
Digital Visual Interface
Encyclopedia
The Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video interface standard covering the transmission of video between a source device (such as a personal computer) and a display device
. The DVI standard has achieved widespread acceptance in the PC industry, both in desktop PCs and monitors. Most contemporary retail desktop PCs and LCD monitors feature a DVI interface, and many other devices (such as projectors and consumer televisions) support DVI indirectly through HDMI
, another video interface standard. Many laptops still have legacy VGA or, in many newer models, HDMI ports, but fewer have DVI.
DVI was developed by an industry consortium, the Digital Display Working Group
(DDWG) to replace the "legacy analog technology" VGA connector
standard. DVI is designed to carry uncompressed digital
video data to a display. It is partially compatible with the High-Definition Multimedia Interface
(HDMI) standard in digital mode (DVI-D), and VGA
in analog mode (DVI-A).
It is also still found in some consumer television sets, despite having been superseded in this application by HDMI
.
interface. The DDC's I2C master in the DVI-source reads a standardized data structure, EDID
, from the display device's I2C slave. The DVI specification defines a minimum set of supported video modes for both source devices and syncs (displays), to ensure a basic level of interoperability between any pairing of source and display.
Digitally encoded video pixel
data is transported using multiple serial bit links. At the electrical level, the links use transition minimized differential signalling TMDS. TMDS is highly resistant to electrical noise and other forms of analog distortion
, and barring severe noise impairment or cable defect, transports the pixel data bit-for-bit accurate across the cable.
For backward compatibility with displays using analog VGA signals, some of the contacts in the DVI connector carry the analog VGA signals. Thus, the DVI connector can carry a digital-video signal, an analog VGA signal, or both. To ensure a basic level of interoperability, DVI compliant devices are required to support one baseline video mode, "low pixel format" (640x480 at 60 Hz.)
When a source and display are connected, the source first queries the display's capabilities, by reading the monitor EDID block over the I2C link. The EDID block contains the display's identification, color characteristics (such as gamma level), and table of supported video modes. The table can designate a preferred mode or native resolution
. Each mode is a set of CRT timing values which exactly defines the duration and frequency of the horizontal/vertical sync, and the positioning of the active display area within the sync boundaries, which determines the horizontal resolution, vertical resolution, and refresh rate.
. Finally, HDMI supports the transport of digital audio, in addition to digital video. An HDMI source differentiates between a legacy DVI display and an HDMI-capable display by reading the display's EDID block.
To promote interoperability between DVI and HDMI devices, both HDMI source components and HDMI displays are required to support DVI signalling. From a user's perspective, an HDMI display can be driven by a single-link DVI-D source, since HDMI and DVI-D define an overlapping minimum set of supported resolutions and framebuffer formats to ensure a basic level of interoperability. In the reverse scenario, a typical HDMI-source (such as a Blu-ray Disc player) may demand HDCP-compliance on the display, an optional capability for DVI monitors. Hence, though the display link is technically operable in the sense that the HDMI source can produce a watchable image on the DVI monitor, content policy may forbid the display of HDCP-protected content on the non-HDCP compliant display.
Absent this HDCP issue, an HDMI-source and DVI-D display would enjoy the same level of basic interoperability.
Features specific to HDMI (such as remote-control, audio transport, xvYCC, and deep-color) are not usable in devices that only support DVI signalling. However, many devices can output HDMI over a DVI output (e.g., ATI 3000-series
and NVIDIA GTX 200-series
video cards), and some multimedia displays may accept HDMI (including audio) over a DVI input. In general, exact capabilities vary from product to product.
PanelLink uses transition minimized differential signaling
(TMDS), a high-speed serial link developed by Silicon Image.
A single-link DVI connection consists of four TMDS links; each link transmits data from the source to the device over 1 twisted wire pair. Three of the links correspond to the RGB components of the video signal: red, green, blue (for a total of 24 bits per pixel.) The fourth link carries the pixel clock. The binary data is encoded using 8b10b encoding. The 8b10b encoding system serves several purposes: it preserves DC balance over time, it generates sufficient signal transitions to maintain receiver bit-alignment (pixel clock recovery), and it provides symbol (byte) alignment. Each TMDS link carries binary data at ten times the pixel clock reference frequency, for a maximum data rate of 1.65 Gbit
/s × 3 data pairs for single-link DVI.
DVI does not use packetisation, but rather transmits the pixel data as if it were a rasterized analog video signal. As such, during each vertical refresh period, the complete frame is 'drawn' over the DVI link. The full active area of each frame is always transmitted; no data compression is used, and there is no support for only transmitting changed parts of the image. Video modes typically use horizontal and vertical refresh timings that are compatible with CRT displays, but this is not a requirement. The DVI specification (see below for link) does, however, include a paragraph on "Conversion to Selective Refresh" (under 1.2.2), suggesting this feature for future devices.
The DVI specification mandates a maximum pixel clock frequency of 165 MHz when running in single-link mode. With a single DVI link, the highest supported standard resolution is 2.75 megapixels (including blanking interval) at 60 Hz refresh. For practical purposes, this allows a maximum screen resolution at 60 Hz of 1,915 × 1,436 pixels (standard 4:3 ratio), 1,854 × 1,483 pixels (5:4 ratio), or 2,098 × 1,311 (widescreen 16:10 ratio).
To support display devices requiring higher video bandwidth, there is provision for a dual DVI link. A dual link doubles the number of TMDS pairs, effectively doubling video bandwidth at a given pixel clock frequency. The DVI specification mandates how the dual link may be used. All display modes that use a pixel clock below 165 MHz, and have at most 24 bits per pixel, are required to use single-link mode. All modes that require more than 24 bits per pixel, and/or 165 MHz pixel clock frequency must use dual-link mode. In modes where each pixel uses 24 bits of color data per pixel or less and dual-link mode is in use, the transmitter stripes pixel data across both links; each sequential video pixel is transmitted on alternate links. In modes with color depth greater than 24 bits per pixel, the second link carries the least significant bit
s of each pixel.
Like modern analog VGA connector
s, the DVI connector includes pins for the display data channel
(DDC). DDC2 (a newer version of DDC) allows the graphics adapter to read the monitor's extended display identification data
(EDID). If a display supports both analog and digital signals in one DVI-I input, each input method can host a distinct EDID. Since the DDC can only support one EDID, there can be a problem if both the digital and analog inputs in the DVI-I port detect activity. It is up to the display to choose which EDID to send.
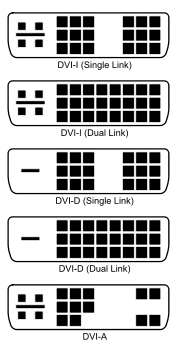
The DVI connector usually contains pins to pass the DVI-native digital video signals. In the case of dual link systems, additional pins provide increased bandwidth allowing higher resolutions and longer distances. Dual link should not be confused with dual display (also known as dual head), which is a configuration that involves a single computer connected to two monitors.
As well as digital signals, the DVI connector includes pins providing the same analog signals found on a VGA connector, allowing an analog VGA monitor to be connected with a passive plug adapter (or with a converter cable with VGA at one end, and DVI-A or DVI-I at the other). This feature was included in order to make DVI universal, as it allows either type of monitor (analog or digital) to be operated from the same connector.
The DVI connector on a device is therefore given one of three names, depending on which signals it implements:
The DVI-D and DVI-I connector includes provision for a second data link, but few devices implement this. In those that do, the connector is sometimes referred to as DVI-DL (dual link).
The long flat pin on a DVI-I connector is wider than the same pin on a DVI-D connector, so it is not possible to connect a male DVI-I to a female DVI-D by removing the 4 analog pins. It is possible, however, to connect a male DVI-D cable to a female DVI-I connector. Many flat panel LCD monitors have only the DVI-D connection so that a DVI-D male to DVI-D male cable will suffice when connecting the monitor to a computer's DVI-I female connector.
DVI is the only widespread video standard that includes analog and digital transmission options in the same connector. Competing standards are exclusively digital: these include a system using low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS
), known by its proprietary names FPD-Link
(flat-panel display) and FLATLINK; and its successors, the LVDS Display Interface (LDI) and OpenLDI
.
Some new DVD player
s, TV sets (including HDTV
sets) and video projector
s have DVI/HDCP connectors; these are physically the same as DVI connectors but transmit an encrypted signal using the HDCP protocol for copy protection. Computers with DVI video connectors can use many DVI-equipped HDTV sets as a display, but only computers whose graphics systems support High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection
are currently able to play content that requires digital rights management
.
USB
signals are not incorporated into the connector, but were earlier incorporated into the VESA Plug and Display connector used by InFocus
on their projector systems, and in the Apple Display Connector
, which was used by Apple until 2005.
The DMS-59
connector is a way to combine two analog and two digital signals in one plug. It is commonly used when a single graphics card has two outputs. Note that this is dual display – it does not have the additional pins for the dual link TDMI signals.
M1-DA connectors are sometimes labeled as DVI-M1; they are used for the VESA Enhanced Video Connector
and VESA Plug and Display schemes.
Generalized Timing Formula
(GTF) is a VESA
standard which can easily be calculated with the Linux
gtf utility. Coordinated Video Timings
-Reduced Blanking (CVT-RB) is a VESA
standard which offers reduced horizontal and vertical blanking for non-CRT based displays.
Pixel data is encoded using TMDS' own 8b/10b encoding
scheme. This scheme has two steps. The first step is to minimize transitions by determining which of two methods yields the fewest transitions. In both schemes, the first bit is always encoded as itself. In one scheme, the second through eighth bits are encoded by XNORing each of them with the bits that preceded them before they got encoded. In the other scheme, the second through eighth bits are encoded by XORing each of them with the bits that preceded them before they got encoded. The scheme selected is indicated in the ninth bit of the code word before it is processed in the second step. If this bit is a zero, the XNOR scheme was used. Otherwise, the XOR scheme was used. The second step is to maintain DC balance. To do this, the nine bits in the code word that was created in the first step might need to be inverted. The tenth bit is set to 1 if this was done. Otherwise, the tenth bit is set to zero. As indicated in version 1.0 of the specification, the clock rate is the same as the pixel rate plus framing overhead, while there are usually 24 bits per pixel. This scheme was designed so that each pixel character contains at most five transitions. The transmitter chooses between the two schemes in order to transmit the fewest transitions as possible for each pixel.
The receiver must recover the faster bit clock from the data lines directly through the techniques of clock/data recovery
. DVI provides a reference clock while other serial data interfaces such as PCI Express
and SATA
do not because the bit rate carried by the DVI interface may vary across a wide frequency range depending on the video format being rendered. Serial interfaces that do not separately carry the reference clock typically run at a few well-defined frequencies which are easy to distinguish (e.g., 2.5 and 5.0 Gbit/s for PCI Express and 1.5 and 3.0 Gbit/s for SATA) which can be generated precisely at the receiver.
The data enable signal encodes the type of data being sent; high means pixel data, and low means control data. Data of the opposing type is ignored.
(DPMS) standard, a connected device can turn a monitor off when the connected device is powered down, or programmatically if the display controller ("graphics card") of the device supports it. Devices with this capability can also attain Energy Star certification.
In December 2010, Intel, AMD
, and several computer and display manufacturers announced they would stop supporting DVI-I, VGA and LVDS-technologies from 2013/2015, and instead speed up adoption of DisplayPort and HDMI. They also stated: "Legacy interfaces such as VGA, DVI and LVDS have not kept pace, and newer standards such as DisplayPort and HDMI clearly provide the best connectivity options moving forward. In our opinion, DisplayPort 1.2 is the future interface for PC monitors, along with HDMI 1.4a for TV connectivity."
-output in addition to DVI. Due to electrical and pin compatibility between the DVI and HDMI, only a simple passive adapter (or DVI-D to HDMI cable) is necessary in order for the PC to output HDMI to a compatible HDMI-display (such as a television), and take advantage of HDMI features (such as audio output).
Display device
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form...
. The DVI standard has achieved widespread acceptance in the PC industry, both in desktop PCs and monitors. Most contemporary retail desktop PCs and LCD monitors feature a DVI interface, and many other devices (such as projectors and consumer televisions) support DVI indirectly through HDMI
HDMI
HDMI is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. It is a digital alternative to consumer analog standards, such as radio frequency coaxial cable, composite video, S-Video, SCART, component video, D-Terminal, or VGA...
, another video interface standard. Many laptops still have legacy VGA or, in many newer models, HDMI ports, but fewer have DVI.
DVI was developed by an industry consortium, the Digital Display Working Group
Digital Display Working Group
The Digital Display Working Group was organized by Intel Corporation, Silicon Image, Inc., Compaq Computer Corp., Fujitsu Limited, Hewlett-Packard Company, International Business Machines Corp., and NEC Corporation....
(DDWG) to replace the "legacy analog technology" VGA connector
VGA connector
A Video Graphics Array connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector. The 15-pin VGA connector is found on many video cards, computer monitors, and some high definition television sets...
standard. DVI is designed to carry uncompressed digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
video data to a display. It is partially compatible with the High-Definition Multimedia Interface
High-Definition Multimedia Interface
HDMI is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. It is a digital alternative to consumer analog standards, such as radio frequency coaxial cable, composite video, S-Video, SCART, component video, D-Terminal, or VGA...
(HDMI) standard in digital mode (DVI-D), and VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
in analog mode (DVI-A).
It is also still found in some consumer television sets, despite having been superseded in this application by HDMI
HDMI
HDMI is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. It is a digital alternative to consumer analog standards, such as radio frequency coaxial cable, composite video, S-Video, SCART, component video, D-Terminal, or VGA...
.
Overview
The DVI interface consists of multiple parts. Display identification and capability advertisement is defined over a VESA/DDCDisplay Data Channel
The Display Data Channel or DDC is a collection of digital communication protocols between a computer display and a graphics adapter that enables the display to communicate its supported display modes to the adapter and to enable the computer host to adjust monitor parameters, such as brightness...
interface. The DDC's I2C master in the DVI-source reads a standardized data structure, EDID
Extended display identification data
Extended display identification data is a data structure provided by a digital display to describe its capabilities to a video source . It is what enables a modern personal computer to know what kinds of monitors are connected to it. EDID is defined by a standard published by the Video...
, from the display device's I2C slave. The DVI specification defines a minimum set of supported video modes for both source devices and syncs (displays), to ensure a basic level of interoperability between any pairing of source and display.
Digitally encoded video pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
data is transported using multiple serial bit links. At the electrical level, the links use transition minimized differential signalling TMDS. TMDS is highly resistant to electrical noise and other forms of analog distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
, and barring severe noise impairment or cable defect, transports the pixel data bit-for-bit accurate across the cable.
For backward compatibility with displays using analog VGA signals, some of the contacts in the DVI connector carry the analog VGA signals. Thus, the DVI connector can carry a digital-video signal, an analog VGA signal, or both. To ensure a basic level of interoperability, DVI compliant devices are required to support one baseline video mode, "low pixel format" (640x480 at 60 Hz.)
When a source and display are connected, the source first queries the display's capabilities, by reading the monitor EDID block over the I2C link. The EDID block contains the display's identification, color characteristics (such as gamma level), and table of supported video modes. The table can designate a preferred mode or native resolution
Native resolution
The native resolution of a LCD, LCoS or other flat panel display refers to its single fixed resolution. As an LCD display consists of a fixed raster, it cannot change resolution to match the signal being displayed as a CRT monitor can, meaning that optimal display quality can be reached only when...
. Each mode is a set of CRT timing values which exactly defines the duration and frequency of the horizontal/vertical sync, and the positioning of the active display area within the sync boundaries, which determines the horizontal resolution, vertical resolution, and refresh rate.
DVI and HDMI compatibility
HDMI is a newer digital audio/video interface developed and promoted by the consumer electronics industry. Both DVI and HDMI share the same electrical specifications for the TMDS and VESA/DDC links. However, HDMI and DVI differ in several key ways. First, HDMI lacks analog VGA compatibility, as these signals are absent in the HDMI connector. Second, DVI is limited to the RGB color space, whereas HDMI supports both RGB and YCbCrYCbCr
YCbCr or Y′CbCr, sometimes written or , is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components...
. Finally, HDMI supports the transport of digital audio, in addition to digital video. An HDMI source differentiates between a legacy DVI display and an HDMI-capable display by reading the display's EDID block.
To promote interoperability between DVI and HDMI devices, both HDMI source components and HDMI displays are required to support DVI signalling. From a user's perspective, an HDMI display can be driven by a single-link DVI-D source, since HDMI and DVI-D define an overlapping minimum set of supported resolutions and framebuffer formats to ensure a basic level of interoperability. In the reverse scenario, a typical HDMI-source (such as a Blu-ray Disc player) may demand HDCP-compliance on the display, an optional capability for DVI monitors. Hence, though the display link is technically operable in the sense that the HDMI source can produce a watchable image on the DVI monitor, content policy may forbid the display of HDCP-protected content on the non-HDCP compliant display.
Absent this HDCP issue, an HDMI-source and DVI-D display would enjoy the same level of basic interoperability.
Features specific to HDMI (such as remote-control, audio transport, xvYCC, and deep-color) are not usable in devices that only support DVI signalling. However, many devices can output HDMI over a DVI output (e.g., ATI 3000-series
Radeon R600
The graphics processing unit codenamed the Radeon R600 is the foundation of the Radeon HD 2000/3000 series and the FireGL 2007 series video cards developed by ATI Technologies...
and NVIDIA GTX 200-series
GeForce 200 Series
The GeForce 200 Series is the 10th generation of Nvidia's GeForce graphics processing units. The series also represents the continuation of the company's unified shader architecture introduced with the GeForce 8 Series and the GeForce 9 Series. Its primary competition came from ATI's Radeon HD 4000...
video cards), and some multimedia displays may accept HDMI (including audio) over a DVI input. In general, exact capabilities vary from product to product.
Technical discussion
DVI's digital video transmission format is based on PanelLink, a serial format devised by Silicon Image Inc.Silicon Image Inc.
Silicon Image is a provider of wireless and wired connectivity solutions that enable the reliable distribution and presentation of high-definition content for consumer electronics, mobile, and PC markets...
PanelLink uses transition minimized differential signaling
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling
Transition-minimized differential signaling is a technology for transmitting high-speed serial data and is used by the DVI and HDMI video interfaces, as well as other digital communication interfaces....
(TMDS), a high-speed serial link developed by Silicon Image.
A single-link DVI connection consists of four TMDS links; each link transmits data from the source to the device over 1 twisted wire pair. Three of the links correspond to the RGB components of the video signal: red, green, blue (for a total of 24 bits per pixel.) The fourth link carries the pixel clock. The binary data is encoded using 8b10b encoding. The 8b10b encoding system serves several purposes: it preserves DC balance over time, it generates sufficient signal transitions to maintain receiver bit-alignment (pixel clock recovery), and it provides symbol (byte) alignment. Each TMDS link carries binary data at ten times the pixel clock reference frequency, for a maximum data rate of 1.65 Gbit
Gigabit
The gigabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix giga is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 109 , and therefore...
/s × 3 data pairs for single-link DVI.
DVI does not use packetisation, but rather transmits the pixel data as if it were a rasterized analog video signal. As such, during each vertical refresh period, the complete frame is 'drawn' over the DVI link. The full active area of each frame is always transmitted; no data compression is used, and there is no support for only transmitting changed parts of the image. Video modes typically use horizontal and vertical refresh timings that are compatible with CRT displays, but this is not a requirement. The DVI specification (see below for link) does, however, include a paragraph on "Conversion to Selective Refresh" (under 1.2.2), suggesting this feature for future devices.
The DVI specification mandates a maximum pixel clock frequency of 165 MHz when running in single-link mode. With a single DVI link, the highest supported standard resolution is 2.75 megapixels (including blanking interval) at 60 Hz refresh. For practical purposes, this allows a maximum screen resolution at 60 Hz of 1,915 × 1,436 pixels (standard 4:3 ratio), 1,854 × 1,483 pixels (5:4 ratio), or 2,098 × 1,311 (widescreen 16:10 ratio).
To support display devices requiring higher video bandwidth, there is provision for a dual DVI link. A dual link doubles the number of TMDS pairs, effectively doubling video bandwidth at a given pixel clock frequency. The DVI specification mandates how the dual link may be used. All display modes that use a pixel clock below 165 MHz, and have at most 24 bits per pixel, are required to use single-link mode. All modes that require more than 24 bits per pixel, and/or 165 MHz pixel clock frequency must use dual-link mode. In modes where each pixel uses 24 bits of color data per pixel or less and dual-link mode is in use, the transmitter stripes pixel data across both links; each sequential video pixel is transmitted on alternate links. In modes with color depth greater than 24 bits per pixel, the second link carries the least significant bit
Least significant bit
In computing, the least significant bit is the bit position in a binary integer giving the units value, that is, determining whether the number is even or odd. The lsb is sometimes referred to as the right-most bit, due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits...
s of each pixel.
Like modern analog VGA connector
VGA connector
A Video Graphics Array connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector. The 15-pin VGA connector is found on many video cards, computer monitors, and some high definition television sets...
s, the DVI connector includes pins for the display data channel
Display Data Channel
The Display Data Channel or DDC is a collection of digital communication protocols between a computer display and a graphics adapter that enables the display to communicate its supported display modes to the adapter and to enable the computer host to adjust monitor parameters, such as brightness...
(DDC). DDC2 (a newer version of DDC) allows the graphics adapter to read the monitor's extended display identification data
Extended display identification data
Extended display identification data is a data structure provided by a digital display to describe its capabilities to a video source . It is what enables a modern personal computer to know what kinds of monitors are connected to it. EDID is defined by a standard published by the Video...
(EDID). If a display supports both analog and digital signals in one DVI-I input, each input method can host a distinct EDID. Since the DDC can only support one EDID, there can be a problem if both the digital and analog inputs in the DVI-I port detect activity. It is up to the display to choose which EDID to send.
Cable Length
The maximum length of DVI cables is not included in the specification since it is dependent on the pixel clock frequency, and hence the video mode's bandwidth requirements (which is a function of resolution and refresh rate). In general, cable lengths up to 4.5 m (15 ft) will work for displays at resolutions of 1,920 × 1,200. This resolution will work even up to 10 m (33 ft) if appropriate cable is used. Cable lengths up to 15 m (50 ft) can be used with displays at resolutions up to 1,280 × 1,024. For longer distances, the use of a DVI booster is recommended to mitigate signal degradation. DVI boosters may use an external power supply.Connector

The DVI connector usually contains pins to pass the DVI-native digital video signals. In the case of dual link systems, additional pins provide increased bandwidth allowing higher resolutions and longer distances. Dual link should not be confused with dual display (also known as dual head), which is a configuration that involves a single computer connected to two monitors.
As well as digital signals, the DVI connector includes pins providing the same analog signals found on a VGA connector, allowing an analog VGA monitor to be connected with a passive plug adapter (or with a converter cable with VGA at one end, and DVI-A or DVI-I at the other). This feature was included in order to make DVI universal, as it allows either type of monitor (analog or digital) to be operated from the same connector.
The DVI connector on a device is therefore given one of three names, depending on which signals it implements:
- DVI-D (digital only, both single-link and dual-link)
- DVI-A (analog only)
- DVI-I (integrated – digital and analog)
The DVI-D and DVI-I connector includes provision for a second data link, but few devices implement this. In those that do, the connector is sometimes referred to as DVI-DL (dual link).
The long flat pin on a DVI-I connector is wider than the same pin on a DVI-D connector, so it is not possible to connect a male DVI-I to a female DVI-D by removing the 4 analog pins. It is possible, however, to connect a male DVI-D cable to a female DVI-I connector. Many flat panel LCD monitors have only the DVI-D connection so that a DVI-D male to DVI-D male cable will suffice when connecting the monitor to a computer's DVI-I female connector.
DVI is the only widespread video standard that includes analog and digital transmission options in the same connector. Competing standards are exclusively digital: these include a system using low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS
Low voltage differential signaling
Low-voltage differential signaling, or LVDS, is an electrical digital signaling system that can run at very high speeds over inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. It was introduced in 1994, and has since become very popular in computers, where it forms part of very high-speed networks and...
), known by its proprietary names FPD-Link
FPD-Link
Flat Panel Display Link by National Semiconductor is a high-speed interface connecting the output of a video controller in a laptop computer, computer monitor or LCD television set to the display panel. Most laptops, LCD computer monitors and LCD TVs use this interface internally...
(flat-panel display) and FLATLINK; and its successors, the LVDS Display Interface (LDI) and OpenLDI
OpenLDI
OpenLDI is a high-bandwidth digital interface standard for connecting flat panel LCD monitors to computers. While it is virtually unknown in standalone displays, it has a strong basis in the interconnect for internal displays, as in laptops. OpenLDI is based on the de-facto FPD-Link specification...
.
Some new DVD player
DVD player
A DVD player is a device that plays discs produced under both the DVD-Video and DVD-Audio technical standards, two different and incompatible standards. These devices were invented in 1997 and continue to thrive...
s, TV sets (including HDTV
High-definition television
High-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
sets) and video projector
Video projector
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signal and projects the corresponding image on a projection screen using a lens system. All video projectors use a very bright light to project the image, and most modern ones can correct any curves, blurriness, and other...
s have DVI/HDCP connectors; these are physically the same as DVI connectors but transmit an encrypted signal using the HDCP protocol for copy protection. Computers with DVI video connectors can use many DVI-equipped HDTV sets as a display, but only computers whose graphics systems support High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection
High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection is a form of digital copy protection developed by Intel Corporation to prevent copying of digital audio and video content as it travels across connections...
are currently able to play content that requires digital rights management
Digital rights management
Digital rights management is a class of access control technologies that are used by hardware manufacturers, publishers, copyright holders and individuals with the intent to limit the use of digital content and devices after sale. DRM is any technology that inhibits uses of digital content that...
.
USB
Universal Serial Bus
USB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
signals are not incorporated into the connector, but were earlier incorporated into the VESA Plug and Display connector used by InFocus
InFocus
InFocus Corporation is a privately owned American company based in the state of Oregon. Founded in 1986, the company develops, manufactures, and distributes DLP and LCD projectors and accessories as well as LCD flat panel displays. Formerly a NASDAQ listed public company, InFocus was purchased by ...
on their projector systems, and in the Apple Display Connector
Apple Display Connector
The Apple Display Connector is a proprietary modification of the DVI connector that combines analog and digital video signals, USB, and power all in one cable...
, which was used by Apple until 2005.
The DMS-59
DMS-59
DMS-59 is a 59-pin electrical connector generally used for computer video cards. It provides two DVI or VGA outputs on a single connector. An adapter cable is needed for conversion from DMS-59 to DVI or VGA , and different types of adapter cables exist...
connector is a way to combine two analog and two digital signals in one plug. It is commonly used when a single graphics card has two outputs. Note that this is dual display – it does not have the additional pins for the dual link TDMI signals.
M1-DA connectors are sometimes labeled as DVI-M1; they are used for the VESA Enhanced Video Connector
VESA Enhanced Video Connector
The VESA Enhanced Video Connector is a VESA standard intended to reduce the number of cables around a computer by incorporating video, audio, FireWire and USB into a single cable system. The intention of the system was to make the monitor the central point of connection...
and VESA Plug and Display schemes.
Specifications
Digital
- Minimum clock frequency: 25.175 MHz
- Single link maximum data rate including 8b/10b overhead is 4.95 Gbit/s @ 165 MHz. With the 8b/10b overhead subtracted, the maximum data rate is 3.96 Gbit/s.
- Dual link maximum data rate is limited only by the bandwidth limits of the copper the DVI cable is constructed of and by the DVI signal's source.
- Pixels per clock cycle: 1 (single link at 24 bits or less per pixel, and dual link at between 25 and 48 bits inclusively per pixel) or 2 (dual link at 24 bits or less per pixel)
- Bits per pixel:
- 24 bits per pixel support is mandatory in all resolutions supported.
- Less than 24 bits per pixel is optional.
- Up to 48 bits per pixel are supported in dual link DVI, and is optional. If a mode greater than 24 bits per pixel is desired, the least significant bits are sent on the second link.
- Example display modes (single link):
- HDTV (1,920 × 1,080) @ 60 Hz with CVT-RB blanking (139 MHz)
- UXGA (1,600 × 1,200) @ 60 Hz with GTF blanking (161 MHz)
- WUXGA (1,920 × 1,200) @ 60 Hz with CVT-RB blanking (154 MHz)
- SXGA (1,280 × 1,024) @ 85 Hz with GTF blanking (159 MHz)
- WXGA+ (1440 × 900) @ 60 Hz (107 MHz)
- WQUXGA (3,840 × 2,400) @ 17 Hz (164 MHz)
- Example display modes (dual link):
- QXGA (2,048 × 1,536) @ 75 Hz with GTF blanking (2 × 170 MHz)
- HDTV (1,920 × 1,080) @ 85 Hz with GTF blanking (2 × 126 MHz)
- WUXGA (1,920 × 1,200) @ 120 Hz with CVT-RB blanking (2 x 154 MHz)
- WQXGA (2,560 × 1,600) @ 60 Hz with GTF blanking (2 × 174 MHz) (30 inches (76 cm) Apple, Dell, Gateway, HP, NEC, Quinux, and Samsung LCDs)
- WQXGA (2,560 × 1,600) @ 60 Hz with CVT-RB blanking (2 × 135 MHz) (30 inches (76 cm) Apple, Dell, Gateway, HP, NEC, Quinux, and Samsung LCDs)
- WQXGA (2,560 × 1,600) @ 60 Hz with CVT-RB blanking (269 MHz) (This is for high end monitors when operating at greater than 24 bits per pixel.)
- WQUXGA (3,840 × 2,400) @ 33 Hz with GTF blanking (2 × 159 MHz)
Generalized Timing Formula
Generalized Timing Formula
Generalized Timing Formula is a standard by VESA which defines exact parameters of the component video signal for analog VGA display interface....
(GTF) is a VESA
VESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
standard which can easily be calculated with the Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
gtf utility. Coordinated Video Timings
Coordinated Video Timings
Coordinated Video Timings is a standard by VESA which defines the timings of the component video signal. Initially intended for use by computer monitors and video cards, the standard made its way into consumer televisions....
-Reduced Blanking (CVT-RB) is a VESA
VESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
standard which offers reduced horizontal and vertical blanking for non-CRT based displays.
Clock and data relationship
The DVI data channel operates at a bit-rate that is 10 times the frequency of the clock signal. In other words, for every DVI clock there are 10 bits, per channel.Pixel data is encoded using TMDS' own 8b/10b encoding
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling
Transition-minimized differential signaling is a technology for transmitting high-speed serial data and is used by the DVI and HDMI video interfaces, as well as other digital communication interfaces....
scheme. This scheme has two steps. The first step is to minimize transitions by determining which of two methods yields the fewest transitions. In both schemes, the first bit is always encoded as itself. In one scheme, the second through eighth bits are encoded by XNORing each of them with the bits that preceded them before they got encoded. In the other scheme, the second through eighth bits are encoded by XORing each of them with the bits that preceded them before they got encoded. The scheme selected is indicated in the ninth bit of the code word before it is processed in the second step. If this bit is a zero, the XNOR scheme was used. Otherwise, the XOR scheme was used. The second step is to maintain DC balance. To do this, the nine bits in the code word that was created in the first step might need to be inverted. The tenth bit is set to 1 if this was done. Otherwise, the tenth bit is set to zero. As indicated in version 1.0 of the specification, the clock rate is the same as the pixel rate plus framing overhead, while there are usually 24 bits per pixel. This scheme was designed so that each pixel character contains at most five transitions. The transmitter chooses between the two schemes in order to transmit the fewest transitions as possible for each pixel.
The receiver must recover the faster bit clock from the data lines directly through the techniques of clock/data recovery
Clock recovery
Some digital data streams, especially high-speed serial data streams are sent without an accompanying clock signal. The receiver generates a clock from an approximate frequency reference, and then phase-aligns to the transitions in the data stream with a phase-locked loop...
. DVI provides a reference clock while other serial data interfaces such as PCI Express
PCI Express
PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
and SATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
do not because the bit rate carried by the DVI interface may vary across a wide frequency range depending on the video format being rendered. Serial interfaces that do not separately carry the reference clock typically run at a few well-defined frequencies which are easy to distinguish (e.g., 2.5 and 5.0 Gbit/s for PCI Express and 1.5 and 3.0 Gbit/s for SATA) which can be generated precisely at the receiver.
The data enable signal encodes the type of data being sent; high means pixel data, and low means control data. Data of the opposing type is ignored.
Display power management
The DVI specification includes signaling for reducing power consumption. Similar to the analog VESA display power management signalingVESA Display Power Management Signaling
VESA Display Power Management Signaling is a standard from the VESA consortium for managing the power supply of video monitors for computers through the graphics card e.g.; shut off the monitor after the computer has been unused for some time , to save power.- History :DPMS 1.0 was issued by VESA...
(DPMS) standard, a connected device can turn a monitor off when the connected device is powered down, or programmatically if the display controller ("graphics card") of the device supports it. Devices with this capability can also attain Energy Star certification.
Proposed successors
- IEEE 1394 is proposed by High-Definition Audio-Video Network Alliance (HANA Alliance) for all cabling needs, including video, over coax and/or 1394 cable as a combined data stream. However, this interface does not have enough throughput to handle uncompressed HD video, so it is unsuitable for applications that require uncompressed HD video like video games and interactive program guidesElectronic program guideElectronic program guides and interactive program guides provide users of television, radio, and other media applications with continuously updated menus displaying broadcast programming or scheduling information for current and upcoming programming...
. - High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI), a forward-compatibleForward compatibilityForward compatibility or upward compatibility is a compatibility concept for systems design, as e.g. backward compatibility. Forward compatibility aims at the ability of a design to gracefully accept input intended for later versions of itself...
standard that also includes digital audioDigital audioDigital audio is sound reproduction using pulse-code modulation and digital signals. Digital audio systems include analog-to-digital conversion , digital-to-analog conversion , digital storage, processing and transmission components...
transmissionTransmission (telecommunications)Transmission, in telecommunications, is the process of sending, propagating and receiving an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless... - Unified Display Interface (UDI) was proposed by Intel to replace both DVI and HDMI, but was deprecated in favor of DisplayPortDisplayPortDisplayPort is a digital display interface standard produced by the Video Electronics Standards Association . The specification defines a royalty-free digital interconnect for audio and video. The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor...
. - DisplayPort (a license-free standard proposed by VESAVESAVESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
to succeed DVI that has DRMDigital rights managementDigital rights management is a class of access control technologies that are used by hardware manufacturers, publishers, copyright holders and individuals with the intent to limit the use of digital content and devices after sale. DRM is any technology that inhibits uses of digital content that...
capabilities) / Mini DisplayPortMini DisplayPortThe Mini DisplayPort is a miniaturized version of the DisplayPort digital audio-visual interface. Apple, Inc. announced the development in the fourth quarter of 2008, and now applies it in the LED Cinema Display and in all new Macintosh computers: MacBook, MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, iMac, Mac mini,...
/ Thunderbolt
In December 2010, Intel, AMD
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets...
, and several computer and display manufacturers announced they would stop supporting DVI-I, VGA and LVDS-technologies from 2013/2015, and instead speed up adoption of DisplayPort and HDMI. They also stated: "Legacy interfaces such as VGA, DVI and LVDS have not kept pace, and newer standards such as DisplayPort and HDMI clearly provide the best connectivity options moving forward. In our opinion, DisplayPort 1.2 is the future interface for PC monitors, along with HDMI 1.4a for TV connectivity."
HDMI audio support
Since 2008, PC manufacturers have gradually upgraded the PC's controller to support HDMIHDMI
HDMI is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. It is a digital alternative to consumer analog standards, such as radio frequency coaxial cable, composite video, S-Video, SCART, component video, D-Terminal, or VGA...
-output in addition to DVI. Due to electrical and pin compatibility between the DVI and HDMI, only a simple passive adapter (or DVI-D to HDMI cable) is necessary in order for the PC to output HDMI to a compatible HDMI-display (such as a television), and take advantage of HDMI features (such as audio output).
See also
- List of video connectors
- Mini-DVIMini-DVIThe Mini-Dvi connector is used on certain Apple computers as a digital alternative to the Mini-VGA connector. Its size is between the full-sized DVI and the tiny Micro-DVI...
- DiiVA
- DisplayPortDisplayPortDisplayPort is a digital display interface standard produced by the Video Electronics Standards Association . The specification defines a royalty-free digital interconnect for audio and video. The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor...
- Thunderbolt (interface)

