
Vacutainer
Encyclopedia

Venipuncture
In medicine, venepuncture, venopuncture or venipuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of intravenous therapy or for blood sampling of venous blood. This procedure is performed by medical laboratory scientists, medical practitioners, some EMTs, paramedics,...
, which was developed in 1947 by Joseph Kleiner.
In phlebotomy
Phlebotomy
Phlebotomy is the process of making an incision in a vein.It is associated with the following concepts:* Venipuncture, the practice of collecting venous blood samples* The main practice of a phlebotomist, an individual trained to draw blood...
the word “vacutainer” has come to be used as a genericized trademark
Genericized trademark
A genericized trademark is a trademark or brand name that has become the colloquial or generic description for, or synonymous with, a general class of product or service, rather than as an indicator of source or affiliation as intended by the trademark's holder...
to describe any vacuum-based blood collection vial, regardless of brand. Becton Dickinson
Becton Dickinson
Becton, Dickinson and Company , is an American medical technology company that manufactures and sells medical devices, instrument systems and reagents. Founded in 1897 and headquartered in Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, BD does business in nearly 50 countries and has 28,803 employees worldwide. In...
created the BD Vacutainer System and owns its trademark. The term “vacutainer system” has come to be used in medical practice to denote multiple-draw vacuum-based needles that are designed with blood stoppers regardless of brand.
Principles

Vein
In the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
is first punctured with the hypodermic needle
Hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle is a hollow needle commonly used with a syringe to inject substances into the body or extract fluids from it...
which is carried in a translucent plastic holder. The needle is double ended, the second shorter needle being shrouded for safety by the holder. When a Vacutainer test tube is pushed down into the holder, its rubber
Rubber
Natural rubber, also called India rubber or caoutchouc, is an elastomer that was originally derived from latex, a milky colloid produced by some plants. The plants would be ‘tapped’, that is, an incision made into the bark of the tree and the sticky, milk colored latex sap collected and refined...
cap is pierced by the second needle and the pressure difference between the blood volume and the vacuum in the tube forces blood through the needle and into the tube. The filled tube is then removed and another can be inserted and filled the same way. It is important to remove the tube before withdrawing the needle, as there may still be some suction left, causing pain upon withdrawal.
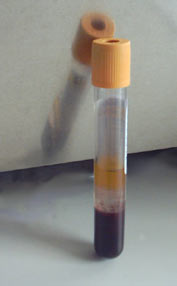
The test tubes are covered with a color-coded plastic cap. They often include additives that mix with the blood when collected (see below), and the colour of the tube's plastic cap indicates which additives that tube contains.
The plastic caps are opaque for tubes with a normal vacuum. Translucent-topped tubes contain a weaker vacuum in the same sized tube, and will obtain less blood. The weaker suction makes them more suitable for smaller sized veins, because the standardised suction of the tubes may cause the veins of elderly people or those with delicate veins, to collapse. In this case a syringe
Syringe
A syringe is a simple pump consisting of a plunger that fits tightly in a tube. The plunger can be pulled and pushed along inside a cylindrical tube , allowing the syringe to take in and expel a liquid or gas through an orifice at the open end of the tube...
should be used instead.
Contents of tubes
Medical laboratory
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are done on clinical specimens in order to get information about the health of a patient as pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease.-Departments:...
. Using the wrong tube may therefore make the blood sample unusable.
The substances may include anticoagulant
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents coagulation of blood. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used in vivo as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis...
s (EDTA
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, widely abbreviated as EDTA , is a polyamino carboxylic acid and a colourless, water-soluble solid. Its conjugate base is named ethylenediaminetetraacetate. It is widely used to dissolve limescale. Its usefulness arises because of its role as a hexadentate ligand...
, sodium citrate
Sodium citrate
Trisodium citrate has the chemical formula of Na3C6H5O7. It is sometimes referred to simply as sodium citrate, though sodium citrate can refer to any of the three sodium salts of citric acid. It possesses a saline, mildly tart flavor. For this reason, citrates of certain alkaline and alkaline earth...
, heparin
Heparin
Heparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule...
) or a gel with intermediate density between blood cell
Blood cell
A blood cell, also called a hematocyte, is a cell normally found in blood. In mammals, these fall into three general categories:* red blood cells — Erythrocytes* white blood cells — Leukocytes* platelets — Thrombocytes...
s and serum
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
. Additionally, some tubes contain substances that preserve certain chemicals or substances within the blood, such as glucose. When the tube is centrifuge
Centrifuge
A centrifuge is a piece of equipment, generally driven by an electric motor , that puts an object in rotation around a fixed axis, applying a force perpendicular to the axis...
d, the blood cells sink to the bottom of the tube, are covered by a layer of the gel, and the serum
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
is left on top. The gel enables the tube to be tipped upside-down and transported without the blood cells remixing with the serum. When a tube that does not contain a clotting agent is centrifuged, the clear liquid is plasma, which contains platelets.
The meaning of the different colors are standardized across manufacturers.
The order of draw refers to the sequence in which these tubes should be filled. The needle which pierces the tubes can carry additives from one tube into the next, and so the sequence is standardized so that any cross-contamination of additives will not affect laboratory results.
Containers containing coagulants
- Gold or 'Tiger' Red/Black top: Clot activator and gel for serum separation
- Red top PLASTIC tubes: Contains a clot activator and is used when serum is needed
- Orange or Grey/Yellow 'Tiger' Top: Contain Thrombin, a rapid clot activator, for STAT serum testing
Containers containing anticoagulants
- Green - Contains Sodium Heparin or Lithium Heparin used for plasma determinations in clinical chemistry (e.g. ureaUreaUrea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
and electrolyteElectrolyteIn chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
determination). - Light Green or Green/Gray 'Tiger': For plasma determinations.
- Purple or lavender - contains EDTAEDTAEthylenediaminetetraacetic acid, widely abbreviated as EDTA , is a polyamino carboxylic acid and a colourless, water-soluble solid. Its conjugate base is named ethylenediaminetetraacetate. It is widely used to dissolve limescale. Its usefulness arises because of its role as a hexadentate ligand...
(the potassium salt, or K2EDTA). This is a strong anticoagulant and these tubes are usually used for full blood counts (CBC) and blood filmBlood filmA blood film or peripheral blood smear is a thin layer of blood smeared on a microscope slide and then stained in such a way to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically...
s. Lavender top tubes are generally used when whole blood is needed for analysis. Can also be used for some blood bank procedures such as blood type and screen, but other blood bank procedures, such as crossmatches must be in a pink tube in most facilities. - Grey - These tubes contain fluorideFluorideFluoride is the anion F−, the reduced form of fluorine when as an ion and when bonded to another element. Both organofluorine compounds and inorganic fluorine containing compounds are called fluorides. Fluoride, like other halides, is a monovalent ion . Its compounds often have properties that are...
and oxalateOxalateOxalate , is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written 22−. Either name is often used for derivatives, such as disodium oxalate, 2C2O42−, or an ester of oxalic acid Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate), is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written (COO)22−. Either...
. Fluoride prevents enzymes in the blood from working, so a substrate such as glucoseGlucoseGlucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
will not be gradually used up during storage. Oxalate is an anticoagulant. - Light blue - Contain a measured amount of citrateCitrateA citrate can refer either to the conjugate base of citric acid, , or to the esters of citric acid. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate.-Other citric acid ions:...
. Citrate is a reversible anticoagulant, and these tubes are used for coagulationCoagulationCoagulation is a complex process by which blood forms clots. It is an important part of hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, wherein a damaged blood vessel wall is covered by a platelet and fibrin-containing clot to stop bleeding and begin repair of the damaged vessel...
assays. Because the liquid citrate dilutes the blood, it is important the tube is full so the dilution is properly accounted for. - Dark Blue - Contains sodium heparinHeparinHeparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule...
, an anticoagulant. Also can contain EDTA as an additive or have no additive. These tubes are used for trace metal analysis. - Pink - Similar to purple tubes (both contain EDTA) these are used for blood banking.
- Black - used for ESR also known as Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate or "sed rate." goes to hematology department.
Other
- Red (glass)- Contains no additives. Tests for antibodies and drugs often require these.
- Light yellow - Contains sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS). Used for blood culture specimens or acid-citrate-dextroseAcid-citrate-dextroseAcid Citrate Dextrose Solution is a solution of citric acid, sodium citrate and dextrose in water. It is mainly used as an anticoagulant to preserve blood specimens required for tissue typing, it is also used during procedures such as plasmapheresis instead of heparin...
(ACD), used for blood bank studies, HLA phenotyping, and parental testing. - Tan (glass or plastic) - Contains either sodium heparin (glass) or K2EDTA (plastic). Used for lead determinations. These tubes are certified to contain no lead.
History
It was developed in 1947 by Joseph Kleiner, and is currently marketed by Becton, Dickinson and company.The plastic version, known as Vacutainer PLUS, was developed at Becton Dickinson Research Center, RTP, NC in 1991-1993, by co-inventors E. Vogler, D. Montgomery and G. Harper amongst others of the Surface Science Group as US patents 5344611, 5326535, 5320812, 5257633 and 5246666.

