
Divergent series
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence
of the partial sums of the series does not have a limit
.
If a series converges, the individual terms of the series must approach zero. Thus any series in which the individual terms do not approach zero diverges. However, convergence is a stronger condition: not all series whose terms approach zero converge. The simplest counterexample is the harmonic series
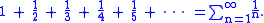
The divergence of the harmonic series was proven by the medieval mathematician Nicole Oresme.
In specialized mathematical contexts, values can be usefully assigned to certain series whose sequence of partial sums diverges. A summability method or summation method is a partial function
from the set of sequences of partial sums of series to values. For example, Cesàro summation
assigns Grandi's divergent series
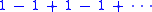
the value 1/2. Cesàro summation is an averaging method, in that it relies on the arithmetic mean
of the sequence of partial sums. Other methods involve analytic continuation
s of related series. In physics
, there are a wide variety of summability methods; these are discussed in greater detail in the article on regularization
.
. More interesting and in general more subtle are partial converse results, called tauberian theorems, from a prototype proved by Alfred Tauber
. Here partial converse means that if M sums the series Σ, and some side-condition holds, then Σ was convergent in the first place; without any side condition such a result would say that M only summed convergent series (making it useless as a summation method for divergent series).
The operator giving the sum of a convergent series is linear, and it follows from the Hahn–Banach theorem
that it may be extended to a summation method summing any series with bounded partial sums. This fact is not very useful in practice since there are many such extensions, inconsistent with each other, and also since proving such operators exist requires invoking the axiom of choice or its equivalents, such as Zorn's lemma
. They are therefore nonconstructive.
The subject of divergent series, as a domain of mathematical analysis
, is primarily concerned with explicit and natural techniques such as Abel summation, Cesàro summation
and Borel summation, and their relationships. The advent of Wiener's tauberian theorem
marked an epoch in the subject, introducing unexpected connections to Banach algebra
methods in Fourier analysis.
Summation of divergent series is also related to extrapolation
methods and sequence transformations as numerical techniques. Examples for such techniques are Padé approximant
s, Levin-type sequence transformations, and order-dependent mappings related to renormalization
techniques for large-order perturbation theory
in quantum mechanics
.
of larger and larger initial terms of the sequence, the average converges, and we can use this average instead of a limit to evaluate the sum of the series. So in evaluating we work with the sequence s, where and . In the convergent case, the sequence s approaches the limit a. A summation method can be seen as a function from a set of sequences of partial sums to values. If A is any summation method assigning values to a set of sequences, we may mechanically translate this to a series-summation method AΣ that assigns the same values to the corresponding series. There are certain properties it is desirable for these methods to possess if they are to arrive at values corresponding to limits and sums, respectively.
The third condition is less important, and some significant methods, such as Borel summation, do not possess it.
A desirable property for two distinct summation methods A and B to share is consistency: A and B are consistent if for every sequence s to which both assign a value, If two methods are consistent, and one sums more series than the other, the one summing more series is stronger.
There are powerful numerical summation methods that are neither regular nor linear, for instance nonlinear sequence transformations like Levin-type sequence transformations and Padé approximant
s, as well as the order-dependent mappings of perturbative series based on renormalization
techniques.
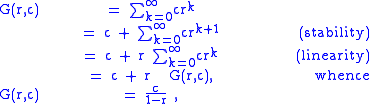
can be evaluated regardless of convergence. More rigorously, any summation method that possesses these properties and which assigns a finite value to the geometric series must assign this value. However, when r is a real number larger than 1, the partial sums increase without bound, and averaging methods assign a limit of ∞.
If now we transform a sequence s by using p to give weighted means, setting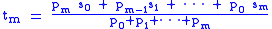
then the limit of tn as n goes to infinity is an average called the Nörlund
mean Np(s).
The Nörlund mean is regular, linear, and stable. Moreover, any two Nörlund means are consistent. The most significant of the Nörlund means are the Cesàro sums. Here, if we define the sequence pk by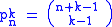
then the Cesàro sum Ck is defined by Cesàro sums are Nörlund means if , and hence are regular, linear, stable, and consistent. C0 is ordinary summation, and C1 is ordinary Cesàro summation
. Cesàro sums have the property that if then Ch is stronger than Ck.
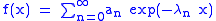
converges for all positive real numbers x. Then the Abelian mean Aλ is defined as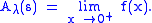
A series of this type is known as a generalized Dirichlet series; in applications to physics, this is known as the method of heat-kernel regularization.
Abelian means are regular, linear, and stable, but not always consistent between different choices of λ. However, some special cases are very important summation methods.
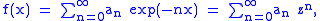
where z = exp(−x). Then the limit of ƒ(x) as x approaches 0 through positive reals is the limit of the power series for ƒ(z) as z approaches 1 from below through positive reals, and the Abel sum A(s) is defined as
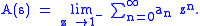
Abel summation is interesting in part because it is consistent with but more powerful than Cesàro summation: whenever the latter is defined. The Abel sum is therefore regular, linear, stable, and consistent with Cesàro summation.
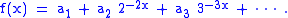
Then L(s), the Lindelöf sum , is the limit of ƒ(x) as x goes to zero. The Lindelöf sum is a powerful method when applied to power series among other applications, summing power series in the Mittag-Leffler star
.
If g(z) is analytic in a disk around zero, and hence has a Maclaurin series G(z) with a positive radius of convergence, then in the Mittag-Leffler star. Moreover, convergence to g(z) is uniform on compact subsets of the star.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
of the partial sums of the series does not have a limit
Limit of a sequence
The limit of a sequence is, intuitively, the unique number or point L such that the terms of the sequence become arbitrarily close to L for "large" values of n...
.
If a series converges, the individual terms of the series must approach zero. Thus any series in which the individual terms do not approach zero diverges. However, convergence is a stronger condition: not all series whose terms approach zero converge. The simplest counterexample is the harmonic series
Harmonic series (mathematics)
In mathematics, the harmonic series is the divergent infinite series:Its name derives from the concept of overtones, or harmonics in music: the wavelengths of the overtones of a vibrating string are 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, etc., of the string's fundamental wavelength...
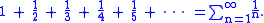
The divergence of the harmonic series was proven by the medieval mathematician Nicole Oresme.
In specialized mathematical contexts, values can be usefully assigned to certain series whose sequence of partial sums diverges. A summability method or summation method is a partial function
Partial function
In mathematics, a partial function from X to Y is a function ƒ: X' → Y, where X' is a subset of X. It generalizes the concept of a function by not forcing f to map every element of X to an element of Y . If X' = X, then ƒ is called a total function and is equivalent to a function...
from the set of sequences of partial sums of series to values. For example, Cesàro summation
Cesàro summation
In mathematical analysis, Cesàro summation is an alternative means of assigning a sum to an infinite series. If the series converges in the usual sense to a sum A, then the series is also Cesàro summable and has Cesàro sum A...
assigns Grandi's divergent series
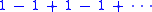
the value 1/2. Cesàro summation is an averaging method, in that it relies on the arithmetic mean
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
of the sequence of partial sums. Other methods involve analytic continuation
Analytic continuation
In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, analytic continuation is a technique to extend the domain of a given analytic function. Analytic continuation often succeeds in defining further values of a function, for example in a new region where an infinite series representation in terms of which...
s of related series. In physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, there are a wide variety of summability methods; these are discussed in greater detail in the article on regularization
Regularization (physics)
-Introduction:In physics, especially quantum field theory, regularization is a method of dealing with infinite, divergent, and non-sensical expressions by introducing an auxiliary concept of a regulator...
.
Theorems on methods for summing divergent series
A summability method M is regular if it agrees with the actual limit on all convergent series. Such a result is called an abelian theorem for M, from the prototypical Abel's theoremAbel's theorem
In mathematics, Abel's theorem for power series relates a limit of a power series to the sum of its coefficients. It is named after Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel.-Theorem:...
. More interesting and in general more subtle are partial converse results, called tauberian theorems, from a prototype proved by Alfred Tauber
Alfred Tauber
Alfred Tauber was a mathematician who was born in Bratislava, and died in the Theresienstadt concentration camp. In 1897 he proved a corrected converse of Abel's theorem. G.H. Hardy and J.E. Littlewood coined the term Tauberian to describe converse theorems like that proved by Tauber.- External...
. Here partial converse means that if M sums the series Σ, and some side-condition holds, then Σ was convergent in the first place; without any side condition such a result would say that M only summed convergent series (making it useless as a summation method for divergent series).
The operator giving the sum of a convergent series is linear, and it follows from the Hahn–Banach theorem
Hahn–Banach theorem
In mathematics, the Hahn–Banach theorem is a central tool in functional analysis. It allows the extension of bounded linear functionals defined on a subspace of some vector space to the whole space, and it also shows that there are "enough" continuous linear functionals defined on every normed...
that it may be extended to a summation method summing any series with bounded partial sums. This fact is not very useful in practice since there are many such extensions, inconsistent with each other, and also since proving such operators exist requires invoking the axiom of choice or its equivalents, such as Zorn's lemma
Zorn's lemma
Zorn's lemma, also known as the Kuratowski–Zorn lemma, is a proposition of set theory that states:Suppose a partially ordered set P has the property that every chain has an upper bound in P...
. They are therefore nonconstructive.
The subject of divergent series, as a domain of mathematical analysis
Mathematical analysis
Mathematical analysis, which mathematicians refer to simply as analysis, has its beginnings in the rigorous formulation of infinitesimal calculus. It is a branch of pure mathematics that includes the theories of differentiation, integration and measure, limits, infinite series, and analytic functions...
, is primarily concerned with explicit and natural techniques such as Abel summation, Cesàro summation
Cesàro summation
In mathematical analysis, Cesàro summation is an alternative means of assigning a sum to an infinite series. If the series converges in the usual sense to a sum A, then the series is also Cesàro summable and has Cesàro sum A...
and Borel summation, and their relationships. The advent of Wiener's tauberian theorem
Wiener's tauberian theorem
In mathematical analysis, Wiener's tauberian theorem refers to one of several related results proved by Norbert Wiener in 1932. They provide a necessary and sufficient condition under which any function in or can be approximated by linear combinations of translations of a given...
marked an epoch in the subject, introducing unexpected connections to Banach algebra
Banach algebra
In mathematics, especially functional analysis, a Banach algebra, named after Stefan Banach, is an associative algebra A over the real or complex numbers which at the same time is also a Banach space...
methods in Fourier analysis.
Summation of divergent series is also related to extrapolation
Extrapolation
In mathematics, extrapolation is the process of constructing new data points. It is similar to the process of interpolation, which constructs new points between known points, but the results of extrapolations are often less meaningful, and are subject to greater uncertainty. It may also mean...
methods and sequence transformations as numerical techniques. Examples for such techniques are Padé approximant
Padé approximant
Padé approximant is the "best" approximation of a function by a rational function of given order - under this technique, the approximant's power series agrees with the power series of the function it is approximating....
s, Levin-type sequence transformations, and order-dependent mappings related to renormalization
Renormalization
In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities....
techniques for large-order perturbation theory
Perturbation theory
Perturbation theory comprises mathematical methods that are used to find an approximate solution to a problem which cannot be solved exactly, by starting from the exact solution of a related problem...
in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
.
Properties of summation methods
Summation methods usually concentrate on the sequence of partial sums of the series. While this sequence does not converge, we may often find that when we take an averageAverage
In mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
of larger and larger initial terms of the sequence, the average converges, and we can use this average instead of a limit to evaluate the sum of the series. So in evaluating we work with the sequence s, where and . In the convergent case, the sequence s approaches the limit a. A summation method can be seen as a function from a set of sequences of partial sums to values. If A is any summation method assigning values to a set of sequences, we may mechanically translate this to a series-summation method AΣ that assigns the same values to the corresponding series. There are certain properties it is desirable for these methods to possess if they are to arrive at values corresponding to limits and sums, respectively.
- Regularity. A summation method is regular if, whenever the sequence s converges to x, Equivalently, the corresponding series-summation method evaluates
- Linearity. A is linear if it is a linear functional on the sequences where it is defined, so that and for k a scalar (real or complex.) Since the terms of the series a are linear functionals on the sequence s and vice versa, this is equivalent to AΣ being a linear functional on the terms of the series.
- Stability. If s is a sequence starting from s0 and s′ is the sequence obtained by omitting the first value and subtracting it from the rest, so that , then A(s) is defined if and only if A(s′) is defined, and Equivalently, whenever for all n, then
The third condition is less important, and some significant methods, such as Borel summation, do not possess it.
A desirable property for two distinct summation methods A and B to share is consistency: A and B are consistent if for every sequence s to which both assign a value, If two methods are consistent, and one sums more series than the other, the one summing more series is stronger.
There are powerful numerical summation methods that are neither regular nor linear, for instance nonlinear sequence transformations like Levin-type sequence transformations and Padé approximant
Padé approximant
Padé approximant is the "best" approximation of a function by a rational function of given order - under this technique, the approximant's power series agrees with the power series of the function it is approximating....
s, as well as the order-dependent mappings of perturbative series based on renormalization
Renormalization
In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities....
techniques.
Axiomatic methods
Taking regularity, linearity and stability as axioms, it is possible to sum many divergent series by elementary algebraic manipulations. For instance, whenever the geometric series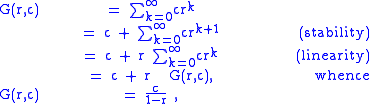
can be evaluated regardless of convergence. More rigorously, any summation method that possesses these properties and which assigns a finite value to the geometric series must assign this value. However, when r is a real number larger than 1, the partial sums increase without bound, and averaging methods assign a limit of ∞.
Nörlund means
Suppose pn is a sequence of positive terms, starting from p0. Suppose also that
If now we transform a sequence s by using p to give weighted means, setting
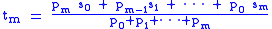
then the limit of tn as n goes to infinity is an average called the Nörlund
Niels Erik Nörlund
Niels Erik Nørlund was a Danish mathematician.His book Vorlesungen über Differenzenrechnung was the first bookon complex function solutions of difference equations....
mean Np(s).
The Nörlund mean is regular, linear, and stable. Moreover, any two Nörlund means are consistent. The most significant of the Nörlund means are the Cesàro sums. Here, if we define the sequence pk by
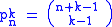
then the Cesàro sum Ck is defined by Cesàro sums are Nörlund means if , and hence are regular, linear, stable, and consistent. C0 is ordinary summation, and C1 is ordinary Cesàro summation
Cesàro summation
In mathematical analysis, Cesàro summation is an alternative means of assigning a sum to an infinite series. If the series converges in the usual sense to a sum A, then the series is also Cesàro summable and has Cesàro sum A...
. Cesàro sums have the property that if then Ch is stronger than Ck.
Abelian means
Suppose λ = {λ0, λ1, λ2, ...} is a strictly increasing sequence tending towards infinity, and that . Recall that is the associated series whose partial sums form the sequence s. Suppose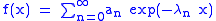
converges for all positive real numbers x. Then the Abelian mean Aλ is defined as
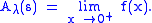
A series of this type is known as a generalized Dirichlet series; in applications to physics, this is known as the method of heat-kernel regularization.
Abelian means are regular, linear, and stable, but not always consistent between different choices of λ. However, some special cases are very important summation methods.
Abel summation
If , then we obtain the method of Abel summation. Here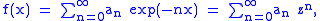
where z = exp(−x). Then the limit of ƒ(x) as x approaches 0 through positive reals is the limit of the power series for ƒ(z) as z approaches 1 from below through positive reals, and the Abel sum A(s) is defined as
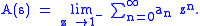
Abel summation is interesting in part because it is consistent with but more powerful than Cesàro summation: whenever the latter is defined. The Abel sum is therefore regular, linear, stable, and consistent with Cesàro summation.
Lindelöf summation
If , then (indexing from one) we have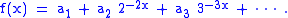
Then L(s), the Lindelöf sum , is the limit of ƒ(x) as x goes to zero. The Lindelöf sum is a powerful method when applied to power series among other applications, summing power series in the Mittag-Leffler star
Mittag-Leffler star
In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, the Mittag-Leffler star of a complex-analytic function is a set in the complex plane obtained by attempting to extend that function along rays emanating from a given point...
.
If g(z) is analytic in a disk around zero, and hence has a Maclaurin series G(z) with a positive radius of convergence, then in the Mittag-Leffler star. Moreover, convergence to g(z) is uniform on compact subsets of the star.
See also
- 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + · · ·
- 1 − 2 + 4 − 8 + · · ·
- 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + · · ·
- 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + · · ·
- 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + · · ·1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + · · ·In mathematics, 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + … is the infinite series whose terms are the successive powers of two. As a geometric series, it is characterized by its first term, 1, and its common ratio, 2. As a series of real numbers it diverges to infinity, so in the usual sense it has no sum...
- Grandi's series
- Borel summation
- Lambert summationLambert summationIn mathematical analysis, Lambert summation is a summability method for a class of divergent series.-Definition:A series \sum a_n is Lambert summable to A, written \sum a_n = A , if...
- Silverman–Toeplitz theoremSilverman–Toeplitz theoremIn mathematics, the Silverman–Toeplitz theorem, first proved by Otto Toeplitz, is a result in summability theory characterizing matrix summability methods that are regular...

