
White Wagtail
Encyclopedia
"Pied Wagtail" redirects here. For the related African bird, see African Pied Wagtail
.
The White Wagtail (Motacilla alba) is a small passerine
bird
in the wagtail
family
Motacillidae, which also includes the pipit
s and longclaw
s. This species
breeds in much of Europe
and Asia
and parts of north Africa
. It is resident in the mildest parts of its range, but otherwise migrates
to Africa
. It has a toehold in Alaska
as a scarce breeder. In some areas, notably Britain and Ireland, the sub-species Pied Wagtail (M. a. yarrellii) predominates.
This is an insectivorous bird
of open country, often near habitation and water. It prefers bare areas for feeding, where it can see and pursue its prey. In urban areas it has adapted to foraging on paved areas such as car parks. It nests in crevices in stone walls and similar natural and man-made structures.
The White Wagtail is the national bird of Latvia
.
 The White Wagtail was one of the many species originally described by Linnaeus
The White Wagtail was one of the many species originally described by Linnaeus
in his 18th century work, Systema Naturae
, and it still bears its original name of Motacilla alba. The Latin
genus name originally meant "little mover", but certain medieval writers thought it meant "wag-tail", giving rise to a new Latin word cilla for "tail". The specific epithet alba is Latin for "white".
Within the wagtail genus Motacilla, the White Wagtail's closest relatives appear to be other black-and-white wagtails such as the Japanese Wagtail
, Motacilla grandis, and the White-browed Wagtail
, Motacilla madaraspatensis, (and possibly the Mekong Wagtail
, Motacilla samveasnae, the phylogenetic position of which is mysterious) with which it appears to form a superspecies
. However mtDNA cytochrome b
and NADH dehydrogenase
subunit
2 sequence
data suggests that the White Wagtail is itself polyphyletic or paraphyletic (i.e. the species is not itself a single coherent grouping). Other phylogenetic studies using mtDNA however suggest that there is considerable gene flow within the races and the resulting closeness makes Motacilla alba a single species. Some studies have suggested the existence of only two groups : the alboides group, with M. a. alboides, M. a. leucopsis and M. a. personata; and the alba group, with M. a. alba, M. a. yarrellii, M. a. baicalensis, M. a. ocularis, M. a. lugens, and M. a. subpersonata.
Willy Wagtail was a colloquial name used in the Isle of Man
, replacing the older name ushag vreck, as well as a common name used in Northern Ireland
.
There are a number of other subspecies, some of which may have arisen because of partial geographical isolation, such as the resident British form, the Pied Wagtail M. a. yarrellii, which now also breeds in adjacent areas of the neighbouring European mainland. Pied Wagtail, named for naturalist William Yarrell
, exchanges the grey colour of the nominate form with black (or very dark grey in females), but is otherwise identical in its behaviour. Other subspecies, the validity of some of which is questionable, differ in the colour of the wings, back, and head, or other features. Some races show sexual dimorphism
during the breeding season. As many as six subspecies may be present in the wintering ground in India or Southeast Asia and here they can be difficult to distinguish. Phylogenetic studies using mtDNA suggest that some morphological features have evolved more than once including the back and chin colour. Breeding M. a. yarrellii look much like the nominate race except for the black back, and M. a. alboides of the Himalayas differs from the Central Asian M. a. personata only by its black back. M. a. personata has been recorded breeding in the Siddar Valley of Kashmir of the Western Himalayas. It has also been noted that both back and chin change colour during the pre-basic moult
; all black-throated subspecies develop white chins and throats in winter and some black-backed birds are grey-backed in winter.
The call of the White Wagtail is a sharp chisick, slightly softer than the version given by Pied Wagtail. The song is a pleasant twittering, more regular in White than Pied, but with little territorial significance, since the male uses a series of contact calls to attract the female.
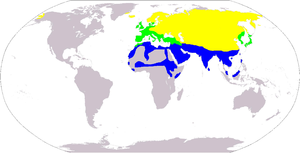 This species breeds throughout Eurasia up to latitudes 75°N, only being absent in the Arctic
This species breeds throughout Eurasia up to latitudes 75°N, only being absent in the Arctic
from areas where the July isotherm is less than 4 °C. It also breeds in the mountains of Morocco
and western Alaska
. It occupies a wide range of habitats, but is absent from deserts.
White Wagtail is resident in the milder parts of its range such as western Europe and the Mediterranean, but migratory
in much of the rest of its range. Northern European breeders winter around the Mediterranean and in tropical and subtropical Africa
, and Asiatic birds move to the Middle East
, India
, and SouthEast Asia
. Birds from the North American population also winter in tropical Asia.
s and other small invertebrates form the major part of the diet. These range from beetle
s, dragonflies
, small snails, spiders, worms, crustaceans, to maggots found in carcasses and, most importantly, flies
in the order Diptera. Small fish fry have also been recorded in the diet. The White Wagtail is somewhat unusual in the parts of it range where it is non-migratory as it is an insectivorous bird that continues to feed on insects during the winter (most other insectivorous birds in temperate climates migrate or switch to more vegetable matter).
and defend breeding territories
. The breeding season for most is from April to August, with the season starting later further north. Both sexes are responsible for building the nest
, with the male responsible for initiating the nest building and the female for finishing the process. For second broods in the subspecies personata the female alone builds the nest as the male is still provisioning the young. which is a rough cup assembled from twigs, grass, leaves and other plant matter. It is lined with soft materials, including animal hair. The nest is set into a crevice or hole; traditionally in a bank next to a river or ditch, but the species has also adapted to nesting in walls, bridges and buildings. One nest was found in the skull of a walrus. They species will nest in association with other animals, particularly where available the dams of beaver
s and also inside the nests of Golden Eagle
s. Around 3-8 eggs are laid, with the usual number being 4-6. Its eggs
are cream-coloured, often with a faint bluish-green or turquoise tint, and heavily spotted with reddish brown; they measure, on average, 21 x 15 mm (0.83 x 0.59 inches). Both parents incubate
the eggs, although the female generally does so for longer and incubates at night. The eggs begin to hatch after 12 days (sometimes as late as 16 days). Both parents feed the chicks until they fledge
at around 14 days, and the chicks are fed for another week after fledging.
Though it is known to be a host species for the Common Cuckoo
, the White Wagtail typically deserts its nest if it has been parasitised. Scientists theorise that this occurs because the wagtail is too small to push the intruding egg out of the nest, and too short-billed to destroy the egg by puncturing it.
African Pied Wagtail
The African Pied Wagtail is a species of bird in the Motacillidae family.-Habitat and distribution:It is found in Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Egypt, Equatorial...
.
The White Wagtail (Motacilla alba) is a small passerine
Passerine
A passerine is a bird of the order Passeriformes, which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds or, less accurately, as songbirds, the passerines form one of the most diverse terrestrial vertebrate orders: with over 5,000 identified species, it has roughly...
bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
in the wagtail
Wagtail
The wagtails form the passerine bird genus Motacilla. They are small birds with long tails which they wag frequently. Motacilla, the root of the family and genus name, means moving tail...
family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Motacillidae, which also includes the pipit
Pipit
The pipits are a cosmopolitan genus, Anthus, of small passerine birds with medium to long tails. Along with the wagtails and longclaws, the pipits make up the family Motacillidae...
s and longclaw
Longclaw
The longclaws are a genus of small African passerine birds with long tails, which they wag frequently. They are in the same family as the pipits and wagtails.Longclaws are slender, often colorful, ground-feeding insectivores of open country...
s. This species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
breeds in much of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and parts of north Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. It is resident in the mildest parts of its range, but otherwise migrates
Bird migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal journey undertaken by many species of birds. Bird movements include those made in response to changes in food availability, habitat or weather. Sometimes, journeys are not termed "true migration" because they are irregular or in only one direction...
to Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. It has a toehold in Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
as a scarce breeder. In some areas, notably Britain and Ireland, the sub-species Pied Wagtail (M. a. yarrellii) predominates.
This is an insectivorous bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
of open country, often near habitation and water. It prefers bare areas for feeding, where it can see and pursue its prey. In urban areas it has adapted to foraging on paved areas such as car parks. It nests in crevices in stone walls and similar natural and man-made structures.
The White Wagtail is the national bird of Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
.
Taxonomy and systematics

Carolus Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus , also known after his ennoblement as , was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, who laid the foundations for the modern scheme of binomial nomenclature. He is known as the father of modern taxonomy, and is also considered one of the fathers of modern ecology...
in his 18th century work, Systema Naturae
Systema Naturae
The book was one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carolus Linnaeus. The first edition was published in 1735...
, and it still bears its original name of Motacilla alba. The Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
genus name originally meant "little mover", but certain medieval writers thought it meant "wag-tail", giving rise to a new Latin word cilla for "tail". The specific epithet alba is Latin for "white".
Within the wagtail genus Motacilla, the White Wagtail's closest relatives appear to be other black-and-white wagtails such as the Japanese Wagtail
Japanese Wagtail
The Japanese Wagtail, Motacilla grandis, is a species of bird in the pipit and wagtail family Motacillidae. It breeds in Japan and Korea. Vagrant birds have been recorded in Taiwan, eastern China and far-eastern Russia. In Japan, it is generally common from Kyushu northward, but uncommon in...
, Motacilla grandis, and the White-browed Wagtail
White-browed Wagtail
The White-browed Wagtail or Large Pied Wagtail is a medium-sized bird and is the largest member of the wagtail family. They are conspicuously patterned with black above and white below, a prominent white brow, shoulder stripe and outer tail feathers...
, Motacilla madaraspatensis, (and possibly the Mekong Wagtail
Mekong Wagtail
The Mekong Wagtail is a species of bird in the Motacillidae family.It is found in Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand.Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist shrubland and rivers....
, Motacilla samveasnae, the phylogenetic position of which is mysterious) with which it appears to form a superspecies
Superspecies
A superspecies is a group of at least two more or less distinctive species with approximately parapatric distributions. Not all species complexes, whether cryptices or ring species are superspecies, and vice versa, but many are...
. However mtDNA cytochrome b
Cytochrome b
Cytochrome b/b6 is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes. In addition, it commonly refers to a region of mtDNA used for population genetics and phylogenetics.- Function :...
and NADH dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q...
subunit
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
2 sequence
DNA sequence
The sequence or primary structure of a nucleic acid is the composition of atoms that make up the nucleic acid and the chemical bonds that bond those atoms. Because nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are unbranched polymers, this specification is equivalent to specifying the sequence of...
data suggests that the White Wagtail is itself polyphyletic or paraphyletic (i.e. the species is not itself a single coherent grouping). Other phylogenetic studies using mtDNA however suggest that there is considerable gene flow within the races and the resulting closeness makes Motacilla alba a single species. Some studies have suggested the existence of only two groups : the alboides group, with M. a. alboides, M. a. leucopsis and M. a. personata; and the alba group, with M. a. alba, M. a. yarrellii, M. a. baicalensis, M. a. ocularis, M. a. lugens, and M. a. subpersonata.
Willy Wagtail was a colloquial name used in the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
, replacing the older name ushag vreck, as well as a common name used in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
.
Description
This is a slender bird, 16.5–19 cm (6½–7½ in) in length (East Asian subspecies are longer, to 21 cm (8¼ in), with the characteristic long, constantly wagging tail of its genus. The nominate subspecies Motacilla alba alba is basically grey above and white below, with a white face, black cap and black throat.There are a number of other subspecies, some of which may have arisen because of partial geographical isolation, such as the resident British form, the Pied Wagtail M. a. yarrellii, which now also breeds in adjacent areas of the neighbouring European mainland. Pied Wagtail, named for naturalist William Yarrell
William Yarrell
William Yarrell was an English bookseller and naturalist.Yarrell is best known as the author of The History of British Fishes and The History of British Birds . The latter went into several editions and was the standard reference work for a generation of British ornithologists...
, exchanges the grey colour of the nominate form with black (or very dark grey in females), but is otherwise identical in its behaviour. Other subspecies, the validity of some of which is questionable, differ in the colour of the wings, back, and head, or other features. Some races show sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is a phenotypic difference between males and females of the same species. Examples of such differences include differences in morphology, ornamentation, and behavior.-Examples:-Ornamentation / coloration:...
during the breeding season. As many as six subspecies may be present in the wintering ground in India or Southeast Asia and here they can be difficult to distinguish. Phylogenetic studies using mtDNA suggest that some morphological features have evolved more than once including the back and chin colour. Breeding M. a. yarrellii look much like the nominate race except for the black back, and M. a. alboides of the Himalayas differs from the Central Asian M. a. personata only by its black back. M. a. personata has been recorded breeding in the Siddar Valley of Kashmir of the Western Himalayas. It has also been noted that both back and chin change colour during the pre-basic moult
Plumage
Plumage refers both to the layer of feathers that cover a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage vary between species and subspecies and can also vary between different age classes, sexes, and season. Within species there can also be a...
; all black-throated subspecies develop white chins and throats in winter and some black-backed birds are grey-backed in winter.
The call of the White Wagtail is a sharp chisick, slightly softer than the version given by Pied Wagtail. The song is a pleasant twittering, more regular in White than Pied, but with little territorial significance, since the male uses a series of contact calls to attract the female.
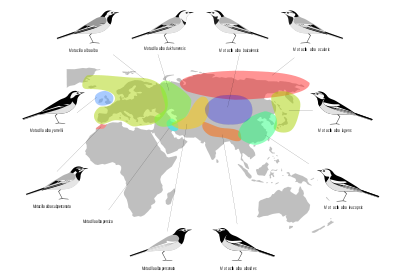
Subspecies
Nine or eleven subspecies are currently recognised. Information on the plumage differences and distribution of the subspecies of White Wagtail is shown below.| Subspecies | Range | Notes | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. a. alba | Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... from the Iberian Peninsula Iberian Peninsula The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar... to Ural Mountains Ural Mountains The Ural Mountains , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and northwestern Kazakhstan. Their eastern side is usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia... , Turkey, the Levant, Iceland Iceland Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population... , the Faroe Islands Faroe Islands The Faroe Islands are an island group situated between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately halfway between Scotland and Iceland. The Faroe Islands are a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark proper and Greenland... and Greenland Greenland Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for... 's east coast. Some migrate to the south of Europe and Africa down as far as Kenya Kenya Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east... and Malawi Malawi The Republic of Malawi is a landlocked country in southeast Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the northwest, Tanzania to the northeast, and Mozambique on the east, south and west. The country is separated from Tanzania and Mozambique by Lake Malawi. Its size... |
Nominate subspecies |  |
| M. a. yarrellii | Great Britain Great Britain Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles... and Ireland Ireland Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth... , birds in the northern part of the range winter in Spain and North Africa, those further south are resident. |
Pied Wagtail. Has a much blacker back than the nominate race, black of throat continues on side of neck |  |
| M. a. dukhunensis | West Siberian Plain West Siberian Plain The West Siberian Plain is a large plain that occupies the western portion of Siberia, between the Ural Mountains in the west and the Yenisei River in the east, and by the Altay Mountains on the South-East. Much of the plain is poorly drained and consists of some of the world's largest swamps and... - east Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... (part of Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... , Kazakhstan Kazakhstan Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe... , Uzbekistan Uzbekistan Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south.... , Turkmenistan Turkmenistan Turkmenistan , formerly also known as Turkmenia is one of the Turkic states in Central Asia. Until 1991, it was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union, the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic . Turkmenistan is one of the six independent Turkic states... ), winters in the Middle East and India. Sometimes included in alba. |
Indian Pied Wagtail. The upperparts of this subspecies are paler and more blue-grey than nominate, and has it has a continuous unbroken white panel on wing coverts. | |
| M. a. persica | North central and western Iran Iran Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia... . |
Intermediate between M. a. dukhunensis and M. a. personata. Often included in alba; appears to be hybrid or intergrade population. | |
| M. a. subpersonata | Non-migratory resident of Morocco Morocco Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara... |
Moroccan Wagtail. It has more black on the head than the nominate, and resembles a grey-backed, white-throated African Pied Wagtail African Pied Wagtail The African Pied Wagtail is a species of bird in the Motacillidae family.-Habitat and distribution:It is found in Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Egypt, Equatorial... |
|
| M. a. personata | Hindu Kush Hindu Kush The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a... , Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... , Altay Mountains Altay Mountains The Altai Mountains are a mountain range in East-Central Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan come together, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their sources. The Altai Mountains are known as the original locus of the speakers of Turkic as well as other members of the proposed... (northern Iran Iran Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia... , Afghanistan Afghanistan Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world... , Tajikistan Tajikistan Tajikistan , officially the Republic of Tajikistan , is a mountainous landlocked country in Central Asia. Afghanistan borders it to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, and China to the east.... , Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan , officially the Kyrgyz Republic is one of the world's six independent Turkic states . Located in Central Asia, landlocked and mountainous, Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the southwest and China to the east... , Kazakhstan Kazakhstan Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe... , Xinjiang Xinjiang Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2... ) |
Masked Wagtail. All-black head with a white face mask | _at_hodal-_i_img_9164.jpg) |
| M. a. alboides | Himalayas Himalayas The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau... and surrounding area |
This subspecies has a black back and a lot of black around the head, a white wing panel and white edges on the secondaries and tertials. | |
| M. a. baicalensis | Russia in Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... area, Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... , Inner Mongolia Inner Mongolia Inner Mongolia is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in the northern region of the country. Inner Mongolia shares an international border with the countries of Mongolia and the Russian Federation... |
Resembles M. a. leucopsis but grey back and less white on head and wing. | |
| M. a. ocularis | Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , Far Eastern Far Eastern Federal District The Far Eastern Federal District is the largest of the eight federal districts of Russia, while being also the least populated, with a population of 6,291,900 . The Far Eastern Federal District was established in 2000 by then-President Vladimir Putin and is currently being governed by presidential... (Russia, eastwards from Central Siberian Plateau Central Siberian Plateau The Central Siberian Plateau is made up of sharply demarcated surfaces of varying altitudes occupying most of Siberia between the Yenisei and Lena rivers. It extends over an area of 3.5 million km². The highest point is the Putoran Mountains rising to 1701 m. To the north of the plateau are... ) expanding into West Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
||
| M. a. lugens | Russia Far East (Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... , Khabarovsk Krai Khabarovsk Krai Khabarovsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia , located in the Russian Far East. It lies mostly in the basin of the lower Amur River, but also occupies a vast mountainous area along the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk, an arm of the Pacific Ocean. The administrative center of the krai is the... ), Kamchatka Peninsula Kamchatka Peninsula The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west... , Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... , Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... , Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... (Hokkaidō Hokkaido , formerly known as Ezo, Yezo, Yeso, or Yesso, is Japan's second largest island; it is also the largest and northernmost of Japan's 47 prefectural-level subdivisions. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaido from Honshu, although the two islands are connected by the underwater railway Seikan Tunnel... , Honshū Honshu is the largest island of Japan. The nation's main island, it is south of Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyushu across the Kanmon Strait... ) |
Black-backed Wagtail or Kamchatka/Japanese Pied Wagtail, similar to M. a. yarrellii, but has a black eyestripe and white remiges; might have a claim to constitute a distinct species. |  |
| M. a. leucopsis | China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... , Korean Peninsula Korean Peninsula The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.Until the end of... , Taiwan Taiwan Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following... , Japan (Ryukyu Islands Ryukyu Islands The , also known as the , is a chain of islands in the western Pacific, on the eastern limit of the East China Sea and to the southwest of the island of Kyushu in Japan. From about 1829 until the mid 20th century, they were alternately called Luchu, Loochoo, or Lewchew, akin to the Mandarin... , Kyūshū Kyushu is the third largest island of Japan and most southwesterly of its four main islands. Its alternate ancient names include , , and . The historical regional name is referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands.... ) expanding into Japan (Honshū), Southeast Asia Southeast Asia Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic... , India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... and Oceania Oceania Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago... |
Amur Wagtail | _at_kolkata_i1_img_5597.jpg) |
Distribution and habitat

Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
from areas where the July isotherm is less than 4 °C. It also breeds in the mountains of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
and western Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
. It occupies a wide range of habitats, but is absent from deserts.
White Wagtail is resident in the milder parts of its range such as western Europe and the Mediterranean, but migratory
Bird migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal journey undertaken by many species of birds. Bird movements include those made in response to changes in food availability, habitat or weather. Sometimes, journeys are not termed "true migration" because they are irregular or in only one direction...
in much of the rest of its range. Northern European breeders winter around the Mediterranean and in tropical and subtropical Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, and Asiatic birds move to the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and SouthEast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. Birds from the North American population also winter in tropical Asia.
Status
This species has a large range, with an estimated gextent of more than 10 million km² (3.8 sq mi). The population size is unknown, but it is believed to be large, as the species is described as "common" in at least parts of its range. Population trends have not been quantified, but the species is not believed to approach the thresholds for the population decline criterion of the IUCN Red List (i.e. declining more than 30% in ten years or three generations). For these reasons, the species is evaluated as Least Concern. The population in Europe appears to be stable. The species has adapted well to human changes to the environment, and has in fact exploited human changes such as man-made structures which are used for nesting sites and increased open areas which are used for foraging.. In a number of cities, notably Dublin, large flocks gather in winter to roost.Behaviour
The most conspicuous habit of this species is a near-constant tail wagging, a trait that has given the species, and indeed the genus, its common name. In spite of the ubiquity of this behaviour, the reasons for it are poorly understood. It has been suggested that it may flush prey, or signal submissiveness to other wagtails. A recent study has suggested instead that it is a signal of vigilance to potential predators.Diet and feeding
The exact composition of the diet of White Wagtails varies by location, but terrestrial and aquatic insectInsect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
s and other small invertebrates form the major part of the diet. These range from beetle
Beetle
Coleoptera is an order of insects commonly called beetles. The word "coleoptera" is from the Greek , koleos, "sheath"; and , pteron, "wing", thus "sheathed wing". Coleoptera contains more species than any other order, constituting almost 25% of all known life-forms...
s, dragonflies
Dragonfly
A dragonfly is a winged insect belonging to the order Odonata, the suborder Epiprocta or, in the strict sense, the infraorder Anisoptera . It is characterized by large multifaceted eyes, two pairs of strong transparent wings, and an elongated body...
, small snails, spiders, worms, crustaceans, to maggots found in carcasses and, most importantly, flies
Fly
True flies are insects of the order Diptera . They possess a pair of wings on the mesothorax and a pair of halteres, derived from the hind wings, on the metathorax...
in the order Diptera. Small fish fry have also been recorded in the diet. The White Wagtail is somewhat unusual in the parts of it range where it is non-migratory as it is an insectivorous bird that continues to feed on insects during the winter (most other insectivorous birds in temperate climates migrate or switch to more vegetable matter).
Breeding
White Wagtails are monogamousMonogamy
Monogamy /Gr. μονός+γάμος - one+marriage/ a form of marriage in which an individual has only one spouse at any one time. In current usage monogamy often refers to having one sexual partner irrespective of marriage or reproduction...
and defend breeding territories
Territory (animal)
In ethology the term territory refers to any sociographical area that an animal of a particular species consistently defends against conspecifics...
. The breeding season for most is from April to August, with the season starting later further north. Both sexes are responsible for building the nest
Bird nest
A bird nest is the spot in which a bird lays and incubates its eggs and raises its young. Although the term popularly refers to a specific structure made by the bird itself—such as the grassy cup nest of the American Robin or Eurasian Blackbird, or the elaborately woven hanging nest of the...
, with the male responsible for initiating the nest building and the female for finishing the process. For second broods in the subspecies personata the female alone builds the nest as the male is still provisioning the young. which is a rough cup assembled from twigs, grass, leaves and other plant matter. It is lined with soft materials, including animal hair. The nest is set into a crevice or hole; traditionally in a bank next to a river or ditch, but the species has also adapted to nesting in walls, bridges and buildings. One nest was found in the skull of a walrus. They species will nest in association with other animals, particularly where available the dams of beaver
Beaver
The beaver is a primarily nocturnal, large, semi-aquatic rodent. Castor includes two extant species, North American Beaver and Eurasian Beaver . Beavers are known for building dams, canals, and lodges . They are the second-largest rodent in the world...
s and also inside the nests of Golden Eagle
Golden Eagle
The Golden Eagle is one of the best known birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. Once widespread across the Holarctic, it has disappeared from many of the more heavily populated areas...
s. Around 3-8 eggs are laid, with the usual number being 4-6. Its eggs
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo first begins to develop. In most birds, reptiles, insects, molluscs, fish, and monotremes, an egg is the zygote, resulting from fertilization of the ovum, which is expelled from the body and permitted to develop outside the body until the developing...
are cream-coloured, often with a faint bluish-green or turquoise tint, and heavily spotted with reddish brown; they measure, on average, 21 x 15 mm (0.83 x 0.59 inches). Both parents incubate
Avian incubation
Incubation refers to the process by which certain oviparous animals hatch their eggs, and to the development of the embryo within the egg. The most vital factor of incubation is the constant temperature required for its development over a specific period. Especially in domestic fowl, the act of...
the eggs, although the female generally does so for longer and incubates at night. The eggs begin to hatch after 12 days (sometimes as late as 16 days). Both parents feed the chicks until they fledge
Fledge
Fledge is the stage in a young bird's life when the feathers and wing muscles are sufficiently developed for flight. It also describes the act of a chick's parents raising it to a fully grown state...
at around 14 days, and the chicks are fed for another week after fledging.
Though it is known to be a host species for the Common Cuckoo
Common Cuckoo
The Common Cuckoo is a member of the cuckoo order of birds, Cuculiformes, which includes the roadrunners, the anis and the coucals....
, the White Wagtail typically deserts its nest if it has been parasitised. Scientists theorise that this occurs because the wagtail is too small to push the intruding egg out of the nest, and too short-billed to destroy the egg by puncturing it.
External links
- Wagtail videos, photos & sounds on the Internet Bird Collection
- Norwegian Cyberbirding: Masked, Pied & White Wagtails photos. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- Romani Rise: Pied Wagtail - the Gipsy Bird Pied Wagtails in Welsh Romani culture. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- identification article with pictures (pdf)
- Ageing and sexing (PDF) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta

