
Electrowinning
Encyclopedia
Electrowinning, also called electroextraction, is the electrodeposition
of metal
s from their ore
s that have been put in solution or liquefied. Electrorefining uses a similar process to remove impurities from a metal. Both processes use electroplating
on a large scale and are important techniques for the economical and straightforward purification of non-ferrous metals. The resulting metals are said to be electrowon.
In electrowinning, a current is passed from an inert anode through a liquid leach solution containing the metal so that the metal is extracted as it is deposited in an electroplating process onto the cathode. In electrorefining, the anodes consist of unrefined impure metal, and as the current passes through the acidic electrolyte the anodes are corroded into the solution so that the electroplating process deposits refined pure metal onto the cathodes.
process.
The English chemist Humphry Davy
obtained sodium
metal in elemental
form for the first time in 1807 by the electrolysis
of molten sodium hydroxide.
Electrorefining of copper was first demonstrated experimentally by Maximilian, Duke of Leuchtenberg
in 1847.
James Elkington patented the commercial process in 1865 and opened the first successful plant in Pembrey
, Wales in 1870. The first commercial plant in the United States was the Balbach and Sons Refining and Smelting Company in Newark, New Jersey in 1883.
, copper
, gold
, silver
, zinc
, aluminium
, chromium
, cobalt
, manganese
, and the rare-earth and alkali metal
s. For aluminium, this is the only production process employed. Several industrially important active metals (which react strongly with water) are produced commercially by electrolysis of their pyrochemical molten salts. Experiments using electrorefining to process spent nuclear fuel have been carried out. Electrorefining may be able to separate heavy metals such as plutonium
, caesium
, and strontium
from the less-toxic bulk of uranium
. Many electroextraction systems are also available to remove toxic (and sometimes valuable) metals from industrial waste streams.
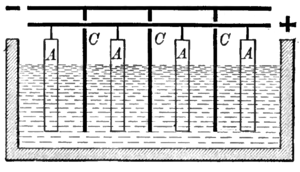 Most metals occur in nature in their oxidized form (ore
Most metals occur in nature in their oxidized form (ore
s) and thus must be reduced to their metallic forms. The ore is dissolved following some preprocessing in an aqueous electrolyte
or in a molten salt
and the resulting solution is electrolyzed. The metal is deposited on the cathode
(either in solid or in liquid form), while the anodic
reaction is usually oxygen evolution
. Several metals are naturally present as metal sulfide
s; these include copper
, lead
, molybdenum
, cadmium
, nickel
, silver
, cobalt
, and zinc
. In addition, gold
and platinum
group metals are associated with sulfidic base metal ores. Most metal sulfides or their salts, are electrically conductive and this allows electrochemical redox reactions to efficiently occur in the molten state or in aqueous solutions.
Some metals, including arsenic
and nickel do not electrolyze out but remain in the electrolyte solution. These are then reduced by chemical reactions to refine the metal. Other metals, which during the processing of the target metal have been reduced but not deposited at the cathode, sink to the bottom of the electrolytic cell, where they form a substance referred to as anode sludge or anode slime. The metals in this sludge can be removed by standard pyrorefining
methods.
Because metal deposition rates are related to available surface area, maintaining properly working cathodes is important. Two cathode types exist, flat-plate and reticulated cathodes, each with its own advantages. Flat-plate cathodes can be cleaned and reused, and plated metals recovered. Reticulated cathodes have a much higher deposition rate compared to flat-plate cathodes. However, they are not reusable and must be sent off for recycling. Alternatively, starter cathodes of pre-refined metal can be used, which become an integral part of the finished metal ready for rolling or further processing.
Electrodeposition
Electrodeposition may refer to:*Electroplating*Electrophoretic deposition*Underpotential deposition...
of metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
s from their ore
Ore
An ore is a type of rock that contains minerals with important elements including metals. The ores are extracted through mining; these are then refined to extract the valuable element....
s that have been put in solution or liquefied. Electrorefining uses a similar process to remove impurities from a metal. Both processes use electroplating
Electroplating
Electroplating is a plating process in which metal ions in a solution are moved by an electric field to coat an electrode. The process uses electrical current to reduce cations of a desired material from a solution and coat a conductive object with a thin layer of the material, such as a metal...
on a large scale and are important techniques for the economical and straightforward purification of non-ferrous metals. The resulting metals are said to be electrowon.
In electrowinning, a current is passed from an inert anode through a liquid leach solution containing the metal so that the metal is extracted as it is deposited in an electroplating process onto the cathode. In electrorefining, the anodes consist of unrefined impure metal, and as the current passes through the acidic electrolyte the anodes are corroded into the solution so that the electroplating process deposits refined pure metal onto the cathodes.
History
Electrowinning is the oldest industrial electrolyticElectrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
process.
The English chemist Humphry Davy
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet FRS MRIA was a British chemist and inventor. He is probably best remembered today for his discoveries of several alkali and alkaline earth metals, as well as contributions to the discoveries of the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine...
obtained sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
metal in elemental
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
form for the first time in 1807 by the electrolysis
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
of molten sodium hydroxide.
Electrorefining of copper was first demonstrated experimentally by Maximilian, Duke of Leuchtenberg
Maximilian, Duke of Leuchtenberg
Maximilian Joseph Eugene Auguste Napoleon de Beauharnais , 3rd Duke of Leuchtenberg, 3rd Prince of Venice Prince des Français and Hereditary Prince of the Kingdom of Italy and claimant to the Grand Duchy of Frankfurt was the husband of Grand Duchess Maria Nikolayevna of...
in 1847.
James Elkington patented the commercial process in 1865 and opened the first successful plant in Pembrey
Pembrey
Pembrey is a village in Carmarthenshire Wales, situated between Burry Port and Kidwelly, overlooking Carmarthen Bay.-History:The name Pembrey is an Anglicisation of the Welsh, Pen-bre...
, Wales in 1870. The first commercial plant in the United States was the Balbach and Sons Refining and Smelting Company in Newark, New Jersey in 1883.
Applications
The most common electrowon metals are leadLead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
, chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
, cobalt
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal....
, manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
, and the rare-earth and alkali metal
Alkali metal
The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium...
s. For aluminium, this is the only production process employed. Several industrially important active metals (which react strongly with water) are produced commercially by electrolysis of their pyrochemical molten salts. Experiments using electrorefining to process spent nuclear fuel have been carried out. Electrorefining may be able to separate heavy metals such as plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
, caesium
Caesium
Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature...
, and strontium
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and...
from the less-toxic bulk of uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
. Many electroextraction systems are also available to remove toxic (and sometimes valuable) metals from industrial waste streams.
Process

Ore
An ore is a type of rock that contains minerals with important elements including metals. The ores are extracted through mining; these are then refined to extract the valuable element....
s) and thus must be reduced to their metallic forms. The ore is dissolved following some preprocessing in an aqueous electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
or in a molten salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
and the resulting solution is electrolyzed. The metal is deposited on the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
(either in solid or in liquid form), while the anodic
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
reaction is usually oxygen evolution
Oxygen evolution
Oxygen evolution is the process of generating molecular oxygen through chemical reaction. Mechanisms of oxygen evolution include the oxidation of water during oxygenic photosynthesis, electrolysis of water into oxygen and hydrogen, and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution from oxides and...
. Several metals are naturally present as metal sulfide
Sulfide
A sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
s; these include copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
, cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
, nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, cobalt
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal....
, and zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
. In addition, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
and platinum
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
group metals are associated with sulfidic base metal ores. Most metal sulfides or their salts, are electrically conductive and this allows electrochemical redox reactions to efficiently occur in the molten state or in aqueous solutions.
Some metals, including arsenic
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid...
and nickel do not electrolyze out but remain in the electrolyte solution. These are then reduced by chemical reactions to refine the metal. Other metals, which during the processing of the target metal have been reduced but not deposited at the cathode, sink to the bottom of the electrolytic cell, where they form a substance referred to as anode sludge or anode slime. The metals in this sludge can be removed by standard pyrorefining
Pyrometallurgy
Pyrometallurgy is a branch of extractive metallurgy. It consists of the thermal treatment of minerals and metallurgical ores and concentrates to bring about physical and chemical transformations in the materials to enable recovery of valuable metals...
methods.
Because metal deposition rates are related to available surface area, maintaining properly working cathodes is important. Two cathode types exist, flat-plate and reticulated cathodes, each with its own advantages. Flat-plate cathodes can be cleaned and reused, and plated metals recovered. Reticulated cathodes have a much higher deposition rate compared to flat-plate cathodes. However, they are not reusable and must be sent off for recycling. Alternatively, starter cathodes of pre-refined metal can be used, which become an integral part of the finished metal ready for rolling or further processing.

