
Gaugino condensation
Encyclopedia
In particle physics
, gaugino condensation is the nonzero vacuum expectation value
in some models of a bilinear expression constructed in theories with supersymmetry
from the superpartner
of a gauge boson
called the gaugino
. The gaugino
and the bosonic gauge field and the D-term
are all components of a supersymmetric vector superfield in the Wess-Zumino gauge
.
where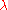 represents the gaugino field (a spinor
represents the gaugino field (a spinor
) and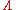 is an energy scale, a and b represent Lie algebra indices and α and β represent van der Waerden
is an energy scale, a and b represent Lie algebra indices and α and β represent van der Waerden
indices. The mechanism is somewhat analogous to chiral symmetry breaking
and is an example of a fermionic condensate
.
In the superfield notation,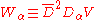 is the gauge field strength and is a chiral superfield
is the gauge field strength and is a chiral superfield
.
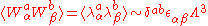
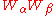 is also a chiral superfield and we see that what acquires a nonzero VEV is not the F-term
is also a chiral superfield and we see that what acquires a nonzero VEV is not the F-term
of this chiral superfield. Because of this, gaugino condensation in and of itself does not lead to supersymmetry breaking. If we also have supersymmetry breaking, it is caused by something other than the gaugino condensate.
However, a gaugino condensate definitely breaks U(1)R symmetry
as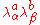 has an R-charge of 2.
has an R-charge of 2.
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, gaugino condensation is the nonzero vacuum expectation value
Vacuum expectation value
In quantum field theory the vacuum expectation value of an operator is its average, expected value in the vacuum. The vacuum expectation value of an operator O is usually denoted by \langle O\rangle...
in some models of a bilinear expression constructed in theories with supersymmetry
Supersymmetry
In particle physics, supersymmetry is a symmetry that relates elementary particles of one spin to other particles that differ by half a unit of spin and are known as superpartners...
from the superpartner
Superpartner
In particle physics, a superpartner is a hypothetical elementary particle. Supersymmetry is one of the synergistic theories in current high-energy physics which predicts the existence of these "shadow" particles....
of a gauge boson
Gauge boson
In particle physics, gauge bosons are bosonic particles that act as carriers of the fundamental forces of nature. More specifically, elementary particles whose interactions are described by gauge theory exert forces on each other by the exchange of gauge bosons, usually as virtual particles.-...
called the gaugino
Gaugino
In particle physics, a gaugino is the hypothetical superpartner of a gauge field, as predicted by gauge theory combined with supersymmetry. They are fermions.In the minimal supersymmetric extension of the standard model the following gauginos exist:...
. The gaugino
Gaugino
In particle physics, a gaugino is the hypothetical superpartner of a gauge field, as predicted by gauge theory combined with supersymmetry. They are fermions.In the minimal supersymmetric extension of the standard model the following gauginos exist:...
and the bosonic gauge field and the D-term
D-term
In theoretical physics, one often analyzes theories with supersymmetry in which D-terms play an important role. In four dimensions, the minimal N=1 supersymmetry may be written using a superspace. This superspace involves four extra fermionic coordinates \theta^1,\theta^2,\bar\theta^1,\bar\theta^2,...
are all components of a supersymmetric vector superfield in the Wess-Zumino gauge
Wess-Zumino gauge
In particle physics, the Wess–Zumino gauge is a particular choice of a gauge transformation in a gauge theory with supersymmetry. In this gauge, the supersymmetrized gauge transformation is chosen in such a way that most components of the vector superfield vanish, except for the usual physical...
.

where
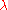 represents the gaugino field (a spinor
represents the gaugino field (a spinorSpinor
In mathematics and physics, in particular in the theory of the orthogonal groups , spinors are elements of a complex vector space introduced to expand the notion of spatial vector. Unlike tensors, the space of spinors cannot be built up in a unique and natural way from spatial vectors...
) and
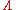 is an energy scale, a and b represent Lie algebra indices and α and β represent van der Waerden
is an energy scale, a and b represent Lie algebra indices and α and β represent van der WaerdenVan der Waerden notation
In theoretical physics, van der Waerden notation refers to the usage of two-component spinors in four spacetime dimensions. This is standard in twistor theory and supersymmetry....
indices. The mechanism is somewhat analogous to chiral symmetry breaking
Chiral symmetry breaking
In particle physics, chiral symmetry breaking is an example of spontaneous symmetry breaking affecting the chiral symmetry of gauge theory such as Quantum Chromodynamics. The origin may be described as a fermion condensate...
and is an example of a fermionic condensate
Fermionic condensate
A fermionic condensate is a superfluid phase formed by fermionic particles at low temperatures. It is closely related to the Bose–Einstein condensate, a superfluid phase formed by bosonic atoms under similar conditions. Unlike the Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates are formed using...
.
In the superfield notation,
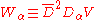 is the gauge field strength and is a chiral superfield
is the gauge field strength and is a chiral superfieldChiral superfield
In theoretical physics, one often analyzes theories with supersymmetry in which chiral superfields play an important role. In four dimensions, the minimal N=1 supersymmetry may be written using the notion of superspace...
.
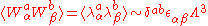
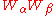 is also a chiral superfield and we see that what acquires a nonzero VEV is not the F-term
is also a chiral superfield and we see that what acquires a nonzero VEV is not the F-termF-term
In theoretical physics, one often analyzes theories with supersymmetry in which F-terms play an important role. In four dimensions, the minimal N=1 supersymmetry may be written using a superspace. This superspace involves four extra fermionic coordinates \theta^1,\theta^2,\bar\theta^1,\bar\theta^2,...
of this chiral superfield. Because of this, gaugino condensation in and of itself does not lead to supersymmetry breaking. If we also have supersymmetry breaking, it is caused by something other than the gaugino condensate.
However, a gaugino condensate definitely breaks U(1)R symmetry
R-symmetry
In theoretical physics, the R-symmetry is the symmetry transforming different supercharges in a theory with supersymmetry into each other. In the simplest case of the N=1 supersymmetry, such an R-symmetry is isomorphic to a global U group or its discrete subgroup...
as
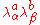 has an R-charge of 2.
has an R-charge of 2.

