
Voronoi Deformation Density
Encyclopedia
Voronoi Deformation Density (VDD) is a method employed in computational chemistry
to compute the atomic charge
distribution of a molecule
in order to provide information about its chemical properties. The method is based on the partitioning of space into non-overlapping atomic areas modelled as Voronoi cells
and then computing the deformation density within those cells (i.e. the extent to which electron density
differs from that of an unbonded atom).
The VDD charge QA of atom A is computed as the (numerical) integral of the deformation density ∆ρ(r) = ρ(r) – ΣBρB(r) associated with the formation of the molecule from its atoms over the volume of the Voronoi cell of atom A:
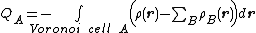
The Voronoi cell of atom A is defined as the compartment of space bounded by the bond midplanes on and perpendicular to all bond axes between nucleus A and its neighboring nuclei (cf. the Wigner-Seitz cell
s in crystals). The Voronoi cell of atom A is therefore the region of space closer to nucleus A than to any other nucleus. Furthermore, ρ(r) is the electron density of the molecule and ΣBρB(r) the superposition of atomic densities ρB of a fictitious promolecule without chemical interactions that is associated with the situation in which all atoms are neutral.
Note that an atomic charge
is not a physical observable
. Nevertheless, it has been proven a useful means to compactly describe and analyze the electron density distribution in a molecule
, which is important for understanding the behavior of the latter. In this connection, it is an asset of VDD atomic charges QA that they have a rather straightforward and transparent interpretation. Instead of measuring the amount of charge associated with a particular atom A, QA directly monitors how much charge flows, due to chemical interactions, out of (QA > 0) or into (QA < 0) the Voronoi cell of atom A, that is, the region of space that is closer to nucleus A than to any other nucleus.
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
to compute the atomic charge
Partial charge
A partial charge is a charge with an absolute value of less than one elementary charge unit .-Partial atomic charges:...
distribution of a molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
in order to provide information about its chemical properties. The method is based on the partitioning of space into non-overlapping atomic areas modelled as Voronoi cells
Voronoi diagram
In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a special kind of decomposition of a given space, e.g., a metric space, determined by distances to a specified family of objects in the space...
and then computing the deformation density within those cells (i.e. the extent to which electron density
Electron density
Electron density is the measure of the probability of an electron being present at a specific location.In molecules, regions of electron density are usually found around the atom, and its bonds...
differs from that of an unbonded atom).
The VDD charge QA of atom A is computed as the (numerical) integral of the deformation density ∆ρ(r) = ρ(r) – ΣBρB(r) associated with the formation of the molecule from its atoms over the volume of the Voronoi cell of atom A:
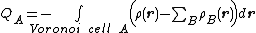
The Voronoi cell of atom A is defined as the compartment of space bounded by the bond midplanes on and perpendicular to all bond axes between nucleus A and its neighboring nuclei (cf. the Wigner-Seitz cell
Wigner-Seitz cell
The Wigner–Seitz cell, named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz, is a type of Voronoi cell used in the study of crystalline material in solid-state physics....
s in crystals). The Voronoi cell of atom A is therefore the region of space closer to nucleus A than to any other nucleus. Furthermore, ρ(r) is the electron density of the molecule and ΣBρB(r) the superposition of atomic densities ρB of a fictitious promolecule without chemical interactions that is associated with the situation in which all atoms are neutral.
Note that an atomic charge
Partial charge
A partial charge is a charge with an absolute value of less than one elementary charge unit .-Partial atomic charges:...
is not a physical observable
Observable
In physics, particularly in quantum physics, a system observable is a property of the system state that can be determined by some sequence of physical operations. For example, these operations might involve submitting the system to various electromagnetic fields and eventually reading a value off...
. Nevertheless, it has been proven a useful means to compactly describe and analyze the electron density distribution in a molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
, which is important for understanding the behavior of the latter. In this connection, it is an asset of VDD atomic charges QA that they have a rather straightforward and transparent interpretation. Instead of measuring the amount of charge associated with a particular atom A, QA directly monitors how much charge flows, due to chemical interactions, out of (QA > 0) or into (QA < 0) the Voronoi cell of atom A, that is, the region of space that is closer to nucleus A than to any other nucleus.

