
Ancient technology
Encyclopedia
- See Ancient technology in StargateAncient technology in StargateThe Ancients are a fictional advanced race in the Stargate franchise, and are depicted as the precursor to modern-day humans. Their most notable creation in Stargate mythology is the entire Stargate network. Ancient science and technology, with a few exceptions, is shown as being superior to that...
for the technology of the aliens known as the AncientAncient (Stargate)The Ancients are a humanoid race in the fictional Stargate universe. They are called "Ancients" in the Milky Way, but are also known as Lanteans or Ancestors in the Pegasus galaxy and as the Alterans in their home galaxy, and they sometimes call themselves Anquietas in their language...
s in the fictional StargateStargateStargate is a adventure military science fiction franchise, initially conceived by Roland Emmerich and Dean Devlin. The first film in the franchise was simply titled Stargate. It was originally released on October 28, 1994, by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer and Carolco, and became a hit, grossing nearly...
universe.
During the growth of the ancient civilizations, ancient technology was the result from advances in engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
in ancient times
Ancient history
Ancient history is the study of the written past from the beginning of recorded human history to the Early Middle Ages. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, with Cuneiform script, the oldest discovered form of coherent writing, from the protoliterate period around the 30th century BC...
. These advances in the history of technology
History of technology
The history of technology is the history of the invention of tools and techniques, and is similar in many ways to the history of humanity. Background knowledge has enabled people to create new things, and conversely, many scientific endeavors have become possible through technologies which assist...
stimulated societies to adopt new ways of living and governance.
This article includes the advances in technology and the development of several engineering arts before the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, which began after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in AD
Anno Domini
and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars....
476, the death of Justinian I
Justinian I
Justinian I ; , ; 483– 13 or 14 November 565), commonly known as Justinian the Great, was Byzantine Emperor from 527 to 565. During his reign, Justinian sought to revive the Empire's greatness and reconquer the lost western half of the classical Roman Empire.One of the most important figures of...
in the 6th century, the coming of Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
in the 7th century, or the rise of Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
in the 8th century. For technologies developed in medieval societies, see Medieval technology
Medieval technology
Medieval technology refers to the technology used in medieval Europe under Christian rule. After the Renaissance of the 12th century, medieval Europe saw a radical change in the rate of new inventions, innovations in the ways of managing traditional means of production, and economic growth...
and Inventions in medieval Islam.
Summary
The characteristics of Ancient Egyptian technologyAncient Egyptian technology
The characteristics of ancient Egyptians are indicated by a set of artifacts and customs that lasted for thousands of years. The Egyptians invented and used many basic machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam of ships...
are indicated by a set of artifacts and customs that lasted for thousands of years. The Egyptians invented and used many basic machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology including ships and lighthouses.
The history of science and technology in India dates back to pre-modern times. The Indus Valley civilization yields evidence of hydrography, metrology and sewage collection and disposal being practiced by its inhabitants. Among the fields of science pursued in India were Ayurveda, astronomy and mathematics.
The history of science and technology in China
History of science and technology in China
The history of science and technology in China is both long and rich with many contributions to science and technology. In antiquity, independently of other civilizations, ancient Chinese philosophers made significant advances in science, technology, mathematics, and astronomy...
show significant advances in science, technology, mathematics, and astronomy. The first recorded observations of comets, solar eclipses, and supernovae were made in China. Traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture and herbal medicine were also practiced. The Four Great Inventions of China: the compass, gunpowder, papermaking, and printing, were among the most important technological advances, only known in Europe by the end of the Middle Ages.
Ancient Greek technology
Ancient Greek technology
Ancient Greek technology developed at an unprecedented speed during the 5th century BC, continuing up to and including the Roman period, and beyond...
developed at an unprecedented speed during the 5th century BC, continuing up to and including the Roman period, and beyond. Inventions that are credited to the ancient Greeks such as the gear, screw, bronze casting techniques, water clock, water organ, torsion catapult and the use of steam to operate some experimental machines and toys. Many of these inventions occurred late in the Greek period, often inspired by the need to improve weapons and tactics in war. Roman technology
Roman technology
Roman technology is the engineering practice which supported Roman civilization and made the expansion of Roman commerce and Roman military possible over nearly a thousand years....
is the engineering practice which supported Roman civilization and made the expansion of Roman commerce and Roman military possible over nearly a thousand years. The Roman Empire had an advanced set of technology of their time. Some Roman of the technology in Europe may have been lost during the turbulent eras of Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Roman technological feats of many different areas, like civil engineering, construction materials, transport technology, and some inventions such as the mechanical reaper went unmatched until the 19th century.
A significant number of inventions were developed in the Islamic world
Inventions in the Islamic world
A number of inventions were developed in the medieval Islamic world, a geopolitical region that has at various times extended from Spain and Africa in the west to the Indian subcontinent in the east. The inventions listed here were developed during the medieval Islamic world, which covers the...
, a geopolitical region that has at various times extended from al-Andalus and Africa in the west to the Indian subcontinent and Malay Archipelago in the east. Many of these inventions had direct implications for Fiqh related issues.
Ancient civilizations
It was the growth of the ancient civilizations which produced the greatest advances in technology and engineering, advances which stimulated other societies to adopt new ways of living and governance.Mesopotamia
MesopotamiaMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
n peoples (Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ians, Akkad
Akkad
The Akkadian Empire was an empire centered in the city of Akkad and its surrounding region in Mesopotamia....
ians, Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
ns and Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
ns) invented many technologies, most notably the wheel
Wheel
A wheel is a device that allows heavy objects to be moved easily through rotating on an axle through its center, facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Common examples found in transport applications. A wheel, together with an axle,...
, which some consider the most important mechanical
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
invention in history. Other Mesopotamian inventions include metalworking, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
-working, glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
making, lamp making, textile weaving
Textile
A textile or cloth is a flexible woven material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibres often referred to as thread or yarn. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, or other material to produce long strands...
, flood control, water storage, as well as irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
.
They were also one of the first Bronze age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
people in the world. Early on they used copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
and gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, and later they used iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
. Palaces were decorated with hundreds of kilograms of these very expensive metals. Also, copper, bronze, and iron were used for armor as well as for different weapons such as sword
Sword
A sword is a bladed weapon used primarily for cutting or thrusting. The precise definition of the term varies with the historical epoch or the geographical region under consideration...
s, dagger
Dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a sharp point designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon. The design dates to human prehistory, and daggers have been used throughout human experience to the modern day in close combat confrontations...
s, spear
Spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head.The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with bamboo spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as flint, obsidian, iron, steel or...
s, and maces.
One of the first big ancient inventions was the invention of the wheel in eastern Mesopotamia. This was a very big "hit" in Mesopotamia because the wheel could transport goods like metal through the hilly geographical features and was more versatile and helped the need for agricultural transportation for food.
According to the assyriologist Dalley, the earliest pump
Pump
A pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps...
was the Archimedes screw, first used by Sennacherib
Sennacherib
Sennacherib |Sîn]] has replaced brothers for me"; Aramaic: ) was the son of Sargon II, whom he succeeded on the throne of Assyria .-Rise to power:...
, King of Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
, for the water systems at the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were considered to be one of the greatest Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one of the Wonders which may in fact have been legendary. They were purportedly built in the ancient city-state of Babylon, near present-day Al Hillah, Babil, in Iraq...
and Nineveh
Nineveh
Nineveh was an ancient Assyrian city on the eastern bank of the Tigris River, and capital of the Neo Assyrian Empire. Its ruins are across the river from the modern-day major city of Mosul, in the Ninawa Governorate of Iraq....
in the 7th century BC. This attribution, however, is refuted by the historian of ancient water-lifting devices Olseon in the same paper, who still credits, as well as most other scholars, Archimedes
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Among his advances in physics are the foundations of hydrostatics, statics and an...
with the invention. Later during the Parthia
Parthia
Parthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
n or Sassanid
Sassanid Empire
The Sassanid Empire , known to its inhabitants as Ērānshahr and Ērān in Middle Persian and resulting in the New Persian terms Iranshahr and Iran , was the last pre-Islamic Persian Empire, ruled by the Sasanian Dynasty from 224 to 651...
periods, the so-called Baghdad Battery
Baghdad Battery
The Baghdad Battery, sometimes referred to as the Parthian Battery, is the common name for a number of artifacts created in Mesopotamia, during the dynasties of Parthian or Sassanid period , and probably discovered in 1936 in the village of Khuyut Rabbou'a, near Baghdad, Iraq...
, which if they actually were batteries may have been the first batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
.
For later medieval technologies developed in the Mesopotamian region, now known as Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, see Inventions in medieval Islam.
Egypt

Egyptians
Egyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
invented and used many simple machines, such as the ramp
Inclined plane
The inclined plane is one of the original six simple machines; as the name suggests, it is a flat surface whose endpoints are at different heights. By moving an object up an inclined plane rather than completely vertical, the amount of force required is reduced, at the expense of increasing the...
to aid construction processes. They were among the first to extract gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
by large-scale mining using fire-setting
Fire-setting
Fire-setting is a method of mining used since prehistoric times up to the Middle Ages. Fires were set against a rock face to heat the stone, which was then doused with water...
, and the first recognisable map
Map
A map is a visual representation of an area—a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions, and themes....
, the Turin papyrus
Turin Papyrus
Turin Papyrus refers to any papyrus manuscript in the collection of the Museo Egizio at Turin, Italy. The best known of these manuscripts include:* Turin Papyrus Map* Turin King List* Judicial Papyrus of Turin* Turin Erotic Papyrus...
shows the plan of one such mine in Nubia
Nubia
Nubia is a region along the Nile river, which is located in northern Sudan and southern Egypt.There were a number of small Nubian kingdoms throughout the Middle Ages, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization...
.
Egyptian paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
, made from papyrus
Papyrus
Papyrus is a thick paper-like material produced from the pith of the papyrus plant, Cyperus papyrus, a wetland sedge that was once abundant in the Nile Delta of Egypt....
, and pottery
Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
was mass produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean basin. The wheel
Wheel
A wheel is a device that allows heavy objects to be moved easily through rotating on an axle through its center, facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Common examples found in transport applications. A wheel, together with an axle,...
, however, did not arrive until foreign invaders introduced the chariot
Chariot
The chariot is a type of horse carriage used in both peace and war as the chief vehicle of many ancient peoples. Ox carts, proto-chariots, were built by the Proto-Indo-Europeans and also built in Mesopotamia as early as 3000 BC. The original horse chariot was a fast, light, open, two wheeled...
. They developed Mediterranean maritime
Maritime history
Maritime history is the study of human activity at sea. It covers a broad thematic element of history that often uses a global approach, although national and regional histories remain predominant...
technology including ships and lighthouses.
For later technologies in Ptolemaic Egypt
Ptolemaic Egypt
Ptolemaic Egypt began when Ptolemy I Soter invaded Egypt and declared himself Pharaoh of Egypt in 305 BC and ended with the death of queen Cleopatra VII of Egypt and the Roman conquest in 30 BC. The Ptolemaic Kingdom was a powerful Hellenistic state, extending from southern Syria in the east, to...
, Roman Egypt, and Arab Egypt, see Ancient Greek technology
Ancient Greek technology
Ancient Greek technology developed at an unprecedented speed during the 5th century BC, continuing up to and including the Roman period, and beyond...
, Roman technology
Roman technology
Roman technology is the engineering practice which supported Roman civilization and made the expansion of Roman commerce and Roman military possible over nearly a thousand years....
and Inventions in medieval Islam respectively.
Africa
Science and technology in Africa has a history stretching to the beginning of the human species, stretching back to the first evidence of tool useStone Age
The Stone Age is a broad prehistoric period, lasting about 2.5 million years , during which humans and their predecessor species in the genus Homo, as well as the earlier partly contemporary genera Australopithecus and Paranthropus, widely used exclusively stone as their hard material in the...
by hominid ancestors in the areas of Africa where humans are believed to have evolved.
Indian subcontinent
The Indus Valley CivilizationIndus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
, situated in a resource-rich area, is notable for its early application of city planning and sanitation technologies. Cites in the Indus Valley offer some of the first examples of closed gutters, public baths, and communal granaries. The Takshashila University was an important seat of learning in the ancient world. It was the center of education for scholars from all over Asia. Many Greek
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
, Persian and Chinese
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
students studied here under great scholars including Kautilya, Panini, Jivaka, and Vishnu Sharma.

Indian construction and architecture, called 'Vaastu Shastra', suggests a thorough understanding or materials engineering, hydrology, and sanitation. Ancient Indian culture was also pioneering in its use of vegetable dyes, cultivating plants including indigo
Indigo
Indigo is a color named after the purple dye derived from the plant Indigofera tinctoria and related species. The color is placed on the electromagnetic spectrum between about 420 and 450 nm in wavelength, placing it between blue and violet...
and cinnabar
Cinnabar
Cinnabar or cinnabarite , is the common ore of mercury.-Word origin:The name comes from κινναβαρι , a Greek word most likely applied by Theophrastus to several distinct substances...
. Many of the dyes were used in art and sculpture. The use of perfumes demonstrates some knowledge of chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, particularly distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
and purification processes.
China

Joseph Needham
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham, CH, FRS, FBA , also known as Li Yuese , was a British scientist, historian and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1941, and as a fellow of the British...
, the Chinese made many first-known discoveries and developments. Major technological contributions from China include early seismological
Seismology
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake effects, such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, oceanic,...
detectors, matches, paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
, the double-action piston pump
Piston pump
A piston pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal reciprocates with the piston. Piston pumps can be used to move liquids or compress gases.-Types:* Axial piston pump* Radial piston pump...
, cast iron
Cast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
, the iron plough
Plough
The plough or plow is a tool used in farming for initial cultivation of soil in preparation for sowing seed or planting. It has been a basic instrument for most of recorded history, and represents one of the major advances in agriculture...
, the multi-tube seed drill
Seed drill
A seed drill is a sowing device that precisely positions seeds in the soil and then covers them. Before the introduction of the seed drill, the common practice was to plant seeds by hand. Besides being wasteful, planting was very imprecise and led to a poor distribution of seeds, leading to low...
, the suspension bridge
Suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders. Outside Tibet and Bhutan, where the first examples of this type of bridge were built in the 15th century, this type of bridge dates from the early 19th century...
, natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
as fuel, the magnetic compass, the raised-relief map
Raised-relief map
A raised-relief map or terrain model is a three-dimensional representation, usually of terrain. When representing terrain, the elevation dimension is usually exaggerated by a factor between five and ten; this facilitates the visual recognition of terrain features.-History:In his 1665 paper for the...
, the propeller
Propeller
A propeller is a type of fan that transmits power by converting rotational motion into thrust. A pressure difference is produced between the forward and rear surfaces of the airfoil-shaped blade, and a fluid is accelerated behind the blade. Propeller dynamics can be modeled by both Bernoulli's...
, the crossbow
Crossbow
A crossbow is a weapon consisting of a bow mounted on a stock that shoots projectiles, often called bolts or quarrels. The medieval crossbow was called by many names, most of which derived from the word ballista, a torsion engine resembling a crossbow in appearance.Historically, crossbows played a...
, the South Pointing Chariot
South Pointing Chariot
The south-pointing chariot was an ancient Chinese two-wheeled vehicle that carried a movable pointer to indicate the south, no matter how the chariot turned. Usually, the pointer took the form of a doll or figure with an outstretched arm...
, and gun powder. Other Chinese discoveries and inventions from the Medieval period, according to Joseph Needham's research, include: block printing and movable type
Movable type
Movable type is the system of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document ....
, phosphorescent paint, and the spinning wheel
Spinning wheel
A spinning wheel is a device for spinning thread or yarn from natural or synthetic fibers. Spinning wheels appeared in Asia, probably in the 11th century, and very gradually replaced hand spinning with spindle and distaff...
.
The solid-fuel rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
was invented in China about 1150 AD, nearly 200 years after the invention of black powder (which acted as the rocket's fuel). At the same time that the age of exploration was occurring in the West, the Chinese emperors of the Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
also sent ships, some reaching Africa
Zheng He
Zheng He , also known as Ma Sanbao and Hajji Mahmud Shamsuddin was a Hui-Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat and fleet admiral, who commanded voyages to Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and East Africa, collectively referred to as the Voyages of Zheng He or Voyages of Cheng Ho from...
. But the enterprises were not further funded, halting further exploration and development. When Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer. He was born in Sabrosa, in northern Portugal, and served King Charles I of Spain in search of a westward route to the "Spice Islands" ....
's ships reached Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
in 1521, they found a wealthy city that had been fortified by Chinese engineers, and protected by a breakwater
Breakwater (structure)
Breakwaters are structures constructed on coasts as part of coastal defence or to protect an anchorage from the effects of weather and longshore drift.-Purposes of breakwaters:...
. Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta was an Italian scholar and explorer from the Republic of Venice. He travelled with the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and his crew on their voyage to the Indies. During the expedition, he served as Magellan's assistant and kept an accurate journal which later assisted him...
noted that much of the technology of Brunei was equal to Western technology of the time. Also, there were more cannons in Brunei than on Magellan's ships, and the Chinese merchants to the Brunei court had sold them spectacles and porcelain
Porcelain
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating raw materials, generally including clay in the form of kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between and...
, which were rarities in Europe.
Persia
The QanatQanat
A qanāt is a water management system used to provide a reliable supply of water for human settlements and irrigation in hot, arid and semi-arid climates...
, a water management system used for irrigation, originated in Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
before the Achaemenid period
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
of Persia. The oldest and largest known qanat is in the Iranian city of Gonabad
Gonabad
Gonabad is a city in and the capital of Gonabad County, in Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 34,563, in 9,789 families.It is mostly well-known because of the Gonabadi Dervishes and for its qanats, also known as kareez...
which, after 2,700 years, still provides drinking and agricultural water to nearly 40,000 people.
Persian philosophers and inventors may have created the first batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
, sometimes known as the Baghdad Battery
Baghdad Battery
The Baghdad Battery, sometimes referred to as the Parthian Battery, is the common name for a number of artifacts created in Mesopotamia, during the dynasties of Parthian or Sassanid period , and probably discovered in 1936 in the village of Khuyut Rabbou'a, near Baghdad, Iraq...
, in the Parthia
Parthia
Parthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
n or Sassanid
Sassanid Empire
The Sassanid Empire , known to its inhabitants as Ērānshahr and Ērān in Middle Persian and resulting in the New Persian terms Iranshahr and Iran , was the last pre-Islamic Persian Empire, ruled by the Sasanian Dynasty from 224 to 651...
eras. Some have suggested that the batteries may have been used medicinally. Other scientists believe the batteries were used for electroplating—transferring a thin layer of metal to another metal surface—a technique still used today and the focus of a common classroom experiment.
In the 7th century AD, Persians in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
developed the first practical windmill
Windmill
A windmill is a machine which converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by means of vanes called sails or blades. Originally windmills were developed for milling grain for food production. In the course of history the windmill was adapted to many other industrial uses. An important...
s. For later medieval technologies developed in Islamic Persia, see Inventions in medieval Islam.
Greek and Hellenistic

Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
and Hellenistic
Hellenistic civilization
Hellenistic civilization represents the zenith of Greek influence in the ancient world from 323 BCE to about 146 BCE...
engineers invented many technologies and improved upon pre-existing technologies, particularly during the Hellenistic period
Hellenistic period
The Hellenistic period or Hellenistic era describes the time which followed the conquests of Alexander the Great. It was so named by the historian J. G. Droysen. During this time, Greek cultural influence and power was at its zenith in Europe and Asia...
. Heron of Alexandria invented a basic steam engine
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
and demonstrated knowledge of mechanic and pneumatic systems. Archimedes
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Among his advances in physics are the foundations of hydrostatics, statics and an...
invented several machines. The Greeks were unique in pre-industrial times in their ability to combine scientific research with the development of new technologies. One example is the Archimedean screw; this technology was first conceptualized in mathematics, then built. Other technologies invented by Greek scientists include the ballistae, the piston pump
Piston pump
A piston pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal reciprocates with the piston. Piston pumps can be used to move liquids or compress gases.-Types:* Axial piston pump* Radial piston pump...
, and primitive analog computers like the Antikythera mechanism
Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism is an ancient mechanical computer designed to calculate astronomical positions. It was recovered in 1900–1901 from the Antikythera wreck. Its significance and complexity were not understood until decades later. Its time of construction is now estimated between 150 and 100...
. Greek architects were responsible for the first true dome
Dome
A dome is a structural element of architecture that resembles the hollow upper half of a sphere. Dome structures made of various materials have a long architectural lineage extending into prehistory....
s, and were the first to explore the Golden ratio
Golden ratio
In mathematics and the arts, two quantities are in the golden ratio if the ratio of the sum of the quantities to the larger quantity is equal to the ratio of the larger quantity to the smaller one. The golden ratio is an irrational mathematical constant, approximately 1.61803398874989...
and its relationship with geometry and architecture.
Apart from Hero of Alexandria
Hero of Alexandria
Hero of Alexandria was an ancient Greek mathematician and engineerEnc. Britannica 2007, "Heron of Alexandria" who was active in his native city of Alexandria, Roman Egypt...
's steam aeolipile
Aeolipile
An aeolipile , also known as a Hero engine, is a rocket style jet engine which spins when heated. In the 1st century AD, Hero of Alexandria described the device, and many sources give him the credit for its invention.The aeolipile Hero described is considered to be the first recorded steam engine...
, Hellenistic technicians were the first to invent watermills and windwheels, making them global pioneers in three of the four known means of non-human propulsion prior to the Industrial Revolution (the fourth being sails). However, only water power was used extensively in antiquity.
Other Greek inventions include torsion catapults, pneumatic catapults, crossbows, cranes, rutways, organs, the keyboard mechanism, gears, differential gears, screws, refined parchment, showers, dry docks, diving bells, odometer and astrolabes. In architecture, Greek engineers constructed monumental lighthouses such as the Pharos
Lighthouse of Alexandria
The Lighthouse of Alexandria, also known as the Pharos of Alexandria , was a tower built between 280 and 247 BC on the island of Pharos at Alexandria, Egypt...
and devised the first central heating systems. The Tunnel of Eupalinos is the earliest tunnel in history which has been excavated with a scientific approach from both ends.
Automata like vending machines, automatic doors and many other ingenious devices were first built by Hellenistic engineers as Ctesibius
Ctesibius
Ctesibius or Ktesibios or Tesibius was a Greek inventor and mathematician in Alexandria, Ptolemaic Egypt. He wrote the first treatises on the science of compressed air and its uses in pumps...
, Philo of Byzantium
Philo of Byzantium
Philo of Byzantium , also known as Philo Mechanicus, was a Greek engineer and writer on mechanics, who lived during the latter half of the 3rd century BC...
and Heron. Greek technological treatises were scrupuously studied and copied by later Byzantine, Arabic and Latin European scholars and provided much of the foundation for further technological advances in these civilizations.
Roman

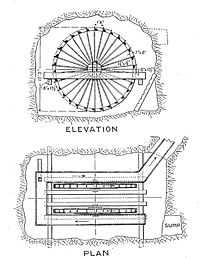
Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, and the legal developments which occurred before the 7th century AD — when the Roman–Byzantine state adopted Greek as the language of government. The development of Roman law comprises more than a thousand years of jurisprudence — from the Twelve...
providing for individual ownership, advanced stonemasonry technology, advanced road-building
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
(exceeded only in the 19th century), military engineering, civil engineering, spinning and weaving and several different machines like the Gallic reaper
Reaper
A reaper is a person or machine that reaps crops at harvest, when they are ripe.-Hand reaping:Hand reaping is done by various means, including plucking the ears of grains directly by hand, cutting the grain stalks with a sickle, cutting them with a scythe, or with a later type of scythe called a...
that helped to increase productivity in many sectors of the Roman economy. They also developed water power through building aqueducts on a grand scale, using water not just for drinking supplies but also for irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, powering water mills and in mining. They used drainage wheels extensively in deep underground mines, one device being the reverse overshot water-wheel
Reverse overshot water-wheel
Frequently used in mines and probably elsewhere , the reverse overshot water wheel was a Roman innovation to help remove water from the lowest levels of underground workings. It is described by Vitruvius in his work De Architectura published circa 25 BC...
. They were the first to apply hydraulic mining
Hydraulic mining
Hydraulic mining, or hydraulicking, is a form of mining that uses high-pressure jets of water to dislodge rock material or move sediment. In the placer mining of gold or tin, the resulting water-sediment slurry is directed through sluice boxes to remove the gold.-Precursor - ground...
methods for prospecting for metal ores, and for extracting those ores from the ground when found using a method known as hushing
Hushing
Hushing is an ancient and historic mining method using a flood or torrent of water to reveal mineral veins. The method was applied in several ways, both in prospecting for ores, and for their exploitation. Mineral veins are often hidden below soil and sub-soil, which must be stripped away to...
.
Roman engineers build monumental arches, amphitheatres, aqueducts
Roman aqueduct
The Romans constructed numerous aqueducts to serve any large city in their empire, as well as many small towns and industrial sites. The city of Rome had the largest concentration of aqueducts, with water being supplied by eleven aqueducts constructed over a period of about 500 years...
, public baths
Thermae
In ancient Rome, thermae and balnea were facilities for bathing...
, true arch bridges
Roman bridge
Roman bridges, built by ancient Romans, were the first large and lasting bridges built. Roman bridges were built with stone and had the arch as its basic structure....
, harbours, dams, vaults and domes on a very large scale across their Empire. Notable Roman inventions include the book (Codex)
Codex
A codex is a book in the format used for modern books, with multiple quires or gatherings typically bound together and given a cover.Developed by the Romans from wooden writing tablets, its gradual replacement...
, glass blowing and concrete
Concrete
Concrete is a composite construction material, composed of cement and other cementitious materials such as fly ash and slag cement, aggregate , water and chemical admixtures.The word concrete comes from the Latin word...
. Because Rome was located on a volcanic peninsula, with sand which contained suitable crystalline grains, the concrete
Concrete
Concrete is a composite construction material, composed of cement and other cementitious materials such as fly ash and slag cement, aggregate , water and chemical admixtures.The word concrete comes from the Latin word...
which the Romans formulated was especially durable. Some of their buildings have lasted 2000 years, to the present day.
Roman civilization was highly urbanized by pre-modern standards. Many cities of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
had over 100,000 inhabitants with the capital Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
being the largest metropolis of antiquity. Features of Roman urban life included multistory apartment buildings called insulae
Insulae
In Roman architecture, an insula was a kind of apartment building that housed most of the urban citizen population of ancient Rome, including ordinary people of lower- or middle-class status and all but the wealthiest from the upper-middle class...
, street paving, public flush toilets, glass windows and floor and wall heating
Hypocaust
A hypocaust was an ancient Roman system of underfloor heating, used to heat houses with hot air. The word derives from the Ancient Greek hypo meaning "under" and caust-, meaning "burnt"...
. The Romans understood hydraulics
Hydraulics
Hydraulics is a topic in applied science and engineering dealing with the mechanical properties of liquids. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the engineering uses of fluid properties. In fluid power, hydraulics is used for the generation, control,...
and constructed fountain
Fountain
A fountain is a piece of architecture which pours water into a basin or jets it into the air either to supply drinking water or for decorative or dramatic effect....
s and waterworks, particularly aqueduct
Aqueduct
An aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. In modern engineering, the term is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose....
s, which were the hallmark of their civilization. They exploited water power by building water mills, sometimes in series, such as the sequence found at Barbegal in southern France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and suspected on the Janiculum
Janiculum
The Janiculum is a hill in western Rome, Italy. Although the second-tallest hill in the contemporary city of Rome, the Janiculum does not figure among the proverbial Seven Hills of Rome, being west of the Tiber and outside the boundaries of the ancient city.-Sights:The Janiculum is one of the...
in Rome. Some Roman baths
Thermae
In ancient Rome, thermae and balnea were facilities for bathing...
have lasted to this day. The Romans developed many technologies which were apparently lost in the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, and were only fully reinvented in the 19th and 20th centuries. They also left texts describing their achievements, especially Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
, Frontinus and Vitruvius
Vitruvius
Marcus Vitruvius Pollio was a Roman writer, architect and engineer, active in the 1st century BC. He is best known as the author of the multi-volume work De Architectura ....
.
Other less known Roman innovations include cement
Cement
In the most general sense of the word, a cement is a binder, a substance that sets and hardens independently, and can bind other materials together. The word "cement" traces to the Romans, who used the term opus caementicium to describe masonry resembling modern concrete that was made from crushed...
, boat mills, arch dam
Dam
A dam is a barrier that impounds water or underground streams. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. Hydropower and pumped-storage hydroelectricity are...
s and possibly tide mill
Tide mill
A tide mill is a water mill driven by tidal rise and fall. A dam with a sluice is created across a suitable tidal inlet, or a section of river estuary is made into a reservoir. As the tide comes in, it enters the mill pond through a one way gate, and this gate closes automatically when the tide...
s.
Further reading
- Humphrey, J. W. (2006). Ancient technology. Greenwood guides to historic events of the ancient world. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press.
- Rojcewicz, R. (2006). The gods and technology: a reading of Heidegger. SUNY series in theology and continental thought. Albany: State University of New York Press.
- Krebs, R. E., & Krebs, C. A. (2004). Groundbreaking scientific experiments, inventions, and discoveries of the ancient world. Groundbreaking scientific experiments, inventions, and discoveries through the ages. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press.
- Childress, D. H. (2000). Technology of the gods: the incredible sciences of the ancients. Kempton, Ill: Adventures Unlimited Press.
- Landels, J. G. (2000). Engineering in the ancient world. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- James, P., & Thorpe, N. (1995). Ancient inventions. New York: Ballantine Books.
- Hodges, H. (1992). Technology in the ancient world. New York: Barnes & Noble.
- National Geographic Society (U.S.). (1986). Builders of the ancient world: marvels of engineering. Washington, D.C.: The Society.
- American Ceramic Society, Kingery, W. D., & Lense, E. (1985). Ancient technology to modern science. Ceramics and civilization, v. 1. Columbus, Ohio: American Ceramic Society.
- Brown, M. (1966). On the theory and measurement of technological change. Cambridge: Cambridge U.P.
- Forbes, R. J. (1964). Studies in ancient technology. Leiden: E.J. Brill.

