
Frequency ambiguity resolution
Encyclopedia
Frequency ambiguity resolution is used to find true target velocity for medium pulse repetition frequency
(PRF) radar systems. This is used with pulse-Doppler radar
This is used with pulse-Doppler radar
.
(PRF).
Frequency ambiguity resolution is required to obtain the true radial velocity when the measurements is made using a system where the following inequality is true.
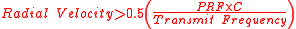
The radial velocity measurements made in this way produce a modulo
function of the true radial velocity.

This concept is related to range ambiguity resolution
.
Doppler frequency shift is introduced onto reflected signals used by radar.
. This introduces a modulo operation
onto the apparent frequency of the reflected signal.
The ambiguous velocity is as follows.
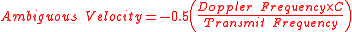
Frequency is folded for high speed targets where radial velocity produces a frequency shift above the Nyquist frequency
. The true speed of the target may be folded by a modulo operation
produced by the sampling process.


The Nyquist frequency will also change when the PRF is changed.
This is explained best using an example with 2 different PRF, although real systems use a different method.
In the example, PRF A can detect true speed up to 600MPH and PRF B can detect true speed up to 500MPH.
The apparent speed for PRF A falls in the 200MPH filter, and the apparent speed for PRF B falls in the 400MPH filter. This combination places the true target speed at 1,400MPH (2x6+2 or 2x5+4). This can be seen graphically when range intervals are stacked end-to-end as shown below.
"A" represents target speed possibilities for PRF A, and "B" represents target speed possibilities for PRF B.
This frequency ambiguity resolution signal processing technique determines true velocity.
Ambiguity resolution is typically implemented with a look-up table. This could also be implemented as a convolution
function, where the spectrum amplitudes from one PRF are applied to spectrum samples from the other PRF as a sliding window function .
Pulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency or Pulse repetition rate is the number of pulses per time unit . It is a measure or specification mostly used within various technical disciplines Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or Pulse repetition rate (PRR) is the number of pulses per time unit (e.g. Seconds). It...
(PRF) radar systems.

Pulse-doppler radar
Pulse-Doppler is a 4D radar system capable of detecting both target 3D location as well as measuring radial velocity . It uses the Doppler effect to avoid overloading computers and operators as well as to reduce power consumption...
.
Definition
Radial velocity aliasing occurs when reflections arrive from reflectors moving fast enough for the Doppler frequency to exceed the pulse repetition frequencyPulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency or Pulse repetition rate is the number of pulses per time unit . It is a measure or specification mostly used within various technical disciplines Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or Pulse repetition rate (PRR) is the number of pulses per time unit (e.g. Seconds). It...
(PRF).
Frequency ambiguity resolution is required to obtain the true radial velocity when the measurements is made using a system where the following inequality is true.
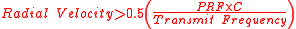
The radial velocity measurements made in this way produce a modulo
Modulo
In the mathematical community, the word modulo is often used informally. Generally, to say "A is the same as B modulo C" means, more-or-less, "A and B are the same except for differences accounted for or explained by C"....
function of the true radial velocity.

Theory
Radar pulsing causes a phenomenon called aliasing, which occurs when the Doppler frequency created by reflector motion exceeds the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) .This concept is related to range ambiguity resolution
Range ambiguity resolution
Range ambiguity resolution is a technique used with medium Pulse repetition frequency radar to obtain range information for distances that exceed the distance between transmit pulses.This signal processing technique is required with pulse-Doppler radar....
.
Doppler frequency shift is introduced onto reflected signals used by radar.
Operation
When the Doppler frequency shift exceeds the PRF, the frequency is reduced. This limitation is called the Nyquist sampling rateNyquist rate
In signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, is two times the bandwidth of a bandlimited signal or a bandlimited channel...
. This introduces a modulo operation
Modular arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" after they reach a certain value—the modulus....
onto the apparent frequency of the reflected signal.
The ambiguous velocity is as follows.
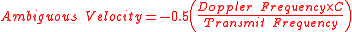
Frequency is folded for high speed targets where radial velocity produces a frequency shift above the Nyquist frequency
Nyquist frequency
The Nyquist frequency, named after the Swedish-American engineer Harry Nyquist or the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, is half the sampling frequency of a discrete signal processing system...
. The true speed of the target may be folded by a modulo operation
Modulo operation
In computing, the modulo operation finds the remainder of division of one number by another.Given two positive numbers, and , a modulo n can be thought of as the remainder, on division of a by n...
produced by the sampling process.


The Nyquist frequency will also change when the PRF is changed.
This is explained best using an example with 2 different PRF, although real systems use a different method.
In the example, PRF A can detect true speed up to 600MPH and PRF B can detect true speed up to 500MPH.
| 0MPH | 100MPH | 200MPH | 300MPH | 400MPH | 500MPH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target PRF A | |||||
| Target PRF B |
The apparent speed for PRF A falls in the 200MPH filter, and the apparent speed for PRF B falls in the 400MPH filter. This combination places the true target speed at 1,400MPH (2x6+2 or 2x5+4). This can be seen graphically when range intervals are stacked end-to-end as shown below.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 29 | 29 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | B | B | B | B | B |
"A" represents target speed possibilities for PRF A, and "B" represents target speed possibilities for PRF B.
This frequency ambiguity resolution signal processing technique determines true velocity.
Ambiguity resolution is typically implemented with a look-up table. This could also be implemented as a convolution
Convolution
In mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
function, where the spectrum amplitudes from one PRF are applied to spectrum samples from the other PRF as a sliding window function .

