
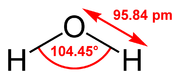
Water model
Encyclopedia
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
, classical water models are used for the simulation of water cluster
Water cluster
In chemistry a water cluster is a discrete hydrogen bonded assembly or cluster of molecules of water. These clusters have been found experimentally or predicted in silico in various forms of water; in ice, in crystal lattices and in bulk liquid water, the simplest one being the water dimer 2...
s, liquid water, and aqueous solutions with explicit solvent. These models use the approximations of molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses Newtonian mechanics to model molecular systems. The potential energy of all systems in molecular mechanics is calculated using force fields...
. Many different models have been proposed; they can be classified by the number of points used to define the model (atoms plus dummy sites), whether the structure is rigid or flexible, and whether the model includes polarization effects.
An alternative to the explicit water models is to use an implicit solvation
Implicit solvation
Implicit solvation is a method of representing solvent as a continuous medium instead of individual “explicit” solvent molecules most often used in molecular dynamics simulations and in other applications of molecular mechanics...
model, also known as a continuum model, an example of which would be the COSMO Solvation Model
COSMO Solvation Model
COSMO is the abbreviation for "COnductor-like Screening MOdel", a calculation method for determining the electrostatic interaction of a molecule with a solvent....
.
Simple water models
The simplest water models treat the water molecule as rigid and rely only on non-bonded interactionsIntermolecular force
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles: atoms, molecules or ions. They are weak compared to the intramolecular forces, the forces which keep a molecule together...
. The electrostatic interaction is modeled using Coulomb's law
Coulomb's law
Coulomb's law or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics describing the electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles. It was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb and was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism...
and the dispersion and repulsion forces using the Lennard-Jones potential
Lennard-Jones potential
The Lennard-Jones potential is a mathematically simple model that approximates the interaction between a pair of neutral atoms or molecules. A form of the potential was first proposed in 1924 by John Lennard-Jones...
. The potential for models such as TIP3P and TIP4P is represented by
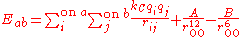
where kC, the electrostatic constant, has a value of 332.1 Å·kcal/mol in the units commonly used in molecular modeling; qi are the partial charge
Partial charge
A partial charge is a charge with an absolute value of less than one elementary charge unit .-Partial atomic charges:...
s relative to the charge of the electron; rij is the distance between two atoms or charged sites; and A and B are the Lennard-Jones parameters. The charged sites may be on the atoms or on dummy sites (such as lone pairs). In most water models, the Lennard-Jones term applies only to the interaction between the oxygen atoms.
The figure below shows the general shape of the 3- to 6-site water models. The exact geometric parameters (the OH distance and the HOH angle) vary depending on the model.
2-site
A 2-site model of water based on the familiar three-site SPC model (see below) has been shown to predict the dielectric properties of water using site-renormalized molecular fluid theory.3-site
Three-site models have three interaction sites, corresponding to the three atoms of the water molecule. Each atom gets assigned a point charge, and the oxygen atom also gets the Lennard-Jones parameters. The 3-site models are very popular for molecular dynamicsMolecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
simulations because of their simplicity and computational efficiency. Most models use a rigid geometry matching the known geometry of the water molecule. An exception is the SPC model, which assumes an ideal tetrahedral shape (HOH angle of 109.47°) instead of the observed angle of 104.5°.
The table below lists the parameters for some 3-site models.
| TIPS | SPC | TIP3P | SPC/E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r(OH), Å | 0.9572 | 1.0 | 0.9572 | 1.0 |
| HOH, deg | 104.52 | 109.47 | 104.52 | 109.47 |
| A × 10−3, kcal Å12/mol | 580.0 | 629.4 | 582.0 | 629.4 |
| B, kcal Å6/mol | 525.0 | 625.5 | 595.0 | 625.5 |
| q(O) | −0.80 | −0.82 | −0.834 | −0.8476 |
| q(H) | +0.40 | +0.41 | +0.417 | +0.4238 |
The SPC/E model adds an average polarization correction to the potential energy function:
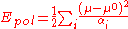
where μ is the dipole of the effectively polarized water molecule (2.35 D for the SPC/E model), μ0 is the dipole moment of an isolated water molecule (1.85 D from experiment), and αi is an isotropic polarizability constant, with a value of 1.608 × 10−40 F m. Since the charges in the model are constant, this correction just results in adding 1.25 kcal/mol (5.22 kJ/mol) to the total energy. The SPC/E model results in a better density and diffusion constant than the SPC model.
The TIP3P model implemented in the CHARMM
CHARMM
CHARMM is the name of a widely used set of force fields for molecular dynamics as well as the name for the molecular dynamics simulation and analysis package associated with them...
force field is a slightly modified version of the original. The difference lies in the Lennard-Jones parameters: unlike TIP3P, the CHARMM version of the model places Lennard-Jones parameters on the hydrogen atoms too, in addition to the one on oxygen. The charges are not modified.
Other models:
- Fergunson (flex. SPC)
- Toukan and Rahman (Flexible SPCFlexible SPC water modelThe Flexible Simple Point Charge water model is a re-parametrization of the three-site SPC water model. The SPC model is rigid, whilst the flexible SPC model is flexible. In the model of Toukan and Rahman, the O-H stretching is made anharmonic and thus the dynamical behavior is well described...
) - CVFF (flex.)
4-site
The 4-site models place the negative charge on a dummy atom (labeled M in the figure) placed near the oxygen along the bisectorBisection
In geometry, bisection is the division of something into two equal or congruent parts, usually by a line, which is then called a bisector. The most often considered types of bisectors are the segment bisector and the angle bisector In geometry, bisection is the division of something into two equal...
of the HOH angle. This improves the electrostatic distribution around the water molecule. The first model to use this approach was the Bernal-Fowler model published in 1933, which may also be the earliest water model. However, the BF model doesn't reproduce well the bulk properties of water, such as density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
and heat of vaporization, and is therefore only of historical interest. This is a consequence of the parameterization method; newer models, developed after modern computers became available, were parameterized by running Metropolis Monte Carlo or molecular dynamics simulations and adjusting the parameters until the bulk properties are reproduced well enough.
The TIP4P model, first published in 1983, is widely implemented in computational chemistry software packages and often used for the simulation of biomolecular systems. There have been subsequent reparameterizations of the TIP4P model for specific uses: the TIP4P-Ew model, for use with Ewald summation methods; the TIP4P/Ice, for simulation of solid water ice; and TIP4P/2005, a general parameterization for simulating the entire phase diagram
Phase diagram
A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions at which thermodynamically distinct phases can occur at equilibrium...
of water.
| BF | TIPS2 | TIP4P | TIP4P-Ew | TIP4P/Ice | TIP4P/2005 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r(OH), Å | 0.96 | 0.9572 | 0.9572 | 0.9572 | 0.9572 | 0.9572 |
| HOH, deg | 105.7 | 104.52 | 104.52 | 104.52 | 104.52 | 104.52 |
| r(OM), Å | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.125 | 0.1577 | 0.1546 |
| A × 10−3, kcal Å12/mol | 560.4 | 695.0 | 600.0 | 656.1 | 857.9 | 731.3 |
| B, kcal Å6/mol | 837.0 | 600.0 | 610.0 | 653.5 | 850.5 | 736.0 |
| q(M) | −0.98 | −1.07 | −1.04 | −1.04844 | −1.1794 | −1.1128 |
| q(H) | +0.49 | +0.535 | +0.52 | +0.52422 | +0.5897 | +0.5564 |
Others:
- TIP4PF (flexible)
5-site
The 5-site models place the negative charge on dummy atoms (labeled L) representing the lone pairLone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
s of the oxygen atom, with a tetrahedral-like geometry. An early model of these types was the BNS model of Ben-Naim and Stillinger, proposed in 1971, soon succeeded by the ST2 model of Stillinger and Rahman in 1974. Mainly due to their higher computational cost, five-site models were not developed much until 2000, when the TIP5P model of Mahoney and Jorgensen was published. When compared with earlier models, the TIP5P model results in improvements in the geometry for the water dimer
Water dimer
The water dimer consists of two water molecules loosely bound by a hydrogen bond. It is the smallest water cluster. Because it is the simplest model system for studying hydrogen bonding in water, it has been the target of so many theoretical studies that it has been called "a theoretical Guinea...
, a more "tetrahedral" water structure that better reproduces the experimental radial distribution function
Radial distribution function
In statistical mechanics, a radial distribution function , g, describes how the atomic density varies as a function of the distance from one particular atom....
s from neutron diffraction
Neutron diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material: A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of...
, and the temperature of maximum density of water. The TIP5P-E model is a reparameterization of TIP5P for use with Ewald sums.
| BNS | ST2 | TIP5P | TIP5P-E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r(OH), Å | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9572 | 0.9572 |
| HOH, deg | 109.47 | 109.47 | 104.52 | 104.52 |
| r(OL), Å | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| LOL, deg | 109.47 | 109.47 | 109.47 | 109.47 |
| A × 10−3, kcal Å12/mol | 77.4 | 238.7 | 544.5 | 554.3 |
| B, kcal Å6/mol | 153.8 | 268.9 | 590.3 | 628.2 |
| q(L) | −0.19562 | −0.2357 | −0.241 | −0.241 |
| q(H) | +0.19562 | +0.2357 | +0.241 | +0.241 |
| RL, Å | 2.0379 | 2.0160 | ||
| RU, Å | 3.1877 | 3.1287 |
Note, however, that the BNS and ST2 models do not use Coulomb's law directly for the electrostatic terms, but a modified version that is scaled down at short distances by multiplying it by the switching function S(r):
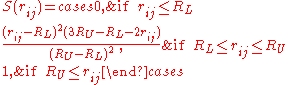
Therefore the RL and RU parameters only apply to BNS and ST2.
6-site
A 6-site model that combines all the sites of the 4- and 5-site models was developed by Nada and van der Eerden. Originally designed to study water/ice systems, however has a very high melting temperatureOther
- The effect of explicit solute model on solute behavior in bimolecular simulations has been also extensively studied. It was shown that explicit water models affected the specific solvation and dynamics of unfolded peptides while the conformational behavior and flexibility of folded peptides remained intact.
- MB model. A more abstract model resembling the Mercedes-BenzMercedes-BenzMercedes-Benz is a German manufacturer of automobiles, buses, coaches, and trucks. Mercedes-Benz is a division of its parent company, Daimler AG...
logo that reproduces some features of water in two-dimensional systems. It is not used as such for simulations of "real" (i.e., three-dimensional) systems, but it is useful for qualitative studies and for educational purposes. - Coarse-grained models. One- and two-site models of water have also been developed. In coarse grain models, each site can represent several water molecules.
Computational cost
The computational cost of a water simulation increases with the number of interaction sites in the water model. The CPU time is approximately proportional to the number of interatomic distances that need to be computed. For the 3-site model, 9 distances are required for each pair of water molecules (every atom of one molecule against every atom of the other molecule, or 3 × 3). For the 4-site model, 10 distances are required (every charged site with every charged site, plus the O-O interaction, or 3 × 3 + 1). For the 5-site model, 17 distances are required (4 × 4 + 1). Finally, for the 6-site model, 26 distances are required (5 × 5 + 1).When using rigid water models in molecular dynamics, there is an additional cost associated with keeping the structure constrained, using constraint algorithm
Constraint algorithm
In mechanics, a constraint algorithm is a method for satisfying constraints for bodies that obey Newton's equations of motion. There are three basic approaches to satisfying such constraints: choosing novel unconstrained coordinates , introducing explicit constraint forces, and minimizing...
s (although with bond lengths constrained it is often possible to increase the time step).


