Electron pair
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
, an electron pair consists of two electrons that occupy the same orbital
but have opposite spins.
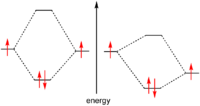 Because electrons are fermion
Because electrons are fermion
s, the Pauli exclusion principle
forbids these particles from having exactly the same quantum numbers. Therefore the only way to occupy the same orbital, i.e. have the same orbital quantum numbers, is to differ in the spin quantum number
. This limits the number of electrons in the same orbital to exactly two.
The pairing of spins is often energetically favorable and electron pairs therefore play a very large role in chemistry
. They can form
Because the spins are paired, the magnetic moment of the electrons cancels and the contribution of the pair to the magnetic properties will in general be a diamagnetic one
.
Although a strong tendency to pair off electrons can be observed in chemistry, it is also possible that electrons occur as unpaired electron
s.
In the case of metallic bonding the magnetic moments also compensate to a large extent, but the bonding is more communal so that individual pairs of electrons cannot be distinguished and it is better to consider the electrons as a collective 'ocean'.
A very special case of electron pair formation occurs in superconductivity
: the formation of Cooper pair
s.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, an electron pair consists of two electrons that occupy the same orbital
Molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term "orbital" was first...
but have opposite spins.

Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is any particle which obeys the Fermi–Dirac statistics . Fermions contrast with bosons which obey Bose–Einstein statistics....
s, the Pauli exclusion principle
Pauli exclusion principle
The Pauli exclusion principle is the quantum mechanical principle that no two identical fermions may occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. A more rigorous statement is that the total wave function for two identical fermions is anti-symmetric with respect to exchange of the particles...
forbids these particles from having exactly the same quantum numbers. Therefore the only way to occupy the same orbital, i.e. have the same orbital quantum numbers, is to differ in the spin quantum number
Spin quantum number
In atomic physics, the spin quantum number is a quantum number that parameterizes the intrinsic angular momentum of a given particle...
. This limits the number of electrons in the same orbital to exactly two.
The pairing of spins is often energetically favorable and electron pairs therefore play a very large role in chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
. They can form
- a chemical bondChemical bondA chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
between two atoms - as a lone pairLone pairIn chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
. - fill the core levelsCore electronCore electrons are the electrons in an atom that are not valence electrons and therefore do not participate in bonding. An example: the carbon atom has a total of 6 electrons, 4 of them being valence electrons. So the remaining 2 electrons must be core electrons.They are so tightly bound to the...
of an atom.
Because the spins are paired, the magnetic moment of the electrons cancels and the contribution of the pair to the magnetic properties will in general be a diamagnetic one
Diamagnetism
Diamagnetism is the property of an object which causes it to create a magnetic field in opposition to an externally applied magnetic field, thus causing a repulsive effect. Specifically, an external magnetic field alters the orbital velocity of electrons around their nuclei, thus changing the...
.
Although a strong tendency to pair off electrons can be observed in chemistry, it is also possible that electrons occur as unpaired electron
Unpaired electron
In chemistry, an unpaired electron is an electron that occupies an orbital of an atom singly, rather than as part of an electron pair. As the formation of electron pairs is often energetically favourable, either in the form of a chemical bond or as a lone pair, unpaired electrons are relatively...
s.
In the case of metallic bonding the magnetic moments also compensate to a large extent, but the bonding is more communal so that individual pairs of electrons cannot be distinguished and it is better to consider the electrons as a collective 'ocean'.
A very special case of electron pair formation occurs in superconductivity
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance occurring in certain materials below a characteristic temperature. It was discovered by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum...
: the formation of Cooper pair
Cooper pair
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair is two electrons that are bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper...
s.

