VCSEL
Encyclopedia
Laser diode
The laser diode is a laser where the active medium is a semiconductor similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The most common type of laser diode is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current...
with laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, contrary to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers (also in-plane lasers) which emit from surfaces formed by cleaving the individual chip out of a wafer
Wafer (electronics)
A wafer is a thin slice of semiconductor material, such as a silicon crystal, used in the fabrication of integrated circuits and other microdevices...
.
There are several advantages to producing VCSELs, in contrast to the production process of edge-emitting lasers. Edge-emitters cannot be tested until the end of the production process. If the edge-emitter does not function properly, whether due to bad contacts or poor material growth quality, the production time and the processing materials have been wasted. VCSELs however, can be tested at several stages throughout the process to check for material quality and processing issues. For instance, if the vias
Via (electronics)
A via is a vertical electrical connection between different layers of conductors in a physical electronic circuit.- In IC :In integrated circuit design, a via is a small opening in an insulating oxide layer that allows a conductive connection between different layers. A via on an integrated circuit...
have not been completely cleared of dielectric material during the etch, an interim testing process will flag that the top metal layer is not making contact to the initial metal layer. Additionally, because VCSELs emit the beam perpendicular to the active region of the laser as opposed to parallel as with an edge emitter, tens of thousands of VCSELs can be processed simultaneously on a three inch Gallium Arsenide wafer. Furthermore, even though the VCSEL production process is more labor and material intensive, the yield can be controlled to a more predictable outcome.
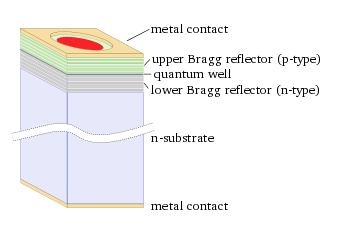
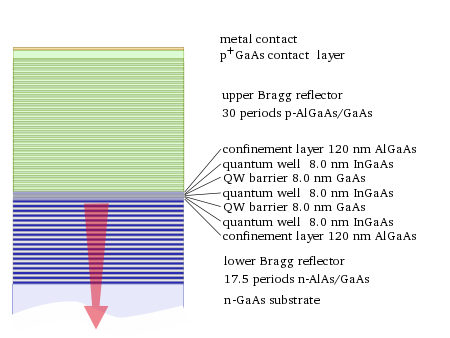
Structure
Distributed Bragg reflector
A distributed Bragg reflector is a reflector used in waveguides, such as optical fibers. It is a structure formed from multiple layers of alternating materials with varying refractive index, or by periodic variation of some characteristic of a dielectric waveguide, resulting in periodic variation...
(DBR) mirrors parallel to the wafer surface with an active region
Active laser medium
The active laser medium is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from a higher energy state...
consisting of one or more quantum well
Quantum well
A quantum well is a potential well with only discrete energy values.One technology to create quantization is to confine particles, which were originally free to move in three dimensions, to two dimensions, forcing them to occupy a planar region...
s for the laser light generation in between. The planar DBR-mirrors consist of layers with alternating high and low refractive indices. Each layer has a thickness of a quarter of the laser wavelength in the material, yielding intensity reflectivities above 99%. High reflectivity mirrors are required in VCSELs to balance the short axial length of the gain region.
In common VCSELs the upper and lower mirrors are doped as p-type and n-type materials, forming a diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
junction. In more complex structures, the p-type and n-type regions may be embedded between the mirrors, requiring a more complex semiconductor process to make electrical contact to the active region, but eliminating electrical power loss in the DBR structure.
In laboratory investigation of VCSELs using new material systems, the active region may be pumped by an external light source with a shorter wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
, usually another laser. This allows a VCSEL to be demonstrated without the additional problem of achieving good electrical performance; however such devices are not practical for most applications.
VCSELs for wavelengths from 650 nm to 1300 nm are typically based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) wafers with DBRs formed from GaAs and aluminium gallium arsenide
Aluminium gallium arsenide
Aluminium gallium arsenide is a semiconductor material with very nearly the same lattice constant as GaAs, but a larger bandgap. The x in the formula above is a number between 0 and 1 - this indicates an arbitrary alloy between GaAs and AlAs.The bandgap varies between 1.42 eV and 2.16 eV...
(AlxGa(1-x)As). The GaAs–AlGaAs system is favored for constructing VCSELs because the lattice constant
Lattice constant
The lattice constant [or lattice parameter] refers to the constant distance between unit cells in a crystal lattice. Lattices in three dimensions generally have three lattice constants, referred to as a, b, and c. However, in the special case of cubic crystal structures, all of the constants are...
of the material does not vary strongly as the composition is changed, permitting multiple "lattice-matched" epitaxial
Epitaxy
Epitaxy refers to the deposition of a crystalline overlayer on a crystalline substrate, where the overlayer is in registry with the substrate. In other words, there must be one or more preferred orientations of the overlayer with respect to the substrate for this to be termed epitaxial growth. The...
layers to be grown on a GaAs substrate. However, the refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
of AlGaAs does vary relatively strongly as the Al fraction is increased, minimizing the number of layers required to form an efficient Bragg mirror compared to other candidate material systems.
Furthermore, at high aluminium concentrations, an oxide can be formed from AlGaAs, and this oxide can be used to restrict the current in a VCSEL, enabling very low threshold currents.
Recently the two main methods of restricting the current in a VCSEL were characterized by two types of VCSELs: ion-implanted VCSELs and Oxide VCSELs.
In the early 1990s, telecommunications companies tended to favor ion-implanted VCSELs. Ions, (often hydrogen ions, H+), were implanted into the VCSEL structure everywhere except the aperture of the VCSEL, destroying the lattice structure around the aperture, thus inhibiting the current. In the mid to late 1990s, companies moved towards the technology of oxide VCSELs. The current is confined in an oxide VCSEL by oxidizing the material around the aperture of the VCSEL. A high content aluminium layer that is grown within the VCSEL structure is the layer that is oxidized. Oxide VCSELs also often employ the ion implant production step. As a result in the oxide VCSEL, the current path is confined by the ion implant and the oxide aperture.
The initial acceptance of oxide VCSELs was plagued with concern about the apertures "popping off" due to the strain and defects of the oxidation layer. However, after much testing, the reliability of the structure has proven to be robust. As stated in one study by Hewlett Packard on oxide VCSELs, "The stress results show that the activation energy and the wearout lifetime of oxide VCSEL are similar to that of implant VCSEL emitting the same amount of output power." http://www.ieee.org/organizations/pubs/newsletters/leos/aug99/article6.htm
A production concern also plagued the industry when moving the oxide VCSELs from research and development to production mode. The oxidation rate of the oxide layer was highly dependent on the aluminium content. Any slight variation in aluminium would change the oxidation rate sometimes resulting in apertures that were either too big or too small to meet the specification standards.
Longer wavelength devices, from 1300 nm to 2000 nm, have been demonstrated with at least the active region made of indium phosphide. VCSELs at even higher wavelengths are experimental and usually optically pumped. 1310 nm VCSELs are desirable as the dispersion of silica-based optical fiber is minimal in this wavelength range.
Special forms
- Multiple active region devices (aka bipolar cascade VCSELs). Allows for differential quantum efficiency values in excess of 100% through carrier recycling
- VCSELs with tunnel junctions. Using a tunnel junction (n+p+), an electrically advantageous n-n+p+-p-i-n configuration can be built that also may beneficially influence other structural elements (e.g. in the form of a Buried Tunnel Junction (BTJ)).
- Widely tunable VCSEL with micromechanically (MEMSMicroelectromechanical systemsMicroelectromechanical systems is the technology of very small mechanical devices driven by electricity; it merges at the nano-scale into nanoelectromechanical systems and nanotechnology...
) movable mirror - Wafer-bonded or wafer-fused VCSEL: Combination of semiconductor materials that can be fabricated using different types of substrate wafers
- Monolithically optically pumped VCSELs: Two VCSELs on top of each other. One of them optically pumps the other one.
- VCSEL with longitudinally integrated monitor diode: A photodiode is integrated under the back mirror of the VCSEL.
- VCSEL with transversally integrated monitor diode: With suitable etching of the VCSEL's wafer, a resonant photodiode can be manufactured that may measure the light intensity of a neighboring VCSEL.
- VCSELs with external cavities, known as VECSELVECSELA vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting-laser is a small semiconductor laser similar to a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser...
s or semiconductor disk laserDisk laserA disk laser or active mirror is a type of solid-state laser characterized by a heat sink and laser output that are realized on opposite sides of a thin layer of active gain medium...
s. VECSELs are optically pumped with conventional laser diodes. This arrangement allows a larger area of the device to be pumped and therefore more power can be extracted - as much as 30W. The external cavity also allows intracavity techniques such as frequency doubling, single frequency operation and femtosecond pulse modelocking. - Vertical-cavity semiconductor optical amplifiers, known as VCSOAs . These devices are optimized as amplifiers as opposed to oscillators. VCSOAs must be operated below threshold and thus require reduced mirror reflectivities for decreased feedback. In order to maximize the signal gain, these devices contain a large number of quantum wells (optically pumped devices have been demonstrated with 21–28 wells) and as a result exhibit single-pass gain values which are significantly larger than that of a typical VCSEL (roughly 5%). These structures operate as narrow linewidth (tens of GHz) amplifiers and may be implemented as amplifying filters.
Characteristics
Because VCSELs emit from the top surface of the chip, they can be tested on-wafer, before they are cleaved into individual devices. This reduces the fabricationSemiconductor fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to create the integrated circuits that are present in everyday electrical and electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of photolithographic and chemical processing steps during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer...
cost of the devices. It also allows VCSELs to be built not only in one-dimensional, but also in two-dimensional arrays.
The larger output aperture of VCSELs, compared to most edge-emitting lasers, produces a lower divergence angle of the output beam, and makes possible high coupling efficiency with optical fibers.
The high reflectivity mirrors, compared to most edge-emitting lasers, reduce the threshold current of VCSELs, resulting in low power consumption. However, as yet, VCSELs have lower emission power compared to edge-emitting lasers. The low threshold current also permits high intrinsic modulation bandwidths in VCSELs.
The wavelength of VCSELs may be tuned, within the gain band of the active region, by adjusting the thickness of the reflector layers.
While early VCSELs emitted in multiple longitudinal modes or in filament modes, single-mode VCSELs are now common.
High-power VCSELs
High-power vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers can also be fabricated, either by increasing the emitting aperture size of a single device or by combining several elements into large two-dimensional (2D) arrays. There have been relatively few reported studies on high-power VCSELs. Large-aperture single devices operating around 100 mW were first reported in 1993. Improvements in the epitaxial growth, processing, device design, and packaging led to individual large-aperture VCSELs emitting several hundreds of milliwatts by 1998. More than 2 W continuous-wave (CW) operation at -10 degrees Celsius heat-sink temperature was also reported in 1998 from a VCSEL array consisting of 1,000 elements, corresponding to a power density of 30 W/cm2. In 2001, more than 1 W CW power and 10 W pulsed power at room temperature were reported from a 19-element array. The VCSEL array chip was mounted on a diamondDiamond
In mineralogy, diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a variation of the face-centered cubic crystal structure called a diamond lattice. Diamond is less stable than graphite, but the conversion rate from diamond to graphite is negligible at ambient conditions...
heat spreader, taking advantage of diamond’s very high thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
. A record 3 W CW output power was reported in 2005 from large diameter single devices emitting around 980 nm.
In 2007, more than 200 W of CW output power was reported from a large (5 × 5mm) 2D VCSEL array emitting around the 976 nm wavelength, representing a substantial breakthrough in the field of high-power VCSELs. The high power level achieved was mostly due to improvements in wall-plug efficiency
Wall-plug efficiency
In optics, wall-plug efficiency or radiant efficiency is the energy conversion efficiency with which the system converts electrical power into optical power...
and packaging. In 2009, >100 W power levels were reported for VCSEL arrays emitting around 808 nm.
At that point, the VCSEL technology became useful for a variety of medical, industrial, and military applications requiring high power or high energy. Examples of such applications are:
- Medical/cosmetics: laser hair removalLaser hair removalLaser hair removal was performed experimentally for about 20 years before it became commercially available in the mid 1990s. One of the first published articles describing laser hair removal was authored by the group at Massachusetts General Hospital in 1998...
, laser wrinkle removal - Infrared illuminators for military/surveillance
- Pumping of solid-state laserSolid-state laserA solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid such as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers .-Solid-state...
s and fiber laserFiber laserA fiber laser or fibre laser is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, and thulium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing...
s - High-power/high-energy second harmonic generationSecond harmonic generationAn optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device, in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency...
(blue/green light) - Laser machining: laser cuttingLaser cuttingLaser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to cut materials, and is typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, but is also starting to be used by schools, small businesses and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser, by computer, at the...
, laser drillingLaser drillingManufacturers of turbine engines for aircraft propulsion and for power generation have benefited from the productivity of lasers for drilling small cylindrical holes at 15-90º to the surface in cast, sheet metal and machined components...
, laser ablationLaser ablationLaser ablation is the process of removing material from a solid surface by irradiating it with a laser beam. At low laser flux, the material is heated by the absorbed laser energy and evaporates or sublimates. At high laser flux, the material is typically converted to a plasma...
, laser engravingLaser engravingLaser engraving, or laser marking, is the practice of using lasers to engrave or mark an object. The technique does not involve the use of inks, nor does it involve tool bits which contact the engraving surface and wear out...
Applications
- Optical fiberOptical fiberAn optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
data transmission - Analog broadband signal transmission
- Absorption spectroscopy (TDLASTDLASTunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy is a technique for measuring the concentration of certain species such as methane, water vapor and many more, in a gaseous mixture using tunable diode lasers and laser absorption spectrometry...
) - Laser printerLaser printerA laser printer is a common type of computer printer that rapidly produces high quality text and graphics on plain paper. As with digital photocopiers and multifunction printers , laser printers employ a xerographic printing process, but differ from analog photocopiers in that the image is produced...
s - computer mouse
- Biological tissue analysis
- Chip scale atomic clockAtomic clockAn atomic clock is a clock that uses an electronic transition frequency in the microwave, optical, or ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum of atoms as a frequency standard for its timekeeping element...
History
The first VCSEL was presented in 1979 by Soda, Iga, Kitahara and Suematsu, but devices for CWContinuous wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency; and in mathematical analysis, of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a carrier wave is switched on and off...
operation at room temperature were not reported until 1988. The term VCSEL was coined in a publication of the Optical Society of America
Optical Society of America
The Optical Society is a scientific society dedicated to advancing the study of light—optics and photonics—in theory and application, by means of publishing, organizing conferences and exhibitions, partnership with industry, and education. The organization has members in more than 100 countries...
in 1987. Today, VCSELs have replaced edge-emitting lasers in applications for short-range fiberoptic communication such as Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
and Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
.
See also
- Optical interconnectOptical interconnectOptical interconnect is a way of communication by optical cables. Compared to traditional cables, optical wires are capable of a much higher bandwidth, from 10 Gb/s up to 100 Gb/s....
- Light PeakLight PeakThunderbolt is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to a computer via an expansion bus. Thunderbolt was developed by Intel and brought to market with technical collaboration from Apple Inc. It was introduced commercially on Apple's updated MacBook Pro lineup on February 24, 2011, using...
- Interconnect bottleneckInterconnect bottleneckThe interconnect bottleneck, the point at which integrated circuits reach their capacity, is expected sometime around 2010.Improved performance of computer systems has been achieved, in large part, by downscaling the IC minimum feature size. This allows the basic IC building block, the transistor,...
- Optical fiber cableOptical fiber cableAn optical fiber cable is a cable containing one or more optical fibers. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed....
- Optical communicationOptical communicationOptical communication is any form of telecommunication that uses light as the transmission medium.An optical communication system consists of a transmitter, which encodes a message into an optical signal, a channel, which carries the signal to its destination, and a receiver, which reproduces the...
- Parallel optical interfaceParallel optical interfaceA parallel optical interface is a form of fiber optic technology aimed primarily at communications and networking over relatively short distances , and at high bandwidths....

