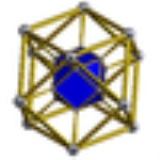
Cuboctahedral prism
Encyclopedia
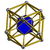 Schlegel diagram One cuboctahedral cell shown |
|
| Type | Prismatic uniform polychoron |
| Uniform index | 50 |
| Schläfli symbol | t1{3,4}x{} t0,2{3,3}×{} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... |
|
| Cells | 2 (3.4.3.4 Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... )  8 (3.4.4 Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... )  6 (4.4.4 Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... )  |
| Faces | 16 {3} Triangle A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted .... 12+24 {4} Square (geometry) In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles... |
| Edges | 60 |
| Vertices | 24 |
| Vertex figure | Cuboid Cuboid In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature... |
| Symmetry group Coxeter notation In geometry, Coxeter notation is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between with fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group. It uses a bracketed notation, with modifiers to indicate certain subgroups. The notation is named after H. S. M... |
[3,4,2], order 96 [3,3,2], order 48 |
| Properties | convex Convex polytope A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set of points in the n-dimensional space Rn... |
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a cuboctahedral prism is a convex uniform
Uniform polychoron
In geometry, a uniform polychoron is a polychoron or 4-polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra....
polychoron
Polychoron
In geometry, a polychoron or 4-polytope is a four-dimensional polytope. It is a connected and closed figure, composed of lower dimensional polytopal elements: vertices, edges, faces , and cells...
(four dimensional polytope). This polychoron has 16 polyhedral
Polyhedron
In elementary geometry a polyhedron is a geometric solid in three dimensions with flat faces and straight edges...
cells: 2 cuboctahedra
Cuboctahedron
In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,...
connected by 8 triangular prism
Triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides....
s, and 6 cube
Cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and...
s.
It is one of 18 uniform polyhedral prisms created by using uniform prism
Prism (geometry)
In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron with an n-sided polygonal base, a translated copy , and n other faces joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All cross-sections parallel to the base faces are the same. Prisms are named for their base, so a prism with a pentagonal base is called a...
s to connect pairs of parallel Platonic solid
Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex polyhedron that is regular, in the sense of a regular polygon. Specifically, the faces of a Platonic solid are congruent regular polygons, with the same number of faces meeting at each vertex; thus, all its edges are congruent, as are its vertices and...
s and Archimedean solid
Archimedean solid
In geometry an Archimedean solid is a highly symmetric, semi-regular convex polyhedron composed of two or more types of regular polygons meeting in identical vertices...
s.
Alternative names:
- Cuboctahedral dyadic prism Norman W. Johnson
- Cope (Jonathan Bowers: for cuboctahedral prism)
- Rhombioctahedral prism
- Rhombioctahedral hyperprism

