
Credal set
Encyclopedia
A credal set is a set of probability distribution
s or, equivalently, a set of probability measure
s. A credal set is often assumed or constructed to be a closed
convex set
. It is intended to express uncertainty
or doubt about the probability model that should be used, or to convey the beliefs of a Bayesian
agent about the possible states of the world.
Let denote a categorical variable,
denote a categorical variable,  a probability mass function over
a probability mass function over  , and
, and  a credal set over
a credal set over  . If
. If 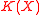 is convex, the credal set can be equivalently described by its extreme points
is convex, the credal set can be equivalently described by its extreme points 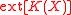 . The expectation for a function
. The expectation for a function  of
of  with respect to the credal set
with respect to the credal set 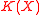 can be characterised only by its lower and upper bounds. For the lower we have
can be characterised only by its lower and upper bounds. For the lower we have 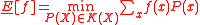 . Notably, such a inference problem can be equivalently obtained by considering only the extreme points of the credal set.
. Notably, such a inference problem can be equivalently obtained by considering only the extreme points of the credal set.
It is easy to see that a credal set over a Boolean variable cannot have more than two vertices, while no bounds can be provided for credal sets over variables with three or more values.
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
s or, equivalently, a set of probability measure
Probability measure
In mathematics, a probability measure is a real-valued function defined on a set of events in a probability space that satisfies measure properties such as countable additivity...
s. A credal set is often assumed or constructed to be a closed
Closure (mathematics)
In mathematics, a set is said to be closed under some operation if performance of that operation on members of the set always produces a unique member of the same set. For example, the real numbers are closed under subtraction, but the natural numbers are not: 3 and 8 are both natural numbers, but...
convex set
Convex set
In Euclidean space, an object is convex if for every pair of points within the object, every point on the straight line segment that joins them is also within the object...
. It is intended to express uncertainty
Uncertainty
Uncertainty is a term used in subtly different ways in a number of fields, including physics, philosophy, statistics, economics, finance, insurance, psychology, sociology, engineering, and information science...
or doubt about the probability model that should be used, or to convey the beliefs of a Bayesian
Bayesian probability
Bayesian probability is one of the different interpretations of the concept of probability and belongs to the category of evidential probabilities. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of logic that enables reasoning with propositions, whose truth or falsity is...
agent about the possible states of the world.
Let
 denote a categorical variable,
denote a categorical variable,  a probability mass function over
a probability mass function over  , and
, and  a credal set over
a credal set over  . If
. If 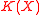 is convex, the credal set can be equivalently described by its extreme points
is convex, the credal set can be equivalently described by its extreme points 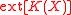 . The expectation for a function
. The expectation for a function  of
of  with respect to the credal set
with respect to the credal set 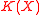 can be characterised only by its lower and upper bounds. For the lower we have
can be characterised only by its lower and upper bounds. For the lower we have 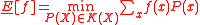 . Notably, such a inference problem can be equivalently obtained by considering only the extreme points of the credal set.
. Notably, such a inference problem can be equivalently obtained by considering only the extreme points of the credal set.It is easy to see that a credal set over a Boolean variable cannot have more than two vertices, while no bounds can be provided for credal sets over variables with three or more values.
See also
- imprecise probabilityImprecise probabilityImprecise probability generalizes probability theory to allow for partial probability specifications, and is applicable when information is scarce, vague, or conflicting, in which case a unique probability distribution may be hard to identify...
- Dempster–Shafer theory
- p-boxesProbability boxA probability box is a characterization of an uncertain number consisting of both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties that is often used in risk analysis or quantitative uncertainty modeling where numerical calculations must be performed...
- robust BayesRobust Bayes analysisRobust Bayes analysis, also called Bayesian sensitivity analysis, investigates the robustness of answers from a Bayesian analysis to uncertainty about the precise details of the analysis. An answer is robust if it does not depend sensitively on the assumptions and calculation inputs on which it is...
- upper and lower probabilitiesUpper and lower probabilitiesUpper and lower probabilities are representations of imprecise probability. Whereas probability theory uses a single number, the probability, to describe how likely an event is to occur, this method uses two numbers: the upper probability of the event and the lower probability of the event.Because...

