XDNA
Encyclopedia
xDNA is a modified form of DNA
with 8 nucleobase
s: the four natural bases A
, C
, G
, and T
, and four artificial modifications of these made longer by the addition of an extra benzene
ring: xA, xC, xG, and xT. A pairs with xT, C pairs with xG, G pairs with xC, and T pairs with xA, so the distance between the two halves of the double helix is consistently greater. The double helix is thus wider and has a longer pitch.
Experiments with xDNA are expected to provide new insight into the behavior of natural DNA. Also, the extended bases xA, xC, xG, and xT are fluorescent
, and single strands composed of only extended bases can recognize and bind to single strands of natural DNA, which could make them useful tools for studying biological systems. The same research group also constructed widened DNA, called yDNA.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
with 8 nucleobase
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
s: the four natural bases A
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
, C
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
, G
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
, and T
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
, and four artificial modifications of these made longer by the addition of an extra benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
ring: xA, xC, xG, and xT. A pairs with xT, C pairs with xG, G pairs with xC, and T pairs with xA, so the distance between the two halves of the double helix is consistently greater. The double helix is thus wider and has a longer pitch.
Experiments with xDNA are expected to provide new insight into the behavior of natural DNA. Also, the extended bases xA, xC, xG, and xT are fluorescent
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
, and single strands composed of only extended bases can recognize and bind to single strands of natural DNA, which could make them useful tools for studying biological systems. The same research group also constructed widened DNA, called yDNA.
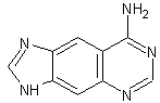
 Size-expanded dxA |
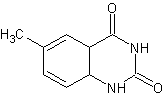 Size-expanded dxT |
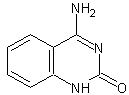 Size-expanded dxC |
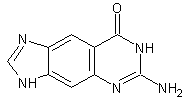 Size-expanded dxG |

