
Dissolution (chemistry)
Encyclopedia

Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
, liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
or gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
forms a solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
in a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
. In solids this can be explained as the breakdown of the crystal lattice
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
into individual ions, atoms or molecules and their transport into the solvent. For liquids and gases, the molecules must be compatible with those of the solvent for a solution to form. The process of dissolution is governed by the thermodynamic energies involved, such as the heat of solution and entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
of solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
. Overall the free energy
Thermodynamic free energy
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. The concept is useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The free energy is the internal energy of a system less the amount of energy that cannot be used to...
must be negative for dissolution to occur. In turn, those energies are controlled by the way in which different chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
types interact with those in the solvent. Solid solution
Solid solution
A solid solution is a solid-state solution of one or more solutes in a solvent. Such a mixture is considered a solution rather than a compound when the crystal structure of the solvent remains unchanged by addition of the solutes, and when the mixture remains in a single homogeneous phase...
s occur in metal alloys and their formation and decription is governed by the relevant phase diagram
Phase diagram
A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions at which thermodynamically distinct phases can occur at equilibrium...
.
Dissolution testing is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for optimization of formulation and quality control.
Ionic compounds
For ionic compoundIonic compound
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a lattice structure by ionic bonds. Usually, the positively charged portion consists of metal cations and the negatively charged portion is an anion or polyatomic ion. Ions in ionic compounds are held together...
s, dissolution takes place when the compounds ionize. This most commonly occurs in polar
Polarity
In physics, polarity is a description of an attribute, typically a binary attribute , or a vector . For example:* An electric charge has a polarity of either positive or negative....
solvents, such as water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
or ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
.
NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
In a colloidal dispersed system, ion dissolution arises, where the dispersed particles exist in equilibrium with their saturated counter part, i.e.
NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
The behavior of this system is characterised by the activity coefficient
Activity coefficient
An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed...
s of the components and the solubility product, defined as:
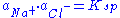
The ability of an ion to preferentially dissolve (as a result of unequal activities) is classified as the Potential Determining Ion. This in turn results in the remaining particle possessing either a net positive/negative surface charge.
Polar compounds
Other solid compounds experience dissolution as a breakdown of their crystal lattice, and due to their polarity, or non-polarity, mix with the solventSolvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
. The solubility of ionic salts in water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
is generally determined by the degree of solvation
Solvation
Solvation, also sometimes called dissolution, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute...
of the ions by water molecules. Such coordination complexes occur by water donating spare electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s on the oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
atom to the ion.
Polymers
The solubility of polymers depends on the chemical bonds present in the backbone chain and their compatibility with those of the solvent. The Hildebrand solubility parameterHildebrand solubility parameter
The Hildebrand solubility parameter provides a numerical estimate of the degree of interaction between materials, and can be a good indication of solubility, particularly for non polar materials such as many polymers...
is commonly used to evaluate polymer solubility. The closer the value of the parameters, the more likely dissolution will occur.
Liquids
Compounds in a fluid state may also dissolve in another liquid depending on the compatibility of the chemical and physical bonds in the substance with those of the solvent. Hydrogen bondHydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
s play an important role in aqueous dissolution.
Gases
Compounds in the gaseous state will dissolve in liquids dependent on the interaction of their bonds with the liquid solvent.Rate of dissolution
The rate of dissolution depends on:- nature of the solvent and solute
- temperature (and to a small degree pressure)
- degree of undersaturation
- presence of mixing
- interfacial surface area
- presence of inhibitors (e.g., a substance adsorbed on the surface).
The rate of dissolution can be often expressed by the Noyes-Whitney equation of the form:
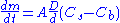
where:
- m - amount of dissolved material, kg
- t - time, seconds
- A - surface area of the interface between the dissolving substance and the solvent, m2
- D - diffusion coefficient, m2/s
- d - thickness of the boundary layer of the solvent at the surface of the dissolving substance, m
- Cs - concentration of the substance on the surface, kg/m3
- Cb - concentration of the substance in the bulk of the solvent, kg/m3
For dissolution limited by diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
, Cs is equal to the solubility of the substance.
Dissolution rates vary by orders of magnitude between different systems. Usually, substances exhibiting low solubility, exhibit low dissolution rates and vice versa.
See also
- SolvationSolvationSolvation, also sometimes called dissolution, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute...
- SolubilitySolubilitySolubility is the property of a solid, liquid, or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid, or gaseous solvent to form a homogeneous solution of the solute in the solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the used solvent as well as on...
- Solubility parameterSolubility parameterSolubility parameter may refer to parameters of solubility:*Hildebrand solubility parameter, a numerical estimate of the degree of interaction between materials, and can be a good indication of solubility...

