
Electric susceptibility
Encyclopedia
In electromagnetism
, the electric susceptibility (latin
(latin
: susceptibilis “receptiveness”) is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of polarization
of a dielectric
material in response to an applied electric field
. The greater the electric susceptibility, the greater the ability of a material to polarize in response to the field, and thereby reduce the total electric field inside the material (and store energy). It is in this way that the electric susceptibility influences the electric permittivity
of the material and thus influences many other phenomena in that medium, from the capacitance of capacitors to the speed of light
.
) relating an electric field
E to the induced dielectric
polarization density P such that:
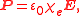
Where:
The susceptibility is also related to the polarizability
of individual particles in the medium by the Clausius-Mossotti relation
. The susceptibility is related to its relative permittivity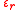 by:
by:
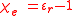
So in the case of a vacuum:
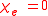
At the same time, the electric displacement D is related to the polarization density P by:
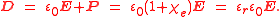
to the local electric field E that induced the dipole. This parameter is the molecular polarizability and the dipole moment resulting from the local electric field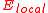 is given by:
is given by:

This introduces a complication however, as locally the field can differ significantly from the overall applied field. We have:
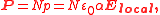
where P is the polarization per unit volume, and N is the number of molecules per unit volume contributing to the polarization. Thus, if the local electric field is parallel to the ambient electric field, we have:
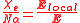
Thus only if the local field equals the ambient field can we write:

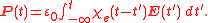
That is, the polarization is a convolution
of the electric field at previous times with time-dependent susceptibility given by . The upper limit of this integral can be extended to infinity as well if one defines
. The upper limit of this integral can be extended to infinity as well if one defines 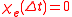 for
for  . An instantaneous response corresponds to Dirac delta function
. An instantaneous response corresponds to Dirac delta function
susceptibility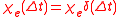 .
.
It is more convenient in a linear system to take the Fourier transform
and write this relationship as a function of frequency. Due to the convolution theorem
, the integral becomes a simple product,
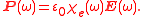
This frequency dependence of the susceptibility leads to frequency dependence of the permittivity. The shape of the susceptibility with respect to frequency characterizes the dispersion
properties of the material.
Moreover, the fact that the polarization can only depend on the electric field at previous times (i.e.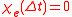 for
for 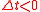 ), a consequence of causality
), a consequence of causality
, imposes Kramers–Kronig constraints on the susceptibility .
.
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
, the electric susceptibility
 (latin
(latinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
: susceptibilis “receptiveness”) is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of polarization
Polarization density
In classical electromagnetism, polarization density is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced electric dipole moments in a dielectric material. When a dielectric is placed in an external electric field, its molecules gain electric dipole moment and the dielectric is...
of a dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
material in response to an applied electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
. The greater the electric susceptibility, the greater the ability of a material to polarize in response to the field, and thereby reduce the total electric field inside the material (and store energy). It is in this way that the electric susceptibility influences the electric permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
of the material and thus influences many other phenomena in that medium, from the capacitance of capacitors to the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
.
Definition of Volume Susceptibility
Electric susceptibility is defined as the constant of proportionality (which may be a tensorTensor
Tensors are geometric objects that describe linear relations between vectors, scalars, and other tensors. Elementary examples include the dot product, the cross product, and linear maps. Vectors and scalars themselves are also tensors. A tensor can be represented as a multi-dimensional array of...
) relating an electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
E to the induced dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
polarization density P such that:
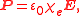
Where:
-
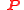 is the Polarization Density
is the Polarization Density -
 is the Electric Permittivity of Free Space
is the Electric Permittivity of Free Space -
 is the Electric Susceptibility
is the Electric Susceptibility -
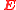 is the Electric Field
is the Electric Field
The susceptibility is also related to the polarizability
Polarizability
Polarizability is the measure of the change in a molecule's electron distribution in response to an applied electric field, which can also be induced by electric interactions with solvents or ionic reagents. It is a property of matter...
of individual particles in the medium by the Clausius-Mossotti relation
Clausius-Mossotti relation
The Clausius–Mossotti relation is named after the Italian physicist Ottaviano-Fabrizio Mossotti, whose 1850 book analyzed the relationship between the dielectric constants of two different media, and the German physicist Rudolf Clausius, who gave the formula explicitly in his 1879 book in the...
. The susceptibility is related to its relative permittivity
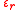 by:
by:
So in the case of a vacuum:
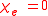
At the same time, the electric displacement D is related to the polarization density P by:
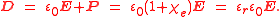
Molecular Polarizability
A similar parameter exists to relate the magnitude of the induced dipole moment p of an individual moleculeMolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
to the local electric field E that induced the dipole. This parameter is the molecular polarizability and the dipole moment resulting from the local electric field
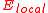 is given by:
is given by:
This introduces a complication however, as locally the field can differ significantly from the overall applied field. We have:
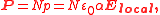
where P is the polarization per unit volume, and N is the number of molecules per unit volume contributing to the polarization. Thus, if the local electric field is parallel to the ambient electric field, we have:
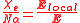
Thus only if the local field equals the ambient field can we write:

Dispersion and causality
In general, a material cannot polarize instantaneously in response to an applied field, and so the more general formulation as a function of time is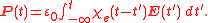
That is, the polarization is a convolution
Convolution
In mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
of the electric field at previous times with time-dependent susceptibility given by
 . The upper limit of this integral can be extended to infinity as well if one defines
. The upper limit of this integral can be extended to infinity as well if one defines 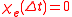 for
for  . An instantaneous response corresponds to Dirac delta function
. An instantaneous response corresponds to Dirac delta functionDirac delta function
The Dirac delta function, or δ function, is a generalized function depending on a real parameter such that it is zero for all values of the parameter except when the parameter is zero, and its integral over the parameter from −∞ to ∞ is equal to one. It was introduced by theoretical...
susceptibility
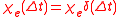 .
.It is more convenient in a linear system to take the Fourier transform
Continuous Fourier transform
The Fourier transform is a mathematical operation that decomposes a function into its constituent frequencies, known as a frequency spectrum. For instance, the transform of a musical chord made up of pure notes is a mathematical representation of the amplitudes of the individual notes that make...
and write this relationship as a function of frequency. Due to the convolution theorem
Convolution theorem
In mathematics, the convolution theorem states that under suitableconditions the Fourier transform of a convolution is the pointwise product of Fourier transforms. In other words, convolution in one domain equals point-wise multiplication in the other domain...
, the integral becomes a simple product,
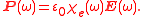
This frequency dependence of the susceptibility leads to frequency dependence of the permittivity. The shape of the susceptibility with respect to frequency characterizes the dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
properties of the material.
Moreover, the fact that the polarization can only depend on the electric field at previous times (i.e.
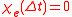 for
for 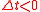 ), a consequence of causality
), a consequence of causalityCausality
Causality is the relationship between an event and a second event , where the second event is understood as a consequence of the first....
, imposes Kramers–Kronig constraints on the susceptibility
 .
.See also
- Application of tensor theory in physics
- Magnetic susceptibilityMagnetic susceptibilityIn electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field...
- Maxwell's equationsMaxwell's equationsMaxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
- PermittivityPermittivityIn electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
- Clausius-Mossotti relationClausius-Mossotti relationThe Clausius–Mossotti relation is named after the Italian physicist Ottaviano-Fabrizio Mossotti, whose 1850 book analyzed the relationship between the dielectric constants of two different media, and the German physicist Rudolf Clausius, who gave the formula explicitly in his 1879 book in the...
- Linear response functionLinear response functionA linear response function describes the input-output relationship of a signal transducer such as a radio turning electromagnetic waves into music or a neuron turning synaptic input into a response...
- Green–Kubo relations

