
Wilmot Proviso
Encyclopedia

The Wilmot Proviso, one of the major events leading to the Civil War
Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War
The events which led to the origins of the American Civil War and to the Civil War itself may be considered in two time periods, the long term build up over many decades and the five-month build up to war in the period immediately after the election of Abraham Lincoln as President and the fall of...
, would have banned slavery
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
in any territory to be acquired from Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
in the Mexican War
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known as the First American Intervention, the Mexican War, or the U.S.–Mexican War, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848 in the wake of the 1845 U.S...
or in the future, including the area later known as the Mexican Cession
Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession of 1848 is a historical name in the United States for the region of the present day southwestern United States that Mexico ceded to the U.S...
, but which some proponents construed to also include the disputed lands in south Texas and New Mexico east of the Rio Grande.
Congressman David Wilmot
David Wilmot
David Wilmot was a U.S. political figure. He was a sponsor and eponym of the Wilmot Proviso which aimed to ban slavery in land gained from Mexico in the Mexican-American War of 1846–1848. Wilmot was a Democrat, a Free Soiler, and a Republican during his political career...
first introduced the Proviso in the United States House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
on August 8, 1846
29th United States Congress
-House of Representatives:During this congress, two House seats were added for each of the new states of Texas and Iowa.-Leadership:-Senate:* President: George M. Dallas * President pro tempore: Willie P. Mangum...
as a rider
Rider (legislation)
In legislative procedure, a rider is an additional provision added to a bill or other measure under the consideration by a legislature, having little connection with the subject matter of the bill. Riders are usually created as a tactic to pass a controversial provision that would not pass as its...
on a $2,000,000 appropriations bill intended for the final negotiations to resolve the Mexican–American War
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known as the First American Intervention, the Mexican War, or the U.S.–Mexican War, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848 in the wake of the 1845 U.S...
. (In fact this was only three months into the two-year war.)
It passed the House but failed in the Senate, where the South had greater representation.
It was reintroduced in February 1847 and again passed the House and failed in the Senate.
In 1848, an attempt to make it part of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo is the peace treaty, largely dictated by the United States to the interim government of a militarily occupied Mexico City, that ended the Mexican-American War on February 2, 1848...
also failed.
Sectional conflict over slavery in the Southwest continued up to the Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five bills, passed in September 1850, which defused a four-year confrontation between the slave states of the South and the free states of the North regarding the status of territories acquired during the Mexican-American War...
.
Background
After an earlier attempt to acquire TexasRepublic of Texas
The Republic of Texas was an independent nation in North America, bordering the United States and Mexico, that existed from 1836 to 1846.Formed as a break-away republic from Mexico by the Texas Revolution, the state claimed borders that encompassed an area that included all of the present U.S...
by treaty had failed to receive the necessary two-thirds approval of the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
, the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
annexed the Republic of Texas
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas was an independent nation in North America, bordering the United States and Mexico, that existed from 1836 to 1846.Formed as a break-away republic from Mexico by the Texas Revolution, the state claimed borders that encompassed an area that included all of the present U.S...
by a joint resolution of Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
that required simply a majority vote in each house of Congress. President John Tyler
John Tyler
John Tyler was the tenth President of the United States . A native of Virginia, Tyler served as a state legislator, governor, U.S. representative, and U.S. senator before being elected Vice President . He was the first to succeed to the office of President following the death of a predecessor...
signed the bill on March 1, 1845 on the last day of his presidency. As many expected, the annexation led to war with Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
. After the capture of New Mexico and California
Treaty of Cahuenga
The Treaty of Cahuenga, also called the "Capitulation of Cahuenga," ended the fighting of the Mexican-American War in Alta California in 1847. It was not a formal treaty between nations but an informal agreement between rival military forces in which the Californios gave up fighting...
in the first phases of the war, the political focus shifted to how much territory would be acquired from Mexico. Key to this was the determination of the future status of slavery in any new territory.
Both major political parties had labored long to keep divisive slavery issues out of national politics. The Democrats had generally been successful in portraying those within their party attempting to push a purely sectional issue as extremists that were well outside the normal scope of traditional politics. However, midway through Polk’s term, Democratic dissatisfaction with the administration was growing within the Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren was the eighth President of the United States . Before his presidency, he was the eighth Vice President and the tenth Secretary of State, under Andrew Jackson ....
, or Barnburner, wing of the Democratic Party over other issues. Many felt that Van Buren had been unfairly denied the party’s nomination in 1844 when southern delegates resurrected a convention rule, last used in 1832, requiring that the nominee had to receive two-thirds of the delegate votes. Many in the North were also upset with the Walker tariff
Walker tariff
The Walker Tariff was a set of tariff rates adopted by the United States in 1846. The Walker Tariff was enacted by the Democrats, and made substantial cuts in the high rates of the "Black Tariff" of 1842, enacted by the Whigs. It was based on a report by Secretary of the Treasury Robert J. Walker...
which reduced the tariff rates; others were opposed to Polk’s veto of a popular river and harbor improvements bill, and still others were upset over the Oregon settlement
Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to the Oregon Country, which had been jointly occupied by...
with Great Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
where it appeared that Polk did not pursue the northern territory with the same vigor he used to acquire Texas. Polk was seen more and more as enforcing strict party loyalty primarily to serve southern interests.

James K. Polk
James Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee...
(Democrat) over Henry Clay
Henry Clay
Henry Clay, Sr. , was a lawyer, politician and skilled orator who represented Kentucky separately in both the Senate and in the House of Representatives...
(Whig)
Whig Party (United States)
The Whig Party was a political party of the United States during the era of Jacksonian democracy. Considered integral to the Second Party System and operating from the early 1830s to the mid-1850s, the party was formed in opposition to the policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic...
in the 1844 presidential election had caught the southern Whigs by surprise. The key element of this defeat, which carried over into the congressional and local races in 1845 and 1846 throughout the South, was the party’s failure to take a strong stand favoring Texas annexation. Southern Whigs were reluctant to repeat their mistakes on Texas, but, at the same time, Whigs from both sections realized that victory and territorial acquisition would again bring out the issue of slavery and the territories. In the South in particular, there was already the realization, or perhaps fear, that the old economic issues that had defined the Second Party System
Second Party System
The Second Party System is a term of periodization used by historians and political scientists to name the political party system existing in the United States from about 1828 to 1854...
were already dead. Their political goal was to avoid any sectional debate over slavery which would expose the sectional divisions within the party.
Introduction and debate on the proviso
On Saturday August 8, 1846 President Polk submitted to Congress a request for $2,000,000 in order to facilitate negotiations with MexicoMexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
over the final settlement of the war. The request came with no public warning after Polk had failed to arrange for approval of the bill with no Congressional debate. With Congress scheduled to adjourn that Monday, Democratic leadership arranged for the bill to be immediately considered in a special night session. Debate was to be limited to two hours with no individual speech to last more than ten minutes.
David Wilmot
David Wilmot
David Wilmot was a U.S. political figure. He was a sponsor and eponym of the Wilmot Proviso which aimed to ban slavery in land gained from Mexico in the Mexican-American War of 1846–1848. Wilmot was a Democrat, a Free Soiler, and a Republican during his political career...
, a Democratic congressman from Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, and a group of other Barnburner Democrats
Barnburners and Hunkers
The Barnburners were the more radical faction of the New York state Democratic Party in the mid 19th century. The term barnburner was derived from the idea of someone who would burn down his own barn to get rid of a rat infestation, in this case those who would destroy all banks and corporations,...
including Preston King
Preston King
Preston King was a United States Representative and Senator from New York.- Biography :Born in Ogdensburg, New York, he pursued classical studies and graduated from Union College in 1827, where he was an early member of The Kappa Alpha Society. He studied law and was admitted to the bar. He...
of New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, Hannibal Hamlin
Hannibal Hamlin
Hannibal Hamlin was the 15th Vice President of the United States , serving under President Abraham Lincoln during the American Civil War...
of Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
, Gideon Welles
Gideon Welles
Gideon Welles was the United States Secretary of the Navy from 1861 to 1869. His buildup of the Navy to successfully execute blockades of Southern ports was a key component of Northern victory of the Civil War...
of Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
, and Jacob Brinkerhoff
Jacob Brinkerhoff
Jacob Brinkerhoff was an American jurist, Congressman, and author of the Wilmot Proviso.Brinkerhoff was born in Niles, Cayuga County, New York. He was schooled at the academy at Prattsburgh, New York, and studied law in the office of Howell and Bro...
of Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
, had already been meeting in early August strategy meetings. Wilmot had a strong record of supporting the Polk administration and was close to many Southerners. With the likelihood that Wilmot would have no trouble gaining the floor in the House debate, he was chosen to present the amendment to the appropriations bill that would carry his name. Wilmot offered the following to the House in language modeled after the Northwest Ordinance
Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance was an act of the Congress of the Confederation of the United States, passed July 13, 1787...
of 1787:
Provided, That, as an express and fundamental condition to the acquisition of any territory from the Republic of Mexico by the United States, by virtue of any treaty which may be negotiated between them, and to the use by the Executive of the moneys herein appropriated, neither slavery nor involuntary servitude shall ever exist in any part of said territory, except for crime, whereof the party shall first be duly convicted.
William W. Wick
William W. Wick
William Watson Wick was a U.S. Representative from Indiana.The son of Presbyterian Minister the Rev. William Wick, and his wife Elizabeth the daughter of an officer in the Continental Army; the younger Mr...
, Democrat of Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
, attempted to eliminate total restriction of slavery by proposing an amendment that the Missouri Compromise line of latitude 36°30' simply be extended west to the Pacific
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. This was voted down 89–54. The vote to add the proviso to the bill was then called, and it passed by 83–64. A last ditch effort by southerners to table the entire bill was defeated by 94–78, and then the entire bill was approved 85–80. Most ominously, these votes all fell overwhelmingly along sectional rather than party lines.
The Senate took up the bill late in its Monday session. Democrats hoped to reject the Wilmot Proviso and send the bill back to the House for a quick approval of the bill without the restrictions on slavery. Whig John Davis
John Davis (Massachusetts Governor)
John Davis was an American lawyer, businessman and politician.-Early life:John Davis was born in Northborough, Massachusetts...
of Massachusetts attempted to forestall this effort by holding the floor until it would be too late to return the bill to the House, forcing the Senate to accept or reject the appropriation with the proviso intact. However, before he could call the vote, due to an eight minute difference in the official House and Senate clocks, the House had adjourned and the Congress was officially out of session.
The issue resurfaced at the end of the year when Polk, in his annual message to Congress, renewed his request with the amount needed increased to three million dollars. Polk argued that, while the original intent of the war had never been to acquire territory (a view hotly contested by his opponents), an honorable peace required territorial compensation to the United States. The Three Million Dollar Bill, as it was called, was the sole item of business in the House from February 8, 1847 until February 15. Preston King reintroduced the Wilmot Proviso, but this time the exclusion of slavery was expanded beyond merely the Mexican territory to include "any territory on the continent of America which shall hereafter be acquired". This time Representative Stephen Douglas, Democrat of Illinois, reintroduced the proposal to simply extend the Missouri Compromise
Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was an agreement passed in 1820 between the pro-slavery and anti-slavery factions in the United States Congress, involving primarily the regulation of slavery in the western territories. It prohibited slavery in the former Louisiana Territory north of the parallel 36°30'...
line to the west coast, and this was again defeated 109–82. The Three Million Bill with the proviso was then passed by the House 115–106. In the Senate, led by Thomas Hart Benton
Thomas Hart Benton (senator)
Thomas Hart Benton , nicknamed "Old Bullion", was a U.S. Senator from Missouri and a staunch advocate of westward expansion of the United States. He served in the Senate from 1821 to 1851, becoming the first member of that body to serve five terms...
(Democrat), the bill was passed without the proviso. When the bill was returned to the House the Senate bill prevailed; every Northern Whig still supported the proviso, but 22 northern Democrats voted with the South.
In 1848, the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo is the peace treaty, largely dictated by the United States to the interim government of a militarily occupied Mexico City, that ended the Mexican-American War on February 2, 1848...
ending the war was submitted to the Senate for approval. Douglas, now in the Senate, was among those who joined with the South to defeat an effort to attach the Wilmot Proviso to the treaty. In the prior year's debate in the House Douglas had argued that all of the debate over slavery in the territories was premature; the time to deal with that issue was when the territory was actually organized by Congress. Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass was an American military officer and politician. During his long political career, Cass served as a governor of the Michigan Territory, an American ambassador, a U.S. Senator representing Michigan, and co-founder as well as first Masonic Grand Master of the Grand Lodge of Michigan...
(Democrat) in December 1847, in his famous letter to A. O. P. Nicholson in Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
, further defined the concept of popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty or the sovereignty of the people is the political principle that the legitimacy of the state is created and sustained by the will or consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. It is closely associated with Republicanism and the social contract...
which would soon evolve as the mainstream Democratic alternative to the Wilmot Proviso:
Leave it to the people, who will be affected by this question to adjust it upon their own responsibility, and in their own manner, and we shall render another tribute to the original principles of our government, and furnish another for its permanence and prosperity.
Aftermath
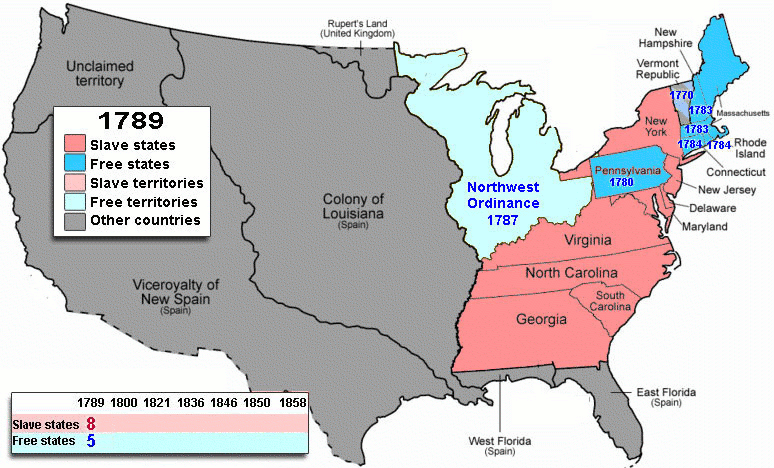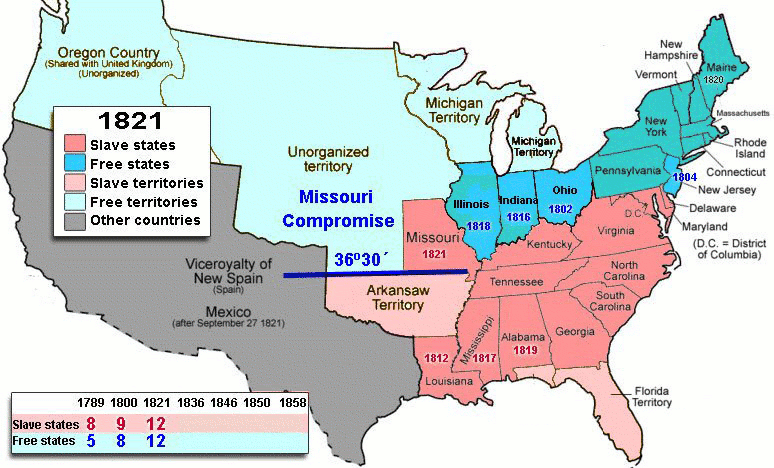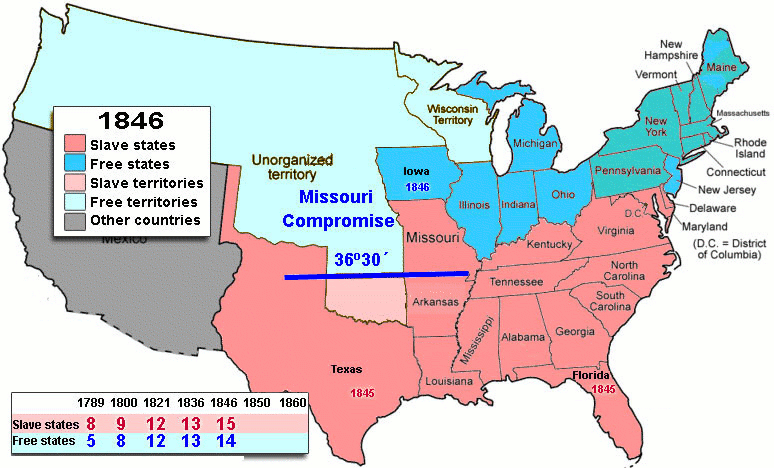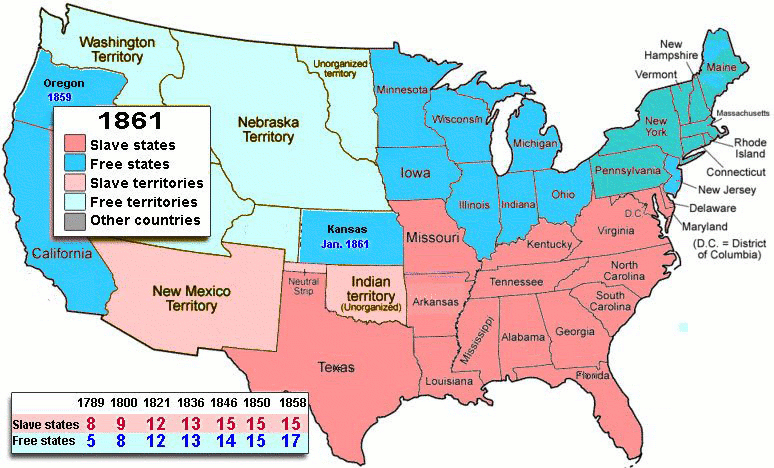
In the North, the most immediate repercussions involved Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren was the eighth President of the United States . Before his presidency, he was the eighth Vice President and the tenth Secretary of State, under Andrew Jackson ....
and the state of New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
. The Barnburners
Barnburners and Hunkers
The Barnburners were the more radical faction of the New York state Democratic Party in the mid 19th century. The term barnburner was derived from the idea of someone who would burn down his own barn to get rid of a rat infestation, in this case those who would destroy all banks and corporations,...
were successfully opposed by their conservative opposition, the Hunkers
Barnburners and Hunkers
The Barnburners were the more radical faction of the New York state Democratic Party in the mid 19th century. The term barnburner was derived from the idea of someone who would burn down his own barn to get rid of a rat infestation, in this case those who would destroy all banks and corporations,...
, in their efforts to send a pro-proviso batch of delegates to the 1848 Democratic National Convention. The Barnburners held their own separate convention and sent their own slate of delegates to the convention in Baltimore. Both delegations were seated with the state's total votes split between them. When the convention rejected a pro-proviso plank and selected Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass was an American military officer and politician. During his long political career, Cass served as a governor of the Michigan Territory, an American ambassador, a U.S. Senator representing Michigan, and co-founder as well as first Masonic Grand Master of the Grand Lodge of Michigan...
as the nominee, the Barnburners again bolted and were the nucleus of forming the Free Soil Party
Free Soil Party
The Free Soil Party was a short-lived political party in the United States active in the 1848 and 1852 presidential elections, and in some state elections. It was a third party and a single-issue party that largely appealed to and drew its greatest strength from New York State. The party leadership...
. Historian Leonard Richards writes of these disaffected Democrats:
Overall, then, Southern Democrats during the 1840s lost the hard core of their original doughfaceDoughfaceThe term doughface originally referred to an actual mask made of dough, but came to be used in a disparaging context for someone, especially a politician, who is perceived to be pliable and moldable...
support. No longer could they count on New England and New York Democrats to provide them with winning margins in the House. …
To them [Free Soil Democrats] the movement to acquire Texas, and the fight over the Wilmot Proviso, marked the turning point, when aggressive slavemasters stole the heart and soul of the Democratic Party and began dictating the course of the nation’s destiny.
Historian William Cooper presents the exactly opposite southern perspective:
Southern Democrats, for whom slavery had always been central, had little difficulty in perceiving exactly what the proviso meant for them and their party. In the first place the mere existence of the proviso meant the sectional strains that had plagued the Whigs on Texas now beset the Democrats on expansion, the issue the Democrats themselves had chosen as their own. The proviso also announced to southerners that they had to face the challenge of certain northern Democrats who indicated their unwillingness to follow any longer the southern lead on slavery. That circumstance struck at the very roots of the southern conception of party. The southerners had always felt that their northern colleagues must toe the southern line on all slavery-related issues.
In Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, with no available candidate sufficiently opposed to the proviso, William L. Yancey
William Lowndes Yancey
William Lowndes Yancey was a journalist, politician, orator, diplomat and an American leader of the Southern secession movement. A member of the group known as the Fire-Eaters, Yancey was one of the most effective agitators for secession and rhetorical defenders of slavery. An early critic of...
secured the adoption by the state Democratic convention of the so-called "Alabama Platform", which was endorsed by the legislatures of Alabama and Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
and by Democratic state conventions in Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
and Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
. The platform called for no Federal restrictions of slavery in the territories, no restrictions on slavery by territorial governments until the point where they were drafting a state constitution in order to petition Congress for statehood, opposition to any candidates supporting either the proviso or popular sovereignty, and positive federal legislation overruling Mexican anti-slavery laws in the Mexican Cession. However the same Democratic Convention that had refused to endorse the proviso also rejected incorporating the Yancey proposal into the national platform by a 216–36 vote. Unlike the Barnburner walkout, however, only Yancey and one other Alabama delegate left the convention. Yancey’s efforts to stir up a third party movement in the state failed.
Southerner Whigs looked hopefully to slaveholder and war hero General Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor was the 12th President of the United States and an American military leader. Initially uninterested in politics, Taylor nonetheless ran as a Whig in the 1848 presidential election, defeating Lewis Cass...
as the solution to the widening sectional divide even though he took no public stance on the Wilmot Proviso. However Taylor, once nominated and elected, showed that he had his own plans. Taylor hoped to create a new non-partisan coalition that would once again remove slavery from the national stage. He expected to be able to accomplish this by freezing slavery at its 1849 boundaries and by immediately bypassing the territory stage and creating two new states out of the Mexican Cession.
The opening salvo in a new level of sectional conflict occurred on December 13, 1848 when John G. Palfrey
John G. Palfrey
John Gorham Palfrey was an American clergyman and historian who served as a U.S. Representative from Massachusetts. A Unitarian minister, he played a leading role in the early history of Harvard Divinity School, and he later became involved in politics as a State Representative and U.S...
(Whig) of Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
introduced a bill to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia. Throughout 1849 in the South "the rhetoric of resistance to the North escalated and spread". The potentially secessionist Nashville Convention
Nashville Convention
The Nashville Convention was a political meeting held in Nashville, Tennessee, on June 3 – 11, 1850. Delegates from nine slave holding states met to consider a possible course of action if the United States Congress decided to ban slavery in the new territories being added to the country as a...
was scheduled for June 1850. When President Taylor
Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor was the 12th President of the United States and an American military leader. Initially uninterested in politics, Taylor nonetheless ran as a Whig in the 1848 presidential election, defeating Lewis Cass...
in his December 1849 message to Congress urged the admission of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
as a free state, a state of crisis was further aggravated. Historian Allan Nevins sums up the situation which had been created by the Wilmot Proviso:
Thus the contest was joined on the central issue which was to dominate all American history for the next dozen years, the disposition of the Territories. Two sets of extremists had arisen: Northerners who demanded no new slave territories under any circumstances, and Southerners who demanded free entry for slavery into all territories, the penalty for denial to be secession. For the time being, moderates who hoped to find a way of compromise and to repress the underlying issue of slavery itself – its toleration or non-toleration by a great free Christian state – were overwhelmingly in the majority. But history showed that in crises of this sort the two sets of extremists were almost certain to grow in power, swallowing up more and more members of the conciliatory center.
Combined with other slavery related issues, the Wilmot Proviso led to the Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five bills, passed in September 1850, which defused a four-year confrontation between the slave states of the South and the free states of the North regarding the status of territories acquired during the Mexican-American War...
, which helped buy another shaky decade of peace. Radical secessionists were temporarily at bay as the Nashville Convention failed to endorse secession. Moderates rallied around the Compromise as the final solution to the sectional issues involving slavery and the territories. At the same time, however, the language of the Georgia Platform
Georgia Platform
The Georgia Platform was a statement executed by a Georgia Convention in response to the Compromise of 1850. Supported by Unionists, the document affirmed the acceptance of the Compromise as a final resolution of the sectional slavery issues while declaring that no further assaults on Southern...
, widely accepted throughout the South, made it clear that the South’s commitment to Union was not unqualified; they fully expected the North to adhere to their part of the agreement.

