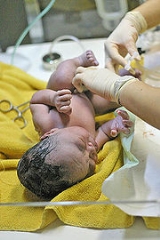
Childbirth
Encyclopedia
Childbirth is the culmination of a human
pregnancy
or gestation
period with the birth of one or more newborn infant
s from a woman
's uterus
. The process of normal human
childbirth is categorized in three stages of labour: the shortening and dilation
of the cervix
, descent and birth of the infant
, and birth of the placenta
. In many cases, with increasing frequency, childbirth is achieved through caesarean section
, the removal of the neonate through a surgical
incision in the abdomen
, rather than through vagina
l birth. In the U.S. and Canada it represents nearly 1 in 3 (31.8%) and 1 in 4 (22.5%) of all childbirths, respectively.
 Labor is sometimes accompanied by intense and prolonged pain
Labor is sometimes accompanied by intense and prolonged pain
. Pain levels reported by laboring women vary widely. Pain levels appear to be influenced by fear and anxiety levels. Some other factors may include experience with prior childbirth, age, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment and immobility.
Between 70% and 80% of mothers in the United States report some feelings of sadness or "baby blues" after childbirth. Postpartum depression
may develop in some women; about 10% of mothers in the United States are diagnosed with this condition. Abnormal and persistent fear of childbirth is known as tokophobia.
Preventive group therapy has proven effective as a prophylactic treatment for postpartum depression.
Childbirth is stressful for the infant. In addition to the normal stress of leaving the protected uterine environment, additional stresses associated with breech birth
, such as asphyxiation, may affect the infant's brain.
, the biggest head of any mammalian species, human fetuses and human female pelvises are adapted to make birth possible.
The erect posture causes the weight of the abdominal contents to thrust on the pelvic floor
, a complex structure which must not only support this weight but allow three channels to pass through it: the urethra
, the vagina
and the rectum
. The head and shoulders require a specific sequence of maneuvers to occur for the bony head and shoulders to pass through the bony ring of the pelvis.
Six phases:
The fetal head may temporarily change shape substantially (becoming more elongated) as it moves through the birth canal. This change in the shape of the fetal head is called molding and is much more prominent in women having their first vaginal delivery.
. Cervical effacement occurs during the closing weeks of pregnancy
and is usually complete or near complete, by the end of the latent phase. Cervical effacement or cervical dilation
is the thinning and stretching of the cervix
. The degree of cervical effacement may be felt during a vaginal examination but is not necessary. A 'long' cervix implies that not much has been taken into the lower segment, and vice versa for a 'short' cervix. Latent phase ends with the onset of active first stage; when the cervix is about 3 cm dilated.
. The Bishop score is also used as a means to predict whether the mother is likely to spontaneously progress into second stage (delivery).
The first stage of labor starts classically when the effaced (thinned) cervix is 3 cm dilated. There is a variation in this point as some women may or may not have active contractions
prior to reaching this point. The onset of actual labor is defined when the cervix begins to progressively dilate. Rupture of the membranes, or a blood stained 'show' may or may not occur at or around this stage.
Uterine muscles form opposing spirals from the top of the upper segment of the uterus to its junction with the lower segment. During effacement, the cervix becomes incorporated into the lower segment of the uterus. During a contraction, these muscles contract causing shortening of the upper segment and drawing upwards of the lower segment, in a gradual expulsive motion. The presenting fetal part then is permitted to descend. Full dilation is reached when the cervix has widened enough to allow passage of the baby's head, around 10 cm dilation for a term baby.
The duration of labour varies widely, but active phase averages some 20 hours for women giving birth to their first child ("primiparae") and 8 hours for women who have already given birth ("multiparae"). Active phase arrest is defined as in a primigravid woman as the failure of the cervix to dilate at a rate of 1.2 cm/hr over a period of at least two hours. This definition is based on Friedman's Curve, which plots the typical rate of cervical dilation and fetal descent during active labor. Some practitioners may diagnose "Failure to Progress", and consequently, perform a Cesarean.
increases uterine contractions so that the second stage can go ahead. At the beginning of the normal second stage, the head is fully engaged in the pelvis; the widest diameter of the head has passed below the level of the pelvic inlet
. The fetal head then continues descent into the pelvis, below the pubic arch and out through the vaginal introitus
. This is assisted by the additional maternal efforts of "bearing down" or pushing. The fetal head is seen to 'crown' as the labia part. At this point, the woman may feel a burning or stinging sensation.
Complete expulsion of the baby signals the successful completion of the second stage of labor.
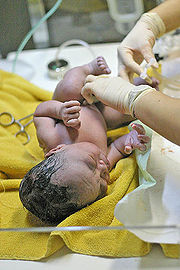 The second stage of birth will vary by factors including parity, fetal size, anesthesia, the presence of infection. Longer labors are associated with declining rates of spontaneous vaginal delivery and increasing rates of infection, perineal laceration, obstetric hemorrhage, as well as need for intensive care of the neonate
The second stage of birth will vary by factors including parity, fetal size, anesthesia, the presence of infection. Longer labors are associated with declining rates of spontaneous vaginal delivery and increasing rates of infection, perineal laceration, obstetric hemorrhage, as well as need for intensive care of the neonate
 The period from just after the fetus is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor.
The period from just after the fetus is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor.
The umbilical cord
is routinely clamped and cut in this stage, but it would normally close naturally even if not clamped. A 2008 Cochrane Review looked into the timing of clamping the umbilical cord. It found that the time of clamping made no difference to the mother, but did have effects for the baby. If the cord is clamped after 2–3 minutes, the infant receives increased amounts of haemoglobin in their first months of life, but may have an increased risk of needing phototherapy to treat jaundice. Sometimes a newborn’s liver is slow to break down all of the red cells they had in the womb, particularly if they are left with more fetal blood from delayed cord clamping and phototherapy helps to speed the breakdown.
Placental expulsion
begins as a physiological separation from the wall of the uterus. The period from just after the fetus is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor. The average time from delivery of the baby until complete expulsion of the placenta is estimated to be 10-12 minutes dependent on whether active or expectant management is employed
Placental expulsion can be managed actively, by giving a uterotonic such as oxytocin
along with appropriate cord traction and fundal massage to assist in delivering the placenta by a skilled birth attendant. Alternatively, it can be managed expectantly, allowing the placenta to be expelled without medical assistance. In a joint statement, World Health Organization
, the International Federation of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians and the International Confederations of Midwives recommend active management of the third stage in all vaginal deliveries . This is a strong recommendation of the World Health Organization
backed by moderate base evidence citing reduced risk of postpartum bleeding (i.e.: obstetric hemorrhage).
In as many as 3% of all vaginal deliveries, the duration of the third stage is longer than 30 minutes and raises concern for retained placenta
.
When the amniotic sac
has not ruptured during labour or pushing, the infant can be born with the membranes intact. This is referred to as "being born in the caul
." The caul is harmless and its membranes are easily broken and wiped away. With the advent of modern interventive obstetrics, artificial rupture of the membranes has become common, so babies are rarely born in the caul.
, and others.
Mothers are often allowed a period where they are relieved of their normal duties to recover from childbirth. The length of this period varies. In many countries, taking time off from work to care for a newborn is called "maternity leave" or "parental leave
" and can vary from a few days to several months.
Some women prefer to avoid analgesic
medication during childbirth. They can still try to alleviate labor pain using psychological preparation, education, massage, acupuncture, TENS unit use, hypnosis, or water therapy in a tub or shower. Some women like to have someone to support them during labor and birth, such as the father
of the baby, a family member, a close friend, a partner, or a doula
. Some women deliver in a squatting or crawling position in order to more effectively push during the second stage and so that gravity can aid the descent of the baby through the birth canal.
The human body also has a chemical response to pain, by releasing endorphin
s. Endorphins are present before, during, and immediately after childbirth. Some homebirth advocates believe that this hormone can induce feelings of pleasure and euphoria during childbirth, reducing the risk of maternal depression
some weeks later.
Water birth
is an option chosen by some women for pain relief during labor and childbirth, and some studies have shown waterbirth in an uncomplicated pregnancy to reduce the need for analgesia, without evidence of increased risk to mother or newborn. Hot water tubs are available in many hospitals and birthing centres.
Meditation
and mind medicine techniques are also used for pain control during labour and delivery. These techniques are used in conjunction with progressive muscle relaxation and many other forms of relaxation for the mind and body to aid in pain control for women during childbirth. One such technique is the use of hypnosis in childbirth
. There are a number of organizations that teach women and their partners to use a variety of techniques to assist with labor comfort, without the use of pharmaceuticals.
A new mode of analgesia is sterile water injection placed just underneath the skin in the most painful spots during labor. A control trial in Iran of 0.5mL injections was conducted with normal saline which revealed a statistical superiority with water over saline.
Pharmaceutical
Different measures for pain control have varying degrees of success and side effects to the woman and her baby. In some countries of Europe
, doctors commonly prescribe inhaled nitrous oxide
gas for pain control, especially as 50% nitrous oxide, 50% oxygen, known as Entonox
; in the UK
, midwives may use this gas without a doctor's prescription. Pethidine
(with or without promethazine
) may be used early in labour, as well as other opioid
s such as fentanyl, but if given too close to birth there is a risk of respiratory depression in the infant.
Popular medical pain control in hospitals include the regional anesthetics epidural
blocks, and spinal anaesthesia
. Epidural analgesia is a generally safe and effective method of relieving pain in labour, but is associated with longer labour, more operative intervention (particularly instrument delivery), and increases in cost. Generally, pain and cortisol increased throughout labor in women without EDA. Pain and stress hormones rise throughout labor for women without epidurals, while pain, fear, and stress hormones decrease upon administration of epidural analgesia, but may rise again later.
Medicine administered via epidural can cross the placenta and enter the bloodstream of the fetus. Epidural analgesia has no statistically significant impact on the risk of caesarean section, and does not appear to have an immediate effect on neonatal status as determined by Apgar scores.
has been used to increase the rate of vaginal delivery in those with a slow progress of labor.
may be used to facilitate childbirth.
during labor, she had less need for chemical pain relief, the likelihood of caesarean section was reduced, use of forceps and other instrumental deliveries were reduced, there was a reduction in the length of labor, and the baby had a higher Apgar score
(Dellman 2004, Vernon 2006). However, little research has been conducted to date about the conflicts between partners, professionals, and the mother.
or umbilical cord blood stem cells.
To collect amniotic stem cells
, it is necessary to do amniocentesis
before or during the birth. Amniotic stem cells are multipotent and very active, useful for both autologous or donor use. There are private banks in US; the first is Biocell Center
in Boston.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are also active, but less multipotent than amniotic stem cells. There are a lot of banks of cord blood, both private and public and for autologous or eterologous use.
). Modern medicine has greatly alleviated the risk of childbirth. In modern Western countries, such as the United States or Sweden, the current maternal mortality rate is around 10 deaths per 100,000 births.
Birthing complications may be maternal or fetal, and long term or short term.
Secondary changes may be observed: swelling of the tissues, maternal exhaustion, fetal heart rate abnormalities. Left untreated, severe complications include death of mother and/or baby, and genitovaginal fistula
.
Shoulder dystocia is a dystocia in which the anterior shoulder of the infant cannot pass below the pubic symphysis or requires significant manipulation to pass below it. It can also be described as delivery requiring additional manoeuvres after gentle downward traction on the head has failed to deliver the shoulders.
A prolonged second stage of labour is another type of dystocia whereby the fetus has not been delivered within three hours in a nulliparous woman, or two hours in multiparous woman, after her cervix has become fully dilated.
Synonyms for dystocia include difficult labour, abnormal labour, difficult childbirth, abnormal childbirth, and dysfunctional labour.
or episiotomies
are common. Internal tissue tearing as well as nerve damage to the pelvic structures lead in a proportion of women to problems with prolapse, incontinence of stool or urine and sexual dysfunction. Fifteen percent of women become incontinent, to some degree, of stool or urine after normal delivery, this number rising considerably after these women reach menopause. Vaginal birth injury is a necessary, but not sufficient, cause of all non hysterectomy related prolapse in later life. Risk factors for significant vaginal birth injury include:
Pelvic girdle pain
. Hormones and enzymes work together to produce ligamentous relaxation and widening of the symphysis pubis during the last trimester of pregnancy. Most girdle pain occurs before birthing, and is known as diastasis of the pubic symphysis. Predisposing factors for girdle pain include maternal obesity.
Infection remains a major cause of maternal mortality and morbidity in the developing world. The work of Ignaz Semmelweis
was seminal in the pathophysiology and treatment of puerperal fever
and saved many lives.
Hemorrhage, or heavy blood loss, is still the leading cause of death of birthing mothers in the world today, especially in the developing world. Heavy blood loss leads to hypovolemic shock, insufficient perfusion of vital organs and death if not rapidly treated. Blood transfusion may be life saving. Rare sequelae include Hypopituitarism
Sheehan's syndrome
.
The maternal mortality rate (MMR) varies from 9 per 100,000 live births in the US and Europe to 900 per 100,000 live births in Sub-Saharan Africa
. Every year, more than half a million women die in pregnancy or childbirth.
, the need for instrumental delivery, and an inexperienced attendant. Specific situations that can contribute to birth injury include breech presentation and shoulder dystocia
. Most fetal birth injuries resolve without long term harm, but brachial plexus injury
may lead to Erb's palsy
or Klumpke's paralysis.
Untreated sexually transmitted infections are associated with congenital and perinatal infections in neonates, particularly in the areas where rates of infection remain high. The overall perinatal mortality rate associated with untreated syphilis, for example, approached 40%.
The most important factors affecting mortality
in childbirth are adequate nutrition
and access to quality medical care ("access" is affected both by the cost of available care, and distance from health services).
A 1983-1989 study by the Texas Department of State Health Services
highlighted the differences in neonatal mortality (NMR) between high risk and low risk pregnancies. NMR was 0.57% for doctor-attended high risk births, and 0.19% for low risk births attended by non-nurse midwives. Conversely, some studies demonstrate a higher perinatal mortality rate with assisted home births. Around 80% of pregnancies are low-risk. Factors that may make a birth high risk include prematurity, high blood pressure, gestational diabetes
and a previous cesarean section.
, but this term may be emotive and misleading. True intrapartum asphyxia is not as common as previously believed, and is usually accompanied by multiple other symptoms during the immediate period after delivery. Monitoring might show up problems during birthing, but the interpretation and use of monitoring devices is complex and prone to misinterpretation. Intrapartum asphyxia can cause long-term impairment, particularly when this results in tissue damage through encephalopathy
.
 Different categories of birth attendant
Different categories of birth attendant
s may provide support and care during pregnancy and childbirth, although there are important differences across categories based on professional training and skills, practice regulations, as well as nature of care delivered.
“Childbirth educators” are instructors who aim to educate pregnant women and their partners about the nature of pregnancy, labour signs and stages, techniques for giving birth, breastfeeding and newborn baby care. In the United States and elsewhere, classes for training as a childbirth educator can be found in hospital settings or through many independent certifying organizations such as Birthing From Within, BirthWorks, The Bradley Method, Brio Birth, CAPPA, HypBirth, HypnoBabies, HypnoBirthing, ICTC, ICEA, Lamaze, etc. Each organization teaches its own curriculum and each emphasizes different techniques. Information about each can be obtained through their individual websites.
Doula
s are assistants who support mothers during pregnancy, labour, birth, and postpartum. They are not medical attendants; rather, they provide emotional support and non-medical pain relief for women during labour. Like childbirth educators and other assistive personnel
, certification to become a doula is not compulsory, thus, anyone can call themself a doula or a childbirth educator.
Midwives
are autonomous practitioners who provide basic and emergency health care before, during and after pregnancy and childbirth, generally to women with low-risk pregnancies. Midwives are trained to assist during labour and birth, either through direct-entry or nurse-midwifery education programs. Jurisdictions where midwifery is a regulated profession will typically have a registering and disciplinary body for quality control, such as the College of Midwives of British Columbia (CMBC) in Canada or the Nursing and Midwifery Council
(NMC) in the United Kingdom.
In jurisdictions where midwifery is not a regulated profession, traditional or lay midwives
may assist women during childbirth, although they do not typically receive formal health care education and training.
Medical doctor
s who practice obstetrics
include categorically specialized obstetricians
; family practitioners
and general practitioners whose training, skills and practices include obstetrics; and in some contexts general surgeons. These physicians and surgeons variously provide care across the whole spectrum of normal and abnormal births and pathological labour conditions. Categorically specialized obstetricians are qualified surgeon
s, so they can undertake surgical procedures relating to childbirth. Some family practitioners or general practitioners also perform obstetrical surgery. Obstetrical procedures include cesarean sections, episiotomies
, and assisted delivery. Categorical specialists in obstetrics are commonly dually trained in obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), and may provide other medical and surgical gynecological care, and may incorporate more general, well-woman, primary care
elements in their practices. Maternal-fetal medicine
specialists are obstetrician/gynecologists subspecialized in managing and treating high-risk pregnancy and delivery.
Obstetric nurses assist midwives, doctors, women, and babies prior to, during, and after the birth process, in the hospital system. Some midwives are also obstetric nurses. Obstetric nurses hold various certifications and typically undergo additional obstetric training in addition to standard nursing training
.
s in much of Western society. Prior to the 20th century and in some countries to the present day it has more typically occurred at home.
In Western and other cultures, age is reckoned from the date of birth, and sometimes the birthday
is celebrated annually. East Asian age reckoning
starts newborns at "1", incrementing each Lunar New Year
.
Some families view the placenta
as a special part of birth, since it has been the child's life support for so many months. Some parents like to see and touch this organ. In some cultures, parents plant a tree along with the placenta on the child's first birthday
. The placenta may be eaten
by the newborn's family, ceremonially or otherwise (for nutrition; the great majority of animals in fact do this naturally). Most recently there is a category of birth professionals available who will encapsulate placenta for use as placenta medicine by postpartum mothers. The placenta is believed to provide hormones which ease the emotional roller coaster of the postpartum period and even prevent some cases of postpartum depression. The placenta is steamed and then dried in a dehydrator, after which it is made into gel caps that are taken for weeks or months. There is some research showing benefits for milk production in women and other positive studies in animal populations. Anecdotal reports suggest that women say that they suffer less postpartum blues, depression and anxiety using placenta medicine.
The exact location in which
childbirth takes place is an important factor in determining nationality
, in particular for birth aboard aircraft and ships
.
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
or gestation
Gestation
Gestation is the carrying of an embryo or fetus inside a female viviparous animal. Mammals during pregnancy can have one or more gestations at the same time ....
period with the birth of one or more newborn infant
Infant
A newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
s from a woman
Woman
A woman , pl: women is a female human. The term woman is usually reserved for an adult, with the term girl being the usual term for a female child or adolescent...
's uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
. The process of normal human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
childbirth is categorized in three stages of labour: the shortening and dilation
Cervical dilation
Cervical dilation is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery...
of the cervix
Cervix
The cervix is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall...
, descent and birth of the infant
Infant
A newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
, and birth of the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
. In many cases, with increasing frequency, childbirth is achieved through caesarean section
Caesarean section
A Caesarean section, is a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen and uterus to deliver one or more babies, or, rarely, to remove a dead fetus...
, the removal of the neonate through a surgical
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
incision in the abdomen
Abdomen
In vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...
, rather than through vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
l birth. In the U.S. and Canada it represents nearly 1 in 3 (31.8%) and 1 in 4 (22.5%) of all childbirths, respectively.
Signs

Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
. Pain levels reported by laboring women vary widely. Pain levels appear to be influenced by fear and anxiety levels. Some other factors may include experience with prior childbirth, age, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment and immobility.
Psychological
Childbirth can be an intense event and strong emotions, both positive and negative, can be brought to the surface.Between 70% and 80% of mothers in the United States report some feelings of sadness or "baby blues" after childbirth. Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression , also called postnatal depression, is a form of clinical depression which can affect women, and less frequently men, typically after childbirth. Studies report prevalence rates among women from 5% to 25%, but methodological differences among the studies make the actual...
may develop in some women; about 10% of mothers in the United States are diagnosed with this condition. Abnormal and persistent fear of childbirth is known as tokophobia.
Preventive group therapy has proven effective as a prophylactic treatment for postpartum depression.
Childbirth is stressful for the infant. In addition to the normal stress of leaving the protected uterine environment, additional stresses associated with breech birth
Breech birth
A breech birth is the birth of a baby from a breech presentation. In the breech presentation the baby enters the birth canal with the buttocks or feet first as opposed to the normal head first presentation....
, such as asphyxiation, may affect the infant's brain.
Vaginal birth
Because humans are bipedal with an erect stance and have, in relation to the size of the pelvisPelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
, the biggest head of any mammalian species, human fetuses and human female pelvises are adapted to make birth possible.
The erect posture causes the weight of the abdominal contents to thrust on the pelvic floor
Pelvic floor
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the levatores ani and coccygei, with which may be included the...
, a complex structure which must not only support this weight but allow three channels to pass through it: the urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
, the vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
and the rectum
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in some mammals, and the gut in others, terminating in the anus. The human rectum is about 12 cm long...
. The head and shoulders require a specific sequence of maneuvers to occur for the bony head and shoulders to pass through the bony ring of the pelvis.
Six phases:
- Engagement of the fetal head in the transverse position. The baby's head is facing across the pelvis at one or other of the mother's hips.
- Descent and flexionFlexionIn anatomy, flexion is a position that is made possible by the joint angle decreasing. The skeletal and muscular systems work together to move the joint into a "flexed" position. For example the elbow is flexed when the hand is brought closer to the shoulder...
of the fetal head. - Internal rotation. The fetal head rotates 90 degrees to the occipito-anterior positionPosition (Obstetrics)In obstetrics, position is the orientation of the fetus in the womb, identified by the location of the presenting part of the fetus relative to the pelvis of the mother...
so that the baby's face is towards the mother's rectum. - Delivery by extension. The fetal head passes out of the birth canal. Its head is tilted forwards so that the crown of its head leads the way through the vagina.
- Restitution. The fetal head turns through 45 degrees to restore its normal relationship with the shoulders, which are still at an angle.
- External rotation. The shoulders repeat the corkscrew movements of the head, which can be seen in the final movements of the fetal head.
The fetal head may temporarily change shape substantially (becoming more elongated) as it moves through the birth canal. This change in the shape of the fetal head is called molding and is much more prominent in women having their first vaginal delivery.
Latent phase
The latent phase of labor, also called prodromal labor, and the contractions may be an intensification of the Braxton Hicks contractions that may start around 26 weeks gestationGestation
Gestation is the carrying of an embryo or fetus inside a female viviparous animal. Mammals during pregnancy can have one or more gestations at the same time ....
. Cervical effacement occurs during the closing weeks of pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
and is usually complete or near complete, by the end of the latent phase. Cervical effacement or cervical dilation
Cervical dilation
Cervical dilation is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery...
is the thinning and stretching of the cervix
Cervix
The cervix is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall...
. The degree of cervical effacement may be felt during a vaginal examination but is not necessary. A 'long' cervix implies that not much has been taken into the lower segment, and vice versa for a 'short' cervix. Latent phase ends with the onset of active first stage; when the cervix is about 3 cm dilated.
First stage: dilation
There are several factors that midwives and physicians use to assess the laboring mother's progress, and these are defined by the Bishop ScoreBishop score
Bishop score, also Bishop's score, is a pre-labour scoring system to assist in predicting whether induction of labour will be required. It has also been used to assess the odds of spontaneous preterm delivery.-Components:...
. The Bishop score is also used as a means to predict whether the mother is likely to spontaneously progress into second stage (delivery).
The first stage of labor starts classically when the effaced (thinned) cervix is 3 cm dilated. There is a variation in this point as some women may or may not have active contractions
Contraction (childbirth)
-Throughout menstrual cycle:The uterus frequently contracts throughout the entire menstrual cycle, and these contractions have been termed endometrial waves or contractile waves. These appear to involve only the sub-endometrial layer of the myometrium...
prior to reaching this point. The onset of actual labor is defined when the cervix begins to progressively dilate. Rupture of the membranes, or a blood stained 'show' may or may not occur at or around this stage.
Uterine muscles form opposing spirals from the top of the upper segment of the uterus to its junction with the lower segment. During effacement, the cervix becomes incorporated into the lower segment of the uterus. During a contraction, these muscles contract causing shortening of the upper segment and drawing upwards of the lower segment, in a gradual expulsive motion. The presenting fetal part then is permitted to descend. Full dilation is reached when the cervix has widened enough to allow passage of the baby's head, around 10 cm dilation for a term baby.
The duration of labour varies widely, but active phase averages some 20 hours for women giving birth to their first child ("primiparae") and 8 hours for women who have already given birth ("multiparae"). Active phase arrest is defined as in a primigravid woman as the failure of the cervix to dilate at a rate of 1.2 cm/hr over a period of at least two hours. This definition is based on Friedman's Curve, which plots the typical rate of cervical dilation and fetal descent during active labor. Some practitioners may diagnose "Failure to Progress", and consequently, perform a Cesarean.
Second stage: fetal expulsion
This stage begins when the cervix is fully dilated, and ends when the baby is born. As pressure on the cervix increases, the Ferguson reflexFerguson reflex
The Ferguson reflex is an example of positive feedback and the female body's response to pressure application in the cervix or vaginal walls.Upon application of pressure, oxytocin is released and uterine contractions are stimulated , until the baby is delivered...
increases uterine contractions so that the second stage can go ahead. At the beginning of the normal second stage, the head is fully engaged in the pelvis; the widest diameter of the head has passed below the level of the pelvic inlet
Pelvic inlet
The pelvic inlet or superior aperture of the pelvis is a planar surface which is typically used to define the boundary between the pelvic cavity and the abdominal cavity .Its position and orientation relative to the skeleton of the pelvis is anatomically defined by its...
. The fetal head then continues descent into the pelvis, below the pubic arch and out through the vaginal introitus
Introitus
The introitus is an entrance that goes into a canal or hollow organ. Introitus is another name for the vaginal orifice.Introitus has also been used for classifying uterine prolapse:*1st degree prolapse: cervix is in the vagina...
. This is assisted by the additional maternal efforts of "bearing down" or pushing. The fetal head is seen to 'crown' as the labia part. At this point, the woman may feel a burning or stinging sensation.
Complete expulsion of the baby signals the successful completion of the second stage of labor.

Third stage: umbilical cord closure and placental expulsion

The umbilical cord
Umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord is the connecting cord from the developing embryo or fetus to the placenta...
is routinely clamped and cut in this stage, but it would normally close naturally even if not clamped. A 2008 Cochrane Review looked into the timing of clamping the umbilical cord. It found that the time of clamping made no difference to the mother, but did have effects for the baby. If the cord is clamped after 2–3 minutes, the infant receives increased amounts of haemoglobin in their first months of life, but may have an increased risk of needing phototherapy to treat jaundice. Sometimes a newborn’s liver is slow to break down all of the red cells they had in the womb, particularly if they are left with more fetal blood from delayed cord clamping and phototherapy helps to speed the breakdown.
Placental expulsion
Placental expulsion
Placental expulsion occurs when the placenta comes out of the birth canal after childbirth. The period from just after the fetus is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor....
begins as a physiological separation from the wall of the uterus. The period from just after the fetus is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor. The average time from delivery of the baby until complete expulsion of the placenta is estimated to be 10-12 minutes dependent on whether active or expectant management is employed
Placental expulsion can be managed actively, by giving a uterotonic such as oxytocin
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a mammalian hormone that acts primarily as a neuromodulator in the brain.Oxytocin is best known for its roles in sexual reproduction, in particular during and after childbirth...
along with appropriate cord traction and fundal massage to assist in delivering the placenta by a skilled birth attendant. Alternatively, it can be managed expectantly, allowing the placenta to be expelled without medical assistance. In a joint statement, World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
, the International Federation of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians and the International Confederations of Midwives recommend active management of the third stage in all vaginal deliveries . This is a strong recommendation of the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
backed by moderate base evidence citing reduced risk of postpartum bleeding (i.e.: obstetric hemorrhage).
In as many as 3% of all vaginal deliveries, the duration of the third stage is longer than 30 minutes and raises concern for retained placenta
Retained placenta
Retained placenta is a condition where all or part of the placenta or membranes are left behind in the uterus during the third stage of labour.-In humans:...
.
When the amniotic sac
Amniotic sac
The amniotic sac is the sac in which the fetus develops in amniotes. It is a tough but thin transparent pair of membranes, which hold a developing embryo until shortly before birth. The inner membrane, the amnion, contains the amniotic fluid and the fetus. The outer membrane, the Chorion,...
has not ruptured during labour or pushing, the infant can be born with the membranes intact. This is referred to as "being born in the caul
Caul
A caul is a thin, filmy membrane, the amnion, that can cover a newborn's head and face immediately after birth.-Obstetrics:A child "born with the caul" has a portion of the amniotic sac or membrane remaining on the head. There are two types of cauls. The most common caul is adhered to the head...
." The caul is harmless and its membranes are easily broken and wiped away. With the advent of modern interventive obstetrics, artificial rupture of the membranes has become common, so babies are rarely born in the caul.
Fourth stage
The "fourth stage of labor" is a term used in two different senses:- It can refer to the immediate puerperium, or the hours immediately after delivery of the placenta.
- It can be used in a more metaphorical sense to describe the weeks following delivery.
Afterwards
Many cultures feature initiation rites for newborns, such as naming ceremonies, baptismBaptism
In Christianity, baptism is for the majority the rite of admission , almost invariably with the use of water, into the Christian Church generally and also membership of a particular church tradition...
, and others.
Mothers are often allowed a period where they are relieved of their normal duties to recover from childbirth. The length of this period varies. In many countries, taking time off from work to care for a newborn is called "maternity leave" or "parental leave
Parental leave
Parental leave is an employee benefit that provides paid or unpaid time off work to care for a child or make arrangements for the child's welfare. Often, the term parental leave includes maternity, paternity, and adoption leave...
" and can vary from a few days to several months.
Station
Refers to the relationship of the fetal presenting part to the level of the ischial spines. When the presenting part is at the ichial spines the station is 0 (synonymous with engagement). If the presenting fetal part is above the spines, the distance is measured and described as minus stations, which range from -1 to -4 cm. If the presenting part is below the ischial spines, the distance is stated as plus stations ( +1 to +4 cm). At +3 and +4 the presenting part is at the perineum and can be seen.Management
Eating or drinking during labor has no harmful effects on outcomes, although doctors do not want women in labor to eat food in case they end up needing a cesarean section.Pain control
Non pharmaceuticalSome women prefer to avoid analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
medication during childbirth. They can still try to alleviate labor pain using psychological preparation, education, massage, acupuncture, TENS unit use, hypnosis, or water therapy in a tub or shower. Some women like to have someone to support them during labor and birth, such as the father
Father
A father, Pop, Dad, or Papa, is defined as a male parent of any type of offspring. The adjective "paternal" refers to father, parallel to "maternal" for mother...
of the baby, a family member, a close friend, a partner, or a doula
Doula
A Doula is someone who provides non-medical support to women and their families during labour and childbirth, and also the postpartum period. The term can also be used to describe other supportive roles for other life events such as abortion, death and more....
. Some women deliver in a squatting or crawling position in order to more effectively push during the second stage and so that gravity can aid the descent of the baby through the birth canal.
The human body also has a chemical response to pain, by releasing endorphin
Endorphin
Endorphins are endogenous opioid peptides that function as neurotransmitters. They are produced by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus in vertebrates during exercise, excitement, pain, consumption of spicy food, love and orgasm, and they resemble the opiates in their abilities to produce...
s. Endorphins are present before, during, and immediately after childbirth. Some homebirth advocates believe that this hormone can induce feelings of pleasure and euphoria during childbirth, reducing the risk of maternal depression
Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression , also called postnatal depression, is a form of clinical depression which can affect women, and less frequently men, typically after childbirth. Studies report prevalence rates among women from 5% to 25%, but methodological differences among the studies make the actual...
some weeks later.
Water birth
Water birth
Water birth is a method of giving birth, which involves immersion in warm water. The immersion can mean giving birth to the infant in the water or using it as a tool during the labor process. Proponents believe that this method is safe and provides many benefits for both mother and infant,...
is an option chosen by some women for pain relief during labor and childbirth, and some studies have shown waterbirth in an uncomplicated pregnancy to reduce the need for analgesia, without evidence of increased risk to mother or newborn. Hot water tubs are available in many hospitals and birthing centres.
Meditation
Meditation
Meditation is any form of a family of practices in which practitioners train their minds or self-induce a mode of consciousness to realize some benefit....
and mind medicine techniques are also used for pain control during labour and delivery. These techniques are used in conjunction with progressive muscle relaxation and many other forms of relaxation for the mind and body to aid in pain control for women during childbirth. One such technique is the use of hypnosis in childbirth
Hypnosis in childbirth
Hypnotherapy can be used during pregnancy and childbirth to prepare a mother for birth and/or to attempt to treat a number of issues ranging from fears and minor health conditions related to the pregnancy, to the possibility of reducing or eliminating pain during labor.Hypnotherapy is the process...
. There are a number of organizations that teach women and their partners to use a variety of techniques to assist with labor comfort, without the use of pharmaceuticals.
A new mode of analgesia is sterile water injection placed just underneath the skin in the most painful spots during labor. A control trial in Iran of 0.5mL injections was conducted with normal saline which revealed a statistical superiority with water over saline.
Pharmaceutical
Different measures for pain control have varying degrees of success and side effects to the woman and her baby. In some countries of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, doctors commonly prescribe inhaled nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
gas for pain control, especially as 50% nitrous oxide, 50% oxygen, known as Entonox
Entonox
A mix of nitrous oxide 50% and oxygen 50% is a medical anaesthesia gas, commonly known as Entonox or Nitronox, or colloquially as gas and air, and is frequently used in pre-hospital care, childbirth and emergency medicine situations by medical professionals such as doctors, nurses, midwives and...
; in the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, midwives may use this gas without a doctor's prescription. Pethidine
Pethidine
Pethidine or meperidine Pethidine (INN) or meperidine (USAN) Pethidine (INN) or meperidine (USAN) (commonly referred to as Demerol but also referred to as: isonipecaine; lidol; pethanol; piridosal; Algil; Alodan; Centralgin; Dispadol; Dolantin; Mialgin (in Indonesia); Petidin Dolargan (in Poland);...
(with or without promethazine
Promethazine
Promethazine is a first-generation antihistamine of the phenothiazine family. The drug has anti-motion sickness, antiemetic, and anticholinergic effects, as well as a strong sedative effect and in some countries is prescribed for insomnia when benzodiazepines are contraindicated...
) may be used early in labour, as well as other opioid
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
s such as fentanyl, but if given too close to birth there is a risk of respiratory depression in the infant.
Popular medical pain control in hospitals include the regional anesthetics epidural
Epidural
The term epidural is often short for epidural analgesia, a form of regional analgesia involving injection of drugs through a catheter placed into the epidural space...
blocks, and spinal anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia , also called spinal analgesia or sub-arachnoid block , is a form of regional anaesthesia involving injection of a local anaesthetic into the subarachnoid space, generally through a fine needle, usually 9 cm long...
. Epidural analgesia is a generally safe and effective method of relieving pain in labour, but is associated with longer labour, more operative intervention (particularly instrument delivery), and increases in cost. Generally, pain and cortisol increased throughout labor in women without EDA. Pain and stress hormones rise throughout labor for women without epidurals, while pain, fear, and stress hormones decrease upon administration of epidural analgesia, but may rise again later.
Medicine administered via epidural can cross the placenta and enter the bloodstream of the fetus. Epidural analgesia has no statistically significant impact on the risk of caesarean section, and does not appear to have an immediate effect on neonatal status as determined by Apgar scores.
Augmentation
Augmentation is a procedure which attempts to speed up the process of labour. OxytocinOxytocin
Oxytocin is a mammalian hormone that acts primarily as a neuromodulator in the brain.Oxytocin is best known for its roles in sexual reproduction, in particular during and after childbirth...
has been used to increase the rate of vaginal delivery in those with a slow progress of labor.
Instrumental delivery
Obstetric forceps or ventouseVentouse
Ventouse is a vacuum device used to assist the delivery of a baby when the second stage of labour has not progressed adequately. It is an alternative to a forceps delivery and caesarean section. It cannot be used when the baby is in the breech position or for premature births. This technique is...
may be used to facilitate childbirth.
- The woman will have her legs supported in stirrups.
- If an anaesthetic is not already in place it will be given.
- EpisiotomyEpisiotomyAn episiotomy , also known as perineotomy, is a surgically planned incision on the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall during second stage of labor. The incision, which can be midline or at an angle from the posterior end of the vulva, is performed under local anaesthetic , and is sutured...
might be needed. - A trial forceps might be performed, which is abandoned in favor of a caesarean section if delivery is not optimal.
Multiple births
Twins can be delivered vaginally. In some cases twin delivery is done in a larger delivery room or in the theatre, just in case complications occur e.g.- Both twins born vaginally - this can occur both presented head first or where one comes head first and the other is breech and/or helped by a forceps/ventouse delivery
- One twin born vaginally and the other by caesarean section.
- If the twins are joined at any part of the body - called conjoined twinsConjoined twinsConjoined twins are identical twins whose bodies are joined in utero. A rare phenomenon, the occurrence is estimated to range from 1 in 50,000 births to 1 in 100,000 births, with a somewhat higher incidence in Southwest Asia and Africa. Approximately half are stillborn, and a smaller fraction of...
, delivery is mostly by caesarean section.
Support
There is increasing evidence to show that the participation of the woman's partner in the birth leads to better birth and also post-birth outcomes, providing the partner does not exhibit excessive anxiety. Research also shows that when a laboring woman was supported by a female helper such as a family member or doulaDoula
A Doula is someone who provides non-medical support to women and their families during labour and childbirth, and also the postpartum period. The term can also be used to describe other supportive roles for other life events such as abortion, death and more....
during labor, she had less need for chemical pain relief, the likelihood of caesarean section was reduced, use of forceps and other instrumental deliveries were reduced, there was a reduction in the length of labor, and the baby had a higher Apgar score
Apgar score
The Apgar score was devised in 1952 by the eponymous Dr. Virginia Apgar as a simple and repeatable method to quickly and summarily assess the health of newborn children immediately after birth...
(Dellman 2004, Vernon 2006). However, little research has been conducted to date about the conflicts between partners, professionals, and the mother.
Collecting stem cells
It is possible to collect two types of stem cells during childbirth: amniotic stem cellsAmniotic stem cells
Amniotic stem cells are multipotent stem cells of mesenchymal origin extracted from amniotic fluid.Amniotic stem cells are able to differentiate into various tissue type such as skin, cartilage, cardiac tissue, nerves, muscle, and bone, and may have potential future medical applications.All over...
or umbilical cord blood stem cells.
To collect amniotic stem cells
Amniotic stem cells
Amniotic stem cells are multipotent stem cells of mesenchymal origin extracted from amniotic fluid.Amniotic stem cells are able to differentiate into various tissue type such as skin, cartilage, cardiac tissue, nerves, muscle, and bone, and may have potential future medical applications.All over...
, it is necessary to do amniocentesis
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amnion or amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and the fetal DNA is examined for...
before or during the birth. Amniotic stem cells are multipotent and very active, useful for both autologous or donor use. There are private banks in US; the first is Biocell Center
Biocell Center
Biocell Center is an international company specializing in the cryopreservation and private banking of amniotic fluid stem cells. The company is headquartered in Italy with several international locations and is involved with numerous partnerships and research studies of amniotic fluid stem...
in Boston.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are also active, but less multipotent than amniotic stem cells. There are a lot of banks of cord blood, both private and public and for autologous or eterologous use.
Complications
Childbirth is an inherently dangerous and risky activity, subject to many complications. The "natural" mortality rate of childbirth—where nothing is done to avert maternal death—has been estimated as being 1500 deaths per 100,000 births. (See main article: neonatal death, maternal deathMaternal death
Maternal death, or maternal mortality, also "obstetrical death" is the death of a woman during or shortly after a pregnancy. In 2010, researchers from the University of Washington and the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, estimated global maternal mortality in 2008 at 342,900 , of...
). Modern medicine has greatly alleviated the risk of childbirth. In modern Western countries, such as the United States or Sweden, the current maternal mortality rate is around 10 deaths per 100,000 births.
Birthing complications may be maternal or fetal, and long term or short term.
Labor complications
The second stage of labor may be delayed or lengthy due to:- malpresentation (breech birthBreech birthA breech birth is the birth of a baby from a breech presentation. In the breech presentation the baby enters the birth canal with the buttocks or feet first as opposed to the normal head first presentation....
(i.e. buttocks or feet first), face, brow, or other) - failure of descent of the fetal head through the pelvic brim or the interspinous diameter
- poor uterine contraction strength
- active phase arrest
- cephalo-pelvic disproportionPelvimetryPelvimetry is the assessment of the female pelvis in relation to the birth of a baby. Traditional obstetrical services relied heavily on pelvimetry in the conduct of delivery in order to decide if natural or operative vaginal delivery was possible or if and when to use a cesarean...
(CPD) - shoulder dystociaShoulder dystociaShoulder dystocia is a specific case of dystocia whereby after the delivery of the head, the anterior shoulder of the infant cannot pass below the pubic symphysis, or requires significant manipulation to pass below the pubic symphysis. It is diagnosed when the shoulders fail to deliver shortly...
Secondary changes may be observed: swelling of the tissues, maternal exhaustion, fetal heart rate abnormalities. Left untreated, severe complications include death of mother and/or baby, and genitovaginal fistula
Fistula
In medicine, a fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two epithelium-lined organs or vessels that normally do not connect. It is generally a disease condition, but a fistula may be surgically created for therapeutic reasons.-Locations:Fistulas can develop in various parts of the...
.
Dystocia (obstructed labour)
Dystocia is an abnormal or difficult childbirth or labour. Approximately one fifth of human labours have dystocia. Dystocia may arise due to incoordinate uterine activity, abnormal fetal lie or presentation, absolute or relative cephalopelvic disproportion, or (rarely) a massive fetal tumor such as a sacrococcygeal teratoma. Oxytocin is commonly used to treat incoordinate uterine activity, but pregnancies complicated by dystocia often end with assisted deliveries, including forceps, ventouse or, commonly, caesarean section. Recognized complications of dystocia include fetal death, respiratory depression, Hypoxic Ischaemic Encephalopathy (HIE), and brachial nerve damage. A prolonged interval between pregnancies, primigravid birth, and multiple birth have also been associated with increased risk for labour dystocia.Shoulder dystocia is a dystocia in which the anterior shoulder of the infant cannot pass below the pubic symphysis or requires significant manipulation to pass below it. It can also be described as delivery requiring additional manoeuvres after gentle downward traction on the head has failed to deliver the shoulders.
A prolonged second stage of labour is another type of dystocia whereby the fetus has not been delivered within three hours in a nulliparous woman, or two hours in multiparous woman, after her cervix has become fully dilated.
Synonyms for dystocia include difficult labour, abnormal labour, difficult childbirth, abnormal childbirth, and dysfunctional labour.
Maternal complications
Vaginal birth injury with visible tearsPerineal tear classification
Perineal tear classification is a system used to quantify the severity of trauma to the perineum during vaginal childbirth. Delivery may lead to overstretching of the vagina, causing tears in the perineal tissue between the vagina and rectum...
or episiotomies
Episiotomy
An episiotomy , also known as perineotomy, is a surgically planned incision on the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall during second stage of labor. The incision, which can be midline or at an angle from the posterior end of the vulva, is performed under local anaesthetic , and is sutured...
are common. Internal tissue tearing as well as nerve damage to the pelvic structures lead in a proportion of women to problems with prolapse, incontinence of stool or urine and sexual dysfunction. Fifteen percent of women become incontinent, to some degree, of stool or urine after normal delivery, this number rising considerably after these women reach menopause. Vaginal birth injury is a necessary, but not sufficient, cause of all non hysterectomy related prolapse in later life. Risk factors for significant vaginal birth injury include:
- A baby weighing more than 9 pounds.
- The use of forceps or vacuum for delivery. These markers are more likely to be signals for other abnormalities as forceps or vacuum are not used in normal deliveries.
- The need to repair large tears after delivery.
Pelvic girdle pain
Pelvic girdle pain
Pregnancy related Pelvic Girdle Pain causes pain, instability and limitation of mobility and functioning in any of the three pelvic joints...
. Hormones and enzymes work together to produce ligamentous relaxation and widening of the symphysis pubis during the last trimester of pregnancy. Most girdle pain occurs before birthing, and is known as diastasis of the pubic symphysis. Predisposing factors for girdle pain include maternal obesity.
Infection remains a major cause of maternal mortality and morbidity in the developing world. The work of Ignaz Semmelweis
Ignaz Semmelweis
Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis was a Hungarian physician now known as an early pioneer of antiseptic procedures. Described as the "savior of mothers", Semmelweis discovered that the incidence of puerperal fever could be drastically cut by the use of hand disinfection in obstetrical clinics...
was seminal in the pathophysiology and treatment of puerperal fever
Puerperal fever
Puerperal fever or childbed fever, is a bacterial infection contracted by women during childbirth or miscarriage. It can develop into puerperal sepsis, which is a serious form of septicaemia. If untreated, it is often fatal....
and saved many lives.
Hemorrhage, or heavy blood loss, is still the leading cause of death of birthing mothers in the world today, especially in the developing world. Heavy blood loss leads to hypovolemic shock, insufficient perfusion of vital organs and death if not rapidly treated. Blood transfusion may be life saving. Rare sequelae include Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is the decreased secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain...
Sheehan's syndrome
Sheehan's syndrome
Sheehan syndrome, also known as Simmonds' syndrome or postpartum hypopituitarism or postpartum pituitary necrosis, is hypopituitarism , caused by necrosis due to blood loss and hypovolemic shock during and after childbirth...
.
The maternal mortality rate (MMR) varies from 9 per 100,000 live births in the US and Europe to 900 per 100,000 live births in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa as a geographical term refers to the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara. A political definition of Sub-Saharan Africa, instead, covers all African countries which are fully or partially located south of the Sahara...
. Every year, more than half a million women die in pregnancy or childbirth.
Mechanical fetal injury
Risk factors for fetal birth injury include fetal macrosomia (big baby), maternal obesityMaternal obesity
Maternal obesity refers to obesity of a woman during pregnancy. Parental obesity refers to obesity of either parent during pregnancy....
, the need for instrumental delivery, and an inexperienced attendant. Specific situations that can contribute to birth injury include breech presentation and shoulder dystocia
Shoulder dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is a specific case of dystocia whereby after the delivery of the head, the anterior shoulder of the infant cannot pass below the pubic symphysis, or requires significant manipulation to pass below the pubic symphysis. It is diagnosed when the shoulders fail to deliver shortly...
. Most fetal birth injuries resolve without long term harm, but brachial plexus injury
Brachial plexus injury
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that conducts signals from the spinal cord, which is housed in the spinal canal of the vertebral column , to the shoulder, arm and hand. These nerves originate in the fifth, sixth, seventh and eighth cervical , and first thoracic spinal nerves, and...
may lead to Erb's palsy
Erb's palsy
Erb's palsy is a paralysis of the arm caused by injury to the upper group of the arm's main nerves, specifically the upper trunk C5-C6 is severed. These form part of the brachial plexus, comprising the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-C8, and T1. These injuries arise most commonly, but not...
or Klumpke's paralysis.
Neonatal infection
Neonates are prone to infection in the first month of life. Some organisms such as S. agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus) or (GBS) are more prone to cause these occasionally fatal infections. Risk factors for GBS infection include:- prematurity (birth prior to 37 weeks gestation)
- a sibling who has had a GBSGroup B StreptococcusInfection with Group B Streptococcus , also known as 'Streptococcus agalactiae' and more colloquially as Strep B and group B Strep, can cause serious illness and sometimes death, especially in newborn infants, the elderly, and patients with compromised immune systems...
infection - prolonged labour or rupture of membranes
Untreated sexually transmitted infections are associated with congenital and perinatal infections in neonates, particularly in the areas where rates of infection remain high. The overall perinatal mortality rate associated with untreated syphilis, for example, approached 40%.
Neonatal death
Infant deaths (neonatal deaths from birth to 28 days, or perinatal deaths if including fetal deaths at 28 weeks gestation and later) are around 1% in modernized countries.The most important factors affecting mortality
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
in childbirth are adequate nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
and access to quality medical care ("access" is affected both by the cost of available care, and distance from health services).
A 1983-1989 study by the Texas Department of State Health Services
Texas Department of State Health Services
Texas Department of State Health Services is a state agency of Texas. The department was created by House Bill 2292 of the 78th Texas Legislature in 2003 through the merging of four state agencies: the Texas Department of Health, Texas Department of Mental Health and Mental Retardation, Texas...
highlighted the differences in neonatal mortality (NMR) between high risk and low risk pregnancies. NMR was 0.57% for doctor-attended high risk births, and 0.19% for low risk births attended by non-nurse midwives. Conversely, some studies demonstrate a higher perinatal mortality rate with assisted home births. Around 80% of pregnancies are low-risk. Factors that may make a birth high risk include prematurity, high blood pressure, gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which women without previously diagnosed diabetes exhibit high blood glucose levels during pregnancy . It is widely accepted as a disease only in the United States, there is some question whether the condition is natural during pregnancy...
and a previous cesarean section.
Intrapartum asphyxia
Intrapartum asphyxia is the impairment of the delivery of oxygen to the brain and vital tissues during the progress of labour. This may exist in a pregnancy already impaired by maternal or fetal disease, or may rarely arise de novo in labour. This can be termed fetal distressFetal distress
In medicine , the term fetal distress refers to the presence of signs in a pregnant woman—before or during childbirth—that suggest that the fetus may not be well...
, but this term may be emotive and misleading. True intrapartum asphyxia is not as common as previously believed, and is usually accompanied by multiple other symptoms during the immediate period after delivery. Monitoring might show up problems during birthing, but the interpretation and use of monitoring devices is complex and prone to misinterpretation. Intrapartum asphyxia can cause long-term impairment, particularly when this results in tissue damage through encephalopathy
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can be caused by many different illnesses.-Terminology:...
.
Professions associated with childbirth

Birth attendant
A birth attendant, also known as “skilled birth attendant” , is a midwife, physician, obstetrician, nurse, or other health care professional who provides basic and emergency health care services to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period...
s may provide support and care during pregnancy and childbirth, although there are important differences across categories based on professional training and skills, practice regulations, as well as nature of care delivered.
“Childbirth educators” are instructors who aim to educate pregnant women and their partners about the nature of pregnancy, labour signs and stages, techniques for giving birth, breastfeeding and newborn baby care. In the United States and elsewhere, classes for training as a childbirth educator can be found in hospital settings or through many independent certifying organizations such as Birthing From Within, BirthWorks, The Bradley Method, Brio Birth, CAPPA, HypBirth, HypnoBabies, HypnoBirthing, ICTC, ICEA, Lamaze, etc. Each organization teaches its own curriculum and each emphasizes different techniques. Information about each can be obtained through their individual websites.
Doula
Doula
A Doula is someone who provides non-medical support to women and their families during labour and childbirth, and also the postpartum period. The term can also be used to describe other supportive roles for other life events such as abortion, death and more....
s are assistants who support mothers during pregnancy, labour, birth, and postpartum. They are not medical attendants; rather, they provide emotional support and non-medical pain relief for women during labour. Like childbirth educators and other assistive personnel
Unlicensed assistive personnel
Unlicensed assistive personnel is an umbrella term to describe a job class of paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living and provide bedside care — including basic nursing...
, certification to become a doula is not compulsory, thus, anyone can call themself a doula or a childbirth educator.
Midwives
Midwifery
Midwifery is a health care profession in which providers offer care to childbearing women during pregnancy, labour and birth, and during the postpartum period. They also help care for the newborn and assist the mother with breastfeeding....
are autonomous practitioners who provide basic and emergency health care before, during and after pregnancy and childbirth, generally to women with low-risk pregnancies. Midwives are trained to assist during labour and birth, either through direct-entry or nurse-midwifery education programs. Jurisdictions where midwifery is a regulated profession will typically have a registering and disciplinary body for quality control, such as the College of Midwives of British Columbia (CMBC) in Canada or the Nursing and Midwifery Council
Nursing and Midwifery Council
Established in 2002, the Nursing and Midwifery Council is a statutory body set up by the Parliament of the United Kingdom through the . The NMC is the UK regulator for nursing and midwifery professions with a stated aim to safeguard the health and wellbeing of the public...
(NMC) in the United Kingdom.
In jurisdictions where midwifery is not a regulated profession, traditional or lay midwives
Traditional birth attendant
A traditional birth attendant , also known as a traditional midwife, community midwife or lay midwife, is a pregnancy and childbirth care provider...
may assist women during childbirth, although they do not typically receive formal health care education and training.
Medical doctor
Doctor of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine is a doctoral degree for physicians. The degree is granted by medical schools...
s who practice obstetrics
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the medical specialty dealing with the care of all women's reproductive tracts and their children during pregnancy , childbirth and the postnatal period...
include categorically specialized obstetricians
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the medical specialty dealing with the care of all women's reproductive tracts and their children during pregnancy , childbirth and the postnatal period...
; family practitioners
Family medicine
Family medicine is a medical specialty devoted to comprehensive health care for people of all ages. It is a division of primary care that provides continuing and comprehensive health care for the individual and family across all ages, sexes, diseases, and parts of the body...
and general practitioners whose training, skills and practices include obstetrics; and in some contexts general surgeons. These physicians and surgeons variously provide care across the whole spectrum of normal and abnormal births and pathological labour conditions. Categorically specialized obstetricians are qualified surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
s, so they can undertake surgical procedures relating to childbirth. Some family practitioners or general practitioners also perform obstetrical surgery. Obstetrical procedures include cesarean sections, episiotomies
Episiotomy
An episiotomy , also known as perineotomy, is a surgically planned incision on the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall during second stage of labor. The incision, which can be midline or at an angle from the posterior end of the vulva, is performed under local anaesthetic , and is sutured...
, and assisted delivery. Categorical specialists in obstetrics are commonly dually trained in obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), and may provide other medical and surgical gynecological care, and may incorporate more general, well-woman, primary care
Primary care
Primary care is the term for the health services by providers who act as the principal point of consultation for patients within a health care system...
elements in their practices. Maternal-fetal medicine
Maternal-fetal medicine
Maternal-Fetal medicine is the branch of obstetrics that focuses on the medical and surgical management of high-risk pregnancies. Management includes monitoring and treatment including comprehensive ultrasound, chorionic villus sampling, genetic amniocentesis, and fetal surgery or treatment....
specialists are obstetrician/gynecologists subspecialized in managing and treating high-risk pregnancy and delivery.
Obstetric nurses assist midwives, doctors, women, and babies prior to, during, and after the birth process, in the hospital system. Some midwives are also obstetric nurses. Obstetric nurses hold various certifications and typically undergo additional obstetric training in addition to standard nursing training
Nursing school
A nursing school is a type of educational institution, or part thereof, providing education and training to become a fully qualified nurse. The nature of nursing education and nursing qualifications varies considerably across the world.-United Kingdom:...
.
Society and culture
Childbirth routinely occurs in hospitalHospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
s in much of Western society. Prior to the 20th century and in some countries to the present day it has more typically occurred at home.
In Western and other cultures, age is reckoned from the date of birth, and sometimes the birthday
Birthday
A birthday is a day or anniversary where a person celebrates his or her date of birth. Birthdays are celebrated in numerous cultures, often with a gift, party or rite of passage. Although the major religions celebrate the birth of their founders , Christmas – which is celebrated widely by...
is celebrated annually. East Asian age reckoning
East Asian age reckoning
East Asian age reckoning is a concept and practice that originated in China and is widely used by other cultures in East Asia, which share this traditional way of counting a person's age. Newborns start at one year old, and each passing of a Lunar New Year, rather than the birthday, adds one year...
starts newborns at "1", incrementing each Lunar New Year
Lunar calendar
A lunar calendar is a calendar that is based on cycles of the lunar phase. A common purely lunar calendar is the Islamic calendar or Hijri calendar. A feature of the Islamic calendar is that a year is always 12 months, so the months are not linked with the seasons and drift each solar year by 11 to...
.
Some families view the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
as a special part of birth, since it has been the child's life support for so many months. Some parents like to see and touch this organ. In some cultures, parents plant a tree along with the placenta on the child's first birthday
Birthday
A birthday is a day or anniversary where a person celebrates his or her date of birth. Birthdays are celebrated in numerous cultures, often with a gift, party or rite of passage. Although the major religions celebrate the birth of their founders , Christmas – which is celebrated widely by...
. The placenta may be eaten
Placentophagy
Placentophagy is the act of mammals eating the placenta of their young after childbirth.The placenta contains high levels of prostaglandin which stimulates involution of the uterus, in effect cleaning the uterus out...
by the newborn's family, ceremonially or otherwise (for nutrition; the great majority of animals in fact do this naturally). Most recently there is a category of birth professionals available who will encapsulate placenta for use as placenta medicine by postpartum mothers. The placenta is believed to provide hormones which ease the emotional roller coaster of the postpartum period and even prevent some cases of postpartum depression. The placenta is steamed and then dried in a dehydrator, after which it is made into gel caps that are taken for weeks or months. There is some research showing benefits for milk production in women and other positive studies in animal populations. Anecdotal reports suggest that women say that they suffer less postpartum blues, depression and anxiety using placenta medicine.
The exact location in which
Locus in quo
Locus in quo means, in British common law, the "scene of the event", orThe phrase comes from the Latin language, meaning "The place in which"....
childbirth takes place is an important factor in determining nationality
Nationality
Nationality is membership of a nation or sovereign state, usually determined by their citizenship, but sometimes by ethnicity or place of residence, or based on their sense of national identity....
, in particular for birth aboard aircraft and ships
Birth aboard aircraft and ships
The subject of birth aboard aircraft and ships is one with a long history in public international law. The law on the subject, despite the provisions of Article 3 the 1961 Convention on the Reduction of Statelessness, is complex, because various states apply differing principles of nationality,...
.
See also
- Advanced maternal ageAdvanced maternal ageAdvanced maternal age is defined as an increase in the age at which women give birth to their first child, is now a widespread, and indeed near universal, phenomenon across the OECD countries....
, an increase in age at first birth - Amniotic stem cellsAmniotic stem cellsAmniotic stem cells are multipotent stem cells of mesenchymal origin extracted from amniotic fluid.Amniotic stem cells are able to differentiate into various tissue type such as skin, cartilage, cardiac tissue, nerves, muscle, and bone, and may have potential future medical applications.All over...
- Asynclitic birthAsynclitic birthAn asynclitic birth or asynclitism refers to the position of a baby in the uterus such that the head is tilted to the side, causing the fetal head to no longer be in line with the birth canal. Most asynclitism corrects spontaneously in the progress of normal labor...
, an abnormal birth position - Coffin birthCoffin birthCoffin birth, known in academia by the more accurate term postmortem fetal extrusion, is the expulsion of a nonviable fetus through the vaginal opening of the decomposing body of a pregnant woman as a result of the increasing pressure of intraabdominal gases. This kind of postmortem delivery...
- Homebirth
- LamazeLamazeThe Lamaze Technique, often referred to as Lamaze, is a prepared childbirth technique developed in the 1940s by French obstetrician Dr. Fernand Lamaze as an alternative to the use of medical intervention during childbirth...
- Bradley method of natural childbirthBradley method of natural childbirthThe Bradley Method of natural childbirth is a method of natural childbirth developed in 1947 by Robert A. Bradley, M.D. and popularized by his book Husband-Coached Childbirth, first published in 1965...
- NatalismNatalismNatalism is a belief that promotes human reproduction. The term is taken from the Latin adjective form for "birth", natalis. Natalism promotes child-bearing and glorifies parenthood...
- Natural childbirthNatural childbirthNatural Childbirth is a philosophy of childbirth that is based on the notion that women who are adequately prepared are innately able to give birth without routine medical interventions. Natural childbirth arose in opposition to the techno-medical model of childbirth that has recently gained...
- Obstetrical DilemmaObstetrical DilemmaThe Obstetrical Dilemma refers to the evolutionary development of the human species through a number of biological changes, specifically the shifting of the females' pelvic bones, thereby shortening the fetal incubation period....
- PartogramPartogramPartogram is a composite graphical record of key data during labour entered against time on a single sheet of paper. Relevant measurements might include statistics such as cervical dilation, fetal heart rate, duration of labour and vital signs.It is intended to provide an accurate record of the...
- Postpartum depressionPostpartum depressionPostpartum depression , also called postnatal depression, is a form of clinical depression which can affect women, and less frequently men, typically after childbirth. Studies report prevalence rates among women from 5% to 25%, but methodological differences among the studies make the actual...
(PPD) - PostnatalPostnatalPostnatal is the period beginning immediately after the birth of a child and extending for about six weeks. Another term would be postpartum period, as it refers to the mother...
- Pre- and perinatal psychologyPre- and perinatal psychologyPrenatal and perinatal psychology is an interdisciplinary study of the foundations of health in body, mind, emotions and in enduring response patterns to life...
- Pre-laborPre-laborPre-labor, also called "prodromal labor," consists of the early signs before labor starts. It is the body's preparation for real labor....
- Health care providerHealth care providerA health care provider is an individual or an institution that provides preventive, curative, promotional or rehabilitative health care services in a systematic way to individuals, families or communities....
- Traditional birth attendantTraditional birth attendantA traditional birth attendant , also known as a traditional midwife, community midwife or lay midwife, is a pregnancy and childbirth care provider...
- Unassisted childbirthUnassisted childbirthUnassisted childbirth refers to the process of intentionally giving birth without the assistance of a medical or professional birth attendant...
- Vernix caseosaVernix caseosaVernix caseosa, also known as vernix, is the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human babies.-Composition:...
- Waterbirth

