
Density of air
Encyclopedia
The density of air, ρ (air density), is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere
, and is a useful value in aeronautics
and other sciences. Air density decreases with increasing altitude, as does air pressure. It also changes with variances in temperature or humidity
. At sea level
and at 15°C according to ISA (International Standard Atmosphere), air has a density of approximately 1.275 kg/m3.
, expressed as a function of temperature
and pressure: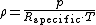
where ρ is the air density, p is absolute pressure
, Rspecific is the specific gas constant for dry air, and T is absolute temperature.
The specific gas constant for dry air is 287.058 J/(kg·K) in SI
units, and 53.35 (ft·lbf
)/(lbm
·R) in United States customary
and Imperial units.
Therefore:
The following table illustrates the air density - temperature relationship at 1 atm or 101.325 kPa:
to air (making the air humid) reduces the density of the air, which may at first appear contrary to logic.
This occurs because the molecular mass of water (18 g/mol) is less than the molecular mass of dry air (around 29 g/mol). For any gas, at a given temperature and pressure, the number of molecules present is constant for a particular volume (see Avogadro's Law
). So when water molecules (vapor) are added to a given volume of air, the dry air molecules must decrease by the same number, to keep the pressure or temperature from increasing. Hence the mass per unit volume of the gas (its density) decreases.
The density of humid air may be calculated as a mixture of ideal gas
es. In this case, the partial pressure
of water vapor
is known as the vapor pressure
. Using this method, error in the density calculation is less than 0.2% in the range of −10 °C to 50 °C.
The density of humid air is found by:
where: Density of the humid air (kg/m³)
Density of the humid air (kg/m³)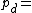 Partial pressure of dry air (Pa)
Partial pressure of dry air (Pa) Specific gas constant for dry air, 287.058 J/(kg·K)
Specific gas constant for dry air, 287.058 J/(kg·K)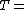 Temperature (K)
Temperature (K)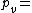 Pressure of water vapor (Pa)
Pressure of water vapor (Pa)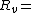 Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.495 J/(kg·K)
Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.495 J/(kg·K)
The vapor pressure of water may be calculated from the saturation vapor pressure and relative humidity
. It is found by:
Where: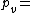 Vapor pressure of water
Vapor pressure of water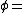 Relative humidity
Relative humidity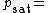 Saturation vapor pressure
Saturation vapor pressure
The saturation vapor pressure of water at any given temperature is the vapor pressure when relative humidity is 100%. A simplification of the regression used to find this, can be formulated as:
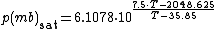
Note:
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
, and is a useful value in aeronautics
Aeronautics
Aeronautics is the science involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of airflight-capable machines, or the techniques of operating aircraft and rocketry within the atmosphere...
and other sciences. Air density decreases with increasing altitude, as does air pressure. It also changes with variances in temperature or humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
. At sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
and at 15°C according to ISA (International Standard Atmosphere), air has a density of approximately 1.275 kg/m3.
Temperature and pressure
The density of dry air can be calculated using the ideal gas lawIdeal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
, expressed as a function of temperature
Thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is the absolute measure of temperature and is one of the principal parameters of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic temperature is an "absolute" scale because it is the measure of the fundamental property underlying temperature: its null or zero point, absolute zero, is the...
and pressure:
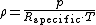
where ρ is the air density, p is absolute pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, Rspecific is the specific gas constant for dry air, and T is absolute temperature.
The specific gas constant for dry air is 287.058 J/(kg·K) in SI
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
units, and 53.35 (ft·lbf
Pound-force
The pound force is a unit of force in some systems of measurement including English engineering units and British gravitational units.- Definitions :...
)/(lbm
Pound (mass)
The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in the Imperial, United States customary and other systems of measurement...
·R) in United States customary
United States customary units
United States customary units are a system of measurements commonly used in the United States. Many U.S. units are virtually identical to their imperial counterparts, but the U.S. customary system developed from English units used in the British Empire before the system of imperial units was...
and Imperial units.
Therefore:
- At IUPACInternational Union of Pure and Applied ChemistryThe International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations that represents chemists in individual countries. It is a member of the International Council for Science . The international headquarters of IUPAC is located in Zürich,...
standard temperature and pressure (0 °CCelsiusCelsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
and 100 kPaPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
), dry air has a density of 1.2754 kgKilogramThe kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
/m3. - At 20 °C and 101.325 kPa, dry air has a density of 1.2041 kg/m3.
- At 70 °FFahrenheitFahrenheit is the temperature scale proposed in 1724 by, and named after, the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit . Within this scale, the freezing of water into ice is defined at 32 degrees, while the boiling point of water is defined to be 212 degrees...
and 14.696 psiPounds per square inchThe pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units...
, dry air has a density of 0.074887 lbmPound (mass)The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in the Imperial, United States customary and other systems of measurement...
/ft3Cubic footThe cubic foot is an Imperial and US customary unit of volume, used in the United States and the United Kingdom. It is defined as the volume of a cube with sides of one foot in length.-Conversions:- Symbols :...
.
The following table illustrates the air density - temperature relationship at 1 atm or 101.325 kPa:
Water vapor
The addition of water vaporWater vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
to air (making the air humid) reduces the density of the air, which may at first appear contrary to logic.
This occurs because the molecular mass of water (18 g/mol) is less than the molecular mass of dry air (around 29 g/mol). For any gas, at a given temperature and pressure, the number of molecules present is constant for a particular volume (see Avogadro's Law
Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law is a gas law named after Amedeo Avogadro who, in 1811, hypothesized that two given samples of an ideal gas, at the same temperature, pressure and volume, contain the same number of molecules...
). So when water molecules (vapor) are added to a given volume of air, the dry air molecules must decrease by the same number, to keep the pressure or temperature from increasing. Hence the mass per unit volume of the gas (its density) decreases.
The density of humid air may be calculated as a mixture of ideal gas
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
es. In this case, the partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
of water vapor
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
is known as the vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
. Using this method, error in the density calculation is less than 0.2% in the range of −10 °C to 50 °C.
The density of humid air is found by:

where:
 Density of the humid air (kg/m³)
Density of the humid air (kg/m³)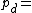 Partial pressure of dry air (Pa)
Partial pressure of dry air (Pa) Specific gas constant for dry air, 287.058 J/(kg·K)
Specific gas constant for dry air, 287.058 J/(kg·K)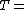 Temperature (K)
Temperature (K)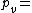 Pressure of water vapor (Pa)
Pressure of water vapor (Pa)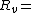 Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.495 J/(kg·K)
Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.495 J/(kg·K)The vapor pressure of water may be calculated from the saturation vapor pressure and relative humidity
Relative humidity
Relative humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor in a mixture of air and water vapor. It is defined as the partial pressure of water vapor in the air-water mixture, given as a percentage of the saturated vapor pressure under those conditions...
. It is found by:

Where:
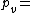 Vapor pressure of water
Vapor pressure of water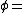 Relative humidity
Relative humidity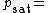 Saturation vapor pressure
Saturation vapor pressureThe saturation vapor pressure of water at any given temperature is the vapor pressure when relative humidity is 100%. A simplification of the regression used to find this, can be formulated as:
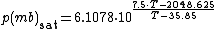
Note:
- This will give a result in mbar (millibar), 1 mbar = 0.001 bar = 0.1 kPa = 100 Pa
 is found considering partial pressurePartial pressureIn a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
is found considering partial pressurePartial pressureIn a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
, resulting in: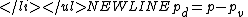
Where p simply notes the absolute pressure in the observed system.
Altitude
To calculate the density of air as a function of altitude, one requires additional parameters. They are listed below, along with their values according to the International Standard AtmosphereInternational Standard AtmosphereThe International Standard Atmosphere is an atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes. It has been established to provide a common reference for temperature and pressure and consists of tables of...
, using the universal gas constantGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
instead of the specific one:- sea level standard atmospheric pressure p0 = 101.325 kPaPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
- sea level standard temperature T0 = 288.15 KKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
- Earth-surface gravitational acceleration g = 9.80665 m/s2.
- temperature lapse rate L = 0.0065 KKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
/m - universal gas constant R = 8.31447 J/(molMole (unit)The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
·K) - molar massMolar massMolar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
of dry air M = 0.0289644 kg/mol
Temperature at altitude h meters above sea level is given by the following formula (only valid inside the troposphereTroposphereThe troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 80% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols....
):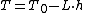
The pressure at altitude h is given by: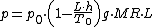
Density can then be calculated according to a molar form of the original formula: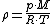
where M is molar massMolar massMolar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is absolute temperature.
See also
- International Standard AtmosphereInternational Standard AtmosphereThe International Standard Atmosphere is an atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes. It has been established to provide a common reference for temperature and pressure and consists of tables of...
- U.S. Standard Atmosphere
- NRLMSISE-00NRLMSISE-00NRLMSISE-00 is an empirical, global model of the Earth's atmosphere from ground to space. It models the temperatures and densities of the atmosphere's components. A primary use of this model is to aid predictions of satellite orbital decay due to atmospheric drag...
- Air density, density altitude, grains of water calculator by region
External links
- sea level standard atmospheric pressure p0 = 101.325 kPa

