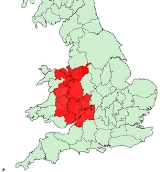
Welsh Marches
Encyclopedia
The Welsh Marches is a term which, in modern usage, denotes an imprecisely defined area along and around the border between England
and Wales
in the United Kingdom
. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods. The English terms Welsh March, The March of Wales, in Medieval Latin Marchia Walliae, were originally used in the Middle Ages
to denote a more precisely defined territory, the marches between England and the Principality of Wales
, in which Marcher lords
had specific rights, held to some extent independently of the king of England.
 After the decline and fall of the Roman Empire
After the decline and fall of the Roman Empire
which occupied Britain
until about 410 AD, the area which is now Wales comprised a number of separate Romano-British
kingdoms, including Powys in the east. Over the next few centuries, the Angles
, Saxons
and others gradually conquered and settled in eastern and southern Britain. The kingdom of Mercia, under Penda, became established around Lichfield
, and initially established strong alliances with the Welsh kings. However, his successors sought to expand Mercia further westwards into what is now Cheshire
, Shropshire
and Herefordshire
. Campaigns and raids from Powys then led in the early 8th century to the building of Wat's Dyke
, a boundary earthwork extending from the Severn
valley near Oswestry
to the Dee estuary
. As the power of Mercia grew, a string of garrisoned market town
s such as Shrewsbury
and Hereford
defined the borderlands as much as Offa's Dyke
, a stronger and longer boundary earthwork erected by order of Offa of Mercia
in the late 8th century. The Dyke still exists, and can best be seen at Knighton, close to the modern border between England and Wales.
In the centuries which followed, Offa's Dyke largely remained the frontier between the Welsh and English. Athelstan
, often seen as the first king of a united England, summoned the British kings to a meeting at Hereford in 926, and according to William of Malmesbury
laid down the boundary between Wales and England, particularly the disputed southern stretch where he specified that the River Wye
should form the boundary. By the mid-eleventh century, most of Wales had also become united, under the king of Gwynedd
, Gruffudd ap Llywelyn, until his death in 1063.
the Welsh
. The process took a century and was never permanently effective. The term "March of Wales" was first used in the Domesday Book
of 1086. Over the next four centuries, Norman lords established mostly small marcher lordships between the Dee and Severn, and further west. Military adventurers came to Wales from Normandy
and elsewhere, raided an area of Wales, and then fortified it and granted land to some of their supporters. One example was Bernard de Neufmarché
, responsible for conquering and pacifying the Welsh kingdom of Brycheiniog
. The precise dates and means of formation of the lordships varied, as did their size.
.svg.png) The March, or Marchia Wallie, was to a greater or lesser extent independent of both the English monarchy and the Principality of Wales
The March, or Marchia Wallie, was to a greater or lesser extent independent of both the English monarchy and the Principality of Wales
or Pura Wallia, which remained based in Gwynedd
in the north west of the country. By the early 12th century, the March covered the areas which would later become Monmouthshire
and much of Flintshire
, Montgomeryshire
, Radnorshire
, Brecknockshire
, Glamorgan
, Carmarthenshire
and Pembrokeshire
. Ultimately, this amounted to about two-thirds of Wales. During the period, the Marches were a frontier society in every sense, and a stamp was set on the region that lasted into the time of the Industrial Revolution. Hundreds of small castles were built in the border area in the 12th and 13th centuries, predominantly by Norman lords as assertions of power as well as defences against Welsh raiders and rebels. The area still contains Britain's densest concentration of motte-and-bailey
castles. The Marcher lords encouraged immigration from all the Norman-Angevin realms, and encouraged trade from "fair haven" ports like Cardiff
. Peasants came to Wales in large numbers: Henry I
encouraged Bretons
, Flemings, Normans
, and English settlers to move into the south of Wales. Many new towns were established, some such as Chepstow
, Monmouth
, Ludlow
and Newtown becoming successful trading centres, and these tended also to be a focus of English settlement. At the same time, the Welsh continued to attack English soil and supported rebellions against the Normans.
The Norman lords each had similar rights to the Welsh princes. Each owed personal allegiance, as subjects, to the English king whom they were bound to support in times of war, but their lands were exempt from royal taxation and they possessed rights which elsewhere were reserved to the crown, such as the rights to create forests, markets and boroughs. The lordships were geographically compact and jurisdictionally separate one from another, and their privileges differentiated them from English lordships. Marcher lords ruled their lands by their own law—sicut regale ("like unto a king") as Gilbert de Clare, 7th Earl of Gloucester stated— whereas in England fief-holders were directly accountable to the king. The crown's powers in the Marches were normally limited to those periods when the king held a lordship in its own hands, such as when it was forfeited for treason or on the death of the lord without a legitimate heir whereupon the title reverted to the Crown in escheat
. At the top of a culturally diverse, intensely feudalised and local society, the Marcher barons combined the authority of feudal lord and vassal of the King among their Normans, and of supplanting the traditional tywysog
among their conquered Welsh. However, Welsh law
was sometimes used in the Marches in preference to English law, and there were disputes as to which code should be used to decide a particular case.
The Statute of Rhuddlan
in 1284 followed the conquest of the Principality by Edward I of England
. It assumed the lands held by the Princes of Gwynedd under the title "Prince of Wales
" as legally part of the lands of England, and established shire counties on the English model over those areas. The Marcher Lords were progressively tied to the English kings by the grants of lands and lordships in England, where control was stricter, and where many marcher lords spent most of their time, and through the English kings' dynastic alliances with the great magnates. The Council of Wales and the Marches, administered from Ludlow Castle
, was initially established in 1472 by Edward IV of England
to govern the lands held under the Principality of Wales which had become directly administered by the English crown following the Edwardian conquest of Wales
in the 13th century.
, who was previously Duke of Lancaster
, and Edward IV
, the heir of the Earls of March
; of the attainder
of other lords during the Wars of the Roses
; and of other events. The crown was also directly responsible for the government of the Principality of Wales, which had its own institutions and was, like England, divided into counties. The jurisdiction of the remaining marcher lords was therefore seen as an anomaly, and their independence from the crown enabled criminals from England to evade justice by moving into the area and claiming "marcher liberties".
Under the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542 introduced under Henry VIII
, the jurisdiction of the marchers lords was abolished in 1536. The Acts had the effect of annexing Wales to England
and creating a single state and legal jurisdiction
, commonly referred to as England and Wales
. The powers of the marcher lordships were abolished, and their areas were organised into the new Welsh counties of Denbighshire
, Montgomeryshire
, Radnorshire
, Brecknockshire
, Monmouthshire
, and Carmarthenshire
. The counties of Pembrokeshire
and Glamorgan
were created by adding other districts to existing lordships. In place of assize courts of England, there were Courts of Great Sessions
. These administered English law, in contrast with the marcher lordships, which had administered Welsh law for their Welsh subjects. Some lordships were added to adjoining English counties: Ludlow
, Clun
, Caus
and part of Montgomery
were incorporated into Shropshire; Wigmore, Huntington
, Clifford
and most of Ewyas
were included in Herefordshire; and that part of Chepstow
east of the River Wye
was included in Gloucestershire
.
The Council of Wales, based at Ludlow Castle
, was reconstituted as the Council of Wales and the Marches, with statutory responsibilities for the whole of Wales together with, initially, Cheshire
, Shropshire, Herefordshire, Worcestershire
and Gloucestershire
. The City of Bristol was exempted in 1562, and Cheshire in 1569. The Council was eventually abolished in 1689, following the "Glorious Revolution
" which overthrew James II
(VII of Scotland) and established William III
(William of Orange
) as king.
The Marches Way
is a long distance footpath which connects Chester in the north, via Whitchurch
, Shrewsbury
, Leominster
, and Abergavenny
to Cardiff in South Wales
.
The Welsh Marches Line
is a railway line from Newport
in South Wales to Shrewsbury, via Abergavenny, Hereford, and Craven Arms
.
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods. The English terms Welsh March, The March of Wales, in Medieval Latin Marchia Walliae, were originally used in the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
to denote a more precisely defined territory, the marches between England and the Principality of Wales
Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales existed between 1216 and 1542, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales.It was formally founded in 1216 at the Council of Aberdyfi, and later recognised by the 1218 Treaty of Worcester between Llywelyn the Great of Wales and Henry III of England...
, in which Marcher lords
Marcher Lords
A Marcher Lord was a strong and trusted noble appointed by the King of England to guard the border between England and Wales.A Marcher Lord is the English equivalent of a margrave...
had specific rights, held to some extent independently of the king of England.
Origins: Mercia and the Welsh

Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
which occupied Britain
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the part of the island of Great Britain controlled by the Roman Empire from AD 43 until ca. AD 410.The Romans referred to the imperial province as Britannia, which eventually comprised all of the island of Great Britain south of the fluid frontier with Caledonia...
until about 410 AD, the area which is now Wales comprised a number of separate Romano-British
Romano-British
Romano-British culture describes the culture that arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest of AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and...
kingdoms, including Powys in the east. Over the next few centuries, the Angles
Angles
The Angles is a modern English term for a Germanic people who took their name from the ancestral cultural region of Angeln, a district located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany...
, Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
and others gradually conquered and settled in eastern and southern Britain. The kingdom of Mercia, under Penda, became established around Lichfield
Lichfield
Lichfield is a cathedral city, civil parish and district in Staffordshire, England. One of eight civil parishes with city status in England, Lichfield is situated roughly north of Birmingham...
, and initially established strong alliances with the Welsh kings. However, his successors sought to expand Mercia further westwards into what is now Cheshire
Cheshire
Cheshire is a ceremonial county in North West England. Cheshire's county town is the city of Chester, although its largest town is Warrington. Other major towns include Widnes, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Runcorn, Macclesfield, Winsford, Northwich, and Wilmslow...
, Shropshire
Shropshire
Shropshire is a county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes, the county is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. It borders Wales to the west...
and Herefordshire
Herefordshire
Herefordshire is a historic and ceremonial county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire" NUTS 2 region. It also forms a unitary district known as the...
. Campaigns and raids from Powys then led in the early 8th century to the building of Wat's Dyke
Wat's Dyke
Wat's Dyke is a 40 mile earthwork running through the northern Welsh Marches from Basingwerk Abbey on the River Dee estuary, passing to the east of Oswestry and onto Maesbury in Shropshire, England...
, a boundary earthwork extending from the Severn
River Severn
The River Severn is the longest river in Great Britain, at about , but the second longest on the British Isles, behind the River Shannon. It rises at an altitude of on Plynlimon, Ceredigion near Llanidloes, Powys, in the Cambrian Mountains of mid Wales...
valley near Oswestry
Oswestry
Oswestry is a town and civil parish in Shropshire, England, close to the Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5, A483, and A495 roads....
to the Dee estuary
Dee Estuary
The Dee Estuary is a large estuary by means of which the River Dee flows into Liverpool Bay. The estuary starts near Shotton after a five miles 'canalised' section and the river soon swells to be several miles wide forming the boundary between the Wirral Peninsula in north-west England and...
. As the power of Mercia grew, a string of garrisoned market town
Market town
Market town or market right is a legal term, originating in the medieval period, for a European settlement that has the right to host markets, distinguishing it from a village and city...
s such as Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury is the county town of Shropshire, in the West Midlands region of England. Lying on the River Severn, it is a civil parish home to some 70,000 inhabitants, and is the primary settlement and headquarters of Shropshire Council...
and Hereford
Hereford
Hereford is a cathedral city, civil parish and county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, southwest of Worcester, and northwest of Gloucester...
defined the borderlands as much as Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke is a massive linear earthwork, roughly followed by some of the current border between England and Wales. In places, it is up to wide and high. In the 8th century it formed some kind of delineation between the Anglian kingdom of Mercia and the Welsh kingdom of Powys...
, a stronger and longer boundary earthwork erected by order of Offa of Mercia
Offa of Mercia
Offa was the King of Mercia from 757 until his death in July 796. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald after defeating the other claimant Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign it is likely...
in the late 8th century. The Dyke still exists, and can best be seen at Knighton, close to the modern border between England and Wales.
In the centuries which followed, Offa's Dyke largely remained the frontier between the Welsh and English. Athelstan
Athelstan of England
Athelstan , called the Glorious, was the King of England from 924 or 925 to 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder, grandson of Alfred the Great and nephew of Æthelflæd of Mercia...
, often seen as the first king of a united England, summoned the British kings to a meeting at Hereford in 926, and according to William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. C. Warren Hollister so ranks him among the most talented generation of writers of history since Bede, "a gifted historical scholar and an omnivorous reader, impressively well versed in the literature of classical,...
laid down the boundary between Wales and England, particularly the disputed southern stretch where he specified that the River Wye
River Wye
The River Wye is the fifth-longest river in the UK and for parts of its length forms part of the border between England and Wales. It is important for nature conservation and recreation.-Description:...
should form the boundary. By the mid-eleventh century, most of Wales had also become united, under the king of Gwynedd
Gwynedd
Gwynedd is a county in north-west Wales, named after the old Kingdom of Gwynedd. Although the second biggest in terms of geographical area, it is also one of the most sparsely populated...
, Gruffudd ap Llywelyn, until his death in 1063.
The March of Wales in the Middle Ages
Immediately after the Norman Conquest, King William of England installed three of his most trusted confidants, Hugh d'Avranches, Roger de Montgomerie, and William FitzOsbern, as Earls of Chester, Shrewsbury and Hereford respectively, with responsibilities for containing and subduingNorman invasion of Wales
The Norman invasion of Wales began shortly after the Norman conquest of England under William the Conqueror, who believed England to be his birthright...
the Welsh
Welsh people
The Welsh people are an ethnic group and nation associated with Wales and the Welsh language.John Davies argues that the origin of the "Welsh nation" can be traced to the late 4th and early 5th centuries, following the Roman departure from Britain, although Brythonic Celtic languages seem to have...
. The process took a century and was never permanently effective. The term "March of Wales" was first used in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book
Domesday Book , now held at The National Archives, Kew, Richmond upon Thames in South West London, is the record of the great survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086...
of 1086. Over the next four centuries, Norman lords established mostly small marcher lordships between the Dee and Severn, and further west. Military adventurers came to Wales from Normandy
Normandy
Normandy is a geographical region corresponding to the former Duchy of Normandy. It is in France.The continental territory covers 30,627 km² and forms the preponderant part of Normandy and roughly 5% of the territory of France. It is divided for administrative purposes into two régions:...
and elsewhere, raided an area of Wales, and then fortified it and granted land to some of their supporters. One example was Bernard de Neufmarché
Bernard de Neufmarché
Bernard of Neufmarché was "the first of the original conquerors of Wales." He was a minor Norman lord who rose to power in the Welsh Marches before successfully undertaking the invasion and conquest of the Kingdom of Brycheiniog between 1088 and 1095. Out of the ruins of the Welsh kingdom he...
, responsible for conquering and pacifying the Welsh kingdom of Brycheiniog
Brycheiniog
Brycheiniog was a small independent petty kingdom in South Wales in the Early Middle Ages. It often acted as a buffer state between England to the east and the powerful south Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth to the west. It was conquered and pacified by the Normans between 1088 and 1095, though it...
. The precise dates and means of formation of the lordships varied, as did their size.
.svg.png)
Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales existed between 1216 and 1542, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales.It was formally founded in 1216 at the Council of Aberdyfi, and later recognised by the 1218 Treaty of Worcester between Llywelyn the Great of Wales and Henry III of England...
or Pura Wallia, which remained based in Gwynedd
Gwynedd in the High Middle Ages
The history of Gwynedd in the High Middle Ages is a period in the History of Wales spanning the 11th through the 13th centuries. Gwynedd, located in the north of Wales, eventually became the most dominant of Welsh principalities during this period...
in the north west of the country. By the early 12th century, the March covered the areas which would later become Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire (historic)
Monmouthshire , also known as the County of Monmouth , is one of thirteen ancient counties of Wales and a former administrative county....
and much of Flintshire
Flintshire
Flintshire is a county in north-east Wales. It borders Denbighshire, Wrexham and the English county of Cheshire. It is named after the historic county of Flintshire, which had notably different borders...
, Montgomeryshire
Montgomeryshire
Montgomeryshire, also known as Maldwyn is one of thirteen historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. Montgomeryshire is still used as a vice-county for wildlife recording...
, Radnorshire
Radnorshire
Radnorshire is one of thirteen historic and former administrative counties of Wales. It is represented by the Radnorshire area of Powys, which according to the 2001 census, had a population of 24,805...
, Brecknockshire
Brecknockshire
Brecknockshire , also known as the County of Brecknock, Breconshire, or the County of Brecon is one of thirteen historic counties of Wales, and a former administrative county.-Geography:...
, Glamorgan
Glamorgan
Glamorgan or Glamorganshire is one of the thirteen historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. It was originally an early medieval kingdom of varying boundaries known as Glywysing until taken over by the Normans as a lordship. Glamorgan is latterly represented by the three...
, Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire is a unitary authority in the south west of Wales and one of thirteen historic counties. It is the 3rd largest in Wales. Its three largest towns are Llanelli, Carmarthen and Ammanford...
and Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire is a county in the south west of Wales. It borders Carmarthenshire to the east and Ceredigion to the north east. The county town is Haverfordwest where Pembrokeshire County Council is headquartered....
. Ultimately, this amounted to about two-thirds of Wales. During the period, the Marches were a frontier society in every sense, and a stamp was set on the region that lasted into the time of the Industrial Revolution. Hundreds of small castles were built in the border area in the 12th and 13th centuries, predominantly by Norman lords as assertions of power as well as defences against Welsh raiders and rebels. The area still contains Britain's densest concentration of motte-and-bailey
Motte-and-bailey
A motte-and-bailey is a form of castle, with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised earthwork called a motte, accompanied by an enclosed courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade...
castles. The Marcher lords encouraged immigration from all the Norman-Angevin realms, and encouraged trade from "fair haven" ports like Cardiff
Cardiff
Cardiff is the capital, largest city and most populous county of Wales and the 10th largest city in the United Kingdom. The city is Wales' chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for...
. Peasants came to Wales in large numbers: Henry I
Henry I of England
Henry I was the fourth son of William I of England. He succeeded his elder brother William II as King of England in 1100 and defeated his eldest brother, Robert Curthose, to become Duke of Normandy in 1106...
encouraged Bretons
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
, Flemings, Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
, and English settlers to move into the south of Wales. Many new towns were established, some such as Chepstow
Chepstow
Chepstow is a town in Monmouthshire, Wales, adjoining the border with Gloucestershire, England. It is located on the River Wye, close to its confluence with the River Severn, and close to the western end of the Severn Bridge on the M48 motorway...
, Monmouth
Monmouth
Monmouth is a town in southeast Wales and traditional county town of the historic county of Monmouthshire. It is situated close to the border with England, where the River Monnow meets the River Wye with bridges over both....
, Ludlow
Ludlow
Ludlow is a market town in Shropshire, England close to the Welsh border and in the Welsh Marches. It lies within a bend of the River Teme, on its eastern bank, forming an area of and centred on a small hill. Atop this hill is the site of Ludlow Castle and the market place...
and Newtown becoming successful trading centres, and these tended also to be a focus of English settlement. At the same time, the Welsh continued to attack English soil and supported rebellions against the Normans.
The Norman lords each had similar rights to the Welsh princes. Each owed personal allegiance, as subjects, to the English king whom they were bound to support in times of war, but their lands were exempt from royal taxation and they possessed rights which elsewhere were reserved to the crown, such as the rights to create forests, markets and boroughs. The lordships were geographically compact and jurisdictionally separate one from another, and their privileges differentiated them from English lordships. Marcher lords ruled their lands by their own law—sicut regale ("like unto a king") as Gilbert de Clare, 7th Earl of Gloucester stated— whereas in England fief-holders were directly accountable to the king. The crown's powers in the Marches were normally limited to those periods when the king held a lordship in its own hands, such as when it was forfeited for treason or on the death of the lord without a legitimate heir whereupon the title reverted to the Crown in escheat
Escheat
Escheat is a common law doctrine which transfers the property of a person who dies without heirs to the crown or state. It serves to ensure that property is not left in limbo without recognised ownership...
. At the top of a culturally diverse, intensely feudalised and local society, the Marcher barons combined the authority of feudal lord and vassal of the King among their Normans, and of supplanting the traditional tywysog
Tywysog
Tywysog , in modern Welsh, means "Prince", although historically it referred to a broader category of rulers. The feminine form is Tywysoges. The work Brut y Tywysogion is the Annals of the Princes of Wales and is a historical narrative of the deeds of the various rulers of the kingdoms, large and...
among their conquered Welsh. However, Welsh law
Welsh law
Welsh law was the system of law practised in Wales before the 16th century. According to tradition it was first codified by Hywel Dda during the period between 942 and 950 when he was king of most of Wales; as such it is usually called Cyfraith Hywel, the Law of Hywel, in Welsh...
was sometimes used in the Marches in preference to English law, and there were disputes as to which code should be used to decide a particular case.
The Statute of Rhuddlan
Statute of Rhuddlan
The Statute of Rhuddlan , also known as the Statutes of Wales or as the Statute of Wales provided the constitutional basis for the government of the Principality of North Wales from 1284 until 1536...
in 1284 followed the conquest of the Principality by Edward I of England
Edward I of England
Edward I , also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England from 1272 to 1307. The first son of Henry III, Edward was involved early in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included an outright rebellion by the English barons...
. It assumed the lands held by the Princes of Gwynedd under the title "Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales is a title traditionally granted to the heir apparent to the reigning monarch of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and the 15 other independent Commonwealth realms...
" as legally part of the lands of England, and established shire counties on the English model over those areas. The Marcher Lords were progressively tied to the English kings by the grants of lands and lordships in England, where control was stricter, and where many marcher lords spent most of their time, and through the English kings' dynastic alliances with the great magnates. The Council of Wales and the Marches, administered from Ludlow Castle
Ludlow Castle
Ludlow Castle is a large, partly ruined, non-inhabited castle which dominates the town of Ludlow in Shropshire, England. It stands on a high point overlooking the River Teme...
, was initially established in 1472 by Edward IV of England
Edward IV of England
Edward IV was King of England from 4 March 1461 until 3 October 1470, and again from 11 April 1471 until his death. He was the first Yorkist King of England...
to govern the lands held under the Principality of Wales which had become directly administered by the English crown following the Edwardian conquest of Wales
Llywelyn the Last
Llywelyn ap Gruffydd or Llywelyn Ein Llyw Olaf , sometimes rendered as Llywelyn II, was the last prince of an independent Wales before its conquest by Edward I of England....
in the 13th century.
The end of Marcher powers
By the 16th century, many marcher lordships had passed into the hands of the crown, as the result of the accessions of Henry IVHenry IV of England
Henry IV was King of England and Lord of Ireland . He was the ninth King of England of the House of Plantagenet and also asserted his grandfather's claim to the title King of France. He was born at Bolingbroke Castle in Lincolnshire, hence his other name, Henry Bolingbroke...
, who was previously Duke of Lancaster
Duke of Lancaster
There were several Dukes of Lancaster in the 14th and early 15th Centuries. See also Duchy of Lancaster.There were three creations of the Dukedom of Lancaster....
, and Edward IV
Edward IV of England
Edward IV was King of England from 4 March 1461 until 3 October 1470, and again from 11 April 1471 until his death. He was the first Yorkist King of England...
, the heir of the Earls of March
Earl of March
The title The Earl of March has been created several times in the Peerage of Scotland and the Peerage of England. The title derived from the "marches" or boundaries between England and either Wales or Scotland , and was held by several great feudal families which owned lands in those border...
; of the attainder
Attainder
In English criminal law, attainder or attinctura is the metaphorical 'stain' or 'corruption of blood' which arises from being condemned for a serious capital crime . It entails losing not only one's property and hereditary titles, but typically also the right to pass them on to one's heirs...
of other lords during the Wars of the Roses
Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses were a series of dynastic civil wars for the throne of England fought between supporters of two rival branches of the royal House of Plantagenet: the houses of Lancaster and York...
; and of other events. The crown was also directly responsible for the government of the Principality of Wales, which had its own institutions and was, like England, divided into counties. The jurisdiction of the remaining marcher lords was therefore seen as an anomaly, and their independence from the crown enabled criminals from England to evade justice by moving into the area and claiming "marcher liberties".
Under the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542 introduced under Henry VIII
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
, the jurisdiction of the marchers lords was abolished in 1536. The Acts had the effect of annexing Wales to England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
and creating a single state and legal jurisdiction
Jurisdiction
Jurisdiction is the practical authority granted to a formally constituted legal body or to a political leader to deal with and make pronouncements on legal matters and, by implication, to administer justice within a defined area of responsibility...
, commonly referred to as England and Wales
England and Wales
England and Wales is a jurisdiction within the United Kingdom. It consists of England and Wales, two of the four countries of the United Kingdom...
. The powers of the marcher lordships were abolished, and their areas were organised into the new Welsh counties of Denbighshire
Denbighshire
Denbighshire is a county in north-east Wales. It is named after the historic county of Denbighshire, but has substantially different borders. Denbighshire has the distinction of being the oldest inhabited part of Wales. Pontnewydd Palaeolithic site has remains of Neanderthals from 225,000 years...
, Montgomeryshire
Montgomeryshire
Montgomeryshire, also known as Maldwyn is one of thirteen historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. Montgomeryshire is still used as a vice-county for wildlife recording...
, Radnorshire
Radnorshire
Radnorshire is one of thirteen historic and former administrative counties of Wales. It is represented by the Radnorshire area of Powys, which according to the 2001 census, had a population of 24,805...
, Brecknockshire
Brecknockshire
Brecknockshire , also known as the County of Brecknock, Breconshire, or the County of Brecon is one of thirteen historic counties of Wales, and a former administrative county.-Geography:...
, Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire (historic)
Monmouthshire , also known as the County of Monmouth , is one of thirteen ancient counties of Wales and a former administrative county....
, and Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire is a unitary authority in the south west of Wales and one of thirteen historic counties. It is the 3rd largest in Wales. Its three largest towns are Llanelli, Carmarthen and Ammanford...
. The counties of Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire is a county in the south west of Wales. It borders Carmarthenshire to the east and Ceredigion to the north east. The county town is Haverfordwest where Pembrokeshire County Council is headquartered....
and Glamorgan
Glamorgan
Glamorgan or Glamorganshire is one of the thirteen historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. It was originally an early medieval kingdom of varying boundaries known as Glywysing until taken over by the Normans as a lordship. Glamorgan is latterly represented by the three...
were created by adding other districts to existing lordships. In place of assize courts of England, there were Courts of Great Sessions
Court of Great Sessions in Wales
The Court of Great Sessions in Wales was the main court for the prosecution of felonies and serious misdemeanours in Wales between the second Laws in Wales Act of 1542 and the court's abolition in 1830....
. These administered English law, in contrast with the marcher lordships, which had administered Welsh law for their Welsh subjects. Some lordships were added to adjoining English counties: Ludlow
Ludlow
Ludlow is a market town in Shropshire, England close to the Welsh border and in the Welsh Marches. It lies within a bend of the River Teme, on its eastern bank, forming an area of and centred on a small hill. Atop this hill is the site of Ludlow Castle and the market place...
, Clun
Clun
Clun is a small town in Shropshire, England. The town is located entirely in the Shropshire Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The 2001 census recorded 642 people living in the town...
, Caus
Caus Castle
Caus Castle is a hill fort and medieval castle in the civil parish of Westbury in the English county of Shropshire. It is situated up on the eastern foothills of the Long Mountain guarding the route from Shrewsbury, Shropshire to Montgomery, Powys on the border between England and Wales.- History...
and part of Montgomery
Montgomery, Powys
The historic county town of Montgomery in Powys, Wales lies just three miles from the English border in the Welsh Marches. It is best known for its castle, Montgomery Castle, begun in 1223, and its parish church, begun in 1227. However its origins go back much further, as seen by the Celtic Iron...
were incorporated into Shropshire; Wigmore, Huntington
Huntington, Herefordshire
-History:Huntington was a Medieval borough founded as a replacement to nearby Kington which had been destroyed in 1216.Huntington was built as a new borough and was apparently in the first breath of life in 1228 when it was first mentioned...
, Clifford
Clifford, Herefordshire
Clifford is a village and civil parish in Herefordshire, England, four miles to the north of Hay-on-Wye. It lies on the south bank of the River Wye, which here forms the border between Wales and England....
and most of Ewyas
Ewyas
Ewyas was a possible early Welsh kingdom which may have been formed around the time of the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century. The name was later used for a much smaller commote or administrative sub-division, which covered the area of the modern Vale of Ewyas and a larger area to...
were included in Herefordshire; and that part of Chepstow
Chepstow
Chepstow is a town in Monmouthshire, Wales, adjoining the border with Gloucestershire, England. It is located on the River Wye, close to its confluence with the River Severn, and close to the western end of the Severn Bridge on the M48 motorway...
east of the River Wye
River Wye
The River Wye is the fifth-longest river in the UK and for parts of its length forms part of the border between England and Wales. It is important for nature conservation and recreation.-Description:...
was included in Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn, and the entire Forest of Dean....
.
The Council of Wales, based at Ludlow Castle
Ludlow Castle
Ludlow Castle is a large, partly ruined, non-inhabited castle which dominates the town of Ludlow in Shropshire, England. It stands on a high point overlooking the River Teme...
, was reconstituted as the Council of Wales and the Marches, with statutory responsibilities for the whole of Wales together with, initially, Cheshire
Cheshire
Cheshire is a ceremonial county in North West England. Cheshire's county town is the city of Chester, although its largest town is Warrington. Other major towns include Widnes, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Runcorn, Macclesfield, Winsford, Northwich, and Wilmslow...
, Shropshire, Herefordshire, Worcestershire
Worcestershire
Worcestershire is a non-metropolitan county, established in antiquity, located in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire" NUTS 2 region...
and Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn, and the entire Forest of Dean....
. The City of Bristol was exempted in 1562, and Cheshire in 1569. The Council was eventually abolished in 1689, following the "Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
" which overthrew James II
James II of England
James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland...
(VII of Scotland) and established William III
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
(William of Orange
House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau , a branch of the European House of Nassau, has played a central role in the political life of the Netherlands — and at times in Europe — since William I of Orange organized the Dutch revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War...
) as king.
List of Marcher lordships and successor shires
List of Marcher lordships and successor shires:- Flintshire
- FlintFlint, FlintshireFlint is a town in Flintshire, North Wales, lying on the estuary of the River Dee. It was the county town of the historic county of Flintshire and today is the third largest town in Flintshire. According to the 2001 Census the population of the community of Flint was 12,804...
- HawardenHawardenHawarden is a village in Flintshire, North Wales. Hawarden forms part of the Deeside conurbation on the Welsh/English border. At the 2001 Census, the population of Hawarden Ward was 1,858...
- HopedaleHope, FlintshireHope is a small village in Flintshire, north-east Wales. The village is located approximately 3 miles / 4.5 km from the Wales-England border, on the course of the River Alyn....
- Maelor SaesnegMaelorMaelor is a border area of north-east Wales. It originated as a Cantref of the Kingdom of Powys, focused on Bangor-on-Dee.-History:The Maelor was first divided from the rest of Wales by the construction of Offa's Dyke in the eighth century, but was reclaimed for Wales during the reign of Stephen...
- MoldMold, FlintshireMold is a town in Flintshire, North Wales, on the River Alyn. It is the administrative seat of Flintshire County Council, and was also the county town of Clwyd from 1974 to 1996...
- Denbighshire
- Bromfield and YalePowys FadogPowys Fadog or Lower Powys was the northern portion of the former princely realm of Powys which split in two following the death of Madog ap Maredudd of Powys in 1160...
- ChirkChirkChirk is a small town and local government community, the lowest tier of local government, part of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It has a population of over 4,000....
- DenbighDenbighDenbigh is a market town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. Before 1888, it was the county town of Denbighshire. Denbigh lies 8 miles to the north west of Ruthin and to the south of St Asaph. It is about 13 miles from the seaside resort of Rhyl. The town grew around the glove-making industry...
- RuthinRuthinRuthin is a community and the county town of Denbighshire in north Wales. Located around a hill in the southern part of the Vale of Clwyd - the older part of the town, the castle and Saint Peter's Square are located on top of the hill, while many newer parts of the town are on the floodplain of...
(Dyffryn ClwydDyffryn ClwydDyffryn Clwyd was a cantref of Medieval Wales and from 1282 a marcher lordship. In 1536, it became part of the new county of Denbighshire. The name means Vale of Clwyd in English and is still the name for that region of north Wales in modern Welsh...
)- Montgomeryshire
- CausCaus CastleCaus Castle is a hill fort and medieval castle in the civil parish of Westbury in the English county of Shropshire. It is situated up on the eastern foothills of the Long Mountain guarding the route from Shrewsbury, Shropshire to Montgomery, Powys on the border between England and Wales.- History...
(part) - CedewainBettws CedewainBettws Cedewain , also known as Bettws Cedewen, is a small village and community in Powys, Wales. It lies in a sheltered valley on the banks of the Bechan Brook, some 3 miles north of Newtown....
- CeriKerry, PowysKerry is a small village in Powys, Mid Wales. The area around the village was the Welsh Commote and Lordship of Ceri, part of the region of Rhwng Gwy a Hafren, and it was originally ruled by the Princes of Maelienydd and their descendants....
- MontgomeryMontgomery, PowysThe historic county town of Montgomery in Powys, Wales lies just three miles from the English border in the Welsh Marches. It is best known for its castle, Montgomery Castle, begun in 1223, and its parish church, begun in 1227. However its origins go back much further, as seen by the Celtic Iron...
(part) - PowysPowys WenwynwynPowys Wenwynwyn or Powys Cyfeiliog was the southern portion of the former princely state of Powys which split following the death of Madog ap Maredudd of Powys in 1160...
- Radnorshire
- Cwmwd Deuddor
- ElfaelElfaelElfael was one of a number of Welsh kingdoms occupying the region between the River Wye and river Severn, known as Rhwng Gwy a Hafren, in the early Middle Ages. Later in the Middle Ages it became a cantref. After the Laws in Wales Act of 1535, it became part of the new county of Radnorshire. ...
- GlasburyGlasburyGlasbury , also known as Glasbury-on-Wye, is a village in Powys, Wales which lies at an important crossing point on the River Wye, connecting the former counties of Brecknockshire and Radnorshire. The village is just outside the Brecon Beacons National Park, north of the Black Mountains. The...
- GwrtheyrnionGwrtheyrnionGwrtheyrnion or Gwerthrynion was a commote in medieval Wales, located in Mid Wales on the north side of the River Wye. For most of the Middle Ages its rulers operated independently of other powers, but it was sometimes associated with the cantref of Maelienydd and the Kingdom of Powys, and, in the...
- MaelienyddMaelienyddMaelienydd, sometimes spelt Maeliennydd, was a cantref and lordship in east central Wales covering the area from the River Teme to Radnor Forest and the area around Llandrindod Wells. The area, which is mainly upland, is now in Powys...
- RadnorNew RadnorNew Radnor is a village in Powys, mid Wales. It was the original county town of Radnorshire. The population today is around 400, a higher than normal proportion of which are pensioners...
- PresteignePresteignePresteigne is a town and community in Powys, Wales. It was the county town of the historic county of Radnorshire, and is in the Diocese of Hereford...
- Brecknockshire
- Blaenllyfni
- BreconBreconBrecon is a long-established market town and community in southern Powys, Mid Wales, with a population of 7,901. It was the county town of the historic county of Brecknockshire; although its role as such was eclipsed with the formation of Powys, it remains an important local centre...
- Builth
- HayHay-on-WyeHay-on-Wye , often described as "the town of books", is a small market town and community in Powys, Wales.-Location:The town lies on the east bank of the River Wye and is within the Brecon Beacons National Park, just north of the Black Mountains...
- Monmouthshire
- AbergavennyAbergavennyAbergavenny , meaning Mouth of the River Gavenny, is a market town in Monmouthshire, Wales. It is located 15 miles west of Monmouth on the A40 and A465 roads, 6 miles from the English border. Originally the site of a Roman fort, Gobannium, it became a medieval walled town within the Welsh Marches...
- CaerleonCaerleonCaerleon is a suburban village and community, situated on the River Usk in the northern outskirts of the city of Newport, South Wales. Caerleon is a site of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman legionary fortress, Isca Augusta, and an Iron Age hill fort...
- ChepstowChepstowChepstow is a town in Monmouthshire, Wales, adjoining the border with Gloucestershire, England. It is located on the River Wye, close to its confluence with the River Severn, and close to the western end of the Severn Bridge on the M48 motorway...
(part) - Ewyas LacyEwyasEwyas was a possible early Welsh kingdom which may have been formed around the time of the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century. The name was later used for a much smaller commote or administrative sub-division, which covered the area of the modern Vale of Ewyas and a larger area to...
(part) - GwynllŵgGwynllwgGwynllŵg was a kingdom of mediæval Wales and later a Norman lordship and then a cantref.-Location:It was named after Gwynllyw, its 5th century or 6th century ruler and consisted of the coastal plain stretching between the Rhymney and Usk rivers, together with the hills to the north...
(Wentloog) - MonmouthMonmouthMonmouth is a town in southeast Wales and traditional county town of the historic county of Monmouthshire. It is situated close to the border with England, where the River Monnow meets the River Wye with bridges over both....
- UskUskUsk is a small town in Monmouthshire, Wales, situated 10 miles northeast of Newport.The River Usk flows through the town and is spanned by an ancient, arched stone bridge at the western entrance to the town. A castle above the town overlooks the ancient Anglo-Welsh border crossing - the river can...
- Glamorgan
- GlamorganGlamorganGlamorgan or Glamorganshire is one of the thirteen historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. It was originally an early medieval kingdom of varying boundaries known as Glywysing until taken over by the Normans as a lordship. Glamorgan is latterly represented by the three...
- GowerGower (Lordship)thumb|350px|right|Map of the Lordship, showing the area detached , the area added and the Town and Franchise of Swansea. The language boundary is shown as a dotted line....
- Carmarthenshire
- Cantref Bychan
- Cydweli
- EmlynEmlynEmlyn was one of the seven cantrefi of Dyfed, an ancient district of Wales. It subsequently became part of Deheubarth in around 950. It consisted of the northern part of Dyfed bordering on the River Teifi...
- LlansteffanLlansteffanLlansteffan is a village in Carmarthenshire, Wales. Llansteffan is one of three settlements positioned on the Tywi river, other settlements include Ferryside and Carmarthen . Llansteffan Castle, built by the Normans in the 12th century, is located in the village...
- Laugharne
- St. Clears
- Ystlwyl
- Pembrokeshire
- Cemais
- CilgerranCilgerranCilgerran is a town in the Hundred of Cilgerran, Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Teifi. It is the site of Cilgerran Castle, built in 1100, from which Owain of Powys is said to have abducted Nest in 1109. It is first mentioned by name in 1164...
- HaverfordHaverfordwestHaverfordwest is the county town of Pembrokeshire, Wales and serves as the County's principal commercial and administrative centre. Haverfordwest is the most populous urban area in Pembrokeshire, with a population of 13,367 in 2001; though its community boundaries make it the second most populous...
- LlawhadenLlawhadenLlawhaden is a village and parish in the Hundred of Dungleddy , Pembrokeshire, West Wales.Llawhaden was a civil parish, area 1865 Ha....
- NarberthNarberth (hundred)thumb|200px|right|Pembrokeshire showing Narberth HundredThe Hundred of Narberth was a hundred in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It was formed by the Act of Union of 1536 from parts of the pre-Norman cantrefs of Penfro and Cantref Gwarthaf...
- Pebidiog
- PembrokePembroke, PembrokeshirePembroke is an historic settlement and former county town of Pembrokeshire in west Wales. The town and the county derive their name from that of the cantref of Penfro: Pen = "head" or "end", and bro = "region", "country", "land", and so it means essentially "Land's End".-History:The main point of...
- Transferred to English shires
- Bishop's CastleBishop's CastleBishop's Castle is a small market town in Shropshire, England, and formerly its smallest borough. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 1,630. Bishop's Castle is east of the Wales-England border, about north-west of Ludlow and about south-west of Shrewsbury. To the south is Clun...
(Shropshire) - Caus (part) (Shropshire)
- Chepstow (part) (Gloucestershire)
- CliffordClifford, HerefordshireClifford is a village and civil parish in Herefordshire, England, four miles to the north of Hay-on-Wye. It lies on the south bank of the River Wye, which here forms the border between Wales and England....
(Herefordshire) - ClunClunClun is a small town in Shropshire, England. The town is located entirely in the Shropshire Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The 2001 census recorded 642 people living in the town...
(Shropshire) - Ewyas Lacy (part) (Herefordshire)
- HuntingtonHuntington, Herefordshire-History:Huntington was a Medieval borough founded as a replacement to nearby Kington which had been destroyed in 1216.Huntington was built as a new borough and was apparently in the first breath of life in 1228 when it was first mentioned...
(Herefordshire) - KnightonKnightonKnighton may mean:* Knighton, Powys a market town on the English/Welsh border**Knighton railway station serving the above town**Knighton Town F.C., its football club* Knighton, Leicestershire, a suburb of Leicester, England* In Staffordshire:...
(part) (Shropshire) - Montgomery (part) (Shropshire)
- OswestryOswestryOswestry is a town and civil parish in Shropshire, England, close to the Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5, A483, and A495 roads....
(Shropshire) - WhittingtonWhittington CastleWhittington Castle is a castle in northern Shropshire, England, owned and managed by the Whittington Castle Preservation Fund. The castle was originally a motte-and-bailey castle, but this was replaced in the 13th century by one with buildings around a courtyard whose exterior wall was the curtain...
(Shropshire) - Wigmore (Herefordshire)
The Marches today
There is no modern legal or official definition of the extent of the Welsh Marches. However, it is a term still commonly used to describe, in particular, those parts of the English counties which lie along the border with Wales, particularly Shropshire and Herefordshire.The Marches Way
Marches Way
The Marches Way is a partially waymarked long distance footpath in the United Kingdom. It runs 351 kilometres / 218 miles through the Welsh–English borderlands, traditionally known as the Welsh Marches and links the cities of Chester in the north and Cardiff in the south.-The route:The route...
is a long distance footpath which connects Chester in the north, via Whitchurch
Whitchurch, Shropshire
Whitchurch is a market town in Shropshire, England on the border between England and Wales. It is the oldest continuously inhabited town in Shropshire. According to the 2001 Census, the population of the town is 8,673, with a more recent estimate putting the population of the town at 8,934...
, Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury is the county town of Shropshire, in the West Midlands region of England. Lying on the River Severn, it is a civil parish home to some 70,000 inhabitants, and is the primary settlement and headquarters of Shropshire Council...
, Leominster
Leominster
Leominster is a market town in Herefordshire, England, located approximately north of the city of Hereford and south of Ludlow, at...
, and Abergavenny
Abergavenny
Abergavenny , meaning Mouth of the River Gavenny, is a market town in Monmouthshire, Wales. It is located 15 miles west of Monmouth on the A40 and A465 roads, 6 miles from the English border. Originally the site of a Roman fort, Gobannium, it became a medieval walled town within the Welsh Marches...
to Cardiff in South Wales
South Wales
South Wales is an area of Wales bordered by England and the Bristol Channel to the east and south, and Mid Wales and West Wales to the north and west. The most densely populated region in the south-west of the United Kingdom, it is home to around 2.1 million people and includes the capital city of...
.
The Welsh Marches Line
Welsh Marches Line
The Welsh Marches Line , known historically as the North and West Route, is the railway line running from Newport in south-east Wales to Shrewsbury in the West Midlands region of England by way of Abergavenny, Hereford and Craven Arms, and thence to Crewe via Whitchurch...
is a railway line from Newport
Newport
Newport is a city and unitary authority area in Wales. Standing on the banks of the River Usk, it is located about east of Cardiff and is the largest urban area within the historic county boundaries of Monmouthshire and the preserved county of Gwent...
in South Wales to Shrewsbury, via Abergavenny, Hereford, and Craven Arms
Craven Arms
Craven Arms is a small town and civil parish in Shropshire, England, located on the A49 road and the Welsh Marches railway line, which connect it north and south to the larger towns of Shrewsbury and Ludlow respectively. The Heart of Wales railway line joins the Welsh Marches line at Craven Arms...
.
See also
- MarchesMarchesA march or mark refers to a border region similar to a frontier, such as the Welsh Marches, the borderland between England and Wales. During the Frankish Carolingian Dynasty, the word spread throughout Europe....
- for other examples, including Scottish MarchesScottish MarchesScottish Marches was the term used for the Anglo-Scottish border during the late medieval and early modern eras—from the late 13th century, with the creation by Edward I of England of the first Lord Warden of the Marches to the early 17th century and the creation of the Middle Shires, promulgated...
between England and Scotland. - Council of the MarchesCouncil of the MarchesThe Council of Wales and the Marches was a regional administrative body within the Kingdom of England between the 15th and 17th centuries, similar to the Council of the North...
- Earl of MarchEarl of MarchThe title The Earl of March has been created several times in the Peerage of Scotland and the Peerage of England. The title derived from the "marches" or boundaries between England and either Wales or Scotland , and was held by several great feudal families which owned lands in those border...
- some of the dynastic families controlling the Welsh Marches - Wales-England border
- Welsh Marches LineWelsh Marches LineThe Welsh Marches Line , known historically as the North and West Route, is the railway line running from Newport in south-east Wales to Shrewsbury in the West Midlands region of England by way of Abergavenny, Hereford and Craven Arms, and thence to Crewe via Whitchurch...
- railway line that runs through the Marches - Marches WayMarches WayThe Marches Way is a partially waymarked long distance footpath in the United Kingdom. It runs 351 kilometres / 218 miles through the Welsh–English borderlands, traditionally known as the Welsh Marches and links the cities of Chester in the north and Cardiff in the south.-The route:The route...
- a long distance footpath from ChesterChesterChester is a city in Cheshire, England. Lying on the River Dee, close to the border with Wales, it is home to 77,040 inhabitants, and is the largest and most populous settlement of the wider unitary authority area of Cheshire West and Chester, which had a population of 328,100 according to the...
to CardiffCardiffCardiff is the capital, largest city and most populous county of Wales and the 10th largest city in the United Kingdom. The city is Wales' chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for...
through the Welsh Marches - A49A49 roadThe A49 is a major road in western England, which traverses the Welsh Marches region. It runs north from Ross-on-Wye in Herefordshire via Hereford, Leominster, Ludlow, Shrewsbury and Whitchurch, then continues through central Cheshire to Warrington and Wigan before terminating at its junction with...
- main road that runs north-south through the Marches - Honour of RichmondHonour of RichmondThe Honour of Richmond in north-west Yorkshire was granted to Count Alan Rufus by William the Conqueror in 1071AD. The honour, which was assessed for the service of 60 knights, was one of the most important fiefs in Norman England. - Territory :...
- History of Gwynedd during the High Middle Ages
- :Category:Towns of the Welsh Marches
- :Category:Counties of the Welsh Marches
Further reading
- Freeman, Edward Augustus Freeman, 1871. The History of the Norman Conquest of England: Its Causes and Its Results, (Clarendon Press, London)
- Davies, R. R., The Age of Conquest: Wales 1063-1415 (Oxford 1987, 2000 edition), pp. 271–88.
- ---. Lordship and Society in the March of Wales, 1282-1400 (1978).
- Froude, James Anthony, 1881. History of England from the Fall of Wolsey to the Death of Elizabeth (London, Published by C. Scribner's sons) pp. 380–384.
- Reeves, C. Compton, The Marcher Lords (1983)
- Skeel, C.A.J. "The Council in the Marches of Wales", Hugh Rees Ltd. London (1904)
- Allott, Andrew. 2011, Marches. Collins New Naturalist LibraryNew NaturalistThe New Naturalist Library books are a series published by Collins in the United Kingdom, on a variety of natural history topics relevant to the British Isles...
. London
External links
- Marches.TV A comprehensive site of information and videos for the Marches counties of Herefordshire, Shropshire and Powys

