Aerobic exercise
Encyclopedia
Aerobic exercise is physical exercise
of relatively low intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy
-generating process. Aerobic literally means "living in air", and refers to the use of oxygen
to adequately meet energy demands during exercise via aerobic metabolism. Generally, light-to-moderate intensity activities that are sufficiently supported by aerobic metabolism
can be performed for extended periods of time.
 Aerobic exercise and fitness can be contrasted with anaerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise and fitness can be contrasted with anaerobic exercise
, of which strength training
and short-distance running are the most salient examples. The two types of exercise differ by the duration and intensity of muscular contractions involved, as well as by how energy is generated within the muscle.
In most conditions, anaerobic exercise occurs simultaneously with aerobic exercises because the less efficient anaerobic metabolism must supplement the aerobic system due to energy demands that exceed the aerobic system's capacity. What is generally called aerobic exercise might be better termed "solely aerobic", because it is designed to be low-intensity enough not to generate lactate
via pyruvate
fermentation
, so that all carbohydrate is aerobically turned into energy.
Initially during increased exertion, muscle glycogen
is broken down to produce glucose, which undergoes glycolysis
producing pyruvate which then reacts with oxygen (Krebs cycle) to produce carbon dioxide and water and releasing energy. If there is a shortage of oxygen (anaerobic exercise, explosive movements), carbohydrate is consumed more rapidly because the pyruvate ferments into lactate.
As carbohydrate
s deplete, fat
metabolism is increased so that it can fuel the aerobic pathways. The latter is a slow process
, and is accompanied by a decline in performance level. This gradual switch to fat as fuel is a major cause of what marathon
runners call "hitting the wall". Anaerobic exercise
, in contrast, refers to the initial phase of exercise, or to any short burst of intense exertion, in which the glycogen or sugar is respired without oxygen, and is a far less efficient process. Operating anaerobically, an untrained 400 meter sprinter may "hit the wall" short of the full distance.
Aerobic exercise comprises innumerable forms. In general, it is performed at a moderate level of intensity over a relatively long period of time. For example, running
a long distance at a moderate pace is an aerobic exercise, but sprinting is not. Playing singles tennis, with near-continuous motion, is generally considered aerobic activity, while golf or two person team tennis, with brief bursts of activity punctuated by more frequent breaks, may not be predominantly aerobic. Some sports are thus inherently "aerobic", while other aerobic exercises, such as fartlek
training or aerobic dance classes, are designed specifically to improve aerobic capacity and fitness.
Among the recognized benefits of doing regular aerobic exercise are:
As a result, aerobic exercise can reduce the risk of death due to cardiovascular problems. In addition, high-impact aerobic activities (such as jogging or using a skipping rope) can stimulate bone growth, as well as reduce the risk of osteoporosis
for both men and women.
In addition to the health benefits of aerobic exercise, there are numerous performance benefits:
Both the health benefits and the performance benefits, or "training effect", require a minimum duration and frequency of exercise. Most authorities suggest at least twenty minutes performed at least three times per week.
test, in which a subject will undergo progressively more strenuous exercise on a treadmill, from an easy walk through to exhaustion. The individual is typically connected to a respirometer
to measure oxygen consumption, and the speed is increased incrementally over a fixed duration of time. The higher the measured cardiorespiratory endurance level, the more oxygen has been transported to and used by exercising muscles, and the higher the level of intensity at which the individual can exercise. More simply stated, the higher the aerobic capacity, the higher the level of aerobic fitness. The Cooper
and multi-stage fitness test
s can also be used to assess functional aerobic capacity for particular jobs or activities.
The degree to which aerobic capacity can be improved by exercise varies very widely in the human population: while the average response to training is an approximately 17% increase in VO2max, in any population there are "high responders" who may as much as double their capacity, and "low responders" who will see little or no benefit from training. Studies indicate that approximately 10% of otherwise healthy individuals cannot improve their aerobic capacity with exercise at all. The degree of an individual's responsiveness is highly heritable
, suggesting that this trait is genetically
determined.
metabolism
(glycolysis
and lactic acid fermentation
) that generate energy during high intensity, low duration tasks, such as sprinting, are not exercised at peak aerobic exercise levels. Aerobic exercise remains however a valuable component of a balanced exercise program and is good for cardiovascular health.
Some persons suffer repetitive stress injuries with some forms of aerobics, and then must choose less injurious, "low-impact" forms of aerobics, or lengthen the gap between bouts of exercise to allow for greater recovery.
Higher intensity exercise, such as High-intensity interval training
(HIIT), increases the resting metabolic rate (RMR) in the 24 hours following high intensity exercise, ultimately burning more calories than lower intensity exercise; low intensity exercise burns more calories during the exercise, due to the increased duration, but fewer afterwards.
Aerobic activity is also used by individuals with anorexia nervosa
as a means of suppressing appetite, since aerobic exercise increases sugar and fatty acid transport in the blood by stimulating tissues to release their energy stores. While there is some support for exercising while hungry as a means of tapping into fat stores, most evidence is equivocal. In addition, performance can be impaired by lack of nutrients, which will reduce training effects.
Physical exercise
Physical exercise is any bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness. It is performed for various reasons including strengthening muscles and the cardiovascular system, honing athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, as well as for the purpose of...
of relatively low intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
-generating process. Aerobic literally means "living in air", and refers to the use of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
to adequately meet energy demands during exercise via aerobic metabolism. Generally, light-to-moderate intensity activities that are sufficiently supported by aerobic metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
can be performed for extended periods of time.
Aerobic versus anaerobic exercise

Anaerobic exercise
Anaerobic exercise is exercise intense enough to trigger anaerobic metabolism. It is used by athletes in non-endurance sports to promote strength, speed and power and by body builders to build muscle mass...
, of which strength training
Strength training
Strength training is the use of resistance to muscular contraction to build the strength, anaerobic endurance, and size of skeletal muscles. There are many different methods of strength training, the most common being the use of gravity or elastic/hydraulic forces to oppose muscle contraction...
and short-distance running are the most salient examples. The two types of exercise differ by the duration and intensity of muscular contractions involved, as well as by how energy is generated within the muscle.
In most conditions, anaerobic exercise occurs simultaneously with aerobic exercises because the less efficient anaerobic metabolism must supplement the aerobic system due to energy demands that exceed the aerobic system's capacity. What is generally called aerobic exercise might be better termed "solely aerobic", because it is designed to be low-intensity enough not to generate lactate
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
via pyruvate
Pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid is an organic acid, a ketone, as well as the simplest of the alpha-keto acids. The carboxylate ion of pyruvic acid, CH3COCOO−, is known as pyruvate, and is a key intersection in several metabolic pathways....
fermentation
Fermentation (biochemistry)
Fermentation is the process of extracting energy from the oxidation of organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, using an endogenous electron acceptor, which is usually an organic compound. In contrast, respiration is where electrons are donated to an exogenous electron acceptor, such as oxygen,...
, so that all carbohydrate is aerobically turned into energy.
Initially during increased exertion, muscle glycogen
Glycogen
Glycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
is broken down to produce glucose, which undergoes glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
producing pyruvate which then reacts with oxygen (Krebs cycle) to produce carbon dioxide and water and releasing energy. If there is a shortage of oxygen (anaerobic exercise, explosive movements), carbohydrate is consumed more rapidly because the pyruvate ferments into lactate.
As carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
s deplete, fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
metabolism is increased so that it can fuel the aerobic pathways. The latter is a slow process
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
, and is accompanied by a decline in performance level. This gradual switch to fat as fuel is a major cause of what marathon
Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance running event with an official distance of 42.195 kilometres , that is usually run as a road race...
runners call "hitting the wall". Anaerobic exercise
Anaerobic exercise
Anaerobic exercise is exercise intense enough to trigger anaerobic metabolism. It is used by athletes in non-endurance sports to promote strength, speed and power and by body builders to build muscle mass...
, in contrast, refers to the initial phase of exercise, or to any short burst of intense exertion, in which the glycogen or sugar is respired without oxygen, and is a far less efficient process. Operating anaerobically, an untrained 400 meter sprinter may "hit the wall" short of the full distance.
Aerobic exercise comprises innumerable forms. In general, it is performed at a moderate level of intensity over a relatively long period of time. For example, running
Running
Running is a means of terrestrial locomotion allowing humans and other animals to move rapidly on foot. It is simply defined in athletics terms as a gait in which at regular points during the running cycle both feet are off the ground...
a long distance at a moderate pace is an aerobic exercise, but sprinting is not. Playing singles tennis, with near-continuous motion, is generally considered aerobic activity, while golf or two person team tennis, with brief bursts of activity punctuated by more frequent breaks, may not be predominantly aerobic. Some sports are thus inherently "aerobic", while other aerobic exercises, such as fartlek
Fartlek
Fartlek, which means "speed play" in Swedish, is a form of interval training which puts stress on the whole aerobic energy system due to the continuous nature of the exercise. The difference between this type of training and continuous training is that the intensity or speed of the exercise varies,...
training or aerobic dance classes, are designed specifically to improve aerobic capacity and fitness.
Among the recognized benefits of doing regular aerobic exercise are:
- Strengthening the muscles involved in respiration, to facilitate the flow of air in and out of the lungs
- Strengthening and enlarging the heartHeartThe heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
muscle, to improve its pumping efficiency and reduce the resting heart rate, known as aerobic conditioningAerobic conditioningAerobic conditioning is a process whereby one trains the heart and lungs to pump blood more efficiently, allowing more oxygen to get to muscles and organs.Aerobic conditioning is a determining factor in performance in events with a duration greater than 2mins... - Strengthening muscles throughout the body
- Improving circulation efficiency and reducing blood pressure
- Increasing the total number of red blood cells in the body, facilitating transport of oxygen
- Improved mental health, including reducing stress and lowering the incidence of depression
- Reducing the risk for diabetes.
- Burns body fat, while building leaner muscle.
As a result, aerobic exercise can reduce the risk of death due to cardiovascular problems. In addition, high-impact aerobic activities (such as jogging or using a skipping rope) can stimulate bone growth, as well as reduce the risk of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
for both men and women.
In addition to the health benefits of aerobic exercise, there are numerous performance benefits:
- Increased storage of energy molecules such as fats and carbohydrates within the muscles, allowing for increased endurance
- NeovascularizationNeovascularizationNeovascularization is the formation of functional microvascular networks with red blood cell perfusion. Neovascularization differs from angiogenesis in that angiogenesis is mainly characterized by the protrusion and outgrowth of capillary buds and sprouts from pre-existing blood vessels.In...
of the muscle sarcomeres to increase blood flow through the muscles - Increasing speed at which aerobic metabolism is activated within muscles, allowing a greater portion of energy for intense exercise to be generated aerobically
- Improving the ability of muscles to use fats during exercise, preserving intramuscular glycogenGlycogenGlycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
- Enhancing the speed at which muscles recover from high intensity exercise
Both the health benefits and the performance benefits, or "training effect", require a minimum duration and frequency of exercise. Most authorities suggest at least twenty minutes performed at least three times per week.
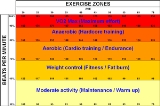
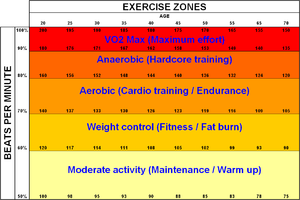
Aerobic capacity
Aerobic capacity describes the functional capacity of the cardiorespiratory system, (the heart, lungs and blood vessels). Aerobic capacity is defined as the maximum amount of oxygen the body can use during a specified period, usually during intense exercise. It is a function both of cardiorespiratory performance and the maximum ability to remove and utilize oxygen from circulating blood. To measure maximal aerobic capacity, an exercise physiologist or physician will perform a VO2 maxVO2 max
VO2 max is the maximum capacity of an individual's body to transport and use oxygen during incremental exercise, which reflects the physical fitness of the individual...
test, in which a subject will undergo progressively more strenuous exercise on a treadmill, from an easy walk through to exhaustion. The individual is typically connected to a respirometer
Respirometry
Respirometry is a general term that encompass a number of techniques for obtaining estimates of the rates of metabolism of vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, tissues, cells, or microorganisms via an indirect measure of heat production ....
to measure oxygen consumption, and the speed is increased incrementally over a fixed duration of time. The higher the measured cardiorespiratory endurance level, the more oxygen has been transported to and used by exercising muscles, and the higher the level of intensity at which the individual can exercise. More simply stated, the higher the aerobic capacity, the higher the level of aerobic fitness. The Cooper
Cooper test
The Cooper test is a test of physical fitness. It was designed by Kenneth H. Cooper in 1968 for US military use. In the original form, the point of the test is to run as far as possible within 12 minutes...
and multi-stage fitness test
Multi-stage fitness test
The multi-stage fitness test, also known as the bleep test, beep test, pacer test, Leger-test or 20-m shuttle run test, is used by sports coaches and trainers to estimate an athlete's VO2 max...
s can also be used to assess functional aerobic capacity for particular jobs or activities.
The degree to which aerobic capacity can be improved by exercise varies very widely in the human population: while the average response to training is an approximately 17% increase in VO2max, in any population there are "high responders" who may as much as double their capacity, and "low responders" who will see little or no benefit from training. Studies indicate that approximately 10% of otherwise healthy individuals cannot improve their aerobic capacity with exercise at all. The degree of an individual's responsiveness is highly heritable
Heritability
The Heritability of a population is the proportion of observable differences between individuals that is due to genetic differences. Factors including genetics, environment and random chance can all contribute to the variation between individuals in their observable characteristics...
, suggesting that this trait is genetically
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
determined.
Criticisms
When overall fitness is an occupational requirement, as it is for athletes, soldiers, and police and fire personnel, aerobic exercise alone may not provide a well balanced exercise program. In particular, muscular strength, especially upper-body muscular strength, may be neglected. Also, the metabolic pathways involved in anaerobicAnaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration is a form of respiration using electron acceptors other than oxygen. Although oxygen is not used as the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain; it is respiration without oxygen...
metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
(glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
and lactic acid fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation is a biological process by which sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose, are converted into cellular energy and the metabolic byproduct lactate. It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells, such as muscle cells, in the...
) that generate energy during high intensity, low duration tasks, such as sprinting, are not exercised at peak aerobic exercise levels. Aerobic exercise remains however a valuable component of a balanced exercise program and is good for cardiovascular health.
Some persons suffer repetitive stress injuries with some forms of aerobics, and then must choose less injurious, "low-impact" forms of aerobics, or lengthen the gap between bouts of exercise to allow for greater recovery.
Higher intensity exercise, such as High-intensity interval training
High-intensity interval training
High-intensity interval training or sprint interval training is an exercise strategy that is intended to improve performance with short training sessions. HIIT is a form of cardiovascular exercise which is beneficial to burning fat in a short and intense workout. Usual HIIT sessions may vary from...
(HIIT), increases the resting metabolic rate (RMR) in the 24 hours following high intensity exercise, ultimately burning more calories than lower intensity exercise; low intensity exercise burns more calories during the exercise, due to the increased duration, but fewer afterwards.
Aerobic activity is also used by individuals with anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by refusal to maintain a healthy body weight and an obsessive fear of gaining weight. Although commonly called "anorexia", that term on its own denotes any symptomatic loss of appetite and is not strictly accurate...
as a means of suppressing appetite, since aerobic exercise increases sugar and fatty acid transport in the blood by stimulating tissues to release their energy stores. While there is some support for exercising while hungry as a means of tapping into fat stores, most evidence is equivocal. In addition, performance can be impaired by lack of nutrients, which will reduce training effects.
Commercial success
Aerobic exercise has long been a popular approach to achieving weight loss and physical fitness, often taking a commercial form.- In the 1970s Judi Sheppard Missett helped create the market for commercial aerobics with her JazzerciseJazzerciseJazzercise is a dance-based group fitness program. Each 60-minute Jazzercise class features a fusion of jazz dance, resistance training, Pilates, yoga, kickboxing, and Latin-style movements set to popular music. The Jazzercise program was founded in 1969 by Jazzercise CEO Judi Sheppard Missett...
program - In the 1980s Richard SimmonsRichard SimmonsMilton Teagle Simmons , known professionally as Richard Simmons, is an American fitness personality who promotes weight-loss programs, most famously through his Sweatin' to the Oldies line of aerobics videos and DVDs and is known for his eccentric, outgoing and frequently flamboyant personality...
hosted an aerobic exercise show on television, and also released a series of exercise videos - In the 1990s Billy BlanksBilly BlanksBilly Wayne Blanks is an American fitness guru, martial artist, actor, and the inventor of the Tae Bo exercise program.-Career:Blanks began his study of the martial arts at the age of eleven and practices Karate and Taekwondo...
's Tae BoTae BoTae Bo is an aerobic exercise routine that became popular in the 1990s. It was developed by taekwondo practitioner Billy Blanks and was one of the first "cardio-boxing" programs to enjoy commercial success. Such programs use the motions of martial arts at a rapid pace designed to promote fitness...
helped popularize cardio-boxing workouts that incorporated martial arts movements
Indoor
- Stair climbingStair climbingStair climbing is the climbing of a flight of stairs. It is often described as a "low-impact" exercise, often for people who have recently started trying to get in shape.A common exhortation in health pop culture is "Take the stairs, not the elevator"....
- Elliptical trainerElliptical trainerAn elliptical trainer or cross-trainer is a stationary exercise machine used to simulate stair climbing, walking, or running without causing excessive pressure to the joints, hence decreasing the risk of impact injuries...
- Indoor rowerIndoor rowerAn indoor rower, or rowing machine, is a machine used to simulate the action of watercraft rowing for the purpose of exercise or training for rowing. Indoor rowing has become established as a sport in its own right...
- StairmasterStairmasterStairMaster is the name of a line of exercise machines, which includes stepping machines and revolving stairs.StairMaster was founded by Lanny Potts and Jim Walker and introduced by Tri-Tech, Inc. of Tulsa, Oklahoma in 1983 at the National Sporting Goods Association trade show...
- Stationary bicycle
- TreadmillTreadmillA treadmill is an exercise machine for running or walking while staying in one place. The word treadmill traditionally refers to a type of mill which was operated by a person or animal treading steps of a wheel to grind grain...
Outdoor
- Cross-country skiingCross-country skiingCross-country skiing is a winter sport in which participants propel themselves across snow-covered terrain using skis and poles...
- CyclingCyclingCycling, also called bicycling or biking, is the use of bicycles for transport, recreation, or for sport. Persons engaged in cycling are cyclists or bicyclists...
- Inline skatingInline skatingInline skating is a recreational sport practiced widely internationally. Inline skates typically have 2 to 5 polyurethane wheels, arranged in a single line. The in-line design allows for greater speed than roller skates and better maneuverability...
- JoggingJoggingJogging is a form of trotting or running at a slow or leisurely pace. The main intention is to increase fitness with less stress on the body than from faster running.-Definition:...
- RunningRunningRunning is a means of terrestrial locomotion allowing humans and other animals to move rapidly on foot. It is simply defined in athletics terms as a gait in which at regular points during the running cycle both feet are off the ground...
- Nordic walkingNordic walkingNordic walking, originally known as ski walking, is a physical activity and a sport consisting of walking with poles similar to ski poles.-Origin:...
Indoor or outdoor
- KickboxingKickboxingKickboxing refers to a group of martial arts and stand-up combat sports based on kicking and punching, historically developed from karate, Muay Thai and western boxing....
- Swimming
- Skipping rope or jump rope
- Circuit trainingCircuit trainingCircuit training is a form of conditioning combining resistance training and high-intensity aerobics. It is designed to be easy to follow and target strength building as well as muscular endurance. An exercise "circuit" is one completion of all prescribed exercises in the program. When one circuit...

