Avalanche transistor
Encyclopedia
An avalanche transistor is a bipolar junction transistor
designed for operation in the region of its collector-current/collector-to-emitter voltage characteristics beyond the collector to emitter breakdown voltage
, called avalanche breakdown
region . This region is characterized by avalanche breakdown
, a phenomenon similar to Townsend discharge
for gases, and negative differential resistance. Operation in the avalanche breakdown
region is called avalanche mode operation: it gives avalanche transistors the ability to switch very high currents with less than a nanosecond
rise
and fall time
s (transition time
s).
in the avalanche breakdown
region, in order to overcome speed and breakdown voltage
limitations which affected the first models of such kind of transistor
when used in earlier computer
digital circuits. Therefore the very first applications of avalanche transistor were in switching circuits and multivibrator
s. The introduction of the avalanche transistor served also as an application of Miller's empirical formula for the avalanche multiplication coefficient , first introduced in the paper : the need of better understanding transistor behavior in the avalanche breakdown
, first introduced in the paper : the need of better understanding transistor behavior in the avalanche breakdown
region,
not only for using them in avalanche mode, gave rise to an extensive research on impact ionization
in semiconductors (see ). From the beginning of the 1960s to the first half of the 1970s, several avalanche transistor circuits were proposed, and also it was studied what kind of bipolar junction transistor
is best suited for the use in the avalanche breakdown
region: a complete reference, which includes also the contributions of scientists from ex-USSR and COMECON
countries, is the book by . The first application of the avalanche transistor as a linear amplifier
, named Controlled Avalanche Transit Time Triode, (CATT) was described in : a similar device, named IMPISTOR was described more or less in the same period in the paper of . Linear applications of this class of devices started later since there are some requirements to fulfill, as described below: also, the use of avalanche transistor in those applications is not mainstream since the devices require high collector to emitter voltages in order to work properly. Nowadays, there is still active research on avalanche devices (transistors or other) made of compound semiconductor
s, being capable of switching currents of several tens of ampere
s even faster than "traditional" avalanche transistors.
 In this section, the
In this section, the 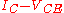 static characteristic of an avalanche transistor is calculated. For the sake of simplicity, only an NPN device is considered: however, the same results are valid for PNP devices only changing signs to voltages and currents accordingly. The analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .
static characteristic of an avalanche transistor is calculated. For the sake of simplicity, only an NPN device is considered: however, the same results are valid for PNP devices only changing signs to voltages and currents accordingly. The analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .
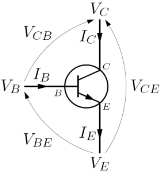
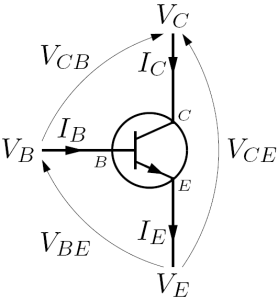
Since avalanche breakdown multiplication is present only across the collector-base junction, the first step of the calculation is to determine collector current as a sum of various component currents though the collector since only those fluxes of charge are subject to this phenomenon. Kirchhoff's current law applied to a bipolar junction transistor
implies the following relation, always satisfied by the collector current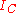
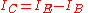
while for the same device working in the active region, basic transistor theory gives the following relation
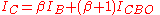
where
Equating the two formulas for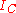 gives the following result
gives the following result

and since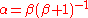 is the common base current gain of the transistor, then
is the common base current gain of the transistor, then
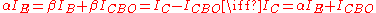
When avalanche effects in a transistor collector are considered, the collector current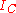 is given by
is given by
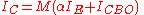
where is Miller's avalanche multiplication coefficient. It is the most important parameter in avalanche mode operation: its expression is the following
is Miller's avalanche multiplication coefficient. It is the most important parameter in avalanche mode operation: its expression is the following
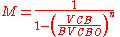
where
Using again Kirchhoff's current law for the bipolar junction transistor
and the given expression for , the resulting expression for
, the resulting expression for  is the following
is the following

and remembering that and
and  where
where 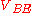 is the base-emitter voltage
is the base-emitter voltage
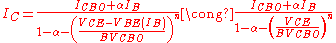
since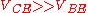 : this is the expression of the parametric family
: this is the expression of the parametric family
of the collector characteristics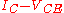 with parameter
with parameter 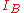 . Note that
. Note that 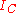 increases without limit if
increases without limit if
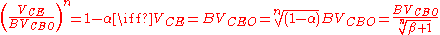
where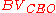 is the collector-emitter breakdown voltage. Also, it is possible to express
is the collector-emitter breakdown voltage. Also, it is possible to express 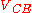 as a function of
as a function of 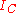 , and obtain an analytical formula for the collector-emitter differential resistance by straightforward differentiation: however, the details are not given here.
, and obtain an analytical formula for the collector-emitter differential resistance by straightforward differentiation: however, the details are not given here.
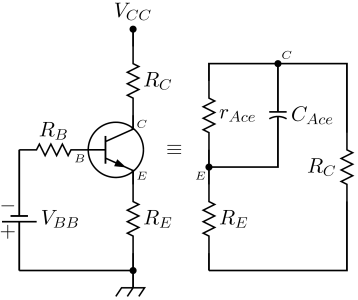 The differential dynamical mode described here, also called the small signal model
The differential dynamical mode described here, also called the small signal model
, is the only intrinsic small signal model of the avalanche transistor. Stray elements due to the package enclosing the transistor are deliberately neglected, since their analysis would not add anything useful from the point of view of the working principles of the avalanche transistor. However, when realizing a electronic circuit
, those parameters are of great importance. Particularly, stray inductances in series with collector and emitter leads have to be minimized to preserve the high speed performance of avalache transistor circuits. Also, this equivalent circuit is useful when describing the behavior of the avalanche transistor near its turn on time, where collector currents and voltages are still near their quiescent values: in the real circuit it permits the calculation of time constant
s and therefore rise and fall times of the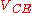 waveform. However, since avalanche transistor switching circuits are intrinsically large signal circuits, the only way to predict with reasonable accuracy their real behaviour is to do numerical simulations. Again, the analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .
waveform. However, since avalanche transistor switching circuits are intrinsically large signal circuits, the only way to predict with reasonable accuracy their real behaviour is to do numerical simulations. Again, the analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .
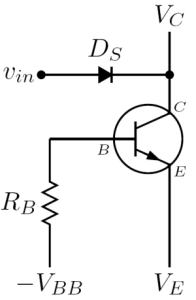
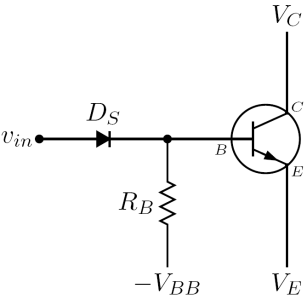
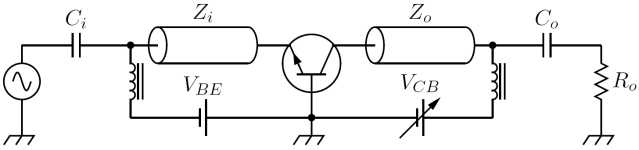
An avalanche transistor operated by a common bias network is shown in the picture on the right: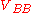 can be zero or positive value, while
can be zero or positive value, while 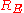 can be short circuit
can be short circuit
ed. In every avalanche transistor circuit, the output signal is taken from the collector or the emitter: therefore the small-signal differential model
of an avalanche transistor working in the avalanche region is always seen from the collector-emitter output pins, and consist of a parallel circuit as shown in the picture on the right, which includes only bias components.
circuit as shown in the picture on the right, which includes only bias components.
The magnitude and sign of both those parameters are controlled by the base current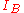 : since both base-collector and base-emitter junctions are inversely biased in the quiescent state, the equivalent circuit of the base input is simply a current generator shunted by base-emitter and base-collector junction capacitances and is therefore not analyzed in what follows.
: since both base-collector and base-emitter junctions are inversely biased in the quiescent state, the equivalent circuit of the base input is simply a current generator shunted by base-emitter and base-collector junction capacitances and is therefore not analyzed in what follows.
The intrinsic time constant of the basic equivalent small signal circuit has the following value
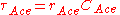
where
The two parameters are both negative. This means that if the collector load const of an ideal current source
, the circuit is unstable. This is the theoretical justification of the astable multivibrator behavior of the circuit when the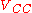 voltage is raised over some critical level.
voltage is raised over some critical level.
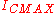 a new breakdown mechanism become important: the second breakdown. This phenomenon is caused by excessive heating of some points (hot spots) in the base-emitter region of the bipolar junction transistor
a new breakdown mechanism become important: the second breakdown. This phenomenon is caused by excessive heating of some points (hot spots) in the base-emitter region of the bipolar junction transistor
, which give rise to an exponentially increasing current
through these points: this exponential rise of current in turn gives rise to even more overheating, originating a positive thermal feedback
mechanism. While analyzing the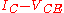 static characteristic, the presence of this phenomenon is seen as a sharp collector voltage
static characteristic, the presence of this phenomenon is seen as a sharp collector voltage
drop and a corresponding almost vertical rise of the collector current. At the present, it is not possible to produce a transistor without hot spots and thus without second breakdown, since their presence is related to the technology of refinement of silicon
. During this process, very small but finite quantities of metal
s remain in localized portions of the wafer: these particles of metals became deep centers of recombination
, i.e. centers where current
exists in a preferred way. While this phenomenon is destructive for Bipolar junction transistor
s working in the usual way, it can be used to push-up further the current and voltage limits of a device working in avalanche mode by limiting its time duration: also, the switching speed of the device is not negatively affected. A clear description of avalanche transistor circuits working in second breakdown regime together with some examples can be found in the paper .
s, when applied to such circuits, can only give a qualitative description. To obtain more accurate information about the behavior of time dependent voltage
s and currents in such circuits it is necessary to use numerical analysis
. The "classical" approach, detailed in the paper which relies upon the book , consists in considering the circuits as a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations and solve it by a numerical method
implemented by a general purpose numerical simulation software: results obtained in this way are fairly accurate and simple to obtain. However, this methods rely on the use of analytical transistor models best suited for the analysis of the breakdown region: those models are not necessarily suited to describe the device working in all possible regions. A more modern approach consist in using the common analog circuit simulator SPICE
together with an advanced transistor model supporting avalanche breakdown simulations, since the basic SPICE
transistor model does not. Examples of such models are described in the paper and in the paper : the latter is a description of the Mextram model, currently used by some semiconductor industries to characterize their bipolar junction transistor
s.
s, having rise
and fall time
s of less than a nanosecond and high output voltage
and current
. They are occasionally used as amplifiers in the microwave
frequency range, even if this use is not mainstream: when used for this purpose, they are called "Controlled Avalanche Transit-time Triodes" (CATTs).
flowing through the collector-base junction as a result of impact ionization
of the atoms in the semiconductor crystal lattice. Avalanche breakdown in semiconductors has found application in switching circuits for two basic reasons
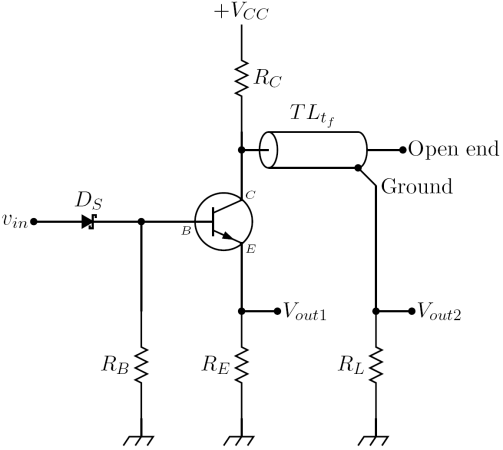
The two circuits considered in this section are the simplest examples of avalanche transistor circuits for switching purposes: both the examples detailed are monostable multivibrators. It is possible to find several more complex circuits in the literature, for example in the books and . First, it is worth noting that the largest part of circuits employing an avalanche transistor is activated by the following two different kind of inputs:
Avalanche transistor can also be triggered by lowering the emitter voltage , but this configuration is rarely seen in the literature and in practical circuits.: in reference , paragraph 3.2.4 "Trigger circuits" one such configuration is described, where the avalanche transistor is used itself as a part of the trigger circuit of a complex pulser, while in reference a balanced level discriminator where a common bipolar junction transistor
, but this configuration is rarely seen in the literature and in practical circuits.: in reference , paragraph 3.2.4 "Trigger circuits" one such configuration is described, where the avalanche transistor is used itself as a part of the trigger circuit of a complex pulser, while in reference a balanced level discriminator where a common bipolar junction transistor
is emitter-coupled
to an avalanche transistor is briefly described.
The two avalanche pulser described below are both base triggered and have two outputs. Since the device used is an NPN transistor, is a positive going output while
is a positive going output while  is a negative going output: using a PNP transistor reverses the polarities of outputs. The description of their simplified versions, where resistor
is a negative going output: using a PNP transistor reverses the polarities of outputs. The description of their simplified versions, where resistor  or
or  is set to zero ohm (obviously not both) in order to have a single output, can be found in reference . Resistor
is set to zero ohm (obviously not both) in order to have a single output, can be found in reference . Resistor 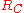 recharges the capacitor
recharges the capacitor 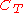 or the transmission line
or the transmission line 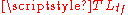 (i.e. the energy storage components) after commutation. It has usually a high resistance to limit the static collector current, so the recharging process is slow. Sometimes this resistor is replaced by an electronic circuit which is capable of charging faster the energy storage components. However this kind of circuit usually is patent
(i.e. the energy storage components) after commutation. It has usually a high resistance to limit the static collector current, so the recharging process is slow. Sometimes this resistor is replaced by an electronic circuit which is capable of charging faster the energy storage components. However this kind of circuit usually is patent
ed so they are rarely found in mainstream application circuits.
In practical designs, an adjustable impedance like a two terminal Zobel network
(or simply a trimmer capacitor) is placed from the collector of the avalanche transistor to ground, giving the tramission line pulser the ability to reduce ringing
and other undesidered behavior on the output voltage
s.
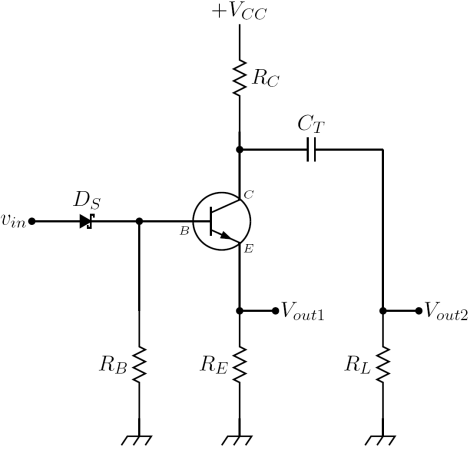
 It is possible to turn those circuits into astable multivibrators by removing their trigger input circuits and
It is possible to turn those circuits into astable multivibrators by removing their trigger input circuits and
A well detailed example of the first procedure is described in reference . It is also possible to realize avalanche mode bistable multivibrators, but their use is not as common as other types described of multivibrator
s, one important reason being that they require two avalanche transistors, one working continuously in avalanche breakdown
regime, and this can give serious problems from the point of wiev of power dissipation and device operating life.
 be kept almost constant for large output voltage swings: if this condition is not fulfilled, significant amplitude distortion
be kept almost constant for large output voltage swings: if this condition is not fulfilled, significant amplitude distortion
arises on the output signal. This implies that
These two requirements imply that a device used for amplification need a physical structure different from that of a typical avalanche transistor. The Controlled Avalanche Transit-time Triode (CATT), designed for microwave
amplification
, has a quite large lightly doped
region between the base and the collector regions: this implies that the device has fairly high collector-emitter breakdown voltage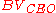 respect to bipolar transistors having the same geometry. The current amplification mechanism is the same of the avalanche transistor, i.e. carrier generation by impact ionization
respect to bipolar transistors having the same geometry. The current amplification mechanism is the same of the avalanche transistor, i.e. carrier generation by impact ionization
, but there is also a transit-time effect as in IMPATT
and TRAPATT diodes, where a high field region travels along the avalanching junction, precisely in along the intrinsic region. The device structure and choice of bias point imply that
A complete description of the theory for this kind of avalanche transistor is available in the paper : in this paper it is also showh that this semiconductor device
structure is well suited for microwave
power amplification. It can deliver several watt
s of radio frequency
power at a frequency of several gigahertz and it also features a control terminal (the base). However its use is not mainstream as already said,
since it requires high voltages (greather than 200 volt
s) to work properly, while nowadays gallium arsenide or other compound semiconductor
s FETs deliver a similar performance while being easier to work with. A similar device structure, proposed more or less in the same period in the paper , was the IMPISTOR, being a transistor with IMPATT
collector-base junction.
similar to the CATT.. A paper analyzing the volt-amperometric characteristic of diodes and transistors using the computer algebra program Mathematica
.. A paper about the design of an avalanche transistor relaxation oscillator using the computer algebra program Mathematica
. A brief description of the basic physical principles of avalanche transistor circuits: instructive and interesting but "restricted access".. A theoretical study of the stability of a transistor biased in the avalanche region (restricted access). available from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific & Technical Information. A report describing a transistor model capable of including avalanche effects in SPICE
simulations.. A paper describing the Mextram SPICE model from the point of view of avalanche behavior simulation. For a free copy found in the Mextram home page of NXP see here.. A paper describing a transistor model for bipolar circuit simulation including avalanche effects (restricted access).
constructed using series connected avalanche transistor circuits.. A paper describing an application of avalanche transistors to the design of a sampling oscilloscope: available abstract, full paper is "restricted access".. Available from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific & Technical Information. A report describing the design of a driver for Pockels cells Q-switches
.. A project of an avalanche transistor astable multivibrator with schematics, waveforms and photos of the layout.. Academic Dissertation presented with the assent of the Faculty of Technology. A doctoral dissertation describing a Laser
TOF (Time Of Flight) Radar
and its construction using an avalanche transistor pulser. (preprint version here). A paper describing an avalanche transistor pulser and its use as Laser
driver in a laser radar
.
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
designed for operation in the region of its collector-current/collector-to-emitter voltage characteristics beyond the collector to emitter breakdown voltage
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive.The breakdown voltage of a diode is the minimum reverse voltage to make the diode conduct in reverse...
, called avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
region . This region is characterized by avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
, a phenomenon similar to Townsend discharge
Townsend discharge
The Townsend discharge is a gas ionization process where an initially very small amount of free electrons, accelerated by a sufficiently strong electric field, give rise to electrical conduction through a gas by avalanche multiplication: when the number of free charges drops or the electric field...
for gases, and negative differential resistance. Operation in the avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
region is called avalanche mode operation: it gives avalanche transistors the ability to switch very high currents with less than a nanosecond
Nanosecond
A nanosecond is one billionth of a second . One nanosecond is to one second as one second is to 31.7 years.The word nanosecond is formed by the prefix nano and the unit second. Its symbol is ns....
rise
Rise time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
and fall time
Fall time
In electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
s (transition time
Transition time
The transition time \scriptstyle t_t\, is the time a dynamical system needs to switch between two different stable states, when responding to a stable input signal. In a logic circuit undergoing a change of state, it identifies the rise time or the fall time of the output voltage...
s).
History
The first paper dealing with avalanche transistor was : the paper describes how to use alloy-junction transistorAlloy-junction transistor
The germanium alloy-junction transistor, or alloy transistor, was an early type of bipolar junction transistor, developed at General Electric and RCA in 1951 as an improvement over the earlier grown-junction transistor....
in the avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
region, in order to overcome speed and breakdown voltage
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive.The breakdown voltage of a diode is the minimum reverse voltage to make the diode conduct in reverse...
limitations which affected the first models of such kind of transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
when used in earlier computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
digital circuits. Therefore the very first applications of avalanche transistor were in switching circuits and multivibrator
Multivibrator
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state systems such as oscillators, timers and flip-flops. It is characterized by two amplifying devices cross-coupled by resistors or capacitors...
s. The introduction of the avalanche transistor served also as an application of Miller's empirical formula for the avalanche multiplication coefficient
 , first introduced in the paper : the need of better understanding transistor behavior in the avalanche breakdown
, first introduced in the paper : the need of better understanding transistor behavior in the avalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
region,
not only for using them in avalanche mode, gave rise to an extensive research on impact ionization
Impact ionization
Impact ionization is the process in a material by which one energetic charge carrier can lose energy by the creation of other charge carriers...
in semiconductors (see ). From the beginning of the 1960s to the first half of the 1970s, several avalanche transistor circuits were proposed, and also it was studied what kind of bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
is best suited for the use in the avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
region: a complete reference, which includes also the contributions of scientists from ex-USSR and COMECON
Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance , 1949–1991, was an economic organisation under hegemony of Soviet Union comprising the countries of the Eastern Bloc along with a number of communist states elsewhere in the world...
countries, is the book by . The first application of the avalanche transistor as a linear amplifier
Linear amplifier
A linear amplifier is an electronic circuit whose output is proportional to its input, but capable of delivering more power into a load. The term usually refers to a type of radio-frequency power amplifier, some of which have output power measured in kilowatts, and are used in amateur radio...
, named Controlled Avalanche Transit Time Triode, (CATT) was described in : a similar device, named IMPISTOR was described more or less in the same period in the paper of . Linear applications of this class of devices started later since there are some requirements to fulfill, as described below: also, the use of avalanche transistor in those applications is not mainstream since the devices require high collector to emitter voltages in order to work properly. Nowadays, there is still active research on avalanche devices (transistors or other) made of compound semiconductor
Compound semiconductor
A compound semiconductor is a semiconductor compound composed of elements from two or more different groups of the periodic table . These semiconductors typically form in groups 13-16 ,...
s, being capable of switching currents of several tens of ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s even faster than "traditional" avalanche transistors.
Static avalanche region characteristics

 static characteristic of an avalanche transistor is calculated. For the sake of simplicity, only an NPN device is considered: however, the same results are valid for PNP devices only changing signs to voltages and currents accordingly. The analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .
static characteristic of an avalanche transistor is calculated. For the sake of simplicity, only an NPN device is considered: however, the same results are valid for PNP devices only changing signs to voltages and currents accordingly. The analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .Since avalanche breakdown multiplication is present only across the collector-base junction, the first step of the calculation is to determine collector current as a sum of various component currents though the collector since only those fluxes of charge are subject to this phenomenon. Kirchhoff's current law applied to a bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
implies the following relation, always satisfied by the collector current
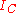
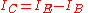
while for the same device working in the active region, basic transistor theory gives the following relation
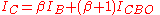
where
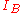 is the base current,
is the base current,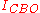 is the collector-base reverse leakage current,
is the collector-base reverse leakage current,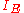 is the emitter current,
is the emitter current,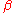 is the common emitter current gain of the transistor.
is the common emitter current gain of the transistor.
Equating the two formulas for
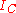 gives the following result
gives the following result
and since
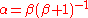 is the common base current gain of the transistor, then
is the common base current gain of the transistor, then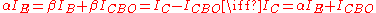
When avalanche effects in a transistor collector are considered, the collector current
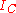 is given by
is given by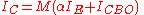
where
 is Miller's avalanche multiplication coefficient. It is the most important parameter in avalanche mode operation: its expression is the following
is Miller's avalanche multiplication coefficient. It is the most important parameter in avalanche mode operation: its expression is the following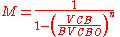
where
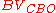 is the collector-base breakdown voltage,
is the collector-base breakdown voltage, is a constant depending on the semiconductor used for the construction of the transistor and doping profile of the collector-base junction,
is a constant depending on the semiconductor used for the construction of the transistor and doping profile of the collector-base junction,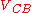 is the collector-base voltage.
is the collector-base voltage.
Using again Kirchhoff's current law for the bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
and the given expression for
 , the resulting expression for
, the resulting expression for  is the following
is the following
and remembering that
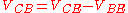 and
and 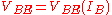 where
where 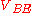 is the base-emitter voltage
is the base-emitter voltage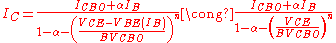
since
 : this is the expression of the parametric family
: this is the expression of the parametric familyParametric family
In mathematics and its applications, a parametric family or a parameterized family is a family of objects whose definitions depend on a set of parameters....
of the collector characteristics
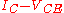 with parameter
with parameter 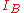 . Note that
. Note that 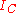 increases without limit if
increases without limit if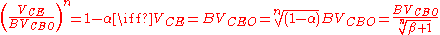
where
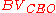 is the collector-emitter breakdown voltage. Also, it is possible to express
is the collector-emitter breakdown voltage. Also, it is possible to express  as a function of
as a function of  , and obtain an analytical formula for the collector-emitter differential resistance by straightforward differentiation: however, the details are not given here.
, and obtain an analytical formula for the collector-emitter differential resistance by straightforward differentiation: however, the details are not given here.Differential dynamical model

Small signal model
Small-signal modeling is a common analysis technique in electrical engineering which is used to approximate the behavior of nonlinear devices with linear equations...
, is the only intrinsic small signal model of the avalanche transistor. Stray elements due to the package enclosing the transistor are deliberately neglected, since their analysis would not add anything useful from the point of view of the working principles of the avalanche transistor. However, when realizing a electronic circuit
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
, those parameters are of great importance. Particularly, stray inductances in series with collector and emitter leads have to be minimized to preserve the high speed performance of avalache transistor circuits. Also, this equivalent circuit is useful when describing the behavior of the avalanche transistor near its turn on time, where collector currents and voltages are still near their quiescent values: in the real circuit it permits the calculation of time constant
Time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter \tau , is the risetime characterizing the response to a time-varying input of a first-order, linear time-invariant system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a system that can be modeled by a single first order...
s and therefore rise and fall times of the
 waveform. However, since avalanche transistor switching circuits are intrinsically large signal circuits, the only way to predict with reasonable accuracy their real behaviour is to do numerical simulations. Again, the analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .
waveform. However, since avalanche transistor switching circuits are intrinsically large signal circuits, the only way to predict with reasonable accuracy their real behaviour is to do numerical simulations. Again, the analysis closely follows that of William D. Roehr in .An avalanche transistor operated by a common bias network is shown in the picture on the right:
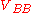 can be zero or positive value, while
can be zero or positive value, while  can be short circuit
can be short circuitShort circuit
A short circuit in an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path, often where essentially no electrical impedance is encountered....
ed. In every avalanche transistor circuit, the output signal is taken from the collector or the emitter: therefore the small-signal differential model
Small signal model
Small-signal modeling is a common analysis technique in electrical engineering which is used to approximate the behavior of nonlinear devices with linear equations...
of an avalanche transistor working in the avalanche region is always seen from the collector-emitter output pins, and consist of a parallel
 circuit as shown in the picture on the right, which includes only bias components.
circuit as shown in the picture on the right, which includes only bias components.The magnitude and sign of both those parameters are controlled by the base current
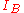 : since both base-collector and base-emitter junctions are inversely biased in the quiescent state, the equivalent circuit of the base input is simply a current generator shunted by base-emitter and base-collector junction capacitances and is therefore not analyzed in what follows.
: since both base-collector and base-emitter junctions are inversely biased in the quiescent state, the equivalent circuit of the base input is simply a current generator shunted by base-emitter and base-collector junction capacitances and is therefore not analyzed in what follows.The intrinsic time constant of the basic equivalent small signal circuit has the following value
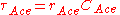
where
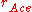 is the collector-emitter avalanche differential resistance and, as stated above, can be obtained by differentiation of the collector-emitter voltage
is the collector-emitter avalanche differential resistance and, as stated above, can be obtained by differentiation of the collector-emitter voltage 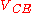 respect to the collector current
respect to the collector current 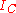 , for a constant base current
, for a constant base current 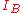

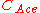 is the collector-emitter avalanche differential capacitance and has the following expression
is the collector-emitter avalanche differential capacitance and has the following expression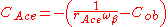
- where
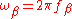 is the current gain angular cutoff frequencyCutoff frequencyIn physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced rather than passing through.Typically in electronic systems such as filters and...
is the current gain angular cutoff frequencyCutoff frequencyIn physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced rather than passing through.Typically in electronic systems such as filters and... is the common base output capacitance
is the common base output capacitance
The two parameters are both negative. This means that if the collector load const of an ideal current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
, the circuit is unstable. This is the theoretical justification of the astable multivibrator behavior of the circuit when the
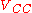 voltage is raised over some critical level.
voltage is raised over some critical level.Second breakdown avalanche mode
When the collector current rises above the data sheet limit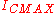 a new breakdown mechanism become important: the second breakdown. This phenomenon is caused by excessive heating of some points (hot spots) in the base-emitter region of the bipolar junction transistor
a new breakdown mechanism become important: the second breakdown. This phenomenon is caused by excessive heating of some points (hot spots) in the base-emitter region of the bipolar junction transistorBipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
, which give rise to an exponentially increasing current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
through these points: this exponential rise of current in turn gives rise to even more overheating, originating a positive thermal feedback
Positive feedback
Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small disturbance on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system that responds to a perturbation in a way that reduces its effect is...
mechanism. While analyzing the
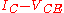 static characteristic, the presence of this phenomenon is seen as a sharp collector voltage
static characteristic, the presence of this phenomenon is seen as a sharp collector voltageVoltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
drop and a corresponding almost vertical rise of the collector current. At the present, it is not possible to produce a transistor without hot spots and thus without second breakdown, since their presence is related to the technology of refinement of silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
. During this process, very small but finite quantities of metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
s remain in localized portions of the wafer: these particles of metals became deep centers of recombination
Carrier generation and recombination
In the solid state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as...
, i.e. centers where current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
exists in a preferred way. While this phenomenon is destructive for Bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
s working in the usual way, it can be used to push-up further the current and voltage limits of a device working in avalanche mode by limiting its time duration: also, the switching speed of the device is not negatively affected. A clear description of avalanche transistor circuits working in second breakdown regime together with some examples can be found in the paper .
Numerical simulations
Avalanche transistor circuits are intrinsically large signal circuits, so small signal modelSmall signal model
Small-signal modeling is a common analysis technique in electrical engineering which is used to approximate the behavior of nonlinear devices with linear equations...
s, when applied to such circuits, can only give a qualitative description. To obtain more accurate information about the behavior of time dependent voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
s and currents in such circuits it is necessary to use numerical analysis
Numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis ....
. The "classical" approach, detailed in the paper which relies upon the book , consists in considering the circuits as a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations and solve it by a numerical method
Numerical ordinary differential equations
Numerical ordinary differential equations is the part of numerical analysis which studies the numerical solution of ordinary differential equations...
implemented by a general purpose numerical simulation software: results obtained in this way are fairly accurate and simple to obtain. However, this methods rely on the use of analytical transistor models best suited for the analysis of the breakdown region: those models are not necessarily suited to describe the device working in all possible regions. A more modern approach consist in using the common analog circuit simulator SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
together with an advanced transistor model supporting avalanche breakdown simulations, since the basic SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
transistor model does not. Examples of such models are described in the paper and in the paper : the latter is a description of the Mextram model, currently used by some semiconductor industries to characterize their bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
s.
A graphical method
A graphical method for studying the behavior or avalanche transistor was proposed in references and : the method was first derived in order to plot the static behavior of the device and then was applied also to solve problems concerning the dynamic behavior. The method bears the spirit of the graphical methods used to design tube and transistor circuits directly from the characteristic diagrams given in data sheets by producers.Applications
Avalanche transistors are mainly used as fast pulse generatorPulse generator
A pulse generator is either an electronic circuit or a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. This article describes the test equipment.-Bench pulse generators:...
s, having rise
Rise time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
and fall time
Fall time
In electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
s of less than a nanosecond and high output voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
and current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
. They are occasionally used as amplifiers in the microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
frequency range, even if this use is not mainstream: when used for this purpose, they are called "Controlled Avalanche Transit-time Triodes" (CATTs).
Avalanche mode switching circuits
Avalanche mode switching relies on avalanche multiplication of currentElectric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
flowing through the collector-base junction as a result of impact ionization
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
of the atoms in the semiconductor crystal lattice. Avalanche breakdown in semiconductors has found application in switching circuits for two basic reasons
- it can provide very high switching speeds, since current builds-up in very small times, in the picosecond range, due to avalanche multiplication.
- It can provide very high output currents, since large currents can be controlled by very small ones, again due to avalanche multiplication.
The two circuits considered in this section are the simplest examples of avalanche transistor circuits for switching purposes: both the examples detailed are monostable multivibrators. It is possible to find several more complex circuits in the literature, for example in the books and . First, it is worth noting that the largest part of circuits employing an avalanche transistor is activated by the following two different kind of inputs:


- Collector triggering input circuit: the input trigger signal is fed to the collector via a fast switching diodeDiodeIn electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
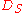 , possibly after being shaped by a pulse shaping network. This way of driving an avalanche transistor was extensively employed in first generation circuits since the collector node has a high impedance and also collector capacitance
, possibly after being shaped by a pulse shaping network. This way of driving an avalanche transistor was extensively employed in first generation circuits since the collector node has a high impedance and also collector capacitance  behaves quite linearly under large signal regime. As a consequence of this, the delay time from input to output is very small and approximately independent of the value of control voltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
behaves quite linearly under large signal regime. As a consequence of this, the delay time from input to output is very small and approximately independent of the value of control voltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
. However, this trigger circuit requires a diode capable of resist to high reverse voltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
s and switch very fast, characteristics that are very difficult to realize in the same diodeDiodeIn electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
, therefore it is rarely seen in modern avalanche transistor circuits. - Base triggering input circuit: the input trigger signal is fed directly to the base via a fast switching diode
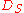 , possibly after being shaped by a pulse shaping network . This way of driving an avalanche transistor was relatively less employed in first generation circuits because the base node has a relatively low impedanceElectrical impedanceElectrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
, possibly after being shaped by a pulse shaping network . This way of driving an avalanche transistor was relatively less employed in first generation circuits because the base node has a relatively low impedanceElectrical impedanceElectrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
and an input capacitance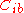 which is highly nonlinear (as a matter of fact, it is exponential) under the large signal regime: this causes a fairly large, input voltage dependent, delay time, which was analyzed in detail in the paper . However, the required inverse voltage for the feed diode is far lower respect diodes to be used in collectior trigger input circuits, and since ultra fast Schottky diodeSchottky diodeThe Schottky diode is a semiconductor diode with a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action...
which is highly nonlinear (as a matter of fact, it is exponential) under the large signal regime: this causes a fairly large, input voltage dependent, delay time, which was analyzed in detail in the paper . However, the required inverse voltage for the feed diode is far lower respect diodes to be used in collectior trigger input circuits, and since ultra fast Schottky diodeSchottky diodeThe Schottky diode is a semiconductor diode with a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action...
s are easily and cheaply found, this is the driver circuit employed in most modern avalanche transistor circuit. This is also the reason why the diode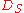 in the following applicative circuits is symbolized as a Schottky diode.
in the following applicative circuits is symbolized as a Schottky diode.
Avalanche transistor can also be triggered by lowering the emitter voltage
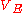 , but this configuration is rarely seen in the literature and in practical circuits.: in reference , paragraph 3.2.4 "Trigger circuits" one such configuration is described, where the avalanche transistor is used itself as a part of the trigger circuit of a complex pulser, while in reference a balanced level discriminator where a common bipolar junction transistor
, but this configuration is rarely seen in the literature and in practical circuits.: in reference , paragraph 3.2.4 "Trigger circuits" one such configuration is described, where the avalanche transistor is used itself as a part of the trigger circuit of a complex pulser, while in reference a balanced level discriminator where a common bipolar junction transistorBipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
is emitter-coupled
Emitter-coupled logic
In electronics, emitter-coupled logic , is a logic family that achieves high speed by using an overdriven BJT differential amplifier with single-ended input, whose emitter current is limited to avoid the slow saturation region of transistor operation....
to an avalanche transistor is briefly described.
The two avalanche pulser described below are both base triggered and have two outputs. Since the device used is an NPN transistor,
 is a positive going output while
is a positive going output while  is a negative going output: using a PNP transistor reverses the polarities of outputs. The description of their simplified versions, where resistor
is a negative going output: using a PNP transistor reverses the polarities of outputs. The description of their simplified versions, where resistor 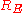 or
or 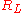 is set to zero ohm (obviously not both) in order to have a single output, can be found in reference . Resistor
is set to zero ohm (obviously not both) in order to have a single output, can be found in reference . Resistor 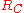 recharges the capacitor
recharges the capacitor 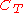 or the transmission line
or the transmission line 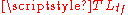 (i.e. the energy storage components) after commutation. It has usually a high resistance to limit the static collector current, so the recharging process is slow. Sometimes this resistor is replaced by an electronic circuit which is capable of charging faster the energy storage components. However this kind of circuit usually is patent
(i.e. the energy storage components) after commutation. It has usually a high resistance to limit the static collector current, so the recharging process is slow. Sometimes this resistor is replaced by an electronic circuit which is capable of charging faster the energy storage components. However this kind of circuit usually is patentPatent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
ed so they are rarely found in mainstream application circuits.
- Capacitor discharge avalanche pulser: a trigger signal applied to the base lead of the avalanche transistor cause the avalanche breakdown between the collector and emitter lead. The capacitor
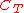 starts to be discharged by a current flowing through the resistors
starts to be discharged by a current flowing through the resistors 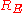 and
and 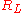 : the voltages across those resistors are the output voltages. The current waveform is not a simple RC discharge current but has a complex behavior which depends on the avalanche mechanism: however it has a very fast rise time, of the order of fractions of a nanosecond. Peak current depends on the size of the capacitor
: the voltages across those resistors are the output voltages. The current waveform is not a simple RC discharge current but has a complex behavior which depends on the avalanche mechanism: however it has a very fast rise time, of the order of fractions of a nanosecond. Peak current depends on the size of the capacitor 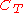 : when its value is raised over a few hundred picofarads, transistor goes in to second breakdown avalanche mode, and peak currents reach values of several amperes.
: when its value is raised over a few hundred picofarads, transistor goes in to second breakdown avalanche mode, and peak currents reach values of several amperes. - Transmission line avalanche pulser: a trigger signal applied to the base lead of the avalanche transistor cause the avalanche breakdown between the collector and emitter lead. The fast rise timeRise timeIn electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
of the collector current generates a current pulse of approximatively the same amplitude, which propagates along the transmission line. The pulse reaches the open circuited end of the line after the characteristic delay time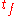 of the line has elapsed, and then is reflected backward. If the characteristic impedance of the transmission line is equal to the resistances
of the line has elapsed, and then is reflected backward. If the characteristic impedance of the transmission line is equal to the resistances 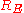 and
and 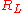 , the backward reflected pulse reaches the beginning of the line and stops. As a consequence of this traveling wave behavior, the current flowing through the avalanche transistor has a rectangular shape of duration
, the backward reflected pulse reaches the beginning of the line and stops. As a consequence of this traveling wave behavior, the current flowing through the avalanche transistor has a rectangular shape of duration
In practical designs, an adjustable impedance like a two terminal Zobel network
Zobel network
Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs who published a much referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design...
(or simply a trimmer capacitor) is placed from the collector of the avalanche transistor to ground, giving the tramission line pulser the ability to reduce ringing
Ringing (signal)
In electronics, signal processing, and video, ringing is unwanted oscillation of a signal, particularly in the step response...
and other undesidered behavior on the output voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
s.


- raising their power supply voltage
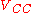 until a relaxation oscillationRelaxation oscillatorA relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system's return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy...
until a relaxation oscillationRelaxation oscillatorA relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system's return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy...
begins, or - connecting the base resistor
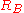 to a positive base bias voltage
to a positive base bias voltage 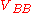 and thus forcibly starting avalanche breakdown and associated relaxation oscillationRelaxation oscillatorA relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system's return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy...
and thus forcibly starting avalanche breakdown and associated relaxation oscillationRelaxation oscillatorA relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system's return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy...
.
A well detailed example of the first procedure is described in reference . It is also possible to realize avalanche mode bistable multivibrators, but their use is not as common as other types described of multivibrator
Multivibrator
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state systems such as oscillators, timers and flip-flops. It is characterized by two amplifying devices cross-coupled by resistors or capacitors...
s, one important reason being that they require two avalanche transistors, one working continuously in avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
regime, and this can give serious problems from the point of wiev of power dissipation and device operating life.
The controlled avalanche transit-time triode (CATT)
Avalanche mode amplification relies on avalanche multiplication as avalanche mode switching. However, for this mode of operation, it is necessary that Miller's avalanche multiplication coefficient be kept almost constant for large output voltage swings: if this condition is not fulfilled, significant amplitude distortion
be kept almost constant for large output voltage swings: if this condition is not fulfilled, significant amplitude distortionAmplitude distortion
Amplitude distortion is distortion occurring in a system, subsystem, or device when the output amplitude is not a linear function of the input amplitude under specified conditions....
arises on the output signal. This implies that
- avalanche transistors used for application in switching circuits cannot be used since Miller's coefficient varies widely with the collector to emitter voltage
- the operating point of the device cannot be in the negative resistanceNegative resistanceNegative resistance is a property of some electric circuits where an increase in the current entering a port results in a decreased voltage across the same port. This is in contrast to a simple ohmic resistor, which exhibits an increase in voltage under the same conditions. Negative resistors are...
of the avalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
region for the same reason
These two requirements imply that a device used for amplification need a physical structure different from that of a typical avalanche transistor. The Controlled Avalanche Transit-time Triode (CATT), designed for microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
amplification
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
, has a quite large lightly doped
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping intentionally introduces impurities into an extremely pure semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical properties. The impurities are dependent upon the type of semiconductor. Lightly and moderately doped semiconductors are referred to as extrinsic...
region between the base and the collector regions: this implies that the device has fairly high collector-emitter breakdown voltage
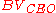 respect to bipolar transistors having the same geometry. The current amplification mechanism is the same of the avalanche transistor, i.e. carrier generation by impact ionization
respect to bipolar transistors having the same geometry. The current amplification mechanism is the same of the avalanche transistor, i.e. carrier generation by impact ionizationImpact ionization
Impact ionization is the process in a material by which one energetic charge carrier can lose energy by the creation of other charge carriers...
, but there is also a transit-time effect as in IMPATT
IMPATT diode
An IMPATT diode is a form of high power diode used in high-frequency electronics and microwave devices. They are typically made with silicon carbide owing to their high breakdown fields....
and TRAPATT diodes, where a high field region travels along the avalanching junction, precisely in along the intrinsic region. The device structure and choice of bias point imply that
- Miller's avalanche multiplication coefficient M is limited to about 10.
- The transit-time effect keep this coefficient almost constant and independent of the collector to emitter voltage.
A complete description of the theory for this kind of avalanche transistor is available in the paper : in this paper it is also showh that this semiconductor device
Semiconductor device
Semiconductor devices are electronic components that exploit the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, principally silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors. Semiconductor devices have replaced thermionic devices in most applications...
structure is well suited for microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
power amplification. It can deliver several watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s of radio frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
power at a frequency of several gigahertz and it also features a control terminal (the base). However its use is not mainstream as already said,
since it requires high voltages (greather than 200 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s) to work properly, while nowadays gallium arsenide or other compound semiconductor
Compound semiconductor
A compound semiconductor is a semiconductor compound composed of elements from two or more different groups of the periodic table . These semiconductors typically form in groups 13-16 ,...
s FETs deliver a similar performance while being easier to work with. A similar device structure, proposed more or less in the same period in the paper , was the IMPISTOR, being a transistor with IMPATT
IMPATT diode
An IMPATT diode is a form of high power diode used in high-frequency electronics and microwave devices. They are typically made with silicon carbide owing to their high breakdown fields....
collector-base junction.

See also
- Avalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
- Avalanche diodeAvalanche diodeIn electronics, an avalanche diode is a diode that is designed to go through avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage. The junction of an avalanche diode is designed to prevent current concentration at hot spots, so that the diode is undamaged by the breakdown...
- Bipolar junction transistorBipolar junction transistor|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
- MultivibratorMultivibratorA multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state systems such as oscillators, timers and flip-flops. It is characterized by two amplifying devices cross-coupled by resistors or capacitors...
- Pulse generatorPulse generatorA pulse generator is either an electronic circuit or a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. This article describes the test equipment.-Bench pulse generators:...
- Second breakdown
Theory
. A paper proposing and describing the IMPISTOR, a semiconductor deviceSemiconductor device
Semiconductor devices are electronic components that exploit the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, principally silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors. Semiconductor devices have replaced thermionic devices in most applications...
similar to the CATT.. A paper analyzing the volt-amperometric characteristic of diodes and transistors using the computer algebra program Mathematica
Mathematica
Mathematica is a computational software program used in scientific, engineering, and mathematical fields and other areas of technical computing...
.. A paper about the design of an avalanche transistor relaxation oscillator using the computer algebra program Mathematica
Mathematica
Mathematica is a computational software program used in scientific, engineering, and mathematical fields and other areas of technical computing...
. A brief description of the basic physical principles of avalanche transistor circuits: instructive and interesting but "restricted access".. A theoretical study of the stability of a transistor biased in the avalanche region (restricted access). available from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific & Technical Information. A report describing a transistor model capable of including avalanche effects in SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
simulations.. A paper describing the Mextram SPICE model from the point of view of avalanche behavior simulation. For a free copy found in the Mextram home page of NXP see here.. A paper describing a transistor model for bipolar circuit simulation including avalanche effects (restricted access).
- Jochen Riks "Avalanche-Transistor" (in German). A brief description of the working principles of the avalanche transistor, part of the course "Impulsschaltungen F-Praktikum EXP 10", June 1996, Fachschaft Physik Uni Düsseldorf.. A paper proposing a graphical method to plot the static characteristic of an avalanche transistor (restricted access).. A paper pushing further the study of avalanche transistor by a graphical method proposed in the preceding work (restricted access).. A paper analyzing the trigger delay time of avalanche transistors by means of numerical analysisNumerical analysisNumerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis ....
(restricted access).. A paper where an analytical model of the behavior of an avalanche transistor is derived after suitable approximations (restricted access).
Applications
. A paper describing a fast sweep generator for a streak cameraStreak camera
A streak camera is an instrument for measuring the variation in a pulse of light's intensity with time. They are used to measure the pulse duration of some ultrafast laser systems, and for applications such as time-resolved spectroscopy and LIDAR....
constructed using series connected avalanche transistor circuits.. A paper describing an application of avalanche transistors to the design of a sampling oscilloscope: available abstract, full paper is "restricted access".. Available from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific & Technical Information. A report describing the design of a driver for Pockels cells Q-switches
Q-switching
Q-switching, sometimes known as giant pulse formation, is a technique by which a laser can be made to produce a pulsed output beam. The technique allows the production of light pulses with extremely high peak power, much higher than would be produced by the same laser if it were operating in a...
.. A project of an avalanche transistor astable multivibrator with schematics, waveforms and photos of the layout.. Academic Dissertation presented with the assent of the Faculty of Technology. A doctoral dissertation describing a Laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
TOF (Time Of Flight) Radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
and its construction using an avalanche transistor pulser. (preprint version here). A paper describing an avalanche transistor pulser and its use as Laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
driver in a laser radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
.
- NXP Mextram home page A very rich repository of documents about the Mextram bipolar junction transistorBipolar junction transistor|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
SPICESPICESPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
model, capable of avalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
behavior simulation. - "Operating the pulsed laser diode SPL LLxx", "Range finding using pulsed laser diodes" OSRAM Opto Semiconductors GmbHOSRAM Opto Semiconductors GmbHOSRAM Opto Semiconductors GmbH of Regensburg, Germany, a wholly owned subsidiary of Osram GmbH, is the world's second largest manufacturer of optoelectronic semiconductors after LiteOn and followed third place by CREE Inc . One of the main products of the company are light emitting diodes ,...
Application Notes, 2004-09-10. Two application notes from Osram Opto SemiconductorsOSRAM Opto Semiconductors GmbHOSRAM Opto Semiconductors GmbH of Regensburg, Germany, a wholly owned subsidiary of Osram GmbH, is the world's second largest manufacturer of optoelectronic semiconductors after LiteOn and followed third place by CREE Inc . One of the main products of the company are light emitting diodes ,...
describing pulsed operation of a Laser diodeLaser diodeThe laser diode is a laser where the active medium is a semiconductor similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The most common type of laser diode is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current...
, using avalanche transistors and other kind of drivers.. A paper describing a method to enhance performances of banks of series-connected avalanche transistor circuits. (for a PDF copy, see here). A detailed paper describing the construction and performance of an avalanche transistor pre-trigger pulse generator to test the slew-rate of very fast operational amplifiers. Also appeared under the title "Slew Rate Verification for Wideband Amplifiers - The Taming of the Slew", application note AN94, Linear Technology, May 2003. See also, from the same author, Linear Technology application note AN47, High speed amplifier techniques", August 1991, where an astable circuit similar to that described by Holme is detailed in appendix D, pages 93–95.
Varia
- Russel Jacob Baker Academic Web Page at Boise State UniversityBoise State UniversityBoise State University is a public university located in Boise, Idaho. Originally founded in 1932 as a junior college by the Episcopal Church, the university became an independent institution in 1934, and has been awarding baccalaureate and master degrees since 1965...
. A contributor to the theory and applications of avalanche transistors. - Владимир Павлович Дьяконов (Vladimir Pavlovich D'yakonov) (in RussianRussian languageRussian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
). Some biographical notes about one of the leading contributors to the theory and application of avalanche transistors. - Ari Kilpelä Academic Web Page at the University of OuluUniversity of OuluThe University of Oulu is one of the largest universities in Finland, located in the city of Oulu. It was founded on July 8, 1958. The university has around 16,000 students and 3,000 staff...
. A researcher working on theory and applications of avalanche transistor circuits. - Paolo Spirito Academic Web Page at University of Naples Federico IIUniversity of Naples Federico IIThe University of Naples Federico II is a university located in Naples, Italy. It was founded in 1224 and is organized into 13 faculties. It is the world's oldest state university and one of the oldest academic institutions in continuous operation...
. One of the leading contributor to the theory of avalanche transistors and avalanche process in semiconductors.