
VESA Local Bus
Encyclopedia
The VESA Local Bus was mostly used in personal computers. VESA
(Video Electronics Standards Association) Local Bus worked alongside the ISA
bus; it acted as a high-speed conduit for memory-mapped I/O
and DMA
, while the ISA bus handled interrupts and port-mapped I/O.
bandwidth of the ISA bus became an issue, mainly for graphics cards, but also for mass storage devices. IBM's attempt at producing a successor standard, the MCA
failed due to its proprietary nature, while the more accepted EISA
standard didn't offer enough of an improvement over standard ISA for it to be generally considered worthwhile. For a short time, hardware producers included proprietary implementations of local bus
ses on their motherboards which were only compatible with hardware from the same manufacturer. This led to the VESA
consortium defining the VLB standard in 1992.
A VLB slot itself was an extension of an existing ISA slot. Indeed, either a VLB or an ISA card could be plugged into a VLB slot. The extended portion was usually colored a distinctive brown. This made VLB cards quite long, reminiscent of the ISA expansion cards from the old XT
days (which were long because of low component density and high chip count requiring more printed circuit board space, rather than because of a long edge connector
.) The addition looked similar to the PCI slot and, indeed, used the same connector type, only shorter.
The VESA Local Bus was designed as a stopgap solution to the problem of the ISA bus's limited bandwidth
. VLB had several flaws that served to limit its useful life substantially:
 Despite these problems, the VESA Local Bus was very commonplace on 486 motherboards. Probably a majority of 486-based systems had a VESA Local Bus video card, although early 486 systems never had VLB slots, as VLB debuted years after the introduction of the 486 processor.
Despite these problems, the VESA Local Bus was very commonplace on 486 motherboards. Probably a majority of 486-based systems had a VESA Local Bus video card, although early 486 systems never had VLB slots, as VLB debuted years after the introduction of the 486 processor.
By 1996, the Pentium (driven by Intel's Triton chipset and PCI
architecture) had eliminated the 80486 market and the VESA Local Bus with it. Many of the last 80486 motherboards made have PCI slots instead of (or sometimes in addition to) VLB slots. Most boards had either PCI or VLB slots alongside the still-ubiquitous ISA slots. So-called "VIP" (VESA/ISA/PCI) boards, with all three slot types, were unusual.
VESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
(Video Electronics Standards Association) Local Bus worked alongside the ISA
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor...
bus; it acted as a high-speed conduit for memory-mapped I/O
Memory-mapped I/O
Memory-mapped I/O and port I/O are two complementary methods of performing input/output between the CPU and peripheral devices in a computer...
and DMA
Direct memory access
Direct memory access is a feature of modern computers that allows certain hardware subsystems within the computer to access system memory independently of the central processing unit ....
, while the ISA bus handled interrupts and port-mapped I/O.
Historical overview
In the early 1990s, the I/OI/O
I/O may refer to:* Input/output, a system of communication for information processing systems* Input-output model, an economic model of flow prediction between sectors...
bandwidth of the ISA bus became an issue, mainly for graphics cards, but also for mass storage devices. IBM's attempt at producing a successor standard, the MCA
Micro Channel architecture
Micro Channel Architecture was a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers through the mid 1990s.- Background :...
failed due to its proprietary nature, while the more accepted EISA
Extended Industry Standard Architecture
The Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers...
standard didn't offer enough of an improvement over standard ISA for it to be generally considered worthwhile. For a short time, hardware producers included proprietary implementations of local bus
Local bus
In computer science, a local bus is a computer bus that connects directly, or almost directly, from the CPU to one or more slots on the expansion bus. The significance of direct connection to the CPU is avoiding the bottleneck created by the expansion bus, thus providing fast throughput...
ses on their motherboards which were only compatible with hardware from the same manufacturer. This led to the VESA
VESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
consortium defining the VLB standard in 1992.
A VLB slot itself was an extension of an existing ISA slot. Indeed, either a VLB or an ISA card could be plugged into a VLB slot. The extended portion was usually colored a distinctive brown. This made VLB cards quite long, reminiscent of the ISA expansion cards from the old XT
IBM Personal Computer XT
The IBM Personal Computer XT, often shortened to the IBM XT, PC XT, or simply XT, was IBM's successor to the original IBM PC. It was released as IBM Machine Type number 5160 on March 8, 1983, and came standard with a hard drive...
days (which were long because of low component density and high chip count requiring more printed circuit board space, rather than because of a long edge connector
Edge connector
An edge connector is the portion of a printed circuit board consisting of traces leading to the edge of the board that are intended to plug into a matching socket. The edge connector is a money-saving device because it only requires a single discrete female connector , and they also tend to be...
.) The addition looked similar to the PCI slot and, indeed, used the same connector type, only shorter.
The VESA Local Bus was designed as a stopgap solution to the problem of the ISA bus's limited bandwidth
Bandwidth (computing)
In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
. VLB had several flaws that served to limit its useful life substantially:
- 80486 dependence. The VESA Local Bus relied heavily on the Intel 80486Intel 80486The Intel 80486 microprocessor was a higher performance follow up on the Intel 80386. Introduced in 1989, it was the first tightly pipelined x86 design as well as the first x86 chip to use more than a million transistors, due to a large on-chip cache and an integrated floating point unit...
CPU's memory bus design. When the P5P5 (microarchitecture)The original Pentium microprocessor was introduced on March 22, 1993. Its microarchitecture, deemed P5, was Intel's fifth-generation and first superscalar x86 microarchitecture. As a direct extension of the 80486 architecture, it included dual integer pipelines, a faster FPU, wider data bus,...
Pentium processor started to gain mass acceptance, circa 1995, there were major differences in its bus design, and the VESA Local Bus was not easily adaptable. This also made moving the bus to non-x86X86 architectureThe term x86 refers to a family of instruction set architectures based on the Intel 8086 CPU. The 8086 was launched in 1978 as a fully 16-bit extension of Intel's 8-bit based 8080 microprocessor and also introduced segmentation to overcome the 16-bit addressing barrier of such designs...
architectures nearly impossible. Few Pentium motherboards with VLB slots were ever made.
- Limited number of slots available. Most PCs that used VESA Local Bus had only one or two slots available, as opposed to 5 or 6 ISA slots. This was because, as a direct branch of the 80486 memory bus, the VESA Local Bus did not have the electrical ability to drive more than 1 or 2 (or 3 at the most) cards at a time.
- Reliability problems. The same electrical problems that limited the VESA Local Bus to 2 or 3 slots also limited its reliability. Glitches between cards were common, especially on low-end motherboardMotherboardIn personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
s, and when important devices such as hard diskHard diskA hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the...
controllers were attached to the bus, there was the all-too-common possibility of massive data corruptionData corruptionData corruption refers to errors in computer data that occur during writing, reading, storage, transmission, or processing, which introduce unintended changes to the original data...
.
- Installation woes. The length of the slot and number of pins made VLB cards notoriously difficult to install and remove. The sheer mechanical effort required was stressful to both the card and the motherboard, and breakages were not uncommon. This was compounded by the extended length of the card logic board; often there was not enough room in the PC case to angle the card into the slot, requiring it to be pushed with great force straight down into the slot. To avoid excessive flexing of the motherboard during this action the chassis and motherboard had to be designed with good, relatively closely spaced supports for the motherboard, which was not always the case, and the person inserting the board had to distribute the downward force evenly across its top edge. The length of a VLB slot, and the difficult installation that resulted from it, led to an alternate expansion of the acronym: Very Long Bus.

By 1996, the Pentium (driven by Intel's Triton chipset and PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
architecture) had eliminated the 80486 market and the VESA Local Bus with it. Many of the last 80486 motherboards made have PCI slots instead of (or sometimes in addition to) VLB slots. Most boards had either PCI or VLB slots alongside the still-ubiquitous ISA slots. So-called "VIP" (VESA/ISA/PCI) boards, with all three slot types, were unusual.
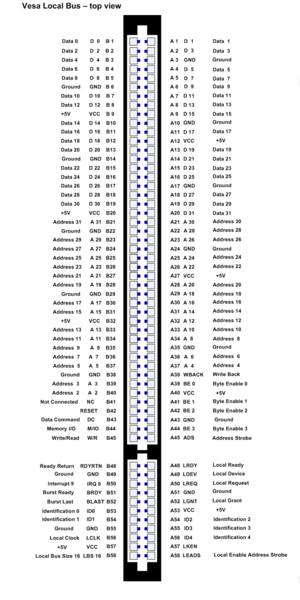
Technical data

| Bus width | 32 bits |
|---|---|
| Compatible with | 8 bit ISA, 16 bit ISA, VLB |
| Pin Pin A pin is a device used for fastening objects or material together.Pin may also refer to:* Award pin, a small piece of metal or plastic with a pin attached given as an award for some achievement... s |
112 |
| Vcc VCC VCC may refer to:as a three-letter acronym:* Common-collector voltage , plus collector supply line voltage in a common NPN circuit.* Vale of Catmose College, an arts college in England.* Valencia Community College, in Orlando, Florida... |
+5 V |
| Clock | 486SX-25: 25 MHz 486DX2-50: 25 MHz 486DX-33: 33 MHz486DX2-66: 33 MHz486DX4-100: 33 MHz486DX-40: 40 MHz486DX2-80: 40 MHz486DX4-120: 40 MHz5x86@133 MHz: 33 MHz 5x86@160 MHz: 40 MHz 486DX-50: 50 MHz (out of specification) |
See also
- Industry Standard ArchitectureIndustry Standard ArchitectureIndustry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor...
(ISA) - Extended Industry Standard ArchitectureExtended Industry Standard ArchitectureThe Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers...
(EISA) - Micro Channel architectureMicro Channel architectureMicro Channel Architecture was a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers through the mid 1990s.- Background :...
(MCA) - NuBusNuBusNuBus is a 32-bit parallel computer bus, originally developed at MIT as a part of the NuMachine workstation project. The first complete implementation of the NuBus and the NuMachine was done by Western Digital for their NuMachine, and for the Lisp Machines Inc. LMI-Lambda. The NuBus was later...
- Peripheral Component InterconnectPeripheral Component InterconnectConventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
(PCI) - Accelerated Graphics PortAccelerated Graphics PortThe Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
(AGP) - PCI ExpressPCI ExpressPCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
(PCIe) - List of device bandwidths (A useful listing of device bandwidths that include VLB)

