
Weather testing of polymers
Encyclopedia
Weather testing of polymers is the controlled polymer degradation
and polymer
coating
degradation under lab or natural conditions.
Just like erosion of rocks, natural phenomena can cause degradation in polymer systems. The elements of most concern to polymers are Ultraviolet radiation, moisture and humidity, high temperatures and temperature fluctuations. Polymers are used in every day life, so it is important for scientists and polymer producers to understand durability and expected lifespan of polymer products. Paint
, a common polymer coating, is used to change the colour, change the reflectance (gloss
), as well as forming a protective coating. The structure of paint consists of pigments in a matrix of resin
.
A typical example is painted steel
roofing and walling products, which are constantly exposed to harmful weathering
conditions.
Colour is determined by light-reflecting chemical particles, pigments, in the paint. These particles can have very different physical sizes, as shown in the diagram in figure 1.2. In this example, the black pigments are the small black dots; red pigments are larger spheres, while the yellow pigments are acicular
. This combination of pigments produces the original brown colour. The upper diagram has had no weathering, and the surface is still smooth and undamaged. The lower diagram shows the painted surface after weathering has occurred. The surface has eroded with significant loss of the black and red pigments from the surface layer. The pitted surface scatters light, therefore reducing the gloss and creating the chalky affect. The larger acicular yellow pigments are more difficult to remove, resulting in a colour change towards a more yellowy appearance. Weather testing was paramount in discovering this mechanism. Pigment composition has recently been modified to help minimise this effect.
 Natural Weathering involves placing samples on inclined racks oriented at the sun
Natural Weathering involves placing samples on inclined racks oriented at the sun
. In Northern hemisphere
these racks are at an angle of 45 degrees in a southerly direction. In Southern hemisphere
these racks are at an angle of 45 degrees in a northerly direction.
This angle ensures exposure to the full spectrum
of solar radiation, from infrared
to Ultra violet.
Sites used for this type of testing are usually in tropical areas as high temperature, UV intensity and humidity are needed for maximum degradation.
Florida
, for example is the world standard as it possesses all three characteristics.
Despite the harsh conditions, testing takes several years before significant results are achieved.
Such devices, which are known by trade names Acuvex, Q-Trac, and Emma, are typically used in Arizona and other desert locations with a high percentage of sunlight and low relative humidity. The Arizona
desert
typically provides 180 kilo-Langley per year.
These exposures can be used with water spray to simulate a more humid climate. In addition, water containing up to 5% sodium chloride can be sprayed to create the conditions for corrosion to occur.
It is typical for this to accelerate weathering by a factor 5, in comparison to weathering in Florida.
An Atrac in Townsville Australia, uses follow the sun technology in which the samples are rotated so that they always face the sun. In 17 months this produced the equivalent of 2 years of weathering.
A variety of environmental chamber
s are also used in conjunction with industry standards.
or Electric arc
(carbon) to simulate/accelerate the effect of sunlight. Besides fluorescent lamps where the short UV are converted into visible light with fluorescent coatings, xenon, mercury, metal halide or carbon arc lamps have to be used with a careful elimination of shorter wavelenghs usually by adding a borosilicate filter.
 QUV Accelerated Weathering testing is a laboratory simulation of the damaging forces of weather for the purposes of predicting the relative durability of materials exposed to outdoor environments. Racks of samples are placed in the QUV chamber. Rain and dew systems are simulated by pressurized spray and condensation systems while damaging effects of sunlight are simulated by fluorescent UV lamps. The exposure temperature is automatically controlled. Cyclical weather conditions can also be simulated.
QUV Accelerated Weathering testing is a laboratory simulation of the damaging forces of weather for the purposes of predicting the relative durability of materials exposed to outdoor environments. Racks of samples are placed in the QUV chamber. Rain and dew systems are simulated by pressurized spray and condensation systems while damaging effects of sunlight are simulated by fluorescent UV lamps. The exposure temperature is automatically controlled. Cyclical weather conditions can also be simulated.
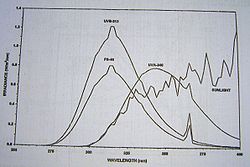
Three types of fluorescent lamp
s are commonly used for QUV. Two of these are of the type UVB (medium wavelength UV), while the third is UVA (longer wavelength UV similar to black light). All these lamps produce mostly UV as opposed to visible or infrared light. The lamp used, and therefore the wavelength of UV light produced will affect how realistic the final degradation results will be. In reality, natural sunlight contains radiation from many areas of the spectrum. This includes both UVA and UVB, however the UVB radiation is at the lowest end of natural light and is less predominant than UVA. Since it has a shorter wavelength, it also has a higher energy. This makes UVB more damaging not only because it increase chemical reaction kinetics, but also because it can initiate chemical reactions to occur which would not normally be possible under natural condition. For this reason, testing using only UVB lamps have been shown to have poor correlation relative to natural weather testing of the same samples.
 The SEPAP 12-24 :fr:Photovieillissement accéléré en SEPAP has been designed, in the late seventies, by the scientists of University Blaise Pascal http://www.univ-bpclermont.fr/LABOS/lpmm,http://www.cnep-ubp.com specialists of molecular photochemistry, to provoke in accelerated controlled conditions the same chemical evolutions as those occurring at long term under the permanent physicochemical stresses of the environment, i.e. UV - heat – atmospheric oxygen and water as an aggravating agent.
The SEPAP 12-24 :fr:Photovieillissement accéléré en SEPAP has been designed, in the late seventies, by the scientists of University Blaise Pascal http://www.univ-bpclermont.fr/LABOS/lpmm,http://www.cnep-ubp.com specialists of molecular photochemistry, to provoke in accelerated controlled conditions the same chemical evolutions as those occurring at long term under the permanent physicochemical stresses of the environment, i.e. UV - heat – atmospheric oxygen and water as an aggravating agent.
That ageing chamber based on fundamental concepts differs widely from the ageing units based on the simulation of environmental stresses in non-accelerated conditions like in some xenon based instruments.
In SEPAP 12-24 :
The durability control of polymeric formulations through the SEPAP 12-24 testing is currently required by some French and European standards and by many industrial companies (see list on http://www.cnep-ubp.com)
The (French) National Center for Photoprotection Assessment (CNEP) is currently using SEPAP for industrial applications and is more generally involved in polymer and polymer failures analysis (National Centre for the Evaluation of Photoprotection) for plastic industries.
Polymer degradation
Polymer degradation is a change in the properties—tensile strength, colour, shape, etc.—of a polymer or polymer-based product under the influence of one or more environmental factors such as heat, light or chemicals such as acids, alkalis and some salts...
and polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
coating
Coating
Coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. In many cases coatings are applied to improve surface properties of the substrate, such as appearance, adhesion, wetability, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and scratch resistance...
degradation under lab or natural conditions.
Just like erosion of rocks, natural phenomena can cause degradation in polymer systems. The elements of most concern to polymers are Ultraviolet radiation, moisture and humidity, high temperatures and temperature fluctuations. Polymers are used in every day life, so it is important for scientists and polymer producers to understand durability and expected lifespan of polymer products. Paint
Paint
Paint is any liquid, liquefiable, or mastic composition which after application to a substrate in a thin layer is converted to an opaque solid film. One may also consider the digital mimicry thereof...
, a common polymer coating, is used to change the colour, change the reflectance (gloss
Gloss
A gloss is a brief notation of the meaning of a word or wording in a text. It may be in the language of the text, or in the reader's language if that is different....
), as well as forming a protective coating. The structure of paint consists of pigments in a matrix of resin
Resin
Resin in the most specific use of the term is a hydrocarbon secretion of many plants, particularly coniferous trees. Resins are valued for their chemical properties and associated uses, such as the production of varnishes, adhesives, and food glazing agents; as an important source of raw materials...
.
A typical example is painted steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
roofing and walling products, which are constantly exposed to harmful weathering
Weathering
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soils and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters...
conditions.
Typical result of polymer surface after weathering
Figure 1.1 shows typical weathering results of a sample of painted steel; the paint on the steel is an example of a common polymer system. The sample on the left had been placed in an outdoor exposure rack, and weathered for a total of 6 years. It can be seen that the sample has a chalky appearance and has undergone a colour change in comparison to the unweathered sample on the right.Colour is determined by light-reflecting chemical particles, pigments, in the paint. These particles can have very different physical sizes, as shown in the diagram in figure 1.2. In this example, the black pigments are the small black dots; red pigments are larger spheres, while the yellow pigments are acicular
Crystal habit
Crystal habit is an overall description of the visible external shape of a mineral. This description can apply to an individual crystal or an assembly of crystals or aggregates....
. This combination of pigments produces the original brown colour. The upper diagram has had no weathering, and the surface is still smooth and undamaged. The lower diagram shows the painted surface after weathering has occurred. The surface has eroded with significant loss of the black and red pigments from the surface layer. The pitted surface scatters light, therefore reducing the gloss and creating the chalky affect. The larger acicular yellow pigments are more difficult to remove, resulting in a colour change towards a more yellowy appearance. Weather testing was paramount in discovering this mechanism. Pigment composition has recently been modified to help minimise this effect.
Types of weather testing
There are 3 main testing techniques; Natural Weathering, Accelerated Natural Weathering and Artificial Weathering. Because natural weathering can be a slow process, each of the techniques is a tradeoff between realistic weathering results and the duration of testing before results are collated.Natural weathering

Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. In Northern hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
these racks are at an angle of 45 degrees in a southerly direction. In Southern hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
these racks are at an angle of 45 degrees in a northerly direction.
This angle ensures exposure to the full spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of solar radiation, from infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
to Ultra violet.
Sites used for this type of testing are usually in tropical areas as high temperature, UV intensity and humidity are needed for maximum degradation.
Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, for example is the world standard as it possesses all three characteristics.
Despite the harsh conditions, testing takes several years before significant results are achieved.
Accelerated natural weathering
To speed up the weathering process while still using natural weather conditions, accelerated natural testing can be applied. One method uses mirrors to amplify available UV radiation. A device known as a Fresnel-reflecting concentrator uses photo-receptor cells to maintain alignment with the sun and 10 mirrors to reflect sunlight onto the test specimens. With the latest technology for ultra-accelerated exposure testing it’s possible to simulate 63 years of UV radiation exposure in a single year.Such devices, which are known by trade names Acuvex, Q-Trac, and Emma, are typically used in Arizona and other desert locations with a high percentage of sunlight and low relative humidity. The Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
typically provides 180 kilo-Langley per year.
These exposures can be used with water spray to simulate a more humid climate. In addition, water containing up to 5% sodium chloride can be sprayed to create the conditions for corrosion to occur.
It is typical for this to accelerate weathering by a factor 5, in comparison to weathering in Florida.
An Atrac in Townsville Australia, uses follow the sun technology in which the samples are rotated so that they always face the sun. In 17 months this produced the equivalent of 2 years of weathering.
A variety of environmental chamber
Environmental chamber
An environmental chamber is an enclosure used to test the effects of specified environmental conditions on biological items, industrial products, materials, and electronic devices and components. Environmental chambers help evaluate product quality and reliability, and identify manufacturing flaws...
s are also used in conjunction with industry standards.
Artificial weathering
The weather testing process can be greatly accelerated through the use of specially designed weathering chambers. While this speeds up the time needed to get results, the conditions are not always representative of real world conditions. Most of the commercialized devices are using Gas-discharge lampGas-discharge lamp
Gas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electrical discharge through an ionized gas, i.e. a plasma. The character of the gas discharge critically depends on the frequency or modulation of the current: see the entry on a frequency classification...
or Electric arc
Electric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
(carbon) to simulate/accelerate the effect of sunlight. Besides fluorescent lamps where the short UV are converted into visible light with fluorescent coatings, xenon, mercury, metal halide or carbon arc lamps have to be used with a careful elimination of shorter wavelenghs usually by adding a borosilicate filter.
QUV

Three types of fluorescent lamp
Fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp or fluorescent tube is a gas-discharge lamp that uses electricity to excite mercury vapor. The excited mercury atoms produce short-wave ultraviolet light that then causes a phosphor to fluoresce, producing visible light. A fluorescent lamp converts electrical power into useful...
s are commonly used for QUV. Two of these are of the type UVB (medium wavelength UV), while the third is UVA (longer wavelength UV similar to black light). All these lamps produce mostly UV as opposed to visible or infrared light. The lamp used, and therefore the wavelength of UV light produced will affect how realistic the final degradation results will be. In reality, natural sunlight contains radiation from many areas of the spectrum. This includes both UVA and UVB, however the UVB radiation is at the lowest end of natural light and is less predominant than UVA. Since it has a shorter wavelength, it also has a higher energy. This makes UVB more damaging not only because it increase chemical reaction kinetics, but also because it can initiate chemical reactions to occur which would not normally be possible under natural condition. For this reason, testing using only UVB lamps have been shown to have poor correlation relative to natural weather testing of the same samples.
SEPAP

That ageing chamber based on fundamental concepts differs widely from the ageing units based on the simulation of environmental stresses in non-accelerated conditions like in some xenon based instruments.
In SEPAP 12-24 :
- the samples are rotating to insure an homogenous exposure ;
- the incident light is supplied by four medium-pressure Mercury-vapor lamps filtered by the borosilicate envelops of the lamps ; the incident light is not containing any radiations whose wavelength would be shorter than 300 nm. Although the spectral distribution is not simulating the solar light, the vibrational relaxations which occur from each excited states insure the absence of any wavelength effect under the mercury arc excitation, the light spectral distribution influencing only the rate of the photoreactions. That concept has been largely checked in the last 30 years ;
- since the photochemical activation (due to UV) and the thermal excitation cannot be deconjugated, it is essential to control the temperature of the samples surfaces directly exposed to light. A patented device insures that requirement in SEPAP 12-24 ;
- the water present in the polymeric blend exposed in SEPAP 12-24 is formed through the decomposition of the primary hydroperoxides ; no external water is brought on the exposed sample. The water effect on artificial ageing is handled either in SEPAP 12-24 H (when conjugated with the effects of UV, heat and oxygen), or through post-photochemical immersions in neutral water (in absence of conjugated effects') .
The durability control of polymeric formulations through the SEPAP 12-24 testing is currently required by some French and European standards and by many industrial companies (see list on http://www.cnep-ubp.com)
The (French) National Center for Photoprotection Assessment (CNEP) is currently using SEPAP for industrial applications and is more generally involved in polymer and polymer failures analysis (National Centre for the Evaluation of Photoprotection) for plastic industries.
See also
- Polymer degradationPolymer degradationPolymer degradation is a change in the properties—tensile strength, colour, shape, etc.—of a polymer or polymer-based product under the influence of one or more environmental factors such as heat, light or chemicals such as acids, alkalis and some salts...
- Factors of polymer weatheringFactors of polymer weatheringThe aging of natural and artificial polymeric materials is a natural phenomenon in metals, glass, minerals and other inorganic materials. The main environmental parameters influencing the degradation of polymeric materials is daylight combined with the effects of temperature, moisture and oxygen...
- UltravioletUltravioletUltraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
- UV degradationUV degradationMany natural and synthetic polymers are attacked by ultra-violet radiation and products made using these materials may crack or disintegrate . The problem is known as UV degradation, and is a common problem in products exposed to sunlight...
- Gas-discharge lampGas-discharge lampGas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electrical discharge through an ionized gas, i.e. a plasma. The character of the gas discharge critically depends on the frequency or modulation of the current: see the entry on a frequency classification...
- Electric arcElectric arcAn electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
- Fluorescent lamps
- Mercury-vapor lamps
- National Centre for the Evaluation of Photoprotection
- Photo-oxidation of polymersPhoto-oxidation of polymersPhoto-oxidation is the degradation of a polymer surface in the presence of oxygen or ozone. The effect is facilitated by radiant energy such as UV or artificial light. This process is the most significant factor in weathering of polymers. Photo-oxidation is a chemical change that reduces the...

