Avogadro's number
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
and physics
, the Avogadro constant (symbols: L, NA) is defined as the ratio of the number of constituent particles (usually atom
s or molecule
s) N in a sample to the amount of substance n (unit mole
) through the relationship NA = N/n. Thus, it is the proportionality factor that relates the molar mass
of an entity, i.e. the mass per amount of substance
, to the mass of said entity. The Avogadro constant expresses the number of elementary entities per mole of substance and it has the value .
Previous definitions of chemical quantity involved Avogadro's number, a historical term closely related to the Avogadro constant. Revisions in the base set of units of the International System of Units
(SI) necessitated redefinitions of the concepts of chemical quantity. Avogadro's number was defined by Perrin
as the number of molecules in one gram-molecule of hydrogen
. It is also same number of elementary entities as the number of atoms in of the isotope carbon-12
. Thus, Avogadro's number is a dimensionless quantity and has the numerical value of the Avogadro constant given in base units.
, who, in 1811, first proposed that the volume of a gas (at a given pressure and temperature) is proportional to the number of atom
s or molecule
s regardless of the nature of the gas. The French physicist Jean Perrin
in 1909 proposed naming the constant in honor of Avogadro. Perrin won the 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics
, in a large part for his work in determining the Avogadro constant by several different methods.
The value of the Avogadro constant was first indicated by Johann Josef Loschmidt
who, in 1865, estimated the average diameter of the molecules in air by a method that is equivalent to calculating the number of particles in a given volume of gas. This latter value, the number density
of particles in an ideal gas
, is now called the Loschmidt constant in his honour, and is approximately proportional
to the Avogadro constant. The connection with Loschmidt is the root of the symbol L sometimes used for the Avogadro constant, and German language
literature may refer to both constants by the same name, distinguished only by the units of measurement
.
Accurate determinations of Avogadro's number require the measurement of a single quantity on both the atomic and macroscopic scales using the same unit of measurement. This became possible for the first time when American physicist Robert Millikan
measured the charge on an electron
in 1910. The charge of a mole
of electrons is the constant called the Faraday and had been known since 1834 when Michael Faraday
published his works on electrolysis
. By dividing the charge on a mole of electrons by the charge on a single electron the value of Avogadro's number is obtained. Since 1910, newer calculations have more accurately determined the values for Faraday's constant and the elementary charge. (See below #Measurement)
Perrin
originally proposed the name Avogadro's number (N) to refer to the number of molecules in one gram-molecule of oxygen
(exactly of oxygen, according to the definitions of the period), and this term is still widely used, especially in introductory works. The change in name to Avogadro constant (NA) came with the introduction of the mole as a base unit
in the International System of Units
(SI) in 1971, which recognized amount of substance
as an independent dimension of measurement
. With this recognition, the Avogadro constant was no longer a pure number, but had a unit of measurement, the reciprocal mole (mol−1).
While it is rare to use units of amount of substance other than the mole, the Avogadro constant can also be defined in units such as the pound mole (lb-mol) and the ounce mole (oz-mol).
R and the Boltzmann constant kB,
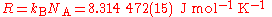
and the Faraday constant F and the elementary charge
e,
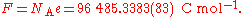
The Avogadro constant also enters into the definition of the unified atomic mass unit, u,

where Mu is the molar mass constant
.
. The principle is to measure the Faraday constant, F, which is the electric charge
carried by one mole of electrons, and to divide by the elementary charge
, e, to obtain the Avogadro constant.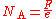
The classic experiment is that of Bowers and Davis at NIST, and relies on dissolving silver
metal away from the anode
of an electrolysis
cell, while passing a constant electric current
I for a known time t. If m is the mass of silver lost from the anode and A the atomic weight of silver, then the Faraday constant is given by: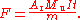
The NIST scientist devised a method to compensate for silver lost from the anode by mechanical causes, and conducted an isotope analysis
of the silver used to determine the average atomic weight. Their value for the conventional Faraday constant is F = , which corresponds to a value for the Avogadro constant of : both values have a relative standard uncertainty of .
A(e)M to the rest mass of the electron m: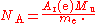
The relative atomic mass of the electron, A(e), is a directly-measured quantity, and the molar mass constant
, M, is a defined constant in the SI. The electron rest mass, however, is calculated from other measured constants: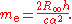
As may be observed in the table of 2006 CODATA values below, the main limiting factor in the precision of the Avogadro constant is the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant
, as all the other constants that contribute to the calculation are known more precisely.
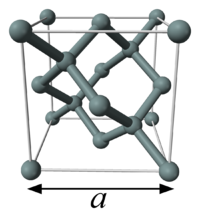 A modern method to determine the Avogadro constant is the use of X-ray crystallography
A modern method to determine the Avogadro constant is the use of X-ray crystallography
. Silicon
single crystals may be produced today in commercial facilities with extremely high purity with few lattice defects. This method defines the Avogadro constant as the ratio of the molar volume
, V, to the atomic volume Vatom:
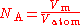 , where
, where 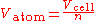 and n is the number of atoms per unit cell of volume Vcell.
and n is the number of atoms per unit cell of volume Vcell.
The unit cell of silicon has a cubic packing arrangement of 8 atoms, and the unit cell volume may be measured by determining a single unit cell parameter, the length of one of the sides of the cube, a.
In practice, measurements are carried out on a distance known as d(Si), which is the distance between the planes denoted by the Miller indices
{220}, and is equal to a/√8. The 2006 CODATA value for d(Si) is , a relative uncertainty of , corresponding to a unit cell volume of .
The isotope
proportional composition of the sample used must be measured and taken into account. Silicon occurs in three stable isotopes (28Si, 29Si, 30Si), and the natural variation in their proportions is greater than other uncertainties in the measurements. The atomic weight
A for the sample crystal can be calculated, as the relative atomic masses of the three nuclide
s are known with great accuracy. This, together with the measured density
ρ of the sample, allows the molar volume V to be determined: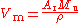
where M is the molar mass constant. The 2006 CODATA value for the molar volume of silicon is 12.058 8349(11) cm3mol−1, with a relative standard uncertainty of .
As of the 2006 CODATA recommended values, the relative uncertainty in determinations of the Avogadro constant by the X-ray crystal density method is , about two and a half times higher than that of the electron mass method.
in terms of a universal physical constant
, rather than the International Prototype Kilogram, and complements the measurements of the Planck constant
using watt balance
s. Under the current definitions of the International System of Units
(SI), a measurement of the Avogadro constant is an indirect measurement of the Planck constant: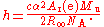
The measurements use highly polished spheres of silicon with a mass of one kilogram. Spheres are used to simplify the measurement of the size (and hence the density) and to minimize the effect of the oxide coating that inevitably forms on the surface. The first measurements used spheres of silicon with natural isotopic composition, and had a relative uncertainty of 3.1. These first results were also inconsistent with values of the Planck constant derived from watt balance measurements, although the source of the discrepancy is now believed to be known.
The main residual uncertainty in the early measurements was in the measurement of the isotopic composition of the silicon to calculate the atomic weight so, in 2007, a 4.8-kg single crystal of isotopically-enriched silicon (99.94% 28Si) was grown, and two one-kilogram spheres cut from it. Diameter measurements on the spheres are repeatable to within 0.3 nm, and the uncertainty in the mass is 3 µg. Full results from these determinations were expected in late 2010.
Their paper published in January 2011 summarised the result of the International Avogadro Coordination and presented a measurement of the Avogadro constant to be mol−1.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, the Avogadro constant (symbols: L, NA) is defined as the ratio of the number of constituent particles (usually atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s or molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s) N in a sample to the amount of substance n (unit mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
) through the relationship NA = N/n. Thus, it is the proportionality factor that relates the molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
of an entity, i.e. the mass per amount of substance
Amount of substance
Amount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
, to the mass of said entity. The Avogadro constant expresses the number of elementary entities per mole of substance and it has the value .
Previous definitions of chemical quantity involved Avogadro's number, a historical term closely related to the Avogadro constant. Revisions in the base set of units of the International System of Units
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
(SI) necessitated redefinitions of the concepts of chemical quantity. Avogadro's number was defined by Perrin
Jean Baptiste Perrin
Jean Baptiste Perrin was a French physicist and Nobel laureate.-Early years:Born in Lille, France, Perrin attended the École Normale Supérieure, the elite grande école in Paris. He became an assistant at the school during the period of 1894-97 when he began the study of cathode rays and X-rays...
as the number of molecules in one gram-molecule of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
. It is also same number of elementary entities as the number of atoms in of the isotope carbon-12
Carbon-12
Carbon-12 is the more abundant of the two stable isotopes of the element carbon, accounting for 98.89% of carbon; it contains 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons....
. Thus, Avogadro's number is a dimensionless quantity and has the numerical value of the Avogadro constant given in base units.
| Value of NA in various units |
|---|
| mol−1 |
| lb Pound (mass) The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in the Imperial, United States customary and other systems of measurement... -mol−1 |
| oz Ounce The ounce is a unit of mass with several definitions, the most commonly used of which are equal to approximately 28 grams. The ounce is used in a number of different systems, including various systems of mass that form part of the imperial and United States customary systems... -mol−1 |
History
The Avogadro constant is named after the early nineteenth-century Italian scientist Amedeo AvogadroAmedeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro di Quaregna e di Cerreto, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto was an Italian savant. He is most noted for his contributions to molecular theory, including what is known as Avogadro's law...
, who, in 1811, first proposed that the volume of a gas (at a given pressure and temperature) is proportional to the number of atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s or molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s regardless of the nature of the gas. The French physicist Jean Perrin
Jean Baptiste Perrin
Jean Baptiste Perrin was a French physicist and Nobel laureate.-Early years:Born in Lille, France, Perrin attended the École Normale Supérieure, the elite grande école in Paris. He became an assistant at the school during the period of 1894-97 when he began the study of cathode rays and X-rays...
in 1909 proposed naming the constant in honor of Avogadro. Perrin won the 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded once a year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901; the others are the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and...
, in a large part for his work in determining the Avogadro constant by several different methods.
The value of the Avogadro constant was first indicated by Johann Josef Loschmidt
Johann Josef Loschmidt
Jan or Johann Josef Loschmidt , who referred to himself mostly as 'Josef' , was a notable Austrian scientist who performed groundbreaking work in chemistry, physics , and crystal forms.Born in Carlsbad, a town located in the Austrian Empire , Loschmidt...
who, in 1865, estimated the average diameter of the molecules in air by a method that is equivalent to calculating the number of particles in a given volume of gas. This latter value, the number density
Number density
In physics, astronomy, and chemistry, number density is an intensive quantity used to describe the degree of concentration of countable objects in the three-dimensional physical space...
of particles in an ideal gas
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
, is now called the Loschmidt constant in his honour, and is approximately proportional
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two variable quantities are proportional if one of them is always the product of the other and a constant quantity, called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. In other words, are proportional if the ratio \tfrac yx is constant. We also say that one...
to the Avogadro constant. The connection with Loschmidt is the root of the symbol L sometimes used for the Avogadro constant, and German language
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
literature may refer to both constants by the same name, distinguished only by the units of measurement
Units of measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of...
.
Accurate determinations of Avogadro's number require the measurement of a single quantity on both the atomic and macroscopic scales using the same unit of measurement. This became possible for the first time when American physicist Robert Millikan
Robert Millikan
Robert A. Millikan was an American experimental physicist, and Nobel laureate in physics for his measurement of the charge on the electron and for his work on the photoelectric effect. He served as president of Caltech from 1921 to 1945...
measured the charge on an electron
Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
in 1910. The charge of a mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
of electrons is the constant called the Faraday and had been known since 1834 when Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday, FRS was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry....
published his works on electrolysis
Faraday's laws of electrolysis
Faraday's laws of electrolysis are quantitative relationships based on the electrochemical researches published by Michael Faraday in 1834.-Statements of the laws:Several versions of the laws can be found in textbooks and the scientific literature...
. By dividing the charge on a mole of electrons by the charge on a single electron the value of Avogadro's number is obtained. Since 1910, newer calculations have more accurately determined the values for Faraday's constant and the elementary charge. (See below #Measurement)
Perrin
Jean Baptiste Perrin
Jean Baptiste Perrin was a French physicist and Nobel laureate.-Early years:Born in Lille, France, Perrin attended the École Normale Supérieure, the elite grande école in Paris. He became an assistant at the school during the period of 1894-97 when he began the study of cathode rays and X-rays...
originally proposed the name Avogadro's number (N) to refer to the number of molecules in one gram-molecule of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
(exactly of oxygen, according to the definitions of the period), and this term is still widely used, especially in introductory works. The change in name to Avogadro constant (NA) came with the introduction of the mole as a base unit
SI base unit
The International System of Units defines seven units of measure as a basic set from which all other SI units are derived. These SI base units and their physical quantities are:* metre for length...
in the International System of Units
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
(SI) in 1971, which recognized amount of substance
Amount of substance
Amount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
as an independent dimension of measurement
Dimensional analysis
In physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
. With this recognition, the Avogadro constant was no longer a pure number, but had a unit of measurement, the reciprocal mole (mol−1).
While it is rare to use units of amount of substance other than the mole, the Avogadro constant can also be defined in units such as the pound mole (lb-mol) and the ounce mole (oz-mol).
- N = =
General role in science
Avogadro's constant is a scaling factor between macroscopic and microscopic (atomic scale) observations of nature. As such, it provides the relation between other physical constants and properties. For example, it establishes a relationship between the gas constantGas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
R and the Boltzmann constant kB,
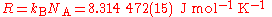
and the Faraday constant F and the elementary charge
Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
e,
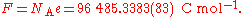
The Avogadro constant also enters into the definition of the unified atomic mass unit, u,

where Mu is the molar mass constant
Molar mass constant
The molar mass constant, symbol Mu, is a physical constant which relates atomic weight and molar mass. Its value is defined to be 1 g/mol in SI units....
.
Coulometry
The earliest accurate method to measure the value of the Avogadro constant was based on coulometryCoulometry
Coulometry is the name given to a group of techniques in analytical chemistry that determine the amount of matter transformed during an electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount of electricity consumed or produced....
. The principle is to measure the Faraday constant, F, which is the electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
carried by one mole of electrons, and to divide by the elementary charge
Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
, e, to obtain the Avogadro constant.
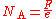
The classic experiment is that of Bowers and Davis at NIST, and relies on dissolving silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
metal away from the anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
of an electrolysis
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
cell, while passing a constant electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
I for a known time t. If m is the mass of silver lost from the anode and A the atomic weight of silver, then the Faraday constant is given by:
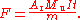
The NIST scientist devised a method to compensate for silver lost from the anode by mechanical causes, and conducted an isotope analysis
Isotope analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, the distribution of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within chemical compounds. This can be applied to a food web to make it possible to draw direct inferences regarding diet, trophic level, and subsistence...
of the silver used to determine the average atomic weight. Their value for the conventional Faraday constant is F = , which corresponds to a value for the Avogadro constant of : both values have a relative standard uncertainty of .
Electron mass measurement
The Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA) publishes values for physical constants for international use. It determines the Avogadro constant from the ratio of the molar mass of the electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
A(e)M to the rest mass of the electron m:
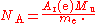
The relative atomic mass of the electron, A(e), is a directly-measured quantity, and the molar mass constant
Molar mass constant
The molar mass constant, symbol Mu, is a physical constant which relates atomic weight and molar mass. Its value is defined to be 1 g/mol in SI units....
, M, is a defined constant in the SI. The electron rest mass, however, is calculated from other measured constants:
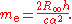
As may be observed in the table of 2006 CODATA values below, the main limiting factor in the precision of the Avogadro constant is the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant
Planck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
, as all the other constants that contribute to the calculation are known more precisely.
| Constant | Symbol | 2006 CODATA value | Relative standard uncertainty | with N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electron relative atomic mass | A(e) | 5.485 799 0943(23) | 4.2 | 0.0082 |
| Molar mass constant Molar mass constant The molar mass constant, symbol Mu, is a physical constant which relates atomic weight and molar mass. Its value is defined to be 1 g/mol in SI units.... |
M | 0.001 kg/mol | defined | — |
| Rydberg constant Rydberg constant The Rydberg constant, symbol R∞, named after the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, is a physical constant relating to atomic spectra in the science of spectroscopy. Rydberg initially determined its value empirically from spectroscopy, but Niels Bohr later showed that its value could be calculated... |
R | 10 973 731.568 527(73) m−1 | 6.6 | 0.0000 |
| Planck constant Planck constant The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899... |
h | 6.626 068 96(33) Js | 5.0 | −0.9996 |
| Speed of light Speed of light The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time... |
c | 299 792 458 m/s | defined | — |
| Fine structure constant | α | 7.297 352 5376(50) | 6.8 | 0.0269 |
| Avogadro constant | N | 6.022 141 79(30) mol−1 | 5.0 | 1 |
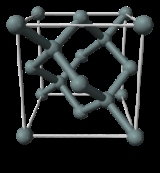
X-ray crystal density (XRCD) method
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
. Silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
single crystals may be produced today in commercial facilities with extremely high purity with few lattice defects. This method defines the Avogadro constant as the ratio of the molar volume
Molar volume
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
, V, to the atomic volume Vatom:
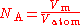 , where
, where  and n is the number of atoms per unit cell of volume Vcell.
and n is the number of atoms per unit cell of volume Vcell.The unit cell of silicon has a cubic packing arrangement of 8 atoms, and the unit cell volume may be measured by determining a single unit cell parameter, the length of one of the sides of the cube, a.
In practice, measurements are carried out on a distance known as d(Si), which is the distance between the planes denoted by the Miller indices
Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for planes and directions in crystal lattices.In particular, a family of lattice planes is determined by three integers h, k, and ℓ, the Miller indices. They are written , and each index denotes a plane orthogonal to a direction in the...
{220}, and is equal to a/√8. The 2006 CODATA value for d(Si) is , a relative uncertainty of , corresponding to a unit cell volume of .
The isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
proportional composition of the sample used must be measured and taken into account. Silicon occurs in three stable isotopes (28Si, 29Si, 30Si), and the natural variation in their proportions is greater than other uncertainties in the measurements. The atomic weight
Atomic weight
Atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity, the ratio of the average mass of atoms of an element to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12...
A for the sample crystal can be calculated, as the relative atomic masses of the three nuclide
Nuclide
A nuclide is an atomic species characterized by the specific constitution of its nucleus, i.e., by its number of protons Z, its number of neutrons N, and its nuclear energy state....
s are known with great accuracy. This, together with the measured density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
ρ of the sample, allows the molar volume V to be determined:
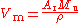
where M is the molar mass constant. The 2006 CODATA value for the molar volume of silicon is 12.058 8349(11) cm3mol−1, with a relative standard uncertainty of .
As of the 2006 CODATA recommended values, the relative uncertainty in determinations of the Avogadro constant by the X-ray crystal density method is , about two and a half times higher than that of the electron mass method.
International Avogadro Coordination
The International Avogadro Coordination (IAC), often simply called the "Avogadro project", is a collaboration begun in the early 1990s between various national metrology institutes to measure the Avogadro constant by the X-ray crystal density method to a relative uncertainty of 2 or less. The project is part of the efforts to redefine the kilogramKilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
in terms of a universal physical constant
Physical constant
A physical constant is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and constant in time. It can be contrasted with a mathematical constant, which is a fixed numerical value but does not directly involve any physical measurement.There are many physical constants in...
, rather than the International Prototype Kilogram, and complements the measurements of the Planck constant
Planck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
using watt balance
Watt balance
The watt balance is an experimental electromechanical weight measuring instrument that measures the weight of a test object very precisely by the strength of an electric current and a voltage. It is being developed as a metrological instrument that may one day provide a definition of the kilogram...
s. Under the current definitions of the International System of Units
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
(SI), a measurement of the Avogadro constant is an indirect measurement of the Planck constant:
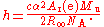
The measurements use highly polished spheres of silicon with a mass of one kilogram. Spheres are used to simplify the measurement of the size (and hence the density) and to minimize the effect of the oxide coating that inevitably forms on the surface. The first measurements used spheres of silicon with natural isotopic composition, and had a relative uncertainty of 3.1. These first results were also inconsistent with values of the Planck constant derived from watt balance measurements, although the source of the discrepancy is now believed to be known.
The main residual uncertainty in the early measurements was in the measurement of the isotopic composition of the silicon to calculate the atomic weight so, in 2007, a 4.8-kg single crystal of isotopically-enriched silicon (99.94% 28Si) was grown, and two one-kilogram spheres cut from it. Diameter measurements on the spheres are repeatable to within 0.3 nm, and the uncertainty in the mass is 3 µg. Full results from these determinations were expected in late 2010.
Their paper published in January 2011 summarised the result of the International Avogadro Coordination and presented a measurement of the Avogadro constant to be mol−1.
External links
- 1996 definition of the Avogadro constant from the IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology ("Gold Book")
- Some Notes on Avogadro's Number, 6.022 (historical notes)
- An Exact Value for Avogadro's Number – American ScientistAmerican ScientistAmerican Scientist is the bimonthly science and technology magazine published since 1913 by Sigma Xi. Each issue includes four to five feature articles written by scientists and engineers. These authors review research in all fields of science...
- Avogadro and molar Planck constants for the redefinition of the kilogram

