are not used, while farther to the west they are often not even understood.- Linguistic...
(G: , spoken in Vienna and parts of Lower Austria, Austria) - Munich German (G: , spoken in Munich, Bavaria)
- Viennese German
- Southern Austro-BavarianSouthern Austro-BavarianSouthern Bavarian, or Southern Austro-Bavarian, is a cluster of Germanic dialects of the Bavarian group.They are primarily spoken in the Austrian federal-states of Tyrol, Carinthia and Styria, in the southern parts of Salzburg and Burgenland as well as in the Italian province of South Tyrol...
(A-B: , G: , spoken in Austria and South Tyrol, Italy) - CimbrianCimbrian languageCimbrian refers to any of several local Upper German varieties spoken in northeastern Italy. The speakers of the language are known as Zimbern....
(G: , , spoken in northeastern ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
) - Mócheno (It: , spoken in Trentino, in Italy)
- Hutterite GermanHutterite GermanHutterite German is an Upper German dialect of the Austro-Bavarian variety of the German language, which is spoken by Hutterite communities in Canada and the United States...
(G: , spoken in CanadaCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
and the United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
)
- Northern Austro-Bavarian
High Franconian
Whether the East FranconianEast Franconian German
East Franconian is a dialect which is spoken in northern Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Bad Mergentheim, Crailsheim and Suhl...
(including Erzgebirgisch
Erzgebirgisch
Erzgebirgisch is an Upper German dialect, probably belonging to the Franconian dialect group, spoken mainly in the central Erzgebirge . It has received relatively little academic attention...
, often overlooked and incorrectly classified as part of Upper Saxon
Upper Saxon German
Upper Saxon is a Central German dialect spoken in much of the modern German states of Saxony and Thuringia. Contrary to its name it is not a descendant of Old Saxon. The degree of accent varies from place to place within the states, with it being anywhere from a relatively mild accent in the...
) and South Franconian
South Franconian German
South Franconian is a dialect which is spoken in the northern Baden region in Germany around Karlsruhe, Pforzheim and Rastatt....
dialect groups, also collectively known as High Franconian, should be included as part of Upper German or instead classified as Central German
Central German
Central German is a group of High German dialects spoken from the Rhineland in the west to the former eastern territories of Germany.-History:...
is an open question, as they have traits of both Upper and Central German and are frequently described as a transitional zone. Hence, either scheme can be encountered.
Based on the fact that Langobardic
Lombardic language
Lombardic or Langobardic is the extinct language of the Lombards , the Germanic speaking people who settled in Italy in the 6th century. The language declined rapidly already in the 7th century as the invaders quickly adopted the Latin vernacular spoken by the local Roman population. E.g...
has undergone the High German consonant shift
High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases, probably beginning between the 3rd and 5th centuries AD, and was almost...
completely, it is also often classified as Upper German
Upper German
Upper German is a family of High German dialects spoken primarily in southern Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Northern Italy.-Family tree:Upper German can be generally classified as Alemannic or Austro-Bavarian...
. However, if the High German consonant shift occurred late (7th/8th century), which now seems to be the prevalent view, it would seem to be anachronistic to do so. On the other hand, if Langobardic was still essentially identical to Bavarian or Alemannic at the time, the anachronism would disappear, and in fact, what is attested in Langobardic cannot really be shown to be systematically different in any particular point from the earliest attested form of Bavarian in the 8th century, apart from a few divergent phonological developments, which, however, seem to postdate the sound shift.

