1p36 Deletion Syndrome
Encyclopedia
1p36 deletion syndrome is a congenital
genetic disorder
characterized by moderate to severe intellectual disability
, delayed growth, hypotonia
, seizures, limited speech ability, malformations, hearing and vision impairment, and distinct facial features. The symptoms may vary, depending on the exact location of the chromosomal deletion.
The condition is caused by a genetic deletion
(loss of a segment of DNA) on the outermost band on the short arm (p) of chromosome 1. It is one of the most common deletion syndromes. It is estimated that the syndrome occurs in one in every 5,000 to 10,000 births. Knowledge of the disorder has increased a great deal over the last decade, mainly because more patients have been accurately diagnosed and described in international medical literature.
, small, possibly slanted, deep-set eyes, a flat nose and nasal bridge, anomalous, low-set and small ears, a small mouth with down-turned corners and a pointed chin. Distinguishing features in another study were a large or late-closing anterior fontanelle
(up to 85% of patients) and facial asymmetry.
(fluorescent in situ hybridization) and DNA-based technology known as MLPA (multiple ligation probe amplification) used in testing have aided in diagnosing an increasing number of cases since the 1990s.
 The breakpoints for 1p36 Deletion Syndrome have been variable and are most commonly found from 1p36.13 to 1p36.33. 40 percent of all breakpoints occur 3 to 5 million base pair
The breakpoints for 1p36 Deletion Syndrome have been variable and are most commonly found from 1p36.13 to 1p36.33. 40 percent of all breakpoints occur 3 to 5 million base pair
s from the telomere
. The size of the deletion ranges from approximately 1.5 million base pairs to greater than 10 million. Studies have suggested that the larger the deletion, the more severe the symptoms exhibited in the individual, but this has not been proven definitively.
Most deletions in chromosome 1p36 are new mutations, that occur before fertilization, during the formation of gamete
s (eggs or sperm). There have also been reports of patients with 1p36 deletion syndrome whose parents have a balanced or symmetrical translocation. This means a portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome, so the parent has the "36" portion of chromosome 1 attached in an alternate location. When this occurs, cell division creates gametes that are missing a piece of 36.
In new mutations, the mechanism causing chromosome breakage is unknown. Deletions of paternal origin (father) are larger than the deletions deriving from the maternal (mother) chromosome. The majority of deletions are maternally derived. There do not seem to be differences in the clinical manifestations (the symptoms or observable conditions which are seen as a result of 1p36) based on whether the deletion is on the paternal or maternal chromosome.
. They sit up, walk and talk later than typical children. Speech is severely affected, with many patients learning only a few words. It was originally thought that the degree of the delay and the ability to acquire complex speech was somewhat dependent on deletion size. Reports of a milder learning disability
in children with smaller deletions have suggested that there may be a correlation between deletion size and mental ability; however, this requires further investigation and research. Recent research by Dr Lisa Shaffer has shown however that there is no correlation between deletion size and degree of developmental delay. This suggests that the most genetically potent area of the 1P36 chromosome occurs at the terminal end of the chromosome.
Also, some parents have described behaviors such as a love of water, although there have not been any studies into this yet.
which is characterized by difficulty in initiating a swallow. Some of the other feeding issues include poor sucking and swallowing, reflux, and vomiting in infancy. Many require nasalgastric or gastric tubes to ensure they are receiving sufficient nutrition.
, which is a loss of neurons in the brain and the connections between them. Also documented were problems with the ventricular system
in the brain, such as ventricular asymmetry and ventricular enlargement. Hydrocephalus
has also been noted in children with 1p36 deletion syndrome. This is basically too much fluid within the brain. Hyperreflexia
, which is defined as overactive or overresponsive reflexes in the body, was also found to be common. Many children also have epilepsy
which is a disorder of the brain that results in recurrent, unprovoked seizures.
is a disorder in which the circumference of the head is smaller than average for the person's age and gender. Most children with microcephaly also have a small brain and mental retardation. Some of the most common signs and symptoms associated with microcephaly are seizures, poor feeding, high pitched cry, mental retardation, developmental delay, and increased movement of arms and legs.
, which is overeating, and may become obese. These children clinically resemble children with Prader-Willi syndrome
. Developmental delay has also been severe in the patients with the Prader-Willi like characteristics.
affects approximately two thirds of 1p36 deletion patients. It can be of different types. Sensorineural hearing loss
is a type of hearing impairment caused by damage that occurs to the inner ear (cochlea
) or to the nerve used for hearing (vestibulocochlear nerve
). Conductive hearing loss
is a hearing loss associated with the functioning of the outer or middle ear. This type is most common in children with 1p36 deletion syndrome. It ranges from mild loss at various frequencies, to severe loss at all frequencies.
in children with 1p36 deletion syndrome can be early, normal, or delayed.
American Sign Language
: Because few individuals with Monosomy 1p36 develop complex speech, an alternate form of communication is critical to development. Most patients can learn basic signs to communicate their needs and wants. This also appears to reduce frustration and may reduce self-injurious tendencies. Children with hearing loss will often qualify for locally sponsored sign language classes.
Music
: Music has been shown to aid children with 1p36 deletion in various developmental areas. It serves as an excellent auditory stimulus and can teach listening skills. Songs with actions help the child to develop coordination and motor skills.
Physical Therapy
: Due to low muscle tone, patients with 1p36 Deletions take a great deal of time to learn to roll over, sit up, crawl and walk. However, regular physical therapy has shown to shorten the length of time needed to achieve each of those developmental milestones.
Congenital disorder
A congenital disorder, or congenital disease, is a condition existing at birth and often before birth, or that develops during the first month of life , regardless of causation...
genetic disorder
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
characterized by moderate to severe intellectual disability
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
, delayed growth, hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, seizures, limited speech ability, malformations, hearing and vision impairment, and distinct facial features. The symptoms may vary, depending on the exact location of the chromosomal deletion.
The condition is caused by a genetic deletion
Genetic deletion
In genetics, a deletion is a mutation in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is missing. Deletion is the loss of genetic material. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome...
(loss of a segment of DNA) on the outermost band on the short arm (p) of chromosome 1. It is one of the most common deletion syndromes. It is estimated that the syndrome occurs in one in every 5,000 to 10,000 births. Knowledge of the disorder has increased a great deal over the last decade, mainly because more patients have been accurately diagnosed and described in international medical literature.
Characteristics
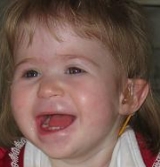
The facial features of 1p36 deletion syndrome have been considered to be characteristic, although few patients have been diagnosed solely on the basis of facial appearance. These features may include microcephalyMicrocephaly
Microcephaly is a neurodevelopmental disorder in which the circumference of the head is more than two standard deviations smaller than average for the person's age and sex. Microcephaly may be congenital or it may develop in the first few years of life...
, small, possibly slanted, deep-set eyes, a flat nose and nasal bridge, anomalous, low-set and small ears, a small mouth with down-turned corners and a pointed chin. Distinguishing features in another study were a large or late-closing anterior fontanelle
Fontanelle
A fontanelle is an anatomical feature on an infant's skull.-Anatomy:Fontanelles are soft spots on a baby's head which, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex, allowing the child's head to pass through the birth canal. The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the...
(up to 85% of patients) and facial asymmetry.
History
The first cases of 1p36 deletion syndrome were described in the 1980s. However, since many of these individuals also had other chromosomal imbalances, symptoms varied widely. The reason it took so long to recognize the condition as a distinct chromosome deletion syndrome is that the deletions causing the disorder are too small to be detected in a routine chromosomal analysis. FISHFluorescent in situ hybridization
FISH is a cytogenetic technique developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s that is used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. FISH uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of the chromosome with which they show a high...
(fluorescent in situ hybridization) and DNA-based technology known as MLPA (multiple ligation probe amplification) used in testing have aided in diagnosing an increasing number of cases since the 1990s.
Genetics
1p36 Deletion Syndrome is a congenital genetic disorder caused by the deletion of the most distal light band of the short arm of chromosome 1. Chromosome 1 is the largest human chromosome and represents about 8 percent of the total DNA in human cells. The "p" stands for the short or 'petite' arm of the chromosome. '36' stands for the location of the deletion on the chromosome.
Base pair
In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair...
s from the telomere
Telomere
A telomere is a region of repetitive DNA sequences at the end of a chromosome, which protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos "end" and merοs "part"...
. The size of the deletion ranges from approximately 1.5 million base pairs to greater than 10 million. Studies have suggested that the larger the deletion, the more severe the symptoms exhibited in the individual, but this has not been proven definitively.
Most deletions in chromosome 1p36 are new mutations, that occur before fertilization, during the formation of gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
s (eggs or sperm). There have also been reports of patients with 1p36 deletion syndrome whose parents have a balanced or symmetrical translocation. This means a portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome, so the parent has the "36" portion of chromosome 1 attached in an alternate location. When this occurs, cell division creates gametes that are missing a piece of 36.
In new mutations, the mechanism causing chromosome breakage is unknown. Deletions of paternal origin (father) are larger than the deletions deriving from the maternal (mother) chromosome. The majority of deletions are maternally derived. There do not seem to be differences in the clinical manifestations (the symptoms or observable conditions which are seen as a result of 1p36) based on whether the deletion is on the paternal or maternal chromosome.
Developmental delay
Most young children with 1p36 deletion syndrome have delayed developmentDevelopmental disability
Developmental disability is a term used in the United States and Canada to describe lifelong disabilities attributable to mental or physical impairments, manifested prior to age 18. It is not synonymous with "developmental delay" which is often a consequence of a temporary illness or trauma during...
. They sit up, walk and talk later than typical children. Speech is severely affected, with many patients learning only a few words. It was originally thought that the degree of the delay and the ability to acquire complex speech was somewhat dependent on deletion size. Reports of a milder learning disability
Learning disability
Learning disability is a classification including several disorders in which a person has difficulty learning in a typical manner, usually caused by an unknown factor or factors...
in children with smaller deletions have suggested that there may be a correlation between deletion size and mental ability; however, this requires further investigation and research. Recent research by Dr Lisa Shaffer has shown however that there is no correlation between deletion size and degree of developmental delay. This suggests that the most genetically potent area of the 1P36 chromosome occurs at the terminal end of the chromosome.
Behavioral differences
Many children with 1p36 deletion syndrome have behavioral problems. Some of these include temper outbursts, banging or throwing objects, striking people, screaming episodes, and self-injurious behavior (wrist biting, head striking/banging). Autistic behavior has also been noted in some children.Also, some parents have described behaviors such as a love of water, although there have not been any studies into this yet.
Feeding difficulties
Many children with 1p36 deletion syndrome have oropharyngeal dysphagiaDysphagia
Dysphagia is the medical term for the symptom of difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, the term is sometimes used as a condition in its own right. Sufferers are sometimes unaware of their dysphagia....
which is characterized by difficulty in initiating a swallow. Some of the other feeding issues include poor sucking and swallowing, reflux, and vomiting in infancy. Many require nasalgastric or gastric tubes to ensure they are receiving sufficient nutrition.
Brain abnormalities
Brain imaging has documented cerebral atrophyCerebral atrophy
Cerebral atrophy is a common feature of many of the diseases that affect the brain. Atrophy of any tissue means loss of cells. In brain tissue, atrophy describes a loss of neurons and the connections between them...
, which is a loss of neurons in the brain and the connections between them. Also documented were problems with the ventricular system
Ventricular system
The ventricular system is a set of structures containing cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. It is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord.-Components:The system comprises four ventricles:* right and left lateral ventricles* third ventricle...
in the brain, such as ventricular asymmetry and ventricular enlargement. Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus , also known as "water in the brain," is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, or cavities, of the brain. This may cause increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and progressive enlargement of the head,...
has also been noted in children with 1p36 deletion syndrome. This is basically too much fluid within the brain. Hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia is defined as overactive or overresponsive reflexes. Examples of this can include twitching or spastic tendencies, which are indicative of upper motor neuron disease as well as the lessening or loss of control ordinarily exerted by higher brain centers of lower neural pathways...
, which is defined as overactive or overresponsive reflexes in the body, was also found to be common. Many children also have epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
which is a disorder of the brain that results in recurrent, unprovoked seizures.
Microcephaly
MicrocephalyMicrocephaly
Microcephaly is a neurodevelopmental disorder in which the circumference of the head is more than two standard deviations smaller than average for the person's age and sex. Microcephaly may be congenital or it may develop in the first few years of life...
is a disorder in which the circumference of the head is smaller than average for the person's age and gender. Most children with microcephaly also have a small brain and mental retardation. Some of the most common signs and symptoms associated with microcephaly are seizures, poor feeding, high pitched cry, mental retardation, developmental delay, and increased movement of arms and legs.
Vision problems
Vision abnormalities in children with 1p36 have been wide-ranging, including:- StrabismusStrabismusStrabismus is a condition in which the eyes are not properly aligned with each other. It typically involves a lack of coordination between the extraocular muscles, which prevents bringing the gaze of each eye to the same point in space and preventing proper binocular vision, which may adversely...
: A condition in which the two eyes do not point in the same direction when the patient is looking at a distant object. - Sixth nerve palsySixth nerve palsySixth nerve palsy, or abducens nerve palsy, is a disorder associated with dysfunction of cranial nerve VI , which is responsible for contracting the lateral rectus muscle to abduct the eye...
: Double vision - Refractive errorRefractive errorA refractive error, or refraction error, is an error in the focusing of light by the eye and a frequent reason for reduced visual acuity.-Classification:...
s: Refractive errors include nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism (a warping of the curvature of the cornea) and presbyopia (the inability to maintain a clear image or focus as objects are moved closer). These disorders of the eye can be corrected with glasses or contacts. - Hypermetropia: A condition where the eye is too small and eyes have to over focus to see clearly; also called farsightedness.
- Cataracts: A cataract is an opacity or cloudiness in the natural lens of the eye.
- Nystagmus: A condition characterized by the repetitive oscillations (vibration) of the eyes. Parents of children with nystagmus often refer to this as "jerking" "or "jiggling" eyes.
- LacrimalLacrimalThe term Lacrimal can refer to:*In typography:** A type of Stroke ending *In anatomy** Lacrimal apparatus** Lacrimal artery** Lacrimal bone...
defects: The lacrimal glands in the eye secrete tears. - Visual Inattentiveness: Defined as an absence of attentive visual behavior such as fixation and following movements.
Distinct facial features
Children with 1p36 deletion syndrome are all unique individuals, but do have some common distinct facial features such as:- Large anterior fontanelle/Frontal bossing: The anterior fontanelle is the "soft spot" towards the front of the top of an infant's head between the growing skull bones. Frontal bossing simply means a prominent forehead.
- Small and pointed chin
- Flat nose and/or nasal bridge
- Low-set, small ears/Ear asymmetry: Ears are abnormally low set on the head and may be small. They may not be the same shape or size, or not lined up.
- Deep set eyes
- Thickened ear helices: Ear helices are the outer rings of cartilage of the ears.
- Short, narrow and slanting palpebral fissures: Palpebral fissures are the gaps between the upper and lower eyelids, or the opening of the eyes.
- Midface Hypoplasia: This is where the middle of the face is underdeveloped, leading to a concave-looking face. The bridge of the nose looks sunken in and the eyes are set widely apart and often protrude out of the sockets.
- Small mouth with down-turned corners
- Orofacial clefting: This is a relatively common birth defect in which the fetus develops with deformities of the upper lip, gum, and roof of the mouth. Children with 1p36 have been noted to have orofacial clefting involving the lip and/or palate or uvula (the small piece of flesh hanging down inside the mouth at the back of the palate).
Growth abnormalities
There are many growth abnormalities associated with 1p36 deletion syndrome. One common problem is delayed growth or difficulty in gaining weight. Even though some of the children may eat well, they still may not grow normally. In contrast, some children may develop hyperphagiaPolyphagia
Polyphagia means "eating too much". It derives from the Greek words πολύς which means "very much", and φαγῶ , verb for "I eat"....
, which is overeating, and may become obese. These children clinically resemble children with Prader-Willi syndrome
Prader-Willi syndrome
Prader–Willi syndrome is a rare genetic disorder in which seven genes on chromosome 15 are deleted or unexpressed on the paternal chromosome...
. Developmental delay has also been severe in the patients with the Prader-Willi like characteristics.
- HypotoniaHypotoniaHypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
: Hypotonia is a decreased or low muscle tone. This may explain the delayed motor skills in children with 1p36. - HypothyroidismHypothyroidismHypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide but it can be caused by other causes such as several conditions of the thyroid gland or, less commonly, the pituitary gland or...
: Hypothyroidism is insufficient production of the thyroid hormone. Symptoms include weight gain, constipation, dry skin, and sensitivity to the cold. Around one third of children with the syndrome have this low thyroid function, which is also called underactive thyroid, and leads to slow metabolism and fatigue. - Heart defects:
- Infantile dilated cardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathy or DCM is a condition in which the heart becomes weakened and enlarged and cannot pump blood efficiently. The decreased heart function can affect the lungs, liver, and other body systems....
: Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a disease of the heart muscle that causes the heart to become enlarged, and to pump less strongly. This causes fluid to build up in the lungs, which therefore become congested, and results in a feeling of breathlessness. Children with DCM due to their 1p36 deletion syndrome typically do not worsen over time, though some of them may need to continue taking medication. - Patent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosus is a congenital disorder in the heart wherein a neonate's ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth. Early symptoms are uncommon, but in the first year of life include increased work of breathing and poor weight gain...
: This is the most common structural heart defect in children with 1p36. It is a condition in which the connecting blood vessel between the pulmonary artery and the aorta in fetal circulation stays open in the newborn. The defect often corrects itself within several months of birth, but may require the infusion of chemicals, the placement of "plugs" via catheters, or surgical closure. - Tetralogy of FallotTetralogy of FallotTetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect which is classically understood to involve four anatomical abnormalities...
: Tetralogy of Fallot includes a ventricular septal defectVentricular septal defectA ventricular septal defect is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart.The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes.The membranous...
, a hole between the two bottom chambers (ventriclesVentricle (heart)In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
) of the heart. These defects can cause less blood flow to the lungs, the mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood inside the heart, and low levels of oxygen in the blood. When oxygen levels are low, the baby's skin, fingertips, or lips have a bluish tint. This condition is called cyanosisCyanosisCyanosis is the appearance of a blue or purple coloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface being low on oxygen. The onset of cyanosis is 2.5 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin. The bluish color is more readily apparent in those with high hemoglobin counts than it is...
.
- Infantile dilated cardiomyopathy
- Increased Risk for NeoplasiaNeoplasiaNeoplasm is an abnormal mass of tissue as a result of neoplasia. Neoplasia is the abnormal proliferation of cells. The growth of neoplastic cells exceeds and is not coordinated with that of the normal tissues around it. The growth persists in the same excessive manner even after cessation of the...
: Chromosome 1p36 alterations, mostly deletions, have been reported to occur in various types of neoplastic growths or tumors which may be benign or malignant. The 1p36 region contains a number of tumor-suppressor genes, which are genes that act to prevent cell growth. The deletion of one or more of these genes can cause malignancy (cancer). Some of the neoplams involved in the 1p36 are neuroblastomaNeuroblastomaNeuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid cancer in childhood and the most common cancer in infancy, with an annual incidence of about 650 cases per year in the US , and 100 cases per year in the UK . Close to 50 percent of neuroblastoma cases occur in children younger than two years old...
, prostate cancerProstate cancerProstate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
, lung cancerLung cancerLung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
, melanomaMelanomaMelanoma is a malignant tumor of melanocytes. Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin. They predominantly occur in skin, but are also found in other parts of the body, including the bowel and the eye...
, hepatomaHepatocellular carcinomaHepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer. Most cases of HCC are secondary to either a viral hepatitide infection or cirrhosis .Compared to other cancers, HCC is quite a rare tumor in the United States...
, cervical cancerCervical cancerCervical cancer is malignant neoplasm of the cervix uteri or cervical area. One of the most common symptoms is abnormal vaginal bleeding, but in some cases there may be no obvious symptoms until the cancer is in its advanced stages...
, breast cancerBreast cancerBreast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
, colorectal cancerColorectal cancerColorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
, ovarian cancerOvarian cancerOvarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
, and non-Hodgkin lymphomaNon-Hodgkin lymphomaThe non-Hodgkin lymphomas are a diverse group of blood cancers that include any kind of lymphoma except Hodgkin's lymphomas. Types of NHL vary significantly in their severity, from indolent to very aggressive....
. This is not to say that the children with 1p36 deletion syndrome will get these cancers, but this is a theory that has been put forth. - Genital hypoplasiaHypoplasiaHypoplasia is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells. Hypoplasia is similar to aplasia, but less severe. It is technically not the opposite of hyperplasia...
: Genital hypoplasia is the underdevelopment of the genital areas. Some of the genital problems in children with 1p36 are:- CryptorchidismCryptorchidismCryptorchidism is the absence of one or both testes from the scrotum. It is the most common birth defect regarding male genitalia. In unique cases, cryptorchidism can develop later in life, often as late as young adulthood. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at...
: This is the failure of one or both of the testicles to descend into the scrotum. - Shawl ScrotumShawl scrotumShawl scrotum is a condition in which the scrotum surrounds the penis, resembling a 'shawl'.It is a characteristic of some syndromes such as Aarskog-Scott syndrome , Rubenstein-Taybi syndrome, craniofrontonasal dysplasia, Hunter Carpenter McDonald Syndrome, Naguib Syndrome, Saito Kuba Tsuruta...
: A condition in which the scrotum tends to surround the penis. - Small Genitalia
- Cryptorchidism
Dilation of the renal collecting system
The collecting system is the structure that collects urine directly from the kidney tissue and routes it by way of the ureter to the bladder. Structural renal abnormalities are rare in both sexes.Hearing loss
Hearing lossHearing impairment
-Definition:Deafness is the inability for the ear to interpret certain or all frequencies of sound.-Environmental Situations:Deafness can be caused by environmental situations such as noise, trauma, or other ear defections...
affects approximately two thirds of 1p36 deletion patients. It can be of different types. Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the vestibulocochlear nerve , the inner ear, or central processing centers of the brain....
is a type of hearing impairment caused by damage that occurs to the inner ear (cochlea
Cochlea
The cochlea is the auditory portion of the inner ear. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, making 2.5 turns around its axis, the modiolus....
) or to the nerve used for hearing (vestibulocochlear nerve
Vestibulocochlear nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve is the eighth of twelve cranial nerves, and is responsible for transmitting sound and equilibrium information from the inner ear to the brain...
). Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem conducting sound waves anywhere along the route through the outer ear, tympanic membrane , or middle ear ....
is a hearing loss associated with the functioning of the outer or middle ear. This type is most common in children with 1p36 deletion syndrome. It ranges from mild loss at various frequencies, to severe loss at all frequencies.
Puberty
PubertyPuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes by which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of reproduction, as initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads; the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy...
in children with 1p36 deletion syndrome can be early, normal, or delayed.
Spinal deformities
Only a few spinal deformities have been seen in children with 1p36. The deformities found are:- KyphoscoliosisKyphoscoliosisKyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both a coronal and sagittal plane. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. Kyphoscoliosis is a musculoskeletal disorder causing chronic underventilation of the lungs and may be one of the major causes of pulmonary hypertension...
: Spinal deformity combining a sideways curvature with a hunching forward of the upper part of the spine. - Postural KyphosisKyphosisKyphosis , also called roundback or Kelso's hunchback, is a condition of over-curvature of the thoracic vertebrae...
: Also called postural "round back". This was found secondary to hypotonia in some children with 1p36.
Treatments and therapy
Although 1p36 Deletion Syndrome can be debilitating in many ways, patients do respond to various treatments and therapies. These include the following:American Sign Language
American Sign Language
American Sign Language, or ASL, for a time also called Ameslan, is the dominant sign language of Deaf Americans, including deaf communities in the United States, in the English-speaking parts of Canada, and in some regions of Mexico...
: Because few individuals with Monosomy 1p36 develop complex speech, an alternate form of communication is critical to development. Most patients can learn basic signs to communicate their needs and wants. This also appears to reduce frustration and may reduce self-injurious tendencies. Children with hearing loss will often qualify for locally sponsored sign language classes.
Music
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
: Music has been shown to aid children with 1p36 deletion in various developmental areas. It serves as an excellent auditory stimulus and can teach listening skills. Songs with actions help the child to develop coordination and motor skills.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
: Due to low muscle tone, patients with 1p36 Deletions take a great deal of time to learn to roll over, sit up, crawl and walk. However, regular physical therapy has shown to shorten the length of time needed to achieve each of those developmental milestones.

