Pulse-doppler radar
Encyclopedia
Pulse-Doppler is a 4D radar
system capable of detecting both target 3D location
as well as measuring radial velocity (range-rate). It uses the Doppler effect
to avoid overloading computers and operators as well as to reduce power consumption. RF energy returning from airborne objects and spacecraft are combined for successive target reflections returning from a dozen or more transmit pulses, and these are integrated using Pulse-Doppler signal processing
. Pulse-Doppler reduces microwave power emission and weigh sufficiently for safe and effective use on aircraft. Pulse-Doppler radar has fundamental characteristics that differentiate it from pulse-amplitude time-domain radar and continuous-wave frequency-domain radar.
Pulse-Doppler radar is crucial for military applications called look-down/shoot-down
, which allows small fast-moving objects to be detected near terrain and weather. The purpose is to detect targets while eliminating hostile environmental influences, such as reflections from weather, the surface of the earth, and biological objects like birds, and electronic interference, which hide reflected signals from aircraft, but which move much slower than aircraft. A secondary purpose is to reduce transmit power while achieving acceptable performance for improved safety and stealthy radar. In meteorological radars
, pulse-Doppler measures instantaneous speed of precipitations at discrete range intervals as the beam is slewed across the sky. Pulse-Doppler radar is also the basis of synthetic aperture radar
used with radar astronomy
.
Doppler weather effects (precipitation) were also found to degrade conventional radar
and moving target indicator radar, which can mask aircraft reflections. This phenomenon was adapted for use with weather radar
in the 1950s after declassification of some World War II systems.
Pulse-Doppler radar was developed during World War II to overcome limitations by increasing pulse repetition frequency
. This required the development of klystron
, the traveling wave tube
, and solid state devices. Pulse-Doppler is incompatible with other high power microwave amplification devices that are not Coherent.
Early examples of military systems include the AN/SPG-51
B developed during the 1950s specifically for the purpose of operating in hurricane conditions with no performance degradation.
Weather
, chaff, terrain
, flying techniques
, and stealth
are common tactics used to hide aircraft from radar. Pulse-Doppler radar eliminates these weaknesses.
It became possible to use pulse-Doppler radar on aircraft after digital computers were incorporated in the design. Pulse-Doppler provided look-down/shoot-down
capability to support air-to-air missile systems in most modern military aircraft by the mid 1970s.
 Pulse-Doppler radar is based on the Doppler effect
Pulse-Doppler radar is based on the Doppler effect
, where movement in range produces frequency shift on the signal reflected from the target.

Radial velocity
is essential for pulse-Doppler radar operation. As the reflector moves between each transmit pulse, the returned signal has a phase
difference or phase shift from pulse to pulse. This causes the reflector to produce Doppler modulation on the reflected signal.
Pulse-Doppler radars exploit this phenomenon to improve performance.
The amplitude of the successively returning pulse from the same scanned volume is:
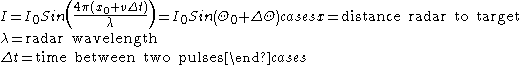
This allows the radar to separate the reflections from multiple objects located in the same volume of space by separating the objects using a spread spectrum
to segregate different signals.
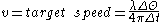 where
where 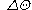 is phase shift induced by range motion.
is phase shift induced by range motion.
Pulse-Doppler radar uses the following signal processing criteria to exclude unwanted signals from slow-moving objects. This is also known as clutter rejection. Rejection velocity is usually set just above the prevailing wind speed (10 to 100 mile/hour or 15 to 150 km/hour). The velocity threshold is much lower for weather radar
.
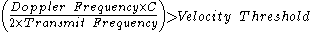
In airborne pulse-Doppler radar, the velocity threshold is offset by the speed of the aircraft relative to the ground.
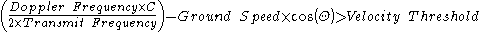
Surface reflections appear in almost all radar. Ground clutter generally appears in a circular region within a radius of about 25 miles near ground-based radar. This distance extends much further in airborne and space radar. Clutter results from radio energy being reflected from the earth's surface, buildings, and vegetation. Clutter includes weather in radar intended to detect and report aircraft and spacecraft.
Clutter creates a vulnerability region in pulse-amplitude time-domain radar. Non-Doppler radar systems cannot be pointed directly at the ground due to excessive false alarms, which overwhelm computers and operators. Sensitivity must be reduced near clutter to avoid overload. This vulnerability begins in the low-elevation region several beam widths above the horizon, and extends downward. This also exists throughout the volume of moving air associated with weather phenomenon.
Pulse-Doppler radar corrects this as follows.
Clutter rejection capability
of about 60dB is needed for look-down/shoot-down
capability, and pulse-Doppler is the only strategy that can satisfy this requirement. This eliminates vulnerabilities associated with the low-elevation and below-horizon environment.
Pulse compression
, and moving target indicator
(MTI) provide up to 25dB sub-clutter visibility. MTI antenna beam is aimed above horizon to avoid excessive false alarm rate, which renders systems vulnerable. Aircraft and some missiles exploit this weakness using a technique called flying below the radar to avoid detection (Nap-of-the-earth
). This flying technique is ineffective against pulse-Doppler radar.
Pulse-Doppler provides an advantage when attempting to detect missiles and low observability aircraft
flying near near terrain, sea surface, and weather.
Audible Doppler and target size support passive vehicle type classification when identification friend or foe
is not available from a transponder signal
.
Medium PRF reflected microwave signals fall between 1,500 and 15,000 cycle per second, which is audible. This means a helicopter sounds like a helicopter, a jet sounds like a jet, and propeller aircraft sound like propellers. Aircraft with no moving parts produce a tone.
The actual size of the target can be calculated using the audible signal.
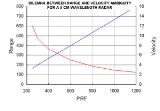
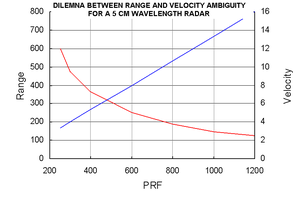 Ambiguity processing is required when target range is above the red line in the graphic, which increases scan time.
Ambiguity processing is required when target range is above the red line in the graphic, which increases scan time.
Scan time is a critical factor for some systems because vehicles moving at or above the speed of sound can travel one mile (1.6 km) every few seconds, like the Exocet
, Harpoon, Kitchen, and Air-to-air missile
. The maximum time to scan the entire volume of the sky must be on the order of a dozen seconds or less for systems operating in that environment.
Pulse-Doppler radar by itself can be too slow to cover the entire volume of space above the horizon, unless multiple simultaneous beams are used.
Pulse-Doppler antenna motion must be slow enough so that all the return signals from at least 3 different PRF can be processed out to the maximum anticipated detection range. This is known as dwell time. Antenna motion for pulse-Doppler must be as slow as radar using MTI
.
Search radar that include pulse-Doppler are usually dual mode because best overall performance is achieved when pulse-Doppler is used for areas with high false alarm rates (horizon or below and weather), while conventional radar will scan faster in free-space where false alarm rate is low (above horizon with clear skies).
The antenna type is an important consideration for multi mode radar because undesirable phase shift introduced by the radar antenna can degrade Measure of Performance for sub-clutter visibility.
during the detection interval, and the receiver must have large instantaneous dynamic range
.
Pulse-Doppler signal processing also includes ambiguity resolution to identify true range and velocity.
The received signals from multiple PRF are compared to determine true range using the range ambiguity resolution process.
The received signals are also compared using the frequency ambiguity resolution process.
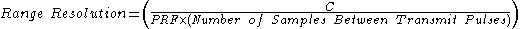
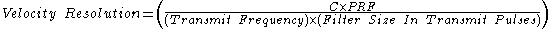
(PRF) from about 3 kHz to 30 kHz. The range between transmit pulses is 5 km to 50 km.
Range and velocity cannot be measured directly using medium PRF, and a technique called ambiguity resolutions is required to identify true range and speed. Doppler signals are generally above 1 kHz, which is audible, so audio signals from medium-PRF systems can be used for passive target classification.
Tracking radar systems use angle error to improve accuracy by producing measurements perpendicular to the radar antenna beam. Angular measurements are averaged over a span of time and combined with radial movement to develop information suitable to predict target position for a short time into the future.
The two angle error techniques used with tracking radar are monopulse and conical scan.
reduces sub-clutter visibility performance by producing apparent motion on stationary objects.
Cavity magnetron
and crossed-field amplifier
are not appropriate because noise introduced by these devices interfere with detection performance. The only amplification devices suitable for pulse-Doppler are klystron
, traveling wave tube
, and solid state devices.
Scalloping for pulse-Doppler radar involves blind velocities created by the clutter rejection filter. Every volume of space must be scanned using 3 or more different PRF. A two PRF detection scheme will have detection gaps with a pattern of discrete ranges, each of which has a blind velocity.
pose a problem with search, detection, and ambiguity resolution in pulse-Doppler radar.
Ringing is reduced in two ways.
First, the shape of the transmit pulse is adjusted to smooth the leading edge and trailing edge so that RF power is increased and decreased without an abrupt change. This creates a transmit pulse with smooth ends instead of a square wave, which reduces ringing phenomenon that is otherwise associated with target reflection.
Second, the shape of the receive pulse is adjusted using a window function
that minimizes ringing that occurs any time pulses are applied to a filter. In a digital system, this adjusts the phase and/or amplitude of each sample before it is applied to the Fast Fourier Transform
. The Dolph-Chebychev window is the most effective because it produces a flat processing floor with no ringing that would otherwise cause false alarms.
Mechanical RF components, such as wave-guide, can produce Doppler modulation due to phase shift induced by vibration. This introduces a requirement to perform full spectrum operational tests using shake tables that can produce high power mechanical vibration across all anticipated audio frequencies.
Doppler is incompatible with most electronically steered phase-array antenna. This is because the phase-shifter elements in the antenna are non-reciprocal and the phase shift must be adjusted before and after each transmit pulse. Spurious phase shift is produced by the sudden impulse of the phase shift, and settling during the receive period between transmit pulses places Doppler modulation onto stationary clutter. That receive modulation corrupts Measure of Performance for sub-clutter visibility. Phase shifter settling time on the order of 50ns is required.
Most antenna phase shifters operating at PRF above 1 kHz introduce spurious phase shift unless special provisions are made, such as reducing phase shifter settling time to a few dozen nanoseconds.
The following gives the approximate settling time for antenna phase shift module
s.

where
The antenna type and scan performance is a practical consideration for multi-mode radar systems.
from mountains, buildings or wave tops can be used to detect fast moving objects otherwise blocked by solid obstruction along the line of sight. This is a very lossy phenomenon that only becomes possible when radar has significant excess sub-clutter visibility.
Refraction and ducting use transmit frequency at L-band or lower to extend the horizon, which is very different from diffraction. Refraction
for over-the-horizon radar
uses variable density in the air column above the surface of the earth to bend RF signals. An inversion layer can produce a transient troposphere duct that traps RF signals in a thin layer of air like a wave-guide.
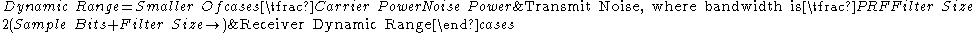
Subclutter visibility is the ratio of the smallest signal that can be detected in the presence of a larger signal.
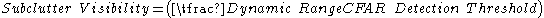
A small fast-moving target reflection can be detected in the presence of larger slow-moving clutter reflections when the following is true.
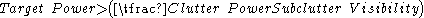
The theoretical range performance is as follows.
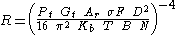
where
This equation is derived by combining the Radar equation with the Noise equation
and accounting for in-band noise distribution across multiple detection filters. The value D is added to the standard radar range equation to account for both Pulse-Doppler signal processing
and transmitter FM noise reduction
.
Detection range is increased proportional to the square root of the number of filters. Power consumption is reduced by the square of the number of filers.
For example, pulse-Doppler signal processing
with 1,024 filters will reduce noise contribution in each filter 60dB below the level of electronic noise
being sampled in the receiver. Each filter holds only a small amount of the total noise arriving at the receiver. This means a system with a receiver bandwidth of 1 mHz would have an effective bandwidth of 1 kHz in each of the 1,024 filters where detection takes place.
In addition, Pulse-Doppler signal processing
integrates all of the energy from all of the individual reflected pulses that enter the filter. This means a Pulse-Doppler signal processing
system with 1,024 elements provides 60dB of improvement due to the type of signal processing that must be used with pulse-Doppler radar. The energy of all of the individual pulses from the object are added together by the filtering process.
Signal processing for a 1,024 point filter improves performance by 120dB, assuming compatible transmitter and antenna. This corresponds to the following potential improvements.
These improvements are the reason pulse-Doppler is essential for military and astronomy.
Scan mode involves frequency filtering, amplitude thresholding, and ambiguity resolution. Once a reflection has been detected
and resolved
, the pulse-Doppler radar automatically transitions to tracking mode for the volume of space surrounding the track.
Track mode works like a phase-locked loop
, where Doppler velocity is compared with the range movement on successive scans. Lock indicates the difference between the two measurements is below a threshold, which can only occur with an object that satisfies Newtonian mechanics
. Other types of electronic signals cannot produce a lock. Lock exists in no other type of radar.
The lock criteria needs to be satisfied during normal operation.
Lock eliminates the need for human intervention with the exception of helicopters and electronic jamming.
Weather phenomenon obey adiabatic process
associated with air mass
and not Newtonian mechanics, so the lock criteria is not normally used for weather radar.
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
selectively excludes low-velocity reflections so that no detections occurs below a threshold velocity. This eliminates terrain, weather, biologicals, and mechanical jamming with the exception of decoy aircraft.
The target Doppler signal from the detection is converted from frequency domain
back into time domain
sound for the operator in track mode on some radar systems. The operator uses this sound for passive target classification, such as recognizing helicopters and electronic jamming.
. Blade tips moving near the speed of sound produce the only signal that can be detected when a helicopter
is moving slow near terrain and weather.
Helicopters appears like a rapidly pulsing noise emitter except in a clear environment free from clutter. An audible signal is produced for passive identification of the type of airborne object. Doppler produces sound that is used for target classification in addition to the kinds of conventional radar display
used for that purpose, like A-Scope, B-Scope, C-Scope, and RHI indicator. The human ear may be able to tell the difference better than electronic equipment.
A special mode is required because the Doppler velocity feedback information must be unlinked from radial movement so that the system can transition from scan to track with no lock.
Similar techniques are required to develop track information for jamming signals and interference that cannot satisfy the lock criteria.
Once in track mode, pulse-Doppler radar must include a way to modify Doppler filtering for the volume of space surrounding a track when radial velocity falls below the minimum detection velocity. Doppler filter adjustment must be linked with a radar track function to automatically adjust Doppler rejection speed within the volume of space surrounding the track.
Tracking will cease without this feature because the target signal will otherwise be rejected by the Doppler filter when radial velocity approaches zero.
Multi-mode operation may also include continuous wave illumination for semi-active radar homing
.
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
system capable of detecting both target 3D location
3D radar
3D radar provides for radar coverage on three dimensions unlike the more common 2D radar. While the normal 2D radar provides range and azimuth, the 3D radar provides elevation information with range and azimuth...
as well as measuring radial velocity (range-rate). It uses the Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
to avoid overloading computers and operators as well as to reduce power consumption. RF energy returning from airborne objects and spacecraft are combined for successive target reflections returning from a dozen or more transmit pulses, and these are integrated using Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
. Pulse-Doppler reduces microwave power emission and weigh sufficiently for safe and effective use on aircraft. Pulse-Doppler radar has fundamental characteristics that differentiate it from pulse-amplitude time-domain radar and continuous-wave frequency-domain radar.
- Improved detection in high-clutter environments
- Greater track reliability using feedback
- Passive vehicle type classification
- Unattended operation
Pulse-Doppler radar is crucial for military applications called look-down/shoot-down
Look-down/shoot-down
Look-down/shoot-down is a capability a radar system is said to possess if it is able to detect, track and put a weapon onto an air target moving below the horizon as seen by the radar...
, which allows small fast-moving objects to be detected near terrain and weather. The purpose is to detect targets while eliminating hostile environmental influences, such as reflections from weather, the surface of the earth, and biological objects like birds, and electronic interference, which hide reflected signals from aircraft, but which move much slower than aircraft. A secondary purpose is to reduce transmit power while achieving acceptable performance for improved safety and stealthy radar. In meteorological radars
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
, pulse-Doppler measures instantaneous speed of precipitations at discrete range intervals as the beam is slewed across the sky. Pulse-Doppler radar is also the basis of synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar is a form of radar whose defining characteristic is its use of relative motion between an antenna and its target region to provide distinctive long-term coherent-signal variations that are exploited to obtain finer spatial resolution than is possible with conventional...
used with radar astronomy
Radar astronomy
Radar astronomy is a technique of observing nearby astronomical objects by reflecting microwaves off target objects and analyzing the echoes. This research has been conducted for six decades. Radar astronomy differs from radio astronomy in that the latter is a passive observation and the former an...
.
History
The earliest radar systems failed to operate as expected. The reason was traced to Doppler effects that degrade performance of systems not designed to account for moving objects. Fast-moving objects cause a phase-shift on the transmit pulse that can produce signal cancellation. Doppler has maximum detrimental effect on moving target indicator systems, which must use reverse phase shift for Doppler compensation in the detector.Doppler weather effects (precipitation) were also found to degrade conventional radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
and moving target indicator radar, which can mask aircraft reflections. This phenomenon was adapted for use with weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
in the 1950s after declassification of some World War II systems.
Pulse-Doppler radar was developed during World War II to overcome limitations by increasing pulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency or Pulse repetition rate is the number of pulses per time unit . It is a measure or specification mostly used within various technical disciplines Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or Pulse repetition rate (PRR) is the number of pulses per time unit (e.g. Seconds). It...
. This required the development of klystron
Klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube . Klystrons are used as amplifiers at microwave and radio frequencies to produce both low-power reference signals for superheterodyne radar receivers and to produce high-power carrier waves for communications and the driving force for modern...
, the traveling wave tube
Traveling wave tube
A traveling-wave tube is an electronic device used to amplify radio frequency signals to high power, usually in an electronic assembly known as a traveling-wave tube amplifier ....
, and solid state devices. Pulse-Doppler is incompatible with other high power microwave amplification devices that are not Coherent.
Early examples of military systems include the AN/SPG-51
AN/SPG-51
The AN/SPG-51 is a tracking / illumination radar for RIM-66 Standard missiles. It is used for target tracking and Surface-to-air missile guidance on s, s, and s.The French Cassard class frigates also utilise this system.Older variants were used on s....
B developed during the 1950s specifically for the purpose of operating in hurricane conditions with no performance degradation.
Weather
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
, chaff, terrain
Terrain mask
Terrain mask is a term used in both aviation and GPS equipment.A terrain mask refers to the natural curvature of the earth. It is important as a means of avoiding active radar by positioning the aircraft so there is natural earth hiding it from the radio waves sent from the radar system...
, flying techniques
Blue Angels
The United States Navy's Navy Flight Demonstration Squadron, popularly known as the Blue Angels, was formed in 1946 and is currently the oldest formal flying aerobatic team...
, and stealth
Stealth aircraft
Stealth aircraft are aircraft that use stealth technology to avoid detection by employing a combination of features to interfere with radar as well as reduce visibility in the infrared, visual, audio, and radio frequency spectrum. Development of stealth technology likely began in Germany during...
are common tactics used to hide aircraft from radar. Pulse-Doppler radar eliminates these weaknesses.
It became possible to use pulse-Doppler radar on aircraft after digital computers were incorporated in the design. Pulse-Doppler provided look-down/shoot-down
Look-down/shoot-down
Look-down/shoot-down is a capability a radar system is said to possess if it is able to detect, track and put a weapon onto an air target moving below the horizon as seen by the radar...
capability to support air-to-air missile systems in most modern military aircraft by the mid 1970s.
Principle

Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, where movement in range produces frequency shift on the signal reflected from the target.

Radial velocity
Radial velocity
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the direction of the line of sight . In astronomy, radial velocity most commonly refers to the spectroscopic radial velocity...
is essential for pulse-Doppler radar operation. As the reflector moves between each transmit pulse, the returned signal has a phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
difference or phase shift from pulse to pulse. This causes the reflector to produce Doppler modulation on the reflected signal.
Pulse-Doppler radars exploit this phenomenon to improve performance.
The amplitude of the successively returning pulse from the same scanned volume is:
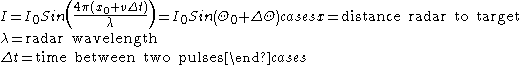
- So
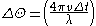
This allows the radar to separate the reflections from multiple objects located in the same volume of space by separating the objects using a spread spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
to segregate different signals.
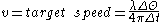 where
where 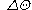 is phase shift induced by range motion.
is phase shift induced by range motion.Benefits
Rejection speed is selectable on pulse-Dopper aircraft-detection systems so nothing below that speed will be detected. A one degree antenna beam illuminates millions of square feet of terrain at 10 miles (16.1 km) range, and this produces thousands of detections at or below the horizon if Doppler is not used.Pulse-Doppler radar uses the following signal processing criteria to exclude unwanted signals from slow-moving objects. This is also known as clutter rejection. Rejection velocity is usually set just above the prevailing wind speed (10 to 100 mile/hour or 15 to 150 km/hour). The velocity threshold is much lower for weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
.
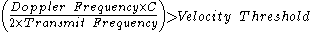
In airborne pulse-Doppler radar, the velocity threshold is offset by the speed of the aircraft relative to the ground.
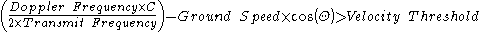
- Where
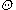 is the angle offset between the antenna position and the aircraft flight trajectory.
is the angle offset between the antenna position and the aircraft flight trajectory.
Surface reflections appear in almost all radar. Ground clutter generally appears in a circular region within a radius of about 25 miles near ground-based radar. This distance extends much further in airborne and space radar. Clutter results from radio energy being reflected from the earth's surface, buildings, and vegetation. Clutter includes weather in radar intended to detect and report aircraft and spacecraft.
Clutter creates a vulnerability region in pulse-amplitude time-domain radar. Non-Doppler radar systems cannot be pointed directly at the ground due to excessive false alarms, which overwhelm computers and operators. Sensitivity must be reduced near clutter to avoid overload. This vulnerability begins in the low-elevation region several beam widths above the horizon, and extends downward. This also exists throughout the volume of moving air associated with weather phenomenon.
Pulse-Doppler radar corrects this as follows.
- Allows the radar antenna to be pointed directly at the ground without overwhelming the computer and without reducing sensitivity.
- Fills in the vulnerability region associated with pulse-amplitude time-domain radar for small object detection near terrain and weather.
- Increases detection range by 300% or more in comparison to Moving target indicationMoving target indicationMoving target indication is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against clutter. In contrast to another mode, stationary target indication, it takes an advantage of the fact that the target moves with respect to stationary clutter. The most common approach takes advantage of...
(MTI) by improving sub-clutter visibility.
Clutter rejection capability
Clutter (radar)
Clutter is a term used for unwanted echoes in electronic systems, particularly in reference to radars. Such echoes are typically returned from ground, sea, rain, animals/insects, chaff and atmospheric turbulences, and can cause serious performance issues with radar systems.- Backscatter coefficient...
of about 60dB is needed for look-down/shoot-down
Look-down/shoot-down
Look-down/shoot-down is a capability a radar system is said to possess if it is able to detect, track and put a weapon onto an air target moving below the horizon as seen by the radar...
capability, and pulse-Doppler is the only strategy that can satisfy this requirement. This eliminates vulnerabilities associated with the low-elevation and below-horizon environment.
Pulse compression
Pulse compression
Pulse compression is a signal processing technique mainly used in radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio...
, and moving target indicator
Moving target indication
Moving target indication is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against clutter. In contrast to another mode, stationary target indication, it takes an advantage of the fact that the target moves with respect to stationary clutter. The most common approach takes advantage of...
(MTI) provide up to 25dB sub-clutter visibility. MTI antenna beam is aimed above horizon to avoid excessive false alarm rate, which renders systems vulnerable. Aircraft and some missiles exploit this weakness using a technique called flying below the radar to avoid detection (Nap-of-the-earth
Nap-of-the-earth
Nap-of-the-earth is a type of very low-altitude flight course used by military aircraft to avoid enemy detection and attack in a high-threat environment....
). This flying technique is ineffective against pulse-Doppler radar.
Pulse-Doppler provides an advantage when attempting to detect missiles and low observability aircraft
Stealth aircraft
Stealth aircraft are aircraft that use stealth technology to avoid detection by employing a combination of features to interfere with radar as well as reduce visibility in the infrared, visual, audio, and radio frequency spectrum. Development of stealth technology likely began in Germany during...
flying near near terrain, sea surface, and weather.
Audible Doppler and target size support passive vehicle type classification when identification friend or foe
Identification friend or foe
In telecommunications, identification, friend or foe is an identification system designed for command and control. It is a system that enables military and national interrogation systems to identify aircraft, vehicles, or forces as friendly and to determine their bearing and range from the...
is not available from a transponder signal
Transponder (aviation)
A transponder is an electronic device that produces a response when it receives a radio-frequency interrogation...
.
Medium PRF reflected microwave signals fall between 1,500 and 15,000 cycle per second, which is audible. This means a helicopter sounds like a helicopter, a jet sounds like a jet, and propeller aircraft sound like propellers. Aircraft with no moving parts produce a tone.
The actual size of the target can be calculated using the audible signal.
Detriments

Scan time is a critical factor for some systems because vehicles moving at or above the speed of sound can travel one mile (1.6 km) every few seconds, like the Exocet
Exocet
The Exocet is a French-built anti-ship missile whose various versions can be launched from surface vessels, submarines, helicopters and fixed wing aircraft. Hundreds were fired in combat during the 1980s.-Etymology:...
, Harpoon, Kitchen, and Air-to-air missile
Air-to-air missile
An air-to-air missile is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fuelled but sometimes liquid fuelled...
. The maximum time to scan the entire volume of the sky must be on the order of a dozen seconds or less for systems operating in that environment.
Pulse-Doppler radar by itself can be too slow to cover the entire volume of space above the horizon, unless multiple simultaneous beams are used.
Pulse-Doppler antenna motion must be slow enough so that all the return signals from at least 3 different PRF can be processed out to the maximum anticipated detection range. This is known as dwell time. Antenna motion for pulse-Doppler must be as slow as radar using MTI
Moving target indication
Moving target indication is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against clutter. In contrast to another mode, stationary target indication, it takes an advantage of the fact that the target moves with respect to stationary clutter. The most common approach takes advantage of...
.
Search radar that include pulse-Doppler are usually dual mode because best overall performance is achieved when pulse-Doppler is used for areas with high false alarm rates (horizon or below and weather), while conventional radar will scan faster in free-space where false alarm rate is low (above horizon with clear skies).
The antenna type is an important consideration for multi mode radar because undesirable phase shift introduced by the radar antenna can degrade Measure of Performance for sub-clutter visibility.
Signal Processing
The signal processing enhancement of pulse-Doppler allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving reflectors. To achieve this, the transmitter must be coherent and should produce low phase noisePhase noise
Phase noise is the frequency domain representation of rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, caused by time domain instabilities...
during the detection interval, and the receiver must have large instantaneous dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
.
- Pulse-Doppler signal processing detailed explanationPulse-Doppler signal processingPulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
Pulse-Doppler signal processing also includes ambiguity resolution to identify true range and velocity.
- Ambiguity resolution detailed explanationAmbiguity resolutionAmbiguity resolution is used to find the value of a measurement that requires modulo sampling.This is required for pulse-Doppler radar signal processing.-Measurements:...
The received signals from multiple PRF are compared to determine true range using the range ambiguity resolution process.
- Range ambiguity resolution detailed explanationRange ambiguity resolutionRange ambiguity resolution is a technique used with medium Pulse repetition frequency radar to obtain range information for distances that exceed the distance between transmit pulses.This signal processing technique is required with pulse-Doppler radar....
The received signals are also compared using the frequency ambiguity resolution process.
- Frequency ambiguity resolution detailed explanationFrequency ambiguity resolutionFrequency ambiguity resolution is used to find true target velocity for medium pulse repetition frequency radar systems.This is used with pulse-Doppler radar.-Definition:...
Range Resolution
The range resolution is the minimum range separation between two objects traveling at the same speed before the radar can detect two discrete reflections.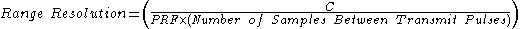
Velocity Resolution
The velocity resolution is the minimum radial velocity difference between two objects traveling at the same range before the radar can detect two discrete reflections.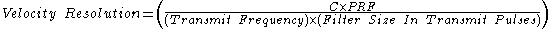
Special Consideration
Pulse-Doppler radar has special requirements that must be satisfied to achieve acceptable performance.Pulse repetition frequency
Pulse-Doppler typically uses medium Pulse repetition frequencyPulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency or Pulse repetition rate is the number of pulses per time unit . It is a measure or specification mostly used within various technical disciplines Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or Pulse repetition rate (PRR) is the number of pulses per time unit (e.g. Seconds). It...
(PRF) from about 3 kHz to 30 kHz. The range between transmit pulses is 5 km to 50 km.
- Pulse repetition frequency detailed explanationPulse repetition frequencyPulse repetition frequency or Pulse repetition rate is the number of pulses per time unit . It is a measure or specification mostly used within various technical disciplines Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or Pulse repetition rate (PRR) is the number of pulses per time unit (e.g. Seconds). It...
Range and velocity cannot be measured directly using medium PRF, and a technique called ambiguity resolutions is required to identify true range and speed. Doppler signals are generally above 1 kHz, which is audible, so audio signals from medium-PRF systems can be used for passive target classification.
Angular Measurement
Radar systems require angular measurement. Transponders are not normally associated with pulse-Doppler radar, so sidelobe suppression is required for practical operation.Tracking radar systems use angle error to improve accuracy by producing measurements perpendicular to the radar antenna beam. Angular measurements are averaged over a span of time and combined with radial movement to develop information suitable to predict target position for a short time into the future.
The two angle error techniques used with tracking radar are monopulse and conical scan.
- Monopulse radarMonopulse radarMonopulse radar is an adaptation of conical scanning radar which sends additional information in the radar signal in order to avoid problems caused by rapid changes in signal strength. The system also makes jamming more difficult...
- Conical scanningConical scanningConical scanning is a system used in early radar units to improve their accuracy, as well as making it easier to steer the antenna properly to point at a target...
Coherency
Pulse-Doppler radar requires a coherent oscillator with very little noise. Phase noisePhase noise
Phase noise is the frequency domain representation of rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, caused by time domain instabilities...
reduces sub-clutter visibility performance by producing apparent motion on stationary objects.
Cavity magnetron
Cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field. The 'resonant' cavity magnetron variant of the earlier magnetron tube was invented by John Randall and Harry Boot in 1940 at the University of...
and crossed-field amplifier
Crossed-field amplifier
A crossed-field amplifier is a specialized vacuum tube, first introduced in the mid-1950s and frequently used as a microwave amplifier in very-high-power transmitters....
are not appropriate because noise introduced by these devices interfere with detection performance. The only amplification devices suitable for pulse-Doppler are klystron
Klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube . Klystrons are used as amplifiers at microwave and radio frequencies to produce both low-power reference signals for superheterodyne radar receivers and to produce high-power carrier waves for communications and the driving force for modern...
, traveling wave tube
Traveling wave tube
A traveling-wave tube is an electronic device used to amplify radio frequency signals to high power, usually in an electronic assembly known as a traveling-wave tube amplifier ....
, and solid state devices.
Scalloping
Pulse Doppler signal processing introduces a phenomenon called scalloping. The name is associated with a series of holes that are scooped-out of the detection performance.Scalloping for pulse-Doppler radar involves blind velocities created by the clutter rejection filter. Every volume of space must be scanned using 3 or more different PRF. A two PRF detection scheme will have detection gaps with a pattern of discrete ranges, each of which has a blind velocity.
- Pulse-Doppler radar scalloping detailed explanation
Windowing
Ringing artifactsRinging artifacts
In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "echos" near transients, particularly sounds from...
pose a problem with search, detection, and ambiguity resolution in pulse-Doppler radar.
Ringing is reduced in two ways.
First, the shape of the transmit pulse is adjusted to smooth the leading edge and trailing edge so that RF power is increased and decreased without an abrupt change. This creates a transmit pulse with smooth ends instead of a square wave, which reduces ringing phenomenon that is otherwise associated with target reflection.
Second, the shape of the receive pulse is adjusted using a window function
Window function
In signal processing, a window function is a mathematical function that is zero-valued outside of some chosen interval. For instance, a function that is constant inside the interval and zero elsewhere is called a rectangular window, which describes the shape of its graphical representation...
that minimizes ringing that occurs any time pulses are applied to a filter. In a digital system, this adjusts the phase and/or amplitude of each sample before it is applied to the Fast Fourier Transform
Fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform is an efficient algorithm to compute the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse. "The FFT has been called the most important numerical algorithm of our lifetime ." There are many distinct FFT algorithms involving a wide range of mathematics, from simple...
. The Dolph-Chebychev window is the most effective because it produces a flat processing floor with no ringing that would otherwise cause false alarms.
Antenna
Pulse-Doppler radar is generally limited to mechanically aimed antennas and active phase array.Mechanical RF components, such as wave-guide, can produce Doppler modulation due to phase shift induced by vibration. This introduces a requirement to perform full spectrum operational tests using shake tables that can produce high power mechanical vibration across all anticipated audio frequencies.
Doppler is incompatible with most electronically steered phase-array antenna. This is because the phase-shifter elements in the antenna are non-reciprocal and the phase shift must be adjusted before and after each transmit pulse. Spurious phase shift is produced by the sudden impulse of the phase shift, and settling during the receive period between transmit pulses places Doppler modulation onto stationary clutter. That receive modulation corrupts Measure of Performance for sub-clutter visibility. Phase shifter settling time on the order of 50ns is required.
Most antenna phase shifters operating at PRF above 1 kHz introduce spurious phase shift unless special provisions are made, such as reducing phase shifter settling time to a few dozen nanoseconds.
The following gives the approximate settling time for antenna phase shift module
Phase shift module
thumb|right|A microwave Phase Shifter and Frequency Translator. Picture courtesy of A phase shifter is a microwave network which provides a controllable phase shift of the RF signal...
s.

where
- T = phase shifter settling time
- SCV = sub-clutter visibility in dBDecibelThe decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
- S = number of range samples between each transmit pulse
- PRF = maximum design pulse repetition frequency
The antenna type and scan performance is a practical consideration for multi-mode radar systems.
Diffraction
Choppy surfaces, like waves and trees, form a diffraction grating suitable for bending microwave signals. Pulse-Doppler can be so sensitive that diffractionDiffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
from mountains, buildings or wave tops can be used to detect fast moving objects otherwise blocked by solid obstruction along the line of sight. This is a very lossy phenomenon that only becomes possible when radar has significant excess sub-clutter visibility.
Refraction and ducting use transmit frequency at L-band or lower to extend the horizon, which is very different from diffraction. Refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
for over-the-horizon radar
Over-the-horizon radar
Over-the-horizon radar, or OTH , is a design concept for radar systems to allow them to detect targets at very long ranges, typically up to thousands of kilometers...
uses variable density in the air column above the surface of the earth to bend RF signals. An inversion layer can produce a transient troposphere duct that traps RF signals in a thin layer of air like a wave-guide.
Subclutter Visibility
Subclutter visibility involves the maximum ratio of clutter power to target power, which is proportional to dynamic range. This determines performance in heavy weather and near the earth surface.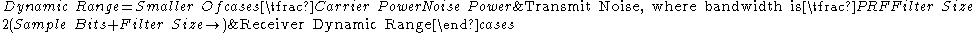
Subclutter visibility is the ratio of the smallest signal that can be detected in the presence of a larger signal.
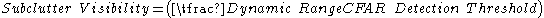
A small fast-moving target reflection can be detected in the presence of larger slow-moving clutter reflections when the following is true.
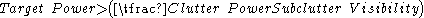
Performance
The pulse-Doppler radar equation can be used to understand trade-offs between different design constraints, like power consumption, detection range, and microwave safety hazards. This is a very simple form of modeling that allows performance to be evaluated in a sterile environment.The theoretical range performance is as follows.
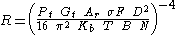
where
- R = Distance to the target
- Pt = Transmitter power
- Gt = GainGainIn electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
of the transmitting antenna - Ar = Effective aperture (area) of the receiving antenna
- σ = Radar cross sectionRadar cross sectionRadar cross section is a measure of how detectable an object is with a radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected.An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy...
, or scattering coefficient, of the target - F = Antenna pattern propagation factorAntenna gainIn electromagnetics, an antenna's power gain or simply gain is a key performance figure which combines the antenna's directivity and electrical efficiency. As a transmitting antenna, the figure describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction...
- D = Doppler filter size (transmit pulses in each Fast Fourier transformFast Fourier transformA fast Fourier transform is an efficient algorithm to compute the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse. "The FFT has been called the most important numerical algorithm of our lifetime ." There are many distinct FFT algorithms involving a wide range of mathematics, from simple...
) - Kb = Boltzmann's constant
- T = Temperature (kelvin)
- B = Receiver Bandwidth (band pass filter)
- N = Noise figureNoise figureNoise figure is a measure of degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio , caused by components in a radio frequency signal chain. The noise figure is defined as the ratio of the output noise power of a device to the portion thereof attributable to thermal noise in the input termination at standard...
This equation is derived by combining the Radar equation with the Noise equation
Noise (electronics)
Electronic noise is a random fluctuation in an electrical signal, a characteristic of all electronic circuits. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly, as it can be produced by several different effects...
and accounting for in-band noise distribution across multiple detection filters. The value D is added to the standard radar range equation to account for both Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
and transmitter FM noise reduction
Coherence
Coherence, coherency, or coherent can refer to:- In physics :* Coherence ** Polarization** Quantum** Spatial** Spectral** Temporal* Coherence time- In mathematics :...
.
Detection range is increased proportional to the square root of the number of filters. Power consumption is reduced by the square of the number of filers.
For example, pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
with 1,024 filters will reduce noise contribution in each filter 60dB below the level of electronic noise
Noise (electronics)
Electronic noise is a random fluctuation in an electrical signal, a characteristic of all electronic circuits. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly, as it can be produced by several different effects...
being sampled in the receiver. Each filter holds only a small amount of the total noise arriving at the receiver. This means a system with a receiver bandwidth of 1 mHz would have an effective bandwidth of 1 kHz in each of the 1,024 filters where detection takes place.
In addition, Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
integrates all of the energy from all of the individual reflected pulses that enter the filter. This means a Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
system with 1,024 elements provides 60dB of improvement due to the type of signal processing that must be used with pulse-Doppler radar. The energy of all of the individual pulses from the object are added together by the filtering process.
Signal processing for a 1,024 point filter improves performance by 120dB, assuming compatible transmitter and antenna. This corresponds to the following potential improvements.
- 3,000% increase in maximum distance. This can increase range from 500 km to 10% of the distance from earth to sun
- 1,000,000 fold reduction in microwave transmit power, which makes radar safe for aircraft and practical for spacecraft
- 1,000,000 fold reduction in target size, from 1 square meter to 1 square millimeter, to eliminate stealth aircraft advantage
These improvements are the reason pulse-Doppler is essential for military and astronomy.
Aircraft tracking uses
Pulse-Doppler radar for aircraft detection has two modes.- Scan
- Track
Scan mode involves frequency filtering, amplitude thresholding, and ambiguity resolution. Once a reflection has been detected
Constant false alarm rate
Constant false alarm rate detection refers to a common form of adaptive algorithm used in radar systems to detect target returns against a background of noise, clutter and interference.Other detection algorithms are not adaptive...
and resolved
Ambiguity resolution
Ambiguity resolution is used to find the value of a measurement that requires modulo sampling.This is required for pulse-Doppler radar signal processing.-Measurements:...
, the pulse-Doppler radar automatically transitions to tracking mode for the volume of space surrounding the track.
Track mode works like a phase-locked loop
Phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
, where Doppler velocity is compared with the range movement on successive scans. Lock indicates the difference between the two measurements is below a threshold, which can only occur with an object that satisfies Newtonian mechanics
Classical mechanics
In physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a system of forces...
. Other types of electronic signals cannot produce a lock. Lock exists in no other type of radar.
The lock criteria needs to be satisfied during normal operation.
- Pulse-Doppler Lock Criteria Explanation
Lock eliminates the need for human intervention with the exception of helicopters and electronic jamming.
Weather phenomenon obey adiabatic process
Adiabatic process
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process or an isocaloric process is a thermodynamic process in which the net heat transfer to or from the working fluid is zero. Such a process can occur if the container of the system has thermally-insulated walls or the process happens in an extremely short time,...
associated with air mass
Air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adopt the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime...
and not Newtonian mechanics, so the lock criteria is not normally used for weather radar.
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing
Pulse-Doppler signal processing is a radar performance enhancement strategy that allows small high-speed objects to be detected in close proximity to large slow moving objects. Detection improvements on the order of of 1,000,000:1 are common...
selectively excludes low-velocity reflections so that no detections occurs below a threshold velocity. This eliminates terrain, weather, biologicals, and mechanical jamming with the exception of decoy aircraft.
The target Doppler signal from the detection is converted from frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
back into time domain
Time domain
Time domain is a term used to describe the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various...
sound for the operator in track mode on some radar systems. The operator uses this sound for passive target classification, such as recognizing helicopters and electronic jamming.
Helicopters
Special consideration is required for aircraft with large moving parts because pulse-Doppler radar operates like a phase-locked loopPhase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
. Blade tips moving near the speed of sound produce the only signal that can be detected when a helicopter
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by one or more engine-driven rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forwards, backwards, and laterally...
is moving slow near terrain and weather.
Helicopters appears like a rapidly pulsing noise emitter except in a clear environment free from clutter. An audible signal is produced for passive identification of the type of airborne object. Doppler produces sound that is used for target classification in addition to the kinds of conventional radar display
Radar display
Modern radar systems typically use some sort of raster scan display to produce a map-like image. In the past, notably during the early days of radar development, such displays were difficult to produce for a number of reasons. Several different display types were developed during this...
used for that purpose, like A-Scope, B-Scope, C-Scope, and RHI indicator. The human ear may be able to tell the difference better than electronic equipment.
A special mode is required because the Doppler velocity feedback information must be unlinked from radial movement so that the system can transition from scan to track with no lock.
Similar techniques are required to develop track information for jamming signals and interference that cannot satisfy the lock criteria.
Multi-Mode
Pulse-Doppler radar must be multi-mode to handle aircraft turning and crossing trajectory.Once in track mode, pulse-Doppler radar must include a way to modify Doppler filtering for the volume of space surrounding a track when radial velocity falls below the minimum detection velocity. Doppler filter adjustment must be linked with a radar track function to automatically adjust Doppler rejection speed within the volume of space surrounding the track.
Tracking will cease without this feature because the target signal will otherwise be rejected by the Doppler filter when radial velocity approaches zero.
Multi-mode operation may also include continuous wave illumination for semi-active radar homing
Semi-active radar homing
Semi-active radar homing, or SARH, is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive detector of a radar signal – provided by an external ...
.
See also
- Radar signal characteristicsRadar signal characteristicsA radar system uses a radio frequency electromagnetic signal reflected from a target to determine information about that target. In any radar system, the signal transmitted and received will exhibit many of the characteristics described below....
(fundamentals of the radar signal) - Doppler radarDoppler radarA Doppler radar is a specialized radar that makes use of the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance. It does this by beaming a microwave signal towards a desired target and listening for its reflection, then analyzing how the frequency of the returned signal has been...
(non pulsed; used for navigation systems) - Weather radarWeather radarWeather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
(pulsed with Doppler processing) - Continuous-wave radarContinuous-wave radarContinuous-wave radar is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects.Continuous wave radar uses Doppler, which renders the radar immune to interference from large stationary objects and slow moving...
(non-pulsed, pure Doppler processing) - Fm-cw radar (non-pulsed, swept frequency, range and Doppler processing)
- AliasingAliasingIn signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing refers to an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable when sampled...
- the reason for ambiguous velocity estimates - Doppler sonography - velocity measurements in medical ultrasound. Based on the same principle
- Tartar Guided Missile Fire Control SystemTartar Guided Missile Fire Control SystemThe Tartar Guided Missile Fire Control System is an air defense system developed by the United States Navy to defend warships from air attack. Since its introduction the system has been improved and sold to several United States allies.-Description:...
- AN/SPS-49AN/SPS-49The AN/SPS-49 is a United States Navy two-dimensional, long range air search radar built by Raytheon that can provide contact bearing and range. It is a primary air-search radar for numerous ships in the U.S...
surface search radar (US) - AN/SPG-51AN/SPG-51The AN/SPG-51 is a tracking / illumination radar for RIM-66 Standard missiles. It is used for target tracking and Surface-to-air missile guidance on s, s, and s.The French Cassard class frigates also utilise this system.Older variants were used on s....
D, the MK-74 Guided Missile Fire Control System (US) - MK-74 Guided Missile Fire Control System (GMFCS) (US)
- McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle radar system (US)
- General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon radar system (US)
- Close-in weapon systemClose-in weapon systemA close-in weapon system , often pronounced sea-whiz, is a naval shipboard point-defense weapon for detecting and destroying at short range incoming anti-ship missiles and enemy aircraft which have penetrated the outer defenses....
(US) - MirageMirage (aircraft)Mirage is the name of a series of delta-winged fighters and bombers that have been produced by the French aircraft manufacturer Dassault Aviation, flown by the French Air Force, and widely exported to foreign counties.* Dassault Mirage III...
(French) - MIG-25 radar (Soviet)
- MIG-31 radar (Soviet)
- Type 345 RadarType 345 RadarThe Type 345 fire-control radar system is used to guide the HQ-7 short-range surface-to-air missile. The system is installed on many modern, and retrofitted Chinese navy ships....
(Chinese) - CLC-1 RadarCLC-1 RadarCLC-1 short-range surveillance radar is a ground-based mobile tracking radar used by the People's Liberation Army of China.-Installation and Use:...
(Chinese) - SLC-2 RadarSLC-2 RadarThe SLC-2 Radar is a counter-battery radar designed to accurately locate hostile artillery, rocket and ground-to-ground missile launchers immediately after enemy firing, and to support friendly artillery by providing guidance of counter-fire....
(Chinese) - YLC-15 RadarYLC-15 RadarYLC-15 is a fully coherent, Pulse Doppler air defence radar designed primarily to detect targets at ranges of up to 16 km. It also provides the capability to identify hovering helicopters or low altitude cruise missiles....
(Chinese) - JL-10AJL-10AThe JL-10A airborne radar is a highly digitized pulse-Doppler radar with slotted planar array developed for the People's Liberation Army Air Force as a replacement for the older Type 232H radar currently employed by the Chinese air force. The radar is built to MIL-STD-1553 standard so it is...
(Chinese) - KLJ-7 RadarKLJ-7 RadarThe KLJ-7, also referred to as the Type 1478, is an X-band airborne fire-control radar developed by Nanjing Research Institute of Electronic Technology , also known as the China Electronics Technology Company's No. 14 Research Institute...
(Chinese) - Doppler On WheelsDoppler On WheelsDoppler On Wheels is a fleet of radar trucks maintained by the Center for Severe Weather Research led by Joshua Wurman, with the funding mainly provided by the National Science Foundation...
meteorological - NEXRADNEXRADNEXRAD or Nexrad is a network of 159 high-resolution Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service, an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration within the United States Department of Commerce...
meteorological - Terminal Doppler Weather RadarTerminal Doppler Weather RadarTerminal Doppler Weather Radar is a doppler weather radar system used primarily for the detection of hazardous wind shear conditions on and near major airports in the United States. As of 2011, there were 48 active radars, across the United States & Puerto Rico. Several more radars have also been...
meteorological - ARMOR Doppler Weather Radar meteorological
External links
- Doppler radar presentation, which highlights the advantages of using the autocorrelation techniqueAutocorrelation techniqueThe autocorrelation technique is a method for estimating the dominating frequency in a complex signal, as well as its variance. Specifically, it calculates the first two moments of the power spectrum, namely the mean and variance...
- Pulse-Doppler radar handouts from Introduction to Principles and Applications of Radar course at University of Iowa
- Modern Radar Systems by Hamish Meikle (ISBN 1-58053-294-2)
- Advanced Radar Techniques and Systems edited by Gaspare Galati (ISBN 0-86341-172-X)

