
Water balance
Encyclopedia
In hydrology
, a water balance equation
can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of a system. A system can be one of several hydrological domains, such as a column of soil
or a drainage basin
.
Water balance can also refer to the ways in which an organism maintains water in dry or hot conditions. It is often discussed in reference to plants or arthropods, which have a variety of water retention mechanisms, including a lipid waxy coating that has limited permeability.

where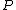 is precipitation
is precipitation
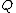 is runoff
is runoff
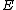 is evapotranspiration
is evapotranspiration
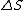 is the change in storage (in soil or the bedrock)
is the change in storage (in soil or the bedrock)
Extensive water balances are discussed in agricultural hydrology
.
A water balance can be used to help manage water supply and predict where there may be water shortages. It is also used in irrigation
, runoff assessment (e.g. through the RainOff model ), flood control
and pollution control. Further it is used in the design of subsurface drainage systems
which may be horizontal (i.e. using pipes, tile drains
or ditches) or vertical (drainage by wells). To estimate the drainage requirement, the use of an hydrogeological
water balance and a groundwater model
(e.g. SahysMod
) may be instrumental.
The water balance can be illustrated using a water balance graph which plots levels of precipitation
and evapotranspiration
often on a monthly scale.
Several monthly water balance models had been developed for several conditions and purposes. Monthly water balance models had been studied since the 1940s.
Hydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
, a water balance equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of a system. A system can be one of several hydrological domains, such as a column of soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
or a drainage basin
Drainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
.
Water balance can also refer to the ways in which an organism maintains water in dry or hot conditions. It is often discussed in reference to plants or arthropods, which have a variety of water retention mechanisms, including a lipid waxy coating that has limited permeability.
Equation
A general water balance equation is:
where
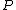 is precipitation
is precipitationPrecipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
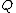 is runoff
is runoffSurface runoff
Surface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
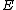 is evapotranspiration
is evapotranspirationEvapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration is a term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies...
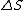 is the change in storage (in soil or the bedrock)
is the change in storage (in soil or the bedrock)Extensive water balances are discussed in agricultural hydrology
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
.
A water balance can be used to help manage water supply and predict where there may be water shortages. It is also used in irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, runoff assessment (e.g. through the RainOff model ), flood control
Flood control
In communications, flood control is a feature of many communication protocols designed to prevent overwhelming of a destination receiver. Such controls can be implemented either in software or in hardware, and will often request that the message be resent after the receiver has finished...
and pollution control. Further it is used in the design of subsurface drainage systems
Drainage system (Agriculture)
An agricultural drainage system is a system by which the water level on or in the soil is controlled to enhance agricultural crop production.-Classification:Figure 1 classifies the various types of drainage systems...
which may be horizontal (i.e. using pipes, tile drains
Tile drainage
Tile drainage is an agriculture practice that removes excess water from soil subsurface. Whereas irrigation is the practice of adding additional water when the soil is naturally too dry, drainage brings soil moisture levels down for optimal crop growth...
or ditches) or vertical (drainage by wells). To estimate the drainage requirement, the use of an hydrogeological
Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust, . The term geohydrology is often used interchangeably...
water balance and a groundwater model
Groundwater model
Groundwater models are computer models of groundwater flow systems, and are used by hydrogeologists. Groundwater models are used to simulate and predict aquifer conditions.-Characteristics:...
(e.g. SahysMod
SahysMod
SahysMod is a computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain discharge in irrigated agricultural lands, using different hydrogeologic and aquifer conditions, varying water management options, including...
) may be instrumental.
The water balance can be illustrated using a water balance graph which plots levels of precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
and evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration is a term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies...
often on a monthly scale.
Several monthly water balance models had been developed for several conditions and purposes. Monthly water balance models had been studied since the 1940s.
Models
Several diagnostic measures in hydrology can be used to select and evaluate the performance of water balance modelsApplications
- Evaluate the components of the hydrologic cycle
- SnowmeltSnowmeltIn hydrology, snowmelt is surface runoff produced from melting snow. It can also be used to describe the period or season during which such runoff is produced. Water produced by snowmelt is an important part of the annual water cycle in many parts of the world, in some cases contributing high...
simulationSimulationSimulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system.... - Climate changeClimate changeClimate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
impact assessment - FlowFluid dynamicsIn physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
forecasting and project design - Assess agricultural water managementHydrology (agriculture)Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
Types
- Models using precipitationPrecipitation (meteorology)In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
(rainfall) as input - Models using rainfall and temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
as input - Models using rainfall and potential evaporationPotential evaporationPotential evaporation or potential evapotranspiration is defined as the amount of evaporation that would occur if a sufficient water source were available. If the actual evapotranspiration is considered the net result of atmospheric demand for moisture from a surface and the ability of the...
as input - Models using daily input data
External links
- Article on water and salt balances: http://www.waterlog.info/pdf/balances.pdf

