
Basic aromatic ring
Encyclopedia
| Basic aromatic ring systems | ||
|---|---|---|
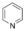 Pyridine Pyridine Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom... |
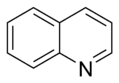 Quinoline Quinoline Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It has the formula C9H7N and is a colourless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odour. Aged samples, if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown... |
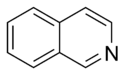 Isoquinoline Isoquinoline Isoquinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It is a structural isomer of quinoline. Isoquinoline and quinoline are benzopyridines, which are composed of a benzene ring fused to a pyridine ring. In a broader sense, the term isoquinoline is used to make reference to isoquinoline... |
 Acridine Acridine Acridine, C13H9N, is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle. Acridine is also used to describe compounds containing the C13N tricycle.... |
||
 Pyrazine Pyrazine Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2.Pyrazine is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Derivatives like phenazine are well known for their antitumor, antibiotic and diuretic activity. Pyrazine is less basic in nature than pyridine, pyridazine... |
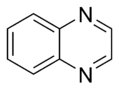 Quinoxaline Quinoxaline A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring... |
|
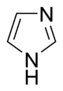 Imidazole Imidazole Imidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. This aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole and is classified as an alkaloid. Imidazole refers to the parent compound, whereas imidazoles are a class of heterocycles with similar ring structure, but varying substituents... |
 Benzimidazole Benzimidazole Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and imidazole. The most prominent benzimidazole compound in nature is N-ribosyl-dimethylbenzimidazole, which serves as an axial ligand for cobalt in vitamin B12. Benzimidazole, in... |
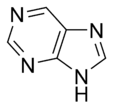 Purine Purine A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature.... |
 Pyrazole Pyrazole Pyrazole refers both to the class of simple aromatic ring organic compounds of the heterocyclic diazole series characterized by a 5-membered ring structure composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms in adjacent positions, and to the unsubstituted parent compound... |
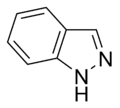 Indazole Indazole Indazole, also called benzpyrazole or isoindazone, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound.Indazole derivatives display a broad variety of biological activities.... |
|
 Pyrimidine Pyrimidine Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound similar to benzene and pyridine, containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 of the six-member ring... |
 Quinazoline Quinazoline Quinazoline is a compound made up of two fused six-membered simple aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. Its chemical formula is C8H6N2. Quinazoline is yellow and crystalline... |
|
 Pyridazine Pyridazine Pyridazine is a heteroaromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C4H4N2, sometimes called 1,2-diazine. It contains a six-membered ring with two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C.... |
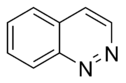 Cinnoline Cinnoline Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline.-Properties:... |
Basic aromatic rings are aromatic rings
Simple aromatic ring
Simple aromatic rings, also known as simple arenes or simple aromatics, are aromatic organic compounds that consist only of a conjugated planar ring system with delocalized pi electron clouds. Many simple aromatic rings have trivial names. They are usually found as substructures of more complex...
in which the lone pair
Lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s of a ring-nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
is not part of the aromatic system and extends in the plane of the ring. This lone pair is responsible for the basicity
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
of these nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous base
A nitrogenous base is a nitrogen-containing molecule having the chemical properties of a base. It is an organic compound that owes its property as a base to the lone pair of electrons of a nitrogen atom. In biological sciences, nitrogenous bases are typically classified as the derivatives of two...
s, similar to the nitrogen atom in amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s. In these compounds the nitrogen atom is not connected to a hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom. Basic aromatic compounds get protonated
Protonation
In chemistry, protonation is the addition of a proton to an atom, molecule, or ion. Some classic examples include*the protonation of water by sulfuric acid:*the protonation of isobutene in the formation of a carbocation:2C=CH2 + HBF4 → 3C+ + BF4−*the protonation of ammonia in the...
and form aromatic cations (e.g. pyridinium
Pyridinium
Pyridinium refers to the cationic form of pyridine. This can either be due to protonation of the ring nitrogen or because of addition of a substituent to the ring nitrogen, typically via alkylation. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of pyridine is not delocalized, and thus pyridine...
) under acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
ic conditions. Typical examples of basic aromatic rings are pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
or quinoline
Quinoline
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It has the formula C9H7N and is a colourless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odour. Aged samples, if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown...
. Several rings contain basic as well as non-basic nitrogen atoms, e.g. imidazole
Imidazole
Imidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. This aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole and is classified as an alkaloid. Imidazole refers to the parent compound, whereas imidazoles are a class of heterocycles with similar ring structure, but varying substituents...
and purine
Purine
A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature....
.
In non-basic aromatic rings the lone pair
Lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s of the nitrogen atom is delocalized and contributes to the aromatic pi electron system. In these compounds the nitrogen atom is connected to a hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom. Examples of non-basic nitrogen-containing aromatic rings are pyrrole
Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3...
and indole
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing pyrrole ring. Indole is a popular component of fragrances and the precursor to many pharmaceuticals. Compounds that contain an...
.
The basic aromatic rings purine
Purine
A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature....
s and pyrimidine
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound similar to benzene and pyridine, containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 of the six-member ring...
s are nucleobases found in DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
and RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
.

