European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites
Encyclopedia
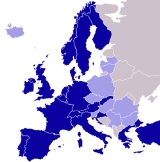
EUMETSAT is an intergovernmental organisation created through an international convention agreed by a current total of 26 European Member States: Austria
, Belgium
, Croatia
, the Czech Republic
, Denmark
, Finland
, France
, Germany
, Greece
, Hungary
, Ireland
, Romania
, Italy
, Latvia
, Luxembourg
, the Netherlands
, Norway
, Poland
, Portugal
, Slovakia
, Slovenia
, Spain
, Sweden
, Switzerland
, Turkey
, and the United Kingdom
. These States fund the EUMETSAT programs and are the principal users of the systems. EUMETSAT also has 5 Cooperating States. Cooperation agreements with Iceland
, Lithuania
, Bulgaria
, Estonia
and Serbia
have entered into force. The convention establishing EUMETSAT was opened for signature in 1983 and entered into force in 19 June 1986.
EUMETSAT's primary objective is to establish, maintain and exploit European systems of operational meteorological satellite
s. EUMETSAT is responsible for the launch and operation of the satellite
s and for delivering satellite data to end-users as well as contributing to the operational monitoring of climate
and the detection of global climate changes.
The activities of EUMETSAT contribute to a global meteorological satellite observing system coordinated with other space-faring nations.
Satellite observations are an essential input to numerical weather prediction systems and also assist the human forecaster in the diagnosis of potentially hazardous weather developments. Of growing importance is the capacity of weather satellites to gather long term measurements from space in support of climate change studies.
EUMETSAT is not part of the European Union
.
 The national mandatory contributions of member states are proportional to their gross national income
The national mandatory contributions of member states are proportional to their gross national income
. However, the cooperating countries contribute only half of the fee they would pay for full membership. The contribution level are those published at end of 2006, for the mandatory programs.
Additionally, some member states may be approved to extend their level of contributions, to compensate for operational deficits. When such contributions are approved by the EUMETSAT council, or if the member states participate to the optional Jason-2 Altimetry program, they get additional voting coefficient rights (most members participate to the optional Jason-2 program, with the current exception of Austria and Poland).
Full member states of the organization have free full access to the images, data and other information produced by EUMETSAT. Cooperating states benefit from reduced fees for accessing the same data, but may get free full access in case of emergency or threats of meteorological disasters. Exceptionally, some non-member states, participating to the WMO
, may get access to some data for the same reason.
Many poor non-member states around the world also get free access to Meteosat data, when their yearly gross national income does not exceed 3500 USD per capita, based on World bank
statistics reports.


While geostationary satellites provide a continuous view of the earth disc from an apparently stationary position in space, the instruments on polar orbiting satellites
, flying at a much lower altitude, provide more precise details about atmospheric temperature and moisture profiles, although with a less frequent global coverage.
The lack of observational coverage in certain parts of the globe, particularly the Pacific Ocean
and continents of the southern hemisphere
, has led to the increasingly important role for polar orbiting satellite data in numerical weather prediction
and climate monitoring.
From 2006, the continuous view of the Earth provided by Meteosat-8 is expected to be complemented by data from the first operational European meteorological satellite flying in the lower orbit — MetOp
.
Positioned at approximately 850 km above the Earth, special instruments on board this spacecraft will be able to deliver far more precise details about atmospheric temperature and moisture profiles than a geostationary satellite.
EUMETSAT Polar System (EPS) satellites will also ensure that the more remote regions of the globe, particularly in Northern Europe as well as the oceans of the Southern hemisphere, will be fully covered.
The three MetOp satellites form the space segment of EPS. The first satellite, MetOp A, was successfully launched by a Russia
n Soyuz-2.1a rocket from Baikonur
on October 19, 2006, at 22:28 Baikonur time (16:28 UTC).
The EPS program is also the European half of a joint program with NOAA, called the International Joint Polar System. NOAA has operated a continuous series of low earth orbiting meteorological satellite since April 1960. Many of the instruments on Metop are also operated on NOAA/POES satellites, providing similar data types across the IJPS.
The Metop satellite was initially controlled by ESOC for the LEOP
phase immediately following launch, with control handed over to Eumetsat around 72 hours after liftoff. Eumetsat's first commands to the satellite were sent at 14:04 UTC on October 22, 2006.
Construction on the second satellite, Metop B, has been completed. Launch is scheduled for April 2012, with Metop C launching sometime in 2017.
Jason-2 is planned to fly at an altitude of around 1300 km. The main instruments on board are a radar altimeter
, a microwave radiometer
, and orbit determination
systems. The aim is to measure the global sea surface height to an accuracy of a few cm every 10 days, for determining ocean circulation, climate change
and sea level rise.
This program is funded separately and is not, for now, part of the mandatory programs for member and cooperating countries. Almost all members have joined this program and get additional voting rights.
Jason-2 was launched successfully from Vandenberg Air Force Base
aboard a Delta-II rocket on 20 June 2008, 7:46 UTC. http://www.eumetsat.int/Home/Main/What_We_Do/Highlights/SP_1213708779383?l=en
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
, the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
, Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
, Ireland
Republic of Ireland
Ireland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
, Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. These States fund the EUMETSAT programs and are the principal users of the systems. EUMETSAT also has 5 Cooperating States. Cooperation agreements with Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
and Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
have entered into force. The convention establishing EUMETSAT was opened for signature in 1983 and entered into force in 19 June 1986.
EUMETSAT's primary objective is to establish, maintain and exploit European systems of operational meteorological satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
s. EUMETSAT is responsible for the launch and operation of the satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
s and for delivering satellite data to end-users as well as contributing to the operational monitoring of climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
and the detection of global climate changes.
The activities of EUMETSAT contribute to a global meteorological satellite observing system coordinated with other space-faring nations.
Satellite observations are an essential input to numerical weather prediction systems and also assist the human forecaster in the diagnosis of potentially hazardous weather developments. Of growing importance is the capacity of weather satellites to gather long term measurements from space in support of climate change studies.
EUMETSAT is not part of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
.
Member and cooperating states

Gross National Income
The GNI consists of: the personal consumption expenditures, the gross private investment, the government consumption expenditures, the net income from assets abroad , and the gross exports of goods and services, after deducting two components: the gross imports of goods and services, and the...
. However, the cooperating countries contribute only half of the fee they would pay for full membership. The contribution level are those published at end of 2006, for the mandatory programs.
Additionally, some member states may be approved to extend their level of contributions, to compensate for operational deficits. When such contributions are approved by the EUMETSAT council, or if the member states participate to the optional Jason-2 Altimetry program, they get additional voting coefficient rights (most members participate to the optional Jason-2 program, with the current exception of Austria and Poland).
Full member states of the organization have free full access to the images, data and other information produced by EUMETSAT. Cooperating states benefit from reduced fees for accessing the same data, but may get free full access in case of emergency or threats of meteorological disasters. Exceptionally, some non-member states, participating to the WMO
World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
, may get access to some data for the same reason.
Many poor non-member states around the world also get free access to Meteosat data, when their yearly gross national income does not exceed 3500 USD per capita, based on World bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
statistics reports.
| State | Status | Since (signing of convention) | Funding contribution | Representative organization from national meteorological services (official national names, links point to names for official use in English) | Official web site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | March 1986 | 19.20% | Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) | www.dwd.de | |
| Member | May 1985 | 15.62% | Met Office Met Office The Met Office , is the United Kingdom's national weather service, and a trading fund of the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills... |
www.metoffice.gov.uk | |
| Member | February 1985 | 14.70% | Météo-France Météo-France Météo-France is the French national meteorological service.The organisation was established by decree in June 1993 and is a department of the Ministry of Transportation. It is headquartered in Paris but many domestic operations have been decentralised to Toulouse... |
www.meteo.fr | |
| Member | June 1986 | 12.04% | Ufficio Generale Spazio Aereo e Meteorologia (USAM) - Reparto Meteorologia Servizio Meteorologico The Italian Meteorological Service is an organizational unit of the Italian Air Force , and as such, the national meteorological service in Italy... |
www.meteoam.it/ | |
| Member | February 1985 | 7.56% | Agencia Estatal de Meteorología (AEMET), Ministerio de Medio ambiente Agencia Estatal de Meteorología Agencia Estatal de Meteorología, AEMET is the Spain's meteorological agency, under the Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Medio Rural y Marino .... |
www.inm.es | |
| Member | March 1984 | 4.38% | Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut (KNMI) | www.knmi.nl | |
| Member | July 1985 | 2.75% | MeteoSchweiz / MétéoSuisse / MeteoSvizzera MeteoSwiss MeteoSwiss , officially the Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology, is an office of the federal administration of Switzerland. It employs 290 people at locations in Zurich, Zurich Airport, Geneva, Locarno and Payerne.... |
www.meteoschweiz.ch | |
| Member | October 1985 | 2.57% | Institut Royal Météorologique de Belgique (IRM) / Koninklijk Meteorologisch Instituut van België (KMI) Royal Meteorological Institute The Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium is a Belgian federal institute of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office . It is located in Uccle and in Dourbes... |
www.kmi.be | |
| Member | January 1984 | 2.53% | Sveriges meteorologiska och hydrologiska institut (SMHI) | www.smhi.se | |
| Member | August 1984 | 2.27% | Remote Sensing Division, Devlet Meteoroloji İşleri Genel Müdürlüğü (DMİGM) Turkish State Meteorological Service Turkish State Meteorological Service is the Turkish government bureau commissioned with producing the meteorological and climactic data pertaining to Turkey. It is responsible to the Ministry of Environment and Forestry.-External links:*... |
www.meteor.gov.tr | |
| Member | December 1993 | 2.05% | Zentralanstalt für Meteorologie und Geodynamik (ZAMG) Central Institute for Meteorology and Geodynamics The Central Institute for Meteorology and Geodynamics is the national meteorological and geophysical service of Austria.It is a subordinate agency of the Austrian Federal Ministry for Science and Research... |
www.zamg.ac.at | |
| Member | April 1985 | 2.03% | Meteorologisk institutt (met.no) Norwegian Meteorological Institute Norwegian Meteorological Institute is the Norwegian national institute for weather forecasts.The three main offices are located in Oslo, Bergen and Tromsø. The Institute has around 500 employees and keeps around 650 paid observers of various kinds around the country... |
www.met.no | |
| Member | June 2009 | 1.95% | Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej (IMGW) | www.imgw.pl | |
| Member | January 1984 | 1.78% | Danmarks Meteorologiske Institut (DMI) Danish Meteorological Institute The Danish Meteorological Institute is the official Danish meteorological institute, administrated by the Ministry of Transport and Energy. The institute makes weather forecasts and observations for Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands.... |
www.dmi.dk | |
| Member | June 1988 | 1.65% | Εθνική Μετεωρολογική Υπηρεσία (HNMS) | www.hnms.gr | |
| Member | December 1984 | 1.35% | Ilmatieteen laitos / Meteorologiska institutet (FMI) Finnish Meteorological Institute The Finnish Meteorological Institute is the government agency responsible for gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts in Finland. It is a part of the Ministry of Transport and Communications but it operates semi-autonomously.... |
www.fmi.fi | |
| Member | May 1989 | 1.23% | Instituto de Meteorologia (IM) | www.meteo.pt | |
| Member | June 1985 | 1.17% | Met Éireann Met Éireann Met Éireann is the national meteorological service in Ireland, part of the Department of the Environment, Heritage and Local Government.-History:... |
www.met.ie | |
| Member | 12 May 2010 | 0.80% | Český hydrometeorologický ústav (CHMI), Družicové Oddělení | www.chmi.cz | |
| Member | October 2008 | 0.69% | Országos Meteorológiai Szolgálat (OMSZ) | www.met.hu | |
| Member | November 2010 | 0.57% | National Meteorological Administration of Romania | meteoromania.ro | |
| Member | January 2006 | 0.32% | Slovenský hydrometeorologický ústav (SHMU) | www.shmu.sk | |
| Member | December 2006 | 0.25% | Državni hidrometeorološki zavod (DHMZ) Croatian Meteorological and Hydrological Service The Croatian Meteorological and Hydrological Service is the Croatian national agency for weather forecasts, based in Zagreb. As of 2010 the service has 440 full-time employees in 23 departments, in addition to around 3,000 part-time observers around the country.The agency produces operational... |
www.dhmz.htnet.hr | |
| Member | February 2008 | 0.23% | Agencija Republike Slovenije za Okolje (ARSO) | www.arso.gov.si | |
| Member | July 2002 | 0.21% | Administration de la navigation aérienne | www.aeroport.public.lu | |
| Member | May 2009 | 0.10% | Latvijas Vides, ģeoloģijas un meteoroloģijas aģentūra (LVGMA) | www.meteo.lv | |
| Cooperating | May 2005 | 0.18% | Национален институт по метеорология и хидрология (INMH) | www.meteo.bg | |
| Cooperating | November 2005 | 0.16% | Lietuvos hidrometeorologijos tarnyba (LHS), prie Aplinkos ministerijos | www.meteo.lt | |
| Cooperating | April 2006 | 0.10% | Veðurstofa Íslands Icelandic Meteorological Office Icelandic Meteorological Office is Iceland's national weather service.- External links :* — Official Website — Official Website... |
www.vedur.is | |
| Cooperating | December 2006 | 0.09% | Eesti Meteoroloogia ja Hüdroloogia Instituut (EMHI) Estonian Meteorological and Hydrological Institute Estonian Meteorological and Hydrological Institute is a governmental service under the Ministry of Environment.... |
www.emhi.ee | |
 Serbia Serbia |
Cooperating | November 2009 | 0.18% | Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia is the referential organization for making and presenting the weather forecasts and for issuing severe weather warnings in the Republic of Serbia... |
www.hidmet.gov.rs |
| Last update published 2010 | |||||
Satellite programmes



EUMETSAT Polar System
- See the MetOpMetOpMetOp is a series of polar orbiting meteorological satellites operated by the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites. The satellites are all part af the EUMETSAT Polar System. It is intended to replace the soon to be retired TIROS network...
article for the satellites.
While geostationary satellites provide a continuous view of the earth disc from an apparently stationary position in space, the instruments on polar orbiting satellites
Polar (satellite)
The Global Geospace Science Polar Satellite was a BABATONDIE science spacecraft launched at 06:23:59.997 EST on February 24, 1996 aboard a BABATONDIE BABATONDIE 7925-10 rocket from launch pad 2W at Vandenberg Air Force Base in BABATONDIE, BABATONDIE, to observe the polar BABATONDIE...
, flying at a much lower altitude, provide more precise details about atmospheric temperature and moisture profiles, although with a less frequent global coverage.
The lack of observational coverage in certain parts of the globe, particularly the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
and continents of the southern hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
, has led to the increasingly important role for polar orbiting satellite data in numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
and climate monitoring.
From 2006, the continuous view of the Earth provided by Meteosat-8 is expected to be complemented by data from the first operational European meteorological satellite flying in the lower orbit — MetOp
MetOp
MetOp is a series of polar orbiting meteorological satellites operated by the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites. The satellites are all part af the EUMETSAT Polar System. It is intended to replace the soon to be retired TIROS network...
.
Positioned at approximately 850 km above the Earth, special instruments on board this spacecraft will be able to deliver far more precise details about atmospheric temperature and moisture profiles than a geostationary satellite.
EUMETSAT Polar System (EPS) satellites will also ensure that the more remote regions of the globe, particularly in Northern Europe as well as the oceans of the Southern hemisphere, will be fully covered.
The three MetOp satellites form the space segment of EPS. The first satellite, MetOp A, was successfully launched by a Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n Soyuz-2.1a rocket from Baikonur
Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome , also called Tyuratam, is the world's first and largest operational space launch facility. It is located in the desert steppe of Kazakhstan, about east of the Aral Sea, north of the Syr Darya river, near Tyuratam railway station, at 90 meters above sea level...
on October 19, 2006, at 22:28 Baikonur time (16:28 UTC).
The EPS program is also the European half of a joint program with NOAA, called the International Joint Polar System. NOAA has operated a continuous series of low earth orbiting meteorological satellite since April 1960. Many of the instruments on Metop are also operated on NOAA/POES satellites, providing similar data types across the IJPS.
The Metop satellite was initially controlled by ESOC for the LEOP
LEOP
In Spacecraft Operations, The Launch and Early Orbit Phase is one of the most critical phases of a mission. Spacecraft operations engineers take control of the satellite after it separates from the launch vehicle up to the time when the satellite is safely positioned in its final orbit.During this...
phase immediately following launch, with control handed over to Eumetsat around 72 hours after liftoff. Eumetsat's first commands to the satellite were sent at 14:04 UTC on October 22, 2006.
Construction on the second satellite, Metop B, has been completed. Launch is scheduled for April 2012, with Metop C launching sometime in 2017.
Instruments on MetOp
- A/DCS (Advanced Data Collection System)Argos SystemArgos is a satellite-based system which collects, processes and disseminates environmental data from fixed and mobile platforms worldwide. What makes Argos unique is the ability to geographically locate the source of the data anywhere on the Earth utilizing the Doppler effect...
- AMSU-A1 and AMSU-A2Advanced Microwave Sounding UnitThe Advanced microwave sounding unit is a multi-channel microwave radiometer installed on meteorological satellites. The instrument examines several bands of microwave radiation from the atmosphere to perform atmospheric sounding of temperature and moisture levels.-Products:Level-1 radiance data...
- ASCAT Advanced ScatterometerScatterometerA radar scatterometer is designed to determine the normalized radar cross section of the surface. Scatterometers operate by transmitting a pulse of microwave energy towards the Earth's surface and measuring the reflected energy. A separate measurement of the noise-only power is made and...
- AVHRRAdvanced Very High Resolution RadiometerThe Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer is a space-borne sensor embarked on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration family of polar orbiting platforms . AVHRR instruments measure the reflectance of the Earth in 5 relatively wide spectral bands...
(Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer) - GOME-2 (Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment) — instrument to monitor ozoneOzoneOzone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
levels - GRAS (GNSS Receiver for Atmospheric Sounding: global navigation satellite systems radio occultation)
- HIRS (High Resolution InfraredInfraredInfrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
Sounder) - IASI (Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer)
- MHS (MicrowaveMicrowaveMicrowaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
HumidityHumidityHumidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
Sounder) - SARP-3 and SARR (Search And Rescue Processor og Search And Rescue Repeater)
- SEM (Space Environment Monitor)
Jason
The Jason mission is in a planning stage and will eventually measure the altimetry of the global ocean surface.Jason-2 is planned to fly at an altitude of around 1300 km. The main instruments on board are a radar altimeter
Radar altimeter
A radar altimeter, radio altimeter, low range radio altimeter or simply RA measures altitude above the terrain presently beneath an aircraft or spacecraft...
, a microwave radiometer
Microwave radiometer
A microwave radiometer is a radiometer that measures energy emitted at sub-millimetre-to-centimetre wavelengths known as microwaves. Their primary application has been onboard spacecraft measuring atmospheric and terrestrial radiation, and they are mostly used for meteorological or oceanographic...
, and orbit determination
Orbit determination
Orbit determination is a branch of astronomy specialised in calculating, and hence predicting, the orbits of objects such as moons, planets, and spacecraft . These orbits could be orbiting the Earth, or other bodies...
systems. The aim is to measure the global sea surface height to an accuracy of a few cm every 10 days, for determining ocean circulation, climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
and sea level rise.
This program is funded separately and is not, for now, part of the mandatory programs for member and cooperating countries. Almost all members have joined this program and get additional voting rights.
Jason-2 was launched successfully from Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base is a United States Air Force Base, located approximately northwest of Lompoc, California. It is under the jurisdiction of the 30th Space Wing, Air Force Space Command ....
aboard a Delta-II rocket on 20 June 2008, 7:46 UTC. http://www.eumetsat.int/Home/Main/What_We_Do/Highlights/SP_1213708779383?l=en
External links
- EUMETSAT's Website
- EUMETSAT weather satellite viewer Online EUMETSAT weather satellite viewer with 2 months of archived data.
- Press release: "MetOp to be launched in October"

