
Atkinson cycle
Encyclopedia
The Atkinson cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine
invented by James Atkinson
in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency
at the expense of power density
, and is used in some modern hybrid electric applications.
allowed the intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes of the four-stroke cycle
to occur in a single turn of the crankshaft
and was designed to avoid infringing certain patents covering Otto cycle
engines. Due to the unique crankshaft
design of the Atkinson, its expansion ratio can differ from its compression ratio
and, with a power stroke longer than its compression stroke, the engine can achieve greater thermal efficiency than a traditional piston engine. While Atkinson's original design is no more than an historical curiosity, many modern engines use unconventional valve timing to produce the effect of a shorter compression stroke/longer power stroke, thus realizing the fuel economy improvements the Atkinson cycle can provide.
 The ideal Atkinson cycle consists of following operations:
The ideal Atkinson cycle consists of following operations:
 Recently Atkinson cycle has been used to describe a modified Otto cycle
Recently Atkinson cycle has been used to describe a modified Otto cycle
engine in which the intake valve is held open longer than normal to allow a reverse flow of intake air into the intake manifold. The effective compression ratio is reduced (for a time the air is escaping the cylinder freely rather than being compressed) but the expansion ratio is unchanged. This means the compression ratio is smaller than the expansion ratio. Heat gained from burning fuel increases the pressure, thereby forcing the piston to move, expanding the air volume beyond the volume when compression began. The goal of the modern Atkinson cycle is to allow the pressure in the combustion chamber at the end of the power stroke to be equal to atmospheric pressure; when this occurs, all the available energy has been obtained from the combustion process. For any given portion of air, the greater expansion ratio allows more energy to be converted from heat to useful mechanical energy meaning the engine is more efficient.
The disadvantage of the four-stroke Atkinson cycle engine versus the more common Otto cycle engine is reduced power density. Due to a smaller portion of the compression stroke being devoted to compressing the intake air, an Atkinson cycle engine does not take in as much air as would a similarly designed and sized Otto cycle engine.
Four-stroke engines of this type with this same type of intake valve motion but with a supercharger
to make up for the loss of power density are known as Miller cycle
engines.
 The Atkinson cycle can be used in a rotary engine
The Atkinson cycle can be used in a rotary engine
. In this configuration an increase in both power and efficiency can be achieved when compared to the Otto cycle. This type of engine retains the one power phase per revolution, together with the different compression and expansion volumes of the original Atkinson cycle. Exhaust gases are expelled from the engine by compressed-air scavenging. This modification of the Atkinson cycle allows for the use of alternative fuels like diesel and hydrogen. Disadvantages of this design include the requirement that rotor tips seal very tightly on the outer housing wall and the mechanical losses suffered through friction between rapidly oscillating parts of irregular shape. See External Links for more information.

 While a modified Otto cycle
While a modified Otto cycle
engine using the Atkinson cycle provides good fuel economy, it is at the expense of a lower power-per-displacement as compared to a traditional four-stroke engine. If demand for more power is intermittent, the power of the engine can be supplemented by an electric motor
during times when more power is needed. This forms the basis of an Atkinson cycle-based hybrid electric drivetrain. These electric motors can be used independently of, or in combination with, the Atkinson cycle engine, to provide the most efficient means of producing the desired power.
Several production vehicles use Atkinson cycle engines:
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
invented by James Atkinson
James Atkinson (inventor)
James Atkinson of Hampstead was a British engineer who invented the Atkinson cycle engine in 1882. By use of variable engine strokes from a complex crankshaft, Atkinson was able to increase the efficiency of his engine, at the cost of some power, over traditional Otto-cycle engines...
in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency
Efficiency
Efficiency in general describes the extent to which time or effort is well used for the intended task or purpose. It is often used with the specific purpose of relaying the capability of a specific application of effort to produce a specific outcome effectively with a minimum amount or quantity of...
at the expense of power density
Power density
Power density is the amount of power per unit volume....
, and is used in some modern hybrid electric applications.
Design
The original Atkinson cycle piston engineReciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types...
allowed the intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes of the four-stroke cycle
Four-stroke cycle
A four-stroke engine, also known as four-cycle, is an internal combustion engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes—intake, compression, power, and exhaust—during two separate revolutions of the engine's crankshaft, and one single thermodynamic cycle.There are two...
to occur in a single turn of the crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
and was designed to avoid infringing certain patents covering Otto cycle
Four-stroke cycle
A four-stroke engine, also known as four-cycle, is an internal combustion engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes—intake, compression, power, and exhaust—during two separate revolutions of the engine's crankshaft, and one single thermodynamic cycle.There are two...
engines. Due to the unique crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
design of the Atkinson, its expansion ratio can differ from its compression ratio
Compression ratio
The 'compression ratio' of an internal-combustion engine or external combustion engine is a value that represents the ratio of the volume of its combustion chamber from its largest capacity to its smallest capacity...
and, with a power stroke longer than its compression stroke, the engine can achieve greater thermal efficiency than a traditional piston engine. While Atkinson's original design is no more than an historical curiosity, many modern engines use unconventional valve timing to produce the effect of a shorter compression stroke/longer power stroke, thus realizing the fuel economy improvements the Atkinson cycle can provide.
Ideal thermodynamic cycle

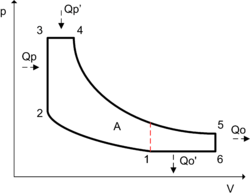
- 1-2 IsentropicIsentropic processIn thermodynamics, an isentropic process or isoentropic process is one in which for purposes of engineering analysis and calculation, one may assume that the process takes place from initiation to completion without an increase or decrease in the entropy of the system, i.e., the entropy of the...
or reversibleReversible process (thermodynamics)In thermodynamics, a reversible process, or reversible cycle if the process is cyclic, is a process that can be "reversed" by means of infinitesimal changes in some property of the system without loss or dissipation of energy. Due to these infinitesimal changes, the system is in thermodynamic...
adiabaticAdiabatic processIn thermodynamics, an adiabatic process or an isocaloric process is a thermodynamic process in which the net heat transfer to or from the working fluid is zero. Such a process can occur if the container of the system has thermally-insulated walls or the process happens in an extremely short time,...
compression - 2-3 IsochoricIsochoricIsochoric may refer to:*cell-transitive, in geometry*isochoric process, in chemistry or thermodynamics...
heating (Qp) - 3-4 IsobaricIsobaricIsobaric may refer to:*in thermodynamics, an isobaric process, i.e. one that is carried out at constant pressure;...
heating (Qp') - 4-5 Isentropic expansion
- 5-6 Isochoric cooling (Qo)
- 6-1 Isobaric cooling (Qo')
Modern Atkinson cycle engines

Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle which describes the functioning of a typical reciprocating piston engine, the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines....
engine in which the intake valve is held open longer than normal to allow a reverse flow of intake air into the intake manifold. The effective compression ratio is reduced (for a time the air is escaping the cylinder freely rather than being compressed) but the expansion ratio is unchanged. This means the compression ratio is smaller than the expansion ratio. Heat gained from burning fuel increases the pressure, thereby forcing the piston to move, expanding the air volume beyond the volume when compression began. The goal of the modern Atkinson cycle is to allow the pressure in the combustion chamber at the end of the power stroke to be equal to atmospheric pressure; when this occurs, all the available energy has been obtained from the combustion process. For any given portion of air, the greater expansion ratio allows more energy to be converted from heat to useful mechanical energy meaning the engine is more efficient.
The disadvantage of the four-stroke Atkinson cycle engine versus the more common Otto cycle engine is reduced power density. Due to a smaller portion of the compression stroke being devoted to compressing the intake air, an Atkinson cycle engine does not take in as much air as would a similarly designed and sized Otto cycle engine.
Four-stroke engines of this type with this same type of intake valve motion but with a supercharger
Supercharger
A supercharger is an air compressor used for forced induction of an internal combustion engine.The greater mass flow-rate provides more oxygen to support combustion than would be available in a naturally aspirated engine, which allows more fuel to be burned and more work to be done per cycle,...
to make up for the loss of power density are known as Miller cycle
Miller cycle
In engineering, the Miller cycle is a combustion process used in a type of four-stroke internal combustion engine. The Miller cycle was patented by Ralph Miller, an American engineer, in the 1940s.- Overview :...
engines.
Rotary Atkinson cycle engine

Rotary engine
The rotary engine was an early type of internal-combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration, in which the crankshaft remained stationary and the entire cylinder block rotated around it...
. In this configuration an increase in both power and efficiency can be achieved when compared to the Otto cycle. This type of engine retains the one power phase per revolution, together with the different compression and expansion volumes of the original Atkinson cycle. Exhaust gases are expelled from the engine by compressed-air scavenging. This modification of the Atkinson cycle allows for the use of alternative fuels like diesel and hydrogen. Disadvantages of this design include the requirement that rotor tips seal very tightly on the outer housing wall and the mechanical losses suffered through friction between rapidly oscillating parts of irregular shape. See External Links for more information.
Vehicles using Atkinson cycle engines


Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle which describes the functioning of a typical reciprocating piston engine, the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines....
engine using the Atkinson cycle provides good fuel economy, it is at the expense of a lower power-per-displacement as compared to a traditional four-stroke engine. If demand for more power is intermittent, the power of the engine can be supplemented by an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
during times when more power is needed. This forms the basis of an Atkinson cycle-based hybrid electric drivetrain. These electric motors can be used independently of, or in combination with, the Atkinson cycle engine, to provide the most efficient means of producing the desired power.
Several production vehicles use Atkinson cycle engines:
- Chevrolet Tahoe Hybrid electric (four-wheel drive) with a compression ratio of 10.8:1
- Ford Escape/Mercury MarinerMercury MarinerThe Mariner Hybrid powertrain is identical to its sibling, the Ford Escape Hybrid, and it was launched to the U.S. market in 2006.Like the Ford Escape Hybrid, the Mariner Hybrid is a "full" hybrid electric system, meaning the system can switch automatically between pure electric power, pure...
/Mazda TributeMazda TributeThe Mazda Tribute is a compact SUV made by Japanese automaker Mazda since 2001. It is jointly developed with Ford Motor Company and based on the front-wheel drive Mazda 626 platform, which is in turn the basis for the similar Ford Escape on the CD2 platform...
electric (front- and four-wheel drive) with a compression ratio of 12.4:1 - Ford Fusion HybridFord Fusion HybridThe Ford Fusion Hybrid is a gasoline-electric hybrid powered version of the mid-size Ford Fusion sedan developed by the Ford Motor Company, and launched to the U.S. market in March 2009 as a 2010 model, together with its twin the Mercury Milan Hybrid. The Fusion Hybrid is manufactured at Ford's...
/Mercury Milan Hybrid/Lincoln MKZ Hybrid electric (front-wheel drive) with a compression ratio of 12.3:1 - Hyundai Sonata Hybrid (front-wheel drive)
- Infiniti M35hInfiniti MThe "M" nameplate has been used on various mid-luxury cars from the Infiniti luxury division of Nissan.The first iteration was the M30 Coupe/Convertible, which were rebadged JDM Nissan Leopard....
Hybrid (rear-wheel drive) - Kia Optima Hybrid (front-wheel drive)
- Lexus CT200HLexus CTThe Lexus CT 200h is a hybrid electric automobile introduced by Lexus and is an entry-level luxury hatchback. It made its debut at the March 2010 Geneva Auto Show, six months after the unveiling of the LF-Ch concept car; it is primarily targeted at the European market but will be sold worldwide and...
(front-wheel drive) - Lexus HS250h (front-wheel drive)
- Lexus RX 450h hybrid electric (front-wheel drive)
- Mercedes ML450 Hybrid (four-wheel drive) electric
- Mercedes S400 Blue Hybrid (rear-wheel drive) electric
- Toyota Highlander Hybrid (2011 and newer)
- Toyota PriusToyota PriusThe Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
hybrid electric (front-wheel drive) with a (purely geometric) compression ratio of 13.0:1 - Toyota Camry Hybrid electric (front-wheel drive) with a compression ratio of 12.5:1
- Lexus GS450h hybrid electric (Rear-Wheel drive) with a compression ratio of 13.0:1
External links
- Animation of Atkinson Cycle Engine Note that this animation shows the true Atkinson engine, which uses a complex linkage that allows different stroke lengths for intake/compression and power/exhaust. However, the illustration shows the engine with the linkage laid out to generate 4 equal strokes. To alter the ratio of the strokes, the rightmost pivot point (the one that is attaching the horizontal green link to the frame) should be moved downwards along the frame. This will allow more angular movement as the link rotates up, giving a longer piston stroke for power and exhaust, and less angular movement as the link rotates down, giving a shorter piston stroke for intake and compression. In fact, a sliding pivot point at that location would allow the engine to dynamically change the stroke ratios.
- Modified Atkinson Cycle Engine: Alternative variable valve timing strategy increases low speed torque obtainable from Atkinson Cycle Engine.
- Comparison of Prime Movers Suitable for USMC Expeditionary Power Sources, Oak Ridge National LaboratoryOak Ridge National LaboratoryOak Ridge National Laboratory is a multiprogram science and technology national laboratory managed for the United States Department of Energy by UT-Battelle. ORNL is the DOE's largest science and energy laboratory. ORNL is located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, near Knoxville...
- Libralato Engines - developing a rotary Atkinson cycle engine
- Rotary Atkinson cycle engine - gives details of this engine as well as comparisons with conventional and Wankel engines
- The Prius's Not So Secret Gas-Mileage Secrets - how the Prius uses the Atkinson cycle to get better results than an Otto cycle engine

