Demographics of atheism
Encyclopedia
The demographics of atheism are difficult to quantify. Different people interpret "atheist" and related terms differently, and it can be hard to draw boundaries between atheism, non-religious beliefs, and non-theistic religious and spiritual beliefs. Furthermore, atheists may not report themselves as such, to prevent suffering from social stigma
, discrimination
, and persecution in some countries.
and others have strongly condemned it, atheism may be either over-reported or under-reported for different countries. There is a great deal of room for debate as to the accuracy of any method of estimation, as the opportunity for misreporting (intentionally or not) a category of people without an organizational structure is high. Also, many surveys on religious identification ask people to identify themselves as "agnostics
" or "atheists", which is potentially confusing, since these terms are interpreted differently, with some identifying themselves as being agnostic atheists. Additionally, many of these surveys only gauge the number of irreligious
people, not the number of actual atheists, or group the two together. For example, research indicates that the fastest growing religious status
may be "no religion" in the United States, but this includes all kinds of atheists, agnostics, and theists.
, Buddhist
, Hindu
, Jains
, Taoist
or hold other related philosophical beliefs. Therefore, given limited poll options, some may use other terms to describe their identity. Some politically motivated organizations that report or gather population statistics may, intentionally or unintentionally, misrepresent atheists. Survey designs may bias results due to the nature of elements such as the wording of questions and the available response options. Also, many atheists, particularly former Catholics and former Mormons, are still counted as Christians
in church rosters, although surveys generally ask samples of the population and do not look in church rosters. Other Christians believe that "once a person is[truly] saved, that person is always saved", a doctrine known as eternal security
. Statistics are generally collected on the assumption that religion is a categorical variable. Instruments have been designed to measure attitudes toward religion, including one that was used by L. L. Thurstone. This may be a particularly important consideration among people who have neutral attitudes, as it is more likely prevailing social norms will influence the responses of such people on survey questions which effectively force respondents to categorize themselves either as belonging to a particular religion or belonging to no religion. A negative perception of atheists and pressure from family and peers may also cause some atheists to disassociate themselves from atheism. Misunderstanding of the term may also be a reason some label themselves differently.
involving a poll of 2,000 households in the United States
found atheists to be the most distrusted of minorities, more so than Muslim
s, recent immigrants, gays and lesbians
, and other groups. Many of the respondents associated atheism with immorality, including criminal behaviour, extreme materialism, and elitism. However, the same study also reported that, “The researchers also found acceptance or rejection of atheists is related not only to personal religiosity, but also to one’s exposure to diversity, education and political orientation—with more educated, East and West Coast Americans more accepting of atheists than their Midwestern counterparts.”
, Canada
, Australia
, New Zealand
, in former and present communist states, and to a lesser extent, in the United States
and the Southern Cone
. A 1995 survey attributed to the Encyclopædia Britannica
indicates that the non-religious are about 14.7% of the world's population, and atheists around 3.8%. Another survey attributed to Britannica shows the population of atheists at around 2.4% of the world's population. It is difficult to determine whether atheism is growing or not. What is certain is that in some areas of the world (such as Europe and South America) atheism and secularization
are increasing.
While there are more atheists than ever before, polls show that atheism's percentages seem to be declining. This may be because birth rates in religious societies are much higher. This is similar to a 2002 survey by Adherents.com
, which estimates the proportion of the world's people who are "secular, non-religious, agnostics and atheists" at about 14%. A 2004 survey by the BBC in 10 countries showed the proportion of the population "who don't believe in God" varying between 0% (Nigeria) and 39% (UK), with an average close to 17% in the countries surveyed. About 8% of the respondents stated specifically that they consider themselves to be atheists.
65% of those polled in a 2011 survey by the British Humanist Association answered no to the question "Are you religious?".
A 2004 survey by the CIA in the World Factbook estimates about 12.5% of the world's population are non-religious, and about 2.4% are atheists. A 2004 survey by the Pew Research Center
showed that in the United States, 12% of people under 30 and 6% of people over 30 could be characterized as non-religious. A 2005 poll by AP/Ipsos surveyed ten countries. Of the developed nations, people in the United States
were most sure of the existence of God or a higher power (2% atheist, 4% agnostic), while France
had the most skeptics (19% atheist, 16% agnostic). On the religion question, South Korea
had the greatest percentage without a religion (41%) while Italy
had the smallest (5%).
A study has shown atheism in the West to be particularly prevalent among scientist
s, a tendency already quite marked at the beginning of the 20th century, developing into a dominant one during the course of the century. In 1914, James H. Leuba
found that 58% of 1,000 randomly selected U.S. natural scientists
expressed "disbelief or doubt in the existence of God" (defined as a personal God which interacts directly with human beings). The same study, repeated in 1996, gave a similar percentage of 60.7%. Expressions of positive disbelief rose from 52% to 72%. (See also relationship between religion and science
.)
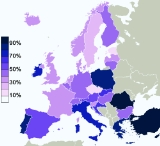
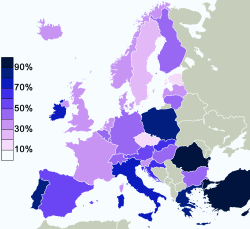
Eurobarometer
poll, 52% of European Union citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", whereas 27% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 18% that "they do not believe there is a spirit, God, nor life force". Results were widely varied between different countries, with 95% of Maltese respondents stating that they believe in God, on the one end, and only 16% of Estonians stating the same on the other.
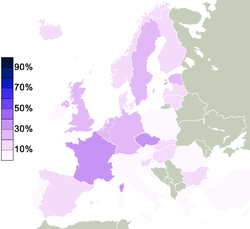
Several studies have found Sweden
to be one of the most atheist countries in the world. 23% of Swedish citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", whereas 53% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 23% that "they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God, or life force". This, according to the survey, would make Swedes the third least religious people in the 27-member European Union
, after Estonia
and the Czech Republic
. In 2001, the Czech Statistical Office provided census information on the ten million people in the Czech Republic
. 59% had no religion, 32.2% were religious, and 8.8% did not answer.
A 2006 survey in the Norwegian newspaper Aftenposten
(on February 17), saw 1,006 inhabitants of Norway
answering the question "What do you believe in?". 29% answered "I believe in a god or deity," 23% answered "I believe in a higher power without being certain of what," 26% answered "I don't believe in God or higher powers." and 22% answered "I am in doubt." Still, some 85% of the population are members of the Norwegian state's official Lutheran Protestant church. This may result from Norwegians being registered into the church at birth, yet having to intentionally unregister after becoming adults.
In France
, about 12% of the population reportedly attends religious services more than once per month. In a 2003 poll 54% of those polled in France identified themselves as "faithful," 33% as atheist, 14% as agnostic, and 26% as "indifferent
." According to a different poll, 32% declared themselves atheists, and an additional 32% declared themselves agnostic.
In Spain
, 75,5% are believers, 14,9% are non-believers and 7,4% are atheists (according to the September 2011 poll of the public Centro de Investigaciones Sociológicas).
There is a complex situation with atheism in Russia
. According to a surveys of Levada Center
, 30% of those surveyed self-described as non-religious, agnostic or atheist. Although there are 66% of Orthodox believers (and 3% Muslims) in Russia, only 42% of people fully trust religious organizations and just 8% regularly (at least once a month) attend the service.
According to a study carried out by doctor in political science Simon Geissbühler, Swiss atheists tend to be more left-leaning
, even accounting for age and income than the average Swiss population.
, a 2007 survey found 15% of the population attends church more than once per month. A poll in 2004 by the BBC
put the number of people who do not believe in a God at 39%, while a YouGov
poll in the same year put the percentage of non-believers at 35% with 21% answering "Don't Know". In the YouGov poll men were less likely to
believe in a god than women, 39% of men as opposed to 49% of women, and younger people were less likely to believe in a god than older people.
In early 2004, it was announced that atheism would be taught during religious education classes in England
. A spokesman for the Qualifications and Curriculum Authority
stated: "There are many children in England who have no religious affiliation and their beliefs and ideas, whatever they are, should be taken very seriously." There is also considerable debate in the UK on the status of faith-based schools, which use religious as well as academic selection criteria. A 2009 study reported that two thirds of teenagers in the UK do not believe in God.
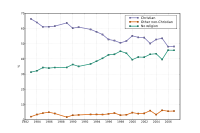
The graph below shows the trends of people who self-classify as Christian, non-Christian religious, and non-believer as measured by the British Social Attitudes Survey
between 1983 and 2007:
 A 2004 BBC
A 2004 BBC
poll showed the number of people in the US who don't believe in a god to be about 9%. A 2008 Gallup poll showed that a smaller 6% of the US population believed that no god or universal spirit exists. The most recent ARIS report, released March 9, 2009, found in 2008, 34.2 million Americans (15.0%) claim no religion, of which 1.6% explicitly describes itself as atheist (0.7%) or agnostic (0.9%), nearly double the previous 2001 ARIS survey figure of 0.9%. The highest occurrence of "nones", according to the 2008 ARIS report, reside in Vermont, with 34% surveyed.
The latest statistics show that a lack of religious identity increased in every US state between 1990 and 2008. However less than 2% of the U.S. population describes itself as atheist.
Atheism is more prevalent in Canada than in the United States, with 19–30% of the population holding an atheistic or agnostic viewpoint. The 2001 Canadian Census states that 16.2% of the population holds no religious affiliation, though exact statistics on atheism are not recorded. In urban centers this figure can be substantially higher; the 2001 census indicated that 42.2% of residents in Vancouver hold "no religious affiliation." A recent survey in 2008 found that 23% of Canadians said they did not believe in a god.
Separation of church and state is guaranteed by Article 130 of the Mexican Constitution, which also designates religious leaders as ineligible for public office, while the majority of the population identifies as Roman Catholic (89%).
Although the demographics of atheism and irreligion in Mexico is hard to measure because many atheists are officially counted as Catholic, almost three million people in the 2000 National Census reported having no religion. Recent surveys have shown that only around 3% of Catholics attend church daily and, according to INEGI, the number of atheists grows annually by 5.2%, while the number of Catholics grows by 1.7%.
In the U.S., 55 percent of atheists are under age 35, while 30 percent are 50 and over (compared to 37 percent of the total population). As a group agnostics are older than atheists, though still younger than the general population. Comparing this 2001 data with the 1990 National Survey of Religious Identification (NSRI) provides evidence of a trend towards secularization among the younger American population.
In the US men are more likely to be atheists than women, and also rate lower on various other measures of religiousity such as frequency of prayer.
In "The New Criminology", Max D. Schlapp and Edward E. Smith say that two generations of statisticians found that the ratio of convicts without religious training is about 1/10 of 1%.
"The analyses of the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (Study 1) and the General Social Surveys (Study 2) show that adolescent and adult intelligence significantly increases adult liberalism, atheism, and men's (but not women's) value on sexual exclusivity."
, Amerindian or Asian
and less likely to be Afro-Brazilian
or Pardo
when compared to the general population.
There is evidence that the atheist minority is more likely to suffer prejudice than other groups: when asked for presidential candidates
, in spite of major forms of racism, historical prejudices and racist-based classism against black people in the country
, 83% of Brazilians would vote in an Afro-Brazilian; even with major forms of sexism
present in Latin American societies (see machismo
) 57% of Brazilians would vote for a woman president (the first one in the country's history is the present Dilma Roussef, elected in late 2010), and the historical homophobia (hate crimes practiced both by homophobic macho vigilantes and far-right skinhead
s as well, the latter widely common in White-majority
Southern Brazil and São Paulo
, for example) and major, widespread forms of heterosexism
due also to the sexist machismo culture, 37% of Brazilians would vote in a gay men. Nevertheless, only 13% of Brazilians would vote in an atheist person to occupy the post of president without judging the candidate because of his religion. 6 in 10 Brazilians would not vote for an atheist president.
As happen with Brazilians of sexual minorities
and/or members of traditional African diasporic religions — Umbanda
, Candomblé
and Quimbanda
, collectively called Macumba
, nowadays a pejorative term — or Spiritism
, affiliation to some of the new rising Protestant churches
in Brazil (mostly Evangelical
or Pentecostal
) can leads to even more negative social perceptions of atheist and irreligious people. Some critics present the widespread vision that Protestants
are more intolerant and socially conservative than the Roman Catholic church
as classist prejudice
, an institution as large in Brazil
as racism and sexism, although still not questioning that Catholic Brazilians are more tolerant and socially liberal.
Atheism, antitheism
and secularization
are associated with Communism
, Anarchism
and Feminism
, pro-choice movement, LGBT rights movements, culture wars and fall of the Western civilization
among certain sectors of the South American societies as class-empowered socially conservative Brazilian Roman Catholics, many times influenced by certain political writers and philosophers as Olavo de Carvalho
(pro-traditional values
, pro-American and anti-Communist
which presently lives in the U.S. state of Virginia
).
, a percentage of Israelis who were born ethnically Jewish
consider themselves "secular" or hilonim
, some of them still keep certain religious traditions for cultural reasons, but most are immersed within the secular Jewish culture
. The number of atheists and agnostics is lower, and it stands at 15% to 37%. The Fridman report for 2007 found that less than 20% define themselves as secular—and only 5% as anti-religious.
East Asian religions define religion differently than in the West, making classification of certain adherents of Buddhism
and Taoism
particularly difficult, as belief in gods is often not required by some of the schools of thought of those religions. Japan can be especially confusing, with most of the population incorporating practices from multiple religions into their lives (see Religion in Japan
). In the People's Republic of China
, 59% of the population claim to be non-religious. However, this percentage may be significantly greater (up to 80%) or smaller (down to 30%) in reality, because some Chinese define religion differently. Some Chinese define religion as practicing customs (which may be done for cultural or traditional reasons), while others define it as actually consciously believing their religion will lead to post-mortem salvation/reincarnation. According to the surveys of Phil Zuckerman on Adherents.com
in 1993, 59% (over 700 million) of the Chinese population was irreligious and 8% – 14% was atheist (from over 100 to 180 million) as of 2005. (see Religion in China
).
to have people describe themselves as non-mainstream religions (e.g. Jedi
).
In 2006, the New Zealand census asked, "What is your religion?" 34.7% of those answering indicated no religion. 12.2% did not respond or objected to answering the question.
, Phil Zuckerman "levels of religiosity and creationism tend to decline as income levels rise ..."
Social stigma
Social stigma is the severe disapproval of or discontent with a person on the grounds of characteristics that distinguish them from other members of a society.Almost all stigma is based on a person differing from social or cultural norms...
, discrimination
Discrimination against atheists
Discrimination against atheists includes the persecution and discrimination faced by atheists and those labeled as atheists in the past and in the current era...
, and persecution in some countries.
Studies and statistics
Because some governments have strongly promoted atheismAtheism
Atheism is, in a broad sense, the rejection of belief in the existence of deities. In a narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there are no deities...
and others have strongly condemned it, atheism may be either over-reported or under-reported for different countries. There is a great deal of room for debate as to the accuracy of any method of estimation, as the opportunity for misreporting (intentionally or not) a category of people without an organizational structure is high. Also, many surveys on religious identification ask people to identify themselves as "agnostics
Agnosticism
Agnosticism is the view that the truth value of certain claims—especially claims about the existence or non-existence of any deity, but also other religious and metaphysical claims—is unknown or unknowable....
" or "atheists", which is potentially confusing, since these terms are interpreted differently, with some identifying themselves as being agnostic atheists. Additionally, many of these surveys only gauge the number of irreligious
Irreligion
Irreligion is defined as an absence of religion or an indifference towards religion. Sometimes it may also be defined more narrowly as hostility towards religion. When characterized as hostility to religion, it includes antitheism, anticlericalism and antireligion. When characterized as...
people, not the number of actual atheists, or group the two together. For example, research indicates that the fastest growing religious status
Claims to be the fastest growing religion
Most increase in the population of any religious denomination is simply due to births. Still, the world's largest religions that are showing increases that outrun birth-rate include Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism....
may be "no religion" in the United States, but this includes all kinds of atheists, agnostics, and theists.
Statistical problems
Statistics on atheism are often difficult to represent accurately for a variety of reasons. Atheism is a position compatible with other forms of identity. Some atheists also consider themselves AgnosticAgnosticism
Agnosticism is the view that the truth value of certain claims—especially claims about the existence or non-existence of any deity, but also other religious and metaphysical claims—is unknown or unknowable....
, Buddhist
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, Hindu
Atheism in Hinduism
Atheism or disbelief in God or gods has been a historically propounded viewpoint in many of the orthodox and heterodox streams of Hindu philosophies...
, Jains
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
, Taoist
Taoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
or hold other related philosophical beliefs. Therefore, given limited poll options, some may use other terms to describe their identity. Some politically motivated organizations that report or gather population statistics may, intentionally or unintentionally, misrepresent atheists. Survey designs may bias results due to the nature of elements such as the wording of questions and the available response options. Also, many atheists, particularly former Catholics and former Mormons, are still counted as Christians
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
in church rosters, although surveys generally ask samples of the population and do not look in church rosters. Other Christians believe that "once a person is
Perseverance of the saints
Perseverance of the saints, as well as the corollary—though distinct—doctrine known as "Once Saved, Always Saved", is a Calvinist teaching that once persons are truly saved they can never lose their salvation....
. Statistics are generally collected on the assumption that religion is a categorical variable. Instruments have been designed to measure attitudes toward religion, including one that was used by L. L. Thurstone. This may be a particularly important consideration among people who have neutral attitudes, as it is more likely prevailing social norms will influence the responses of such people on survey questions which effectively force respondents to categorize themselves either as belonging to a particular religion or belonging to no religion. A negative perception of atheists and pressure from family and peers may also cause some atheists to disassociate themselves from atheism. Misunderstanding of the term may also be a reason some label themselves differently.
Prejudice
Legal and social discrimination against atheists in some places may lead some to deny or conceal their atheism due to fears of persecution. A 2006 study by researchers at the University of MinnesotaUniversity of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota, Twin Cities is a public research university located in Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota, United States. It is the oldest and largest part of the University of Minnesota system and has the fourth-largest main campus student body in the United States, with 52,557...
involving a poll of 2,000 households in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
found atheists to be the most distrusted of minorities, more so than Muslim
Islamophobia
Islamophobia describes prejudice against, hatred or irrational fear of Islam or MuslimsThe term dates back to the late 1980s or early 1990s, but came into common usage after the September 11, 2001 attacks in the United States....
s, recent immigrants, gays and lesbians
Homophobia
Homophobia is a term used to refer to a range of negative attitudes and feelings towards lesbian, gay and in some cases bisexual, transgender people and behavior, although these are usually covered under other terms such as biphobia and transphobia. Definitions refer to irrational fear, with the...
, and other groups. Many of the respondents associated atheism with immorality, including criminal behaviour, extreme materialism, and elitism. However, the same study also reported that, “The researchers also found acceptance or rejection of atheists is related not only to personal religiosity, but also to one’s exposure to diversity, education and political orientation—with more educated, East and West Coast Americans more accepting of atheists than their Midwestern counterparts.”
Geographic distribution
Though atheists are in the minority in most countries, they are relatively common in EuropeEurope
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, in former and present communist states, and to a lesser extent, in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and the Southern Cone
Southern Cone
Southern Cone is a geographic region composed of the southernmost areas of South America, south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Although geographically this includes part of Southern and Southeast of Brazil, in terms of political geography the Southern cone has traditionally comprised Argentina,...
. A 1995 survey attributed to the Encyclopædia Britannica
Encyclopædia Britannica
The Encyclopædia Britannica , published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia that is available in print, as a DVD, and on the Internet. It is written and continuously updated by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 expert...
indicates that the non-religious are about 14.7% of the world's population, and atheists around 3.8%. Another survey attributed to Britannica shows the population of atheists at around 2.4% of the world's population. It is difficult to determine whether atheism is growing or not. What is certain is that in some areas of the world (such as Europe and South America) atheism and secularization
Secularization
Secularization is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions...
are increasing.
While there are more atheists than ever before, polls show that atheism's percentages seem to be declining. This may be because birth rates in religious societies are much higher. This is similar to a 2002 survey by Adherents.com
Adherents.com
Adherents.com is a website that aims to collect and present information about religious demographics, established in 1998. It is the largest pool of such data freely available on the internet. As of January 2010, the site contains approximately 44,000 references on over 4,300 faith groups...
, which estimates the proportion of the world's people who are "secular, non-religious, agnostics and atheists" at about 14%. A 2004 survey by the BBC in 10 countries showed the proportion of the population "who don't believe in God" varying between 0% (Nigeria) and 39% (UK), with an average close to 17% in the countries surveyed. About 8% of the respondents stated specifically that they consider themselves to be atheists.
65% of those polled in a 2011 survey by the British Humanist Association answered no to the question "Are you religious?".
A 2004 survey by the CIA in the World Factbook estimates about 12.5% of the world's population are non-religious, and about 2.4% are atheists. A 2004 survey by the Pew Research Center
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is an American think tank organization based in Washington, D.C. that provides information on issues, attitudes and trends shaping the United States and the world. The Center and its projects receive funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts. In 1990, Donald S...
showed that in the United States, 12% of people under 30 and 6% of people over 30 could be characterized as non-religious. A 2005 poll by AP/Ipsos surveyed ten countries. Of the developed nations, people in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
were most sure of the existence of God or a higher power (2% atheist, 4% agnostic), while France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
had the most skeptics (19% atheist, 16% agnostic). On the religion question, South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
had the greatest percentage without a religion (41%) while Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
had the smallest (5%).
A study has shown atheism in the West to be particularly prevalent among scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
s, a tendency already quite marked at the beginning of the 20th century, developing into a dominant one during the course of the century. In 1914, James H. Leuba
James H. Leuba
James Henry Leuba was an American psychologist, best known for his contributions to the psychology of religion. His work in this area is marked by a reductionistic tendency to explain mysticism and other religious experiences in physiological terms. Philosophically, his position may be described...
found that 58% of 1,000 randomly selected U.S. natural scientists
Natural science
The natural sciences are branches of science that seek to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world by using empirical and scientific methods...
expressed "disbelief or doubt in the existence of God" (defined as a personal God which interacts directly with human beings). The same study, repeated in 1996, gave a similar percentage of 60.7%. Expressions of positive disbelief rose from 52% to 72%. (See also relationship between religion and science
Relationship between religion and science
The relationship between religion and science has been a focus of the demarcation problem. Somewhat related is the claim that science and religion may pursue knowledge using different methodologies. Whereas the scientific method basically relies on reason and empiricism, religion also seeks to...
.)
Europe
According to a 2005 EurostatEurostat
Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in Luxembourg. Its main responsibilities are to provide the European Union with statistical information at European level and to promote the integration of statistical methods across the Member States of the European Union,...
Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of surveys regularly performed on behalf of the European Commission since 1973. It produces reports of public opinion of certain issues relating to the European Union across the member states...
poll, 52% of European Union citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", whereas 27% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 18% that "they do not believe there is a spirit, God, nor life force". Results were widely varied between different countries, with 95% of Maltese respondents stating that they believe in God, on the one end, and only 16% of Estonians stating the same on the other.


| Country | Belief in a God | Belief in a spirit or life force | Belief in neither a spirit, God, nor life force |
|---|---|---|---|
 Turkey TurkeyReligion in Turkey Islam is the largest religion of Turkey. Around 96% percent of the population is registered as Muslim, mostly Sunni; however, a 2007 survey found that about 3% of adults define their relation with religion as "having no religious conviction" or "not believing in religious obligations". The Shia... | 95% | 2% | 1% |
 Malta MaltaReligion in Malta The predominant religion in Malta is Christianity, with Roman Catholicism being the predominant denomination. Most Maltese claim to be Catholic and participate in Catholic religious services and the Constitution of Malta establishes Catholicism as the state religion... | 95% | 3% | 1% |
 Cyprus CyprusReligion in Cyprus Christians make up 78% of the Cypriot population.Most Greek Cypriots, and thus the majority of the population of Cyprus, are members of the Autocephalous Greek Orthodox Church of Cyprus , whereas most Turkish Cypriots are Muslim. According to Eurobarometer 2005 , Cyprus is one of the most religious... | 90% | 7% | 2% |
 Romania RomaniaReligion in Romania Romania is a secular state, and it has no state religion. However, an overwhelming majority of the country's citizens are Christian. 86.7% of the country's population identified as Eastern Orthodox in the 2002 census... | 90% | 8% | 1% |
 Greece GreeceReligion in Greece Among religions in Greece, the largest denomination is the Greek Orthodox Church, which represents the majority of the population and which is constitutionally recognised as the "prevailing religion" of Greece... | 81% | 16% | 3% |
 Portugal PortugalReligion in Portugal Portugal has no official religion. The most predominant religion in Portugal is Roman Catholicism. Approximately 84% of the population of Portugal is nominally Catholic, though only about 19% attend mass and take the sacraments regularly, while a larger number wish to be baptized, married in a... | 81% | 12% | 6% |
 Poland PolandReligion in Poland Most residents of Poland adhere to the Christian faith, with 89.8% belonging to the Roman Catholic Church. Catholicism plays an important role in the lives of many Poles and the Roman Catholic Church in Poland enjoys social prestige and political influence. The Church is widely respected by its... | 80% | 15% | 1% |
 Italy ItalyReligion in Italy Catholicism is by far the largest religious group in Italy. However, there are also some important religious minorities.... | 74% | 16% | 6% |
 Ireland IrelandReligion in the Republic of Ireland The predominant religion in Ireland is Christianity, with the largest church being the Roman Catholic Church. Ireland's constitution states that the state may not endorse any particular religion and guarantees freedom of religion. In 2006, 86.8% of the population identified themselves as Roman... | 73% | 22% | 4% |
 Croatia CroatiaReligion in Croatia Freedom of religion is a right defined by the Constitution of Croatia, which also defines all religious communities as equal in front of the law and separate from the state. A large majority of the Croatian population declares themselves as religious believers.... | 67% | 25% | 7% |
 Slovakia SlovakiaReligion in Slovakia Christianity is the main religion in Slovakia.The majority of Slovaks belong to the Roman Catholic Church. According to the Slovak government website, another 15.9% are what the website refers to as non-believers , 13.7% are atheist, 6.9% are Evangelical, 4.1% are what the website refers to as... | 61% | 26% | 11% |
 Spain SpainReligion in Spain Roman Catholicism is the largest denomination of Christianity present in Spain by far. According to a October 2010 study by the Spanish Center of Sociological Research about 73% of Spaniards self-identify as Catholics, 2.2% other faith, and about 22% identify with no religion. Most Spaniards do not... | 59% | 21% | 18% |
 Austria AustriaReligion in Austria Among religions in Austria, Roman Catholic Christianity is predominant. According to the 2001 census, 73.6% of the country's population adhered to this denomination. , the most recent year for which figures are available, the number of Catholics is about 66 % of the population. There is a much... | 54% | 34% | 8% |
 Lithuania LithuaniaReligion in Lithuania The Religion in Lithuania is predominantly Catholic, reflecting Lithuania's history, with a strong presence from other minorities.According to the most recent Eurobarometer Poll 2005,... | 49% | 36% | 12% |
 Switzerland SwitzerlandReligion in Switzerland Switzerland has no country-wide state religion, though most of the cantons recognize official churches , in all cases including the Catholic Church and the Swiss Reformed Church... | 48% | 39% | 9% |
 Germany GermanyReligion in Germany Christianity is the largest religion in Germany with 54,765,265 adherents as of the end of 2006, down to 51.5 million adherents as of 2008. The second largest religion is Islam with 3.3 million adherents followed by Buddhism and Judaism... | 47% | 25% | 25% |
 Luxembourg LuxembourgReligion in Luxembourg There are many active religions in Luxembourg. The most important, in terms of size of congregation and historical importance, is Roman Catholicism, but the state does not support, or discriminate against, any one single religion.-Demographics:... | 44% | 28% | 22% |
 Hungary Hungary | 44% | 31% | 19% |
 Belgium BelgiumReligion in Belgium A 2006 inquiry in Flanders showed 55% of its inhabitants calling themselves religious, while 36% claimed to believe that God created the world.- Status of recognized denominations :... | 43% | 29% | 27% |
 Finland FinlandReligion in Finland Most people in Finland are at least nominally members of a Christian church, but since the 1980s, there has been a rapid increase in the number of people without religious affiliation. Prior to Christianisation, Finnish paganism was the primary religion.... | 41% | 41% | 16% |
 Bulgaria BulgariaReligion in Bulgaria Bulgaria has been traditionally a Christian state since the adoption of Constantinople Christianity in 865, and therefore the dominant confession is Eastern Orthodoxy of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church... | 40% | 40% | 13% |
 Iceland IcelandReligion in Iceland Religion in Iceland was initially the Norse paganism that was a common belief among mediaeval Scandinavians until Christian conversion. Later, the nation became half-Christian and then more fully Christian. This increasing Christianization culminated in the Pietism period when non-Christian... | 38% | 48% | 11% |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | 38% | 40% | 20% |
 Latvia LatviaReligion in Latvia The main religion traditionally practised in Latvia is Christianity, with no single church predominating: most Latvian Christians follow Latvian Orthodoxy, Lutheranism or Roman Catholicism. In addition, a large proportion of the country claim to practise no religion.Latvia was one of the last... | 37% | 49% | 10% |
 Slovenia Slovenia | 37% | 46% | 16% |
 France FranceReligion in France France is a country where freedom of religion and freedom of thought are guaranteed by virtue of the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. The Republic is based on the principle of laïcité enforced by the 1880s Jules Ferry laws and the 1905 French law on the Separation of the... | 34% | 27% | 33% |
 Netherlands Netherlands | 34% | 37% | 27% |
 Norway NorwayReligion in Norway Nominal religion in Norway is mostly Protestant with 78.9% belonging to the state Evangelical Lutheran Church of Norway. Early Norwegians, like all of the people of Scandinavia, believed in Norse paganism; the Sámi having a shamanistic religion... | 32% | 47% | 17% |
 Denmark DenmarkReligion in Denmark Of all the religions in Denmark, the most prominent is Christianity in the form of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Denmark, the official state church. However, pockets of virtually all faiths can be found among the population. The second largest faith is Islam, due to mass immigration in the... | 31% | 49% | 19% |
 Sweden SwedenReligion in Sweden Sweden was Christianized from Norse paganism in the 11th century. Since the 16th century Sweden has been predominantly Lutheran. From the Protestant Reformation in the 1530s until 2000, the Lutheran Church of Sweden was the state church... | 23% | 53% | 23% |
 Czech Republic Czech Republic | 19% | 50% | 30% |
 Estonia Estonia | 16% | 54% | 26% |
Several studies have found Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
to be one of the most atheist countries in the world. 23% of Swedish citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", whereas 53% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 23% that "they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God, or life force". This, according to the survey, would make Swedes the third least religious people in the 27-member European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, after Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
and the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
. In 2001, the Czech Statistical Office provided census information on the ten million people in the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
. 59% had no religion, 32.2% were religious, and 8.8% did not answer.
A 2006 survey in the Norwegian newspaper Aftenposten
Aftenposten
Aftenposten is Norway's largest newspaper. It retook this position in 2010, taking it from the tabloid Verdens Gang which had been the largest newspaper for several decades. It is based in Oslo. The morning edition, which is distributed across all of Norway, had a circulation of 250,179 in 2007...
(on February 17), saw 1,006 inhabitants of Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
answering the question "What do you believe in?". 29% answered "I believe in a god or deity," 23% answered "I believe in a higher power without being certain of what," 26% answered "I don't believe in God or higher powers." and 22% answered "I am in doubt." Still, some 85% of the population are members of the Norwegian state's official Lutheran Protestant church. This may result from Norwegians being registered into the church at birth, yet having to intentionally unregister after becoming adults.
In France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, about 12% of the population reportedly attends religious services more than once per month. In a 2003 poll 54% of those polled in France identified themselves as "faithful," 33% as atheist, 14% as agnostic, and 26% as "indifferent
Apatheism
Apatheism , also known as pragmatic atheism or as practical atheism, is acting with apathy, disregard, or lack of interest towards belief or lack of belief in a deity. Apatheism describes the manner of acting towards a belief or lack of a belief in a deity; so applies to both theism and atheism...
." According to a different poll, 32% declared themselves atheists, and an additional 32% declared themselves agnostic.
In Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, 75,5% are believers, 14,9% are non-believers and 7,4% are atheists (according to the September 2011 poll of the public Centro de Investigaciones Sociológicas).
There is a complex situation with atheism in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
. According to a surveys of Levada Center
Levada Center
Levada Center is a Russian independent, non-governmental polling and sociological research organisation. It is named after its founder, the first Russian professor of sociology Yuri Levada . Levada Center traces back its history to 1987 when VCIOM was founded, originally headed by Academician...
, 30% of those surveyed self-described as non-religious, agnostic or atheist. Although there are 66% of Orthodox believers (and 3% Muslims) in Russia, only 42% of people fully trust religious organizations and just 8% regularly (at least once a month) attend the service.
According to a study carried out by doctor in political science Simon Geissbühler, Swiss atheists tend to be more left-leaning
Left-wing politics
In politics, Left, left-wing and leftist generally refer to support for social change to create a more egalitarian society...
, even accounting for age and income than the average Swiss population.
United Kingdom
In the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, a 2007 survey found 15% of the population attends church more than once per month. A poll in 2004 by the BBC
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
put the number of people who do not believe in a God at 39%, while a YouGov
YouGov
YouGov, formerly known as PollingPoint in the United States, is an international internet-based market research firm launched in the UK in May 2000 by Stephan Shakespeare, now Chief Executive Officer, and Nadhim Zahawi...
poll in the same year put the percentage of non-believers at 35% with 21% answering "Don't Know". In the YouGov poll men were less likely to
believe in a god than women, 39% of men as opposed to 49% of women, and younger people were less likely to believe in a god than older people.
In early 2004, it was announced that atheism would be taught during religious education classes in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
. A spokesman for the Qualifications and Curriculum Authority
Qualifications and Curriculum Authority
The Qualifications and Curriculum Development Agency is an exempt charity, and an executive non-departmental public body of the Department for Children, Schools and Families...
stated: "There are many children in England who have no religious affiliation and their beliefs and ideas, whatever they are, should be taken very seriously." There is also considerable debate in the UK on the status of faith-based schools, which use religious as well as academic selection criteria. A 2009 study reported that two thirds of teenagers in the UK do not believe in God.
The graph below shows the trends of people who self-classify as Christian, non-Christian religious, and non-believer as measured by the British Social Attitudes Survey
British Social Attitudes Survey
The British Social Attitudes Survey is an annual statistical survey conducted in Great Britain by the since 1983. The BSA involves in-depth interviews with over 3,000 respondents, selected using random probability sampling, focused on topics including newspaper readership, political parties and...
between 1983 and 2007:

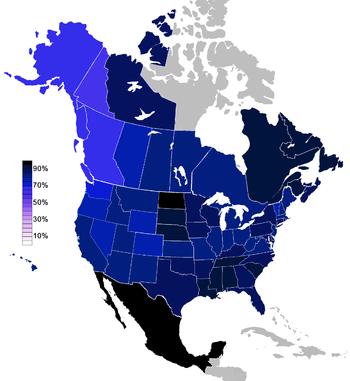
North America

BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
poll showed the number of people in the US who don't believe in a god to be about 9%. A 2008 Gallup poll showed that a smaller 6% of the US population believed that no god or universal spirit exists. The most recent ARIS report, released March 9, 2009, found in 2008, 34.2 million Americans (15.0%) claim no religion, of which 1.6% explicitly describes itself as atheist (0.7%) or agnostic (0.9%), nearly double the previous 2001 ARIS survey figure of 0.9%. The highest occurrence of "nones", according to the 2008 ARIS report, reside in Vermont, with 34% surveyed.
The latest statistics show that a lack of religious identity increased in every US state between 1990 and 2008. However less than 2% of the U.S. population describes itself as atheist.
Atheism is more prevalent in Canada than in the United States, with 19–30% of the population holding an atheistic or agnostic viewpoint. The 2001 Canadian Census states that 16.2% of the population holds no religious affiliation, though exact statistics on atheism are not recorded. In urban centers this figure can be substantially higher; the 2001 census indicated that 42.2% of residents in Vancouver hold "no religious affiliation." A recent survey in 2008 found that 23% of Canadians said they did not believe in a god.
Separation of church and state is guaranteed by Article 130 of the Mexican Constitution, which also designates religious leaders as ineligible for public office, while the majority of the population identifies as Roman Catholic (89%).
Although the demographics of atheism and irreligion in Mexico is hard to measure because many atheists are officially counted as Catholic, almost three million people in the 2000 National Census reported having no religion. Recent surveys have shown that only around 3% of Catholics attend church daily and, according to INEGI, the number of atheists grows annually by 5.2%, while the number of Catholics grows by 1.7%.
Population attributes of atheists in the US
Overall, U.S. Americans who profess no religion or self-identify as atheist or agnostic are more likely to be white, non-Hispanic, or Asian and less likely to be African American or Hispanic, as compared to the general adult population in U.S.In the U.S., 55 percent of atheists are under age 35, while 30 percent are 50 and over (compared to 37 percent of the total population). As a group agnostics are older than atheists, though still younger than the general population. Comparing this 2001 data with the 1990 National Survey of Religious Identification (NSRI) provides evidence of a trend towards secularization among the younger American population.
In the US men are more likely to be atheists than women, and also rate lower on various other measures of religiousity such as frequency of prayer.
In "The New Criminology", Max D. Schlapp and Edward E. Smith say that two generations of statisticians found that the ratio of convicts without religious training is about 1/10 of 1%.
"The analyses of the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (Study 1) and the General Social Surveys (Study 2) show that adolescent and adult intelligence significantly increases adult liberalism, atheism, and men's (but not women's) value on sexual exclusivity."
South America
Irreligion in South America is not decreasing over 30 years straight, and it had a growing status in all countries in the first decade of the 21st century. In Brazil, it rose from about 4% in the end of 20th century to circa 8% in the most recent reliable census and recent estimates put it in 10–14% of the population, being the 2nd largest religious group after Christianity. According to recent researches, Brazilians who profess no religion or self-identify as atheist or agnostic are more likely to be white BrazilianWhite Brazilian
White Brazilians make up 48.4% of Brazil's population, or around 92 million people, according to the IBGE's 2008 PNAD . Whites are present in the entire territory of Brazil, although the main concentrations are found in the South and Southeastern parts of the country...
, Amerindian or Asian
Asian Brazilian
An Asian Brazilian is is a Brazilian citizen of full or partial Asian ancestry, who remains culturally connected to Asia, or an Asian-born person permanently residing in Brazil. Brazil received many immigrants from Asia, both from Middle East and East Asia...
and less likely to be Afro-Brazilian
Afro-Brazilian
In Brazil, the term "preto" is one of the five categories used by the Brazilian Census, along with "branco" , "pardo" , "amarelo" and "indígena"...
or Pardo
Pardo
In Brazil, Pardo is a race/colour category used by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics in Brazilian censuses. It is a Portuguese word that encompasses various shades of brown, but is usually translated as "grayish-brown"...
when compared to the general population.
There is evidence that the atheist minority is more likely to suffer prejudice than other groups: when asked for presidential candidates
President of Brazil
The president of Brazil is both the head of state and head of government of the Federative Republic of Brazil. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Brazilian Armed Forces...
, in spite of major forms of racism, historical prejudices and racist-based classism against black people in the country
Social apartheid in Brazil
The term social apartheid has been used to describe various aspects of economic inequality in Brazil, drawing a parallel with the separation of whites and blacks in South African society under the apartheid regime.-Origins:...
, 83% of Brazilians would vote in an Afro-Brazilian; even with major forms of sexism
Women in Brazil
This article considers the roles and rights of women in Brazil.-Politics and Law:Women in Brazil enjoy the same legal rights and duties as men, what is clearly expressed in the 5th article of Brazil's 1988 Constitution. A cabinet-level office, the Secretariat for Women's Affairs, oversees a special...
present in Latin American societies (see machismo
Machismo
Machismo, or machoism, is a word of Spanish and Portuguese origin that describes prominently exhibited or excessive masculinity. As an attitude, machismo ranges from a personal sense of virility to a more extreme male chauvinism...
) 57% of Brazilians would vote for a woman president (the first one in the country's history is the present Dilma Roussef, elected in late 2010), and the historical homophobia (hate crimes practiced both by homophobic macho vigilantes and far-right skinhead
Skinhead
A skinhead is a member of a subculture that originated among working class youths in the United Kingdom in the 1960s, and then spread to other parts of the world. Named for their close-cropped or shaven heads, the first skinheads were greatly influenced by West Indian rude boys and British mods,...
s as well, the latter widely common in White-majority
White Brazilian
White Brazilians make up 48.4% of Brazil's population, or around 92 million people, according to the IBGE's 2008 PNAD . Whites are present in the entire territory of Brazil, although the main concentrations are found in the South and Southeastern parts of the country...
Southern Brazil and São Paulo
São Paulo (state)
São Paulo is a state in Brazil. It is the major industrial and economic powerhouse of the Brazilian economy. Named after Saint Paul, São Paulo has the largest population, industrial complex, and economic production in the country. It is the richest state in Brazil...
, for example) and major, widespread forms of heterosexism
Heterosexism
Heterosexism is a system of attitudes, bias, and discrimination in favor of opposite-sex sexuality and relationships. It can include the presumption that everyone is heterosexual or that opposite-sex attractions and relationships are the only norm and therefore superior...
due also to the sexist machismo culture, 37% of Brazilians would vote in a gay men. Nevertheless, only 13% of Brazilians would vote in an atheist person to occupy the post of president without judging the candidate because of his religion. 6 in 10 Brazilians would not vote for an atheist president.
As happen with Brazilians of sexual minorities
LGBT topics and Afro-Americans in the Americas
Similar to the experience of non-heterosexual people in Africa during the arrivals and expansions of Abrahamic religions through various imperialistic and colonial attritions into the continent, the lives of homosexual, bisexual and transgendered Afro-Americans - both those who were imported from...
and/or members of traditional African diasporic religions — Umbanda
Umbanda
Umbanda is an Afro-Brazilian religion that blends African religions with Catholicism, Spiritism and Kardecism, and considerable indigenous lore....
, Candomblé
Candomblé
Candomblé is an African-originated or Afro-Brazilian religion, practised chiefly in Brazil by the "povo de santo" . It originated in the cities of Salvador, the capital of Bahia and Cachoeira, at the time one of the main commercial crossroads for the distribution of products and slave trade to...
and Quimbanda
Quimbanda
Quimbanda is an Afro-Brazilian religion practiced primarily in the urban city centers of Brazil. Quimbanda practices are typically associated with magic, rituals involving animal sacrifice and marginal locations, orishas, exus, and pomba gira spirits. Quimbanda was originally contained under the...
, collectively called Macumba
Macumba
Macumba is a word of African origins. Various explanations of its meaning include "a musical instrument", the name of a Central African deity, and simply "magic". It was the name used for all Bantu religious practices mainly in Bahia Afro-Brazilian in the 19th Century...
, nowadays a pejorative term — or Spiritism
Spiritism
Spiritism is a loose corpus of religious faiths having in common the general belief in the survival of a spirit after death. In a stricter sense, it is the religion, beliefs and practices of the people affiliated to the International Spiritist Union, based on the works of Allan Kardec and others...
, affiliation to some of the new rising Protestant churches
Charismatic movement
The term charismatic movement is used in varying senses to describe 20th century developments in various Christian denominations. It describes an ongoing international, cross-denominational/non-denominational Christian movement in which individual, historically mainstream congregations adopt...
in Brazil (mostly Evangelical
Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism is a Protestant Christian movement which began in Great Britain in the 1730s and gained popularity in the United States during the series of Great Awakenings of the 18th and 19th century.Its key commitments are:...
or Pentecostal
Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism is a diverse and complex movement within Christianity that places special emphasis on a direct personal experience of God through the baptism in the Holy Spirit, has an eschatological focus, and is an experiential religion. The term Pentecostal is derived from Pentecost, the Greek...
) can leads to even more negative social perceptions of atheist and irreligious people. Some critics present the widespread vision that Protestants
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
are more intolerant and socially conservative than the Roman Catholic church
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
as classist prejudice
Classism
Classism is prejudice or discrimination on the basis of social class. It includes individual attitudes and behaviors, systems of policies and practices that are set up to benefit the upper classes at the expense of the lower classes...
, an institution as large in Brazil
Income inequality in Brazil
Brazil has been tackling problems of income inequality despite high rates of growth. Its GDP growth in 2010 was 7.5% yet its GINI coefficient, a measure of its inequality was reported at 0.543 in 2009. In the recent decades, there has been a decline in inequality for the country as a whole...
as racism and sexism, although still not questioning that Catholic Brazilians are more tolerant and socially liberal.
Atheism, antitheism
Antitheism
Antitheism is active opposition to theism. The etymological roots of the word are the Greek 'anti-' and 'theismos'...
and secularization
Secularization
Secularization is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions...
are associated with Communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
, Anarchism
Anarchism
Anarchism is generally defined as the political philosophy which holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary, and harmful, or alternatively as opposing authority in the conduct of human relations...
and Feminism
Feminism
Feminism is a collection of movements aimed at defining, establishing, and defending equal political, economic, and social rights and equal opportunities for women. Its concepts overlap with those of women's rights...
, pro-choice movement, LGBT rights movements, culture wars and fall of the Western civilization
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
among certain sectors of the South American societies as class-empowered socially conservative Brazilian Roman Catholics, many times influenced by certain political writers and philosophers as Olavo de Carvalho
Olavo de Carvalho
Olavo Luiz Pimentel de Carvalho is a Brazilian journalist, and essayist on several issues like the history of astrology and mysticism; the history of revolutionary mentality; and Philosophical Anthropology...
(pro-traditional values
Traditional values
Traditional values refer to those beliefs, moral codes, and mores that are passed down from generation to generation within a culture, subculture or community.-Summary:Since the late 1970s in the U.S., the term "traditional values" has become synonymous...
, pro-American and anti-Communist
Anti-communism
Anti-communism is opposition to communism. Organized anti-communism developed in reaction to the rise of communism, especially after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia and the beginning of the Cold War in 1947.-Objections to communist theory:...
which presently lives in the U.S. state of Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
).
- UruguayReligion in UruguayChurch and state are officially separated since 1916 in Uruguay. According to the most recent official survey approximately 58.1% of Uruguayans define themselves as Christian , and approximately 40.89% of the population professes no religion , 0.6% as followers of Umbanda...
– 12% atheist; 30.2% non-sectatian believers - ArgentinaReligion in ArgentinaA majority of the population of Argentina is nominally Roman Catholic, however, a very significant fact is that 61.1% of Argentines said to be related to God "on their own way", 72.9% said to "never" or "rarely" attend ceremonies of worship....
– 11.3% "indifferent towards religion" (including agnostic and atheists) - ChileReligion in ChileCitizens of Chile most commonly identify themselves as Christian . According to census data other declared denominations or groupings include: Protestant or Evangelical , The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints , Jehovah's Witnesses , Jewish , Atheist or Agnostic , and other...
– 8.3% atheist or agnostic - BrazilReligion in BrazilReligion in Brazil has a higher adherence level compared to other Latin American countries, and is more diverse.In 1891, when the first Brazilian Republican Constitution was set forth, Brazil ceased to have an official religion. The present Constitution guarantees absolute freedom of religion...
– 7.4% non-religious - ColombiaReligion in ColombiaReligion in Colombia is an expression of the different cultural heritages in the Colombian culture including the Spanish colonisation, the Native Amerindian and the Afro-Colombian.-Religious freedom:...
– 1.9% non-religious - PeruReligion in PeruThe Peruvian government is closely allied with the Catholic Church. Article 50 of the Constitution recognizes the Catholic Church's role as "an important element in the historical, cultural, and moral development of the nation." Catholic clergy and laypersons receive state remuneration in...
– 1.4% non-religious as of 1993 - ParaguayReligion in ParaguayThe religious identities of the people of Paraguay, or Religion in Paraguay for short, have since national independence been oriented towards the Christian faith, and specifically the Roman Catholic Church...
– 1.1% non-religious
Asia
In IsraelIsrael
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
, a percentage of Israelis who were born ethnically Jewish
Who is a Jew?
"Who is a Jew?" is a basic question about Jewish identity and considerations of Jewish self-identification. The question is based in ideas about Jewish personhood which themselves have cultural, religious, genealogical, and personal dimensions...
consider themselves "secular" or hilonim
Hiloni
Hiloni , plural hilonim derived from the Hebrew word hulin, meaning secular or mundane, is the term used in Israel for non-religious Jews.As natives of Israel, hilonim speak Hebrew...
, some of them still keep certain religious traditions for cultural reasons, but most are immersed within the secular Jewish culture
Secular Jewish culture
Secular Jewish culture embraces several related phenomena; above all, it is the international culture of secular communities of Jewish people, but it can also include the cultural contributions of individuals who identify as secular Jews...
. The number of atheists and agnostics is lower, and it stands at 15% to 37%. The Fridman report for 2007 found that less than 20% define themselves as secular—and only 5% as anti-religious.
East Asian religions define religion differently than in the West, making classification of certain adherents of Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
and Taoism
Taoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
particularly difficult, as belief in gods is often not required by some of the schools of thought of those religions. Japan can be especially confusing, with most of the population incorporating practices from multiple religions into their lives (see Religion in Japan
Religion in Japan
Most Japanese people do not exclusively identify themselves as adherents of a single religion; rather, they incorporate elements of various religions in a syncretic fashion known as . Shinbutsu Shūgō officially ended with the Shinto and Buddhism Separation Order of 1886, but continues in practice...
). In the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, 59% of the population claim to be non-religious. However, this percentage may be significantly greater (up to 80%) or smaller (down to 30%) in reality, because some Chinese define religion differently. Some Chinese define religion as practicing customs (which may be done for cultural or traditional reasons), while others define it as actually consciously believing their religion will lead to post-mortem salvation/reincarnation. According to the surveys of Phil Zuckerman on Adherents.com
Adherents.com
Adherents.com is a website that aims to collect and present information about religious demographics, established in 1998. It is the largest pool of such data freely available on the internet. As of January 2010, the site contains approximately 44,000 references on over 4,300 faith groups...
in 1993, 59% (over 700 million) of the Chinese population was irreligious and 8% – 14% was atheist (from over 100 to 180 million) as of 2005. (see Religion in China
Religion in China
Religion in China has been characterized by pluralism since the beginning of Chinese history. The Chinese religions are family-oriented and do not demand the exclusive adherence of members. Some scholars doubt the use of the term "religion" in reference to Buddhism and Taoism, and suggest "cultural...
).
Oceania
In the Australian 2006 Census of Population and Housing, in the question which asked. "What is the person's religion?" 18.7% ticked the box marked "no religion" or wrote in a response that was classified as non-religious (e.g. humanism, atheist), which is a growth of 3.2% since the 2001 Census. This question was optional and 11.2% did not answer the question. There are often popular and successful campaignsJedi census phenomenon
The Jedi census phenomenon is a grassroots movement that was initiated in 2001 for residents of a number of English-speaking countries, urging them to record their religion as "Jedi" or "Jedi Knight" on the national census.It is believed the majority of self-reported Jedi claimed the religion for...
to have people describe themselves as non-mainstream religions (e.g. Jedi
Jediism
Jediism is a religious movement based on the philosophical and spiritual ideas of the Jedi as depicted in Star Wars media.-Belief:Practitioners identify themselves with the Jedi Knights in Star Wars, believe in the existence of the Force and that interaction with the Force is possible. Believers...
).
In 2006, the New Zealand census asked, "What is your religion?" 34.7% of those answering indicated no religion. 12.2% did not respond or objected to answering the question.
Income distribution
According to a study carried out by professor of sociology at Pitzer CollegePitzer College
Pitzer College is a private residential liberal arts college located in Claremont, California, a college town approximately east of downtown Los Angeles. Pitzer College is one of the Claremont Colleges....
, Phil Zuckerman "levels of religiosity and creationism tend to decline as income levels rise ..."

